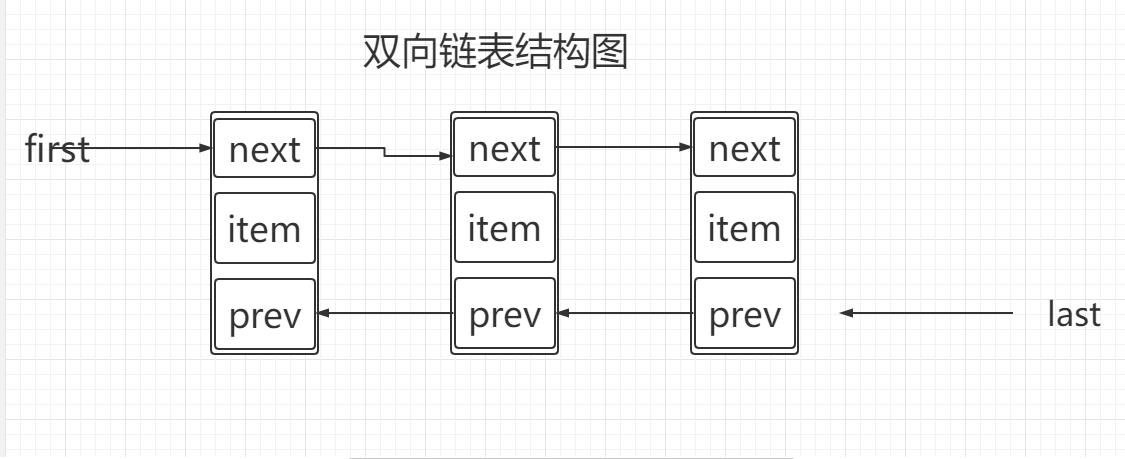
LinkedList双向链表
package Collection;
public class LinkedList01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟简单的双向链表
Node jack = new Node("jack");
Node tom = new Node("tom");
Node mark = new Node("mark");
//连接三个节点,形成双向链表
//jack指向tom,tom指向mark,
jack.next = tom;
tom.next = mark;
mark.prev = tom;
tom.prev = jack;
//first指向jack,做为双向链表的头节点;
//last直系那个mark,做为双向链表的尾节点;
Node first = jack;
Node last = mark;
System.out.println("从头到尾进行遍历==========");
//从头到尾进行遍历
while (true) {
if (first == null){
break;
}
//输出信息
System.out.println(first);
first= first.next;
}
System.out.println("从尾到头进行遍历========");
//从尾到头进行遍历
while (true) {
if (last == null){
break;
}
//输出信息
System.out.println(last);
last= last.prev;
}
System.out.println("添加一个smith数据===============");
//要求在双向链表中添加一个对象/数据,如在jack和Tom之间添加smith
//先添加一个node对象,名字为smith
Node smith = new Node("smith");
jack.next = smith;
tom.prev= smith;
smith.next= tom;
smith.prev=jack;
first = jack;
//从头到尾进行遍历
while (true) {
if (first == null){
break;
}
//输出信息
System.out.println(first);
first= first.next;
}
last =mark;
System.out.println("从尾到头进行遍历======================");
//从尾到头进行遍历
while (true) {
if (last == null){
break;
}
//输出信息
System.out.println(last);
last= last.prev;
}
}
}
//定义一个node类,node对象表示双向链表的一个节点
class Node {
public Object item;//存放非数据
public Node next;
public Node prev;
//创建一个构造器
public Node(Object item) {
this.item = item;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node name=" + item;
}
}
想多了都是问题,做多了才是答案




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号