Android - 自定义ScrollLayout
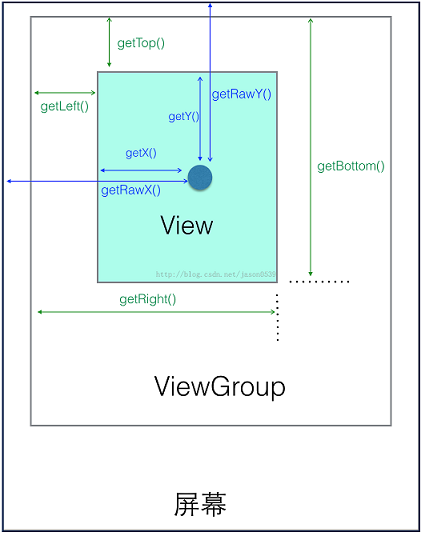
View
scrollTo:相对于初始位置
scrollBy:相对于当前位置
1.滚动对象是View内部的内容
2.X轴 负值:向右,正值:向左 (左正右负)
Y轴 负值:向下,正值:向上
3.滚动效果为跳跃式,没有平滑滚动效果
Scroller使用步骤:
1.创建Scroller实例
2.调用Scroller.startScoll()方法,传入起始位置与滑动偏移量
3.调用View.invalidate()
4.Scroller不负责滑动View, 只负责计算滑动值(数学引擎), View的invalidate()中将回调onComputeScroll(), 可以在该方法中利用Scroller执行滚动逻辑
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin">
<com.yizhui.customviewdemo.ScrollLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:padding="2dp"
android:background="#515151">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="First Button"
android:background="#ff0000"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Second Button"
android:background="#ff00ff"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Third Button"
android:background="#eeee00"/>
</com.yizhui.customviewdemo.ScrollLayout>
</LinearLayout>
package com.yizhui.customviewdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewConfiguration;
import android.view.animation.AccelerateInterpolator;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
import android.widget.Scroller;
/**
* Created by Yizhui on 2016/6/9.
*/
public class ScrollLayout extends FrameLayout {
/**
* 用于计算滚动数值的实例
*/
private Scroller mScroller;
/**
* 可滚动内容的左右边界
*/
private int mLeftBound, mRightBound;
/**
* 判定为拖动的最小移动像素数
*/
private int mTouchSlop;
/**
* 手指移动时所处屏幕的X坐标
*/
private int mLastX;
/**
* 手指按下时所处屏幕的X坐标
*/
private int mDownX;
public ScrollLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public ScrollLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public ScrollLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mScroller = new Scroller(context,new AccelerateInterpolator());
mTouchSlop = ViewConfiguration.get(context).getScaledPagingTouchSlop();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
if (changed) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
//为每个子控件进行水平方法的布局
child.layout(getMeasuredWidth() * i, 0, (i + 1) * getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
mLeftBound = getChildAt(0).getLeft();
mRightBound = getChildAt(getChildCount() - 1).getRight();
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
switch (ev.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mDownX = (int) ev.getRawX();
mLastX = mDownX;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
if (Math.abs(ev.getRawX() - mDownX) > mTouchSlop) {
return true;
}
}
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int curX, deltaX;
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
curX = (int) event.getRawX();
deltaX = mLastX - curX; //左滑为正,右滑为负
mLastX = curX;
//Log.d("Scroll", deltaX + ", "+curX+", " + getScrollX() + ", ");
//不能继续左滑
if (getScrollX() + deltaX > mRightBound - getWidth()) {
scrollTo(mRightBound - getWidth(), 0);
return true;
}
//不能继续右滑
if (getScrollX() + deltaX < mLeftBound) {
scrollTo(0, 0);
return true;
}
scrollBy(deltaX, 0);
return true;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
boolean isScrollToLeft=mDownX-event.getRawX()>0?true:false;
//滑动1/4
//int targetIndex=(getScrollX()+getWidth()*3/4)/getWidth();
/*
* 滑动1/4视为滑动上下块,若当前index=1
* 左滑: ((1+x)+3/4) 取整 , x=[0,1] -> f=[1,2] 1/4处为临界点
* 右滑: ((1-x)+1/4) 取整 , x=[0,1] -> f=[1,0] 1/4处为临界点
*/
int targetIndex=(int)((getScrollX()+(isScrollToLeft?(3.0/4):(1.0/4))*getWidth())/getWidth());
mScroller.startScroll(getScrollX(), 0, targetIndex * getWidth() - getScrollX(), 0);
invalidate();
break;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if(mScroller.computeScrollOffset()){
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
invalidate();
}
}
}
代码说明:
1、ScrollLayout 重载onInterceptTouchEvent,拦截ACTION_MOVE事件
2、ScrollLayout 需要消费ACTION_DOWN事件,因为子View可能不会消费ACTION_DOWN(如:TextView并且没有设置clickable为true)
3、startScroll()中关于滑动偏移量的计算公式为:targetIndex * getWidth() - getScrollX() ,可分为如下四种情况分析:
左滑:满足条件,继续左滑进入下一个,offset= targetX-curX
不满足条件,右滑进行还原,offset=targetX-curX
右滑:同上
结果演示:

另附:
参考文章:
Android Scroller完全解析,关于Scroller你所需知道的一切

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号