红黑树--整理参考学习
一、参考学习:
图解集合7:红黑树概念、红黑树的插入及旋转操作详细解读:http://www.importnew.com/24930.html
漫画:什么是红黑树?:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31805309
彻底搞懂红黑树:http://www.akathink.com/2016/08/08/%E5%BD%BB%E5%BA%95%E6%90%9E%E6%87%82%E7%BA%A2%E9%BB%91%E6%A0%91/
红黑树详细分析,看了都说好:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1113702
红黑树(一)之 原理和算法详细介绍:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3245399.html#top
教你初步了解红黑树:https://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6105630
数据结构之红黑树:http://dongxicheng.org/structure/red-black-tree/
维基百科:https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%BA%A2%E9%BB%91%E6%A0%91
https://blog.csdn.net/eson_15/article/details/51144079
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html
《算法导论》
二、什么是红黑树?
由于红黑树本质上就是一棵二叉查找树
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),也称有序二叉树(ordered binary tree),排序二叉树(sorted binary tree),是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若任意结点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若任意结点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 任意结点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
- 没有键值相等的结点(no duplicate nodes)。
红黑树(R-B Tree,全称是Red-Black Tree),本质上来说就是一棵二叉查找树,但它在二叉查找树的基础上增加了着色和相关的性质使得红黑树相对平衡,从而保证了红黑树的查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度最坏为O(log n)。
但它是如何保证一棵n个结点的红黑树的高度始终保持在h = logn的呢?这就引出了红黑树的5条性质:
1)每个结点要么是红的,要么是黑的。
2)根结点是黑的。
3)每个叶结点(叶结点即指树尾端NIL指针或NULL结点)是黑的。
4)如果一个结点是红的,那么它的俩个儿子都是黑的。
5)对于任一结点而言,其到叶结点树尾端NIL指针的每一条路径都包含相同数目的黑结点。
正是红黑树的这5条性质,使得一棵n个结点是红黑树始终保持了logn的高度,从而也就解释了上面我们所说的“红黑树的查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度最坏为O(log n)”这一结论的原因。
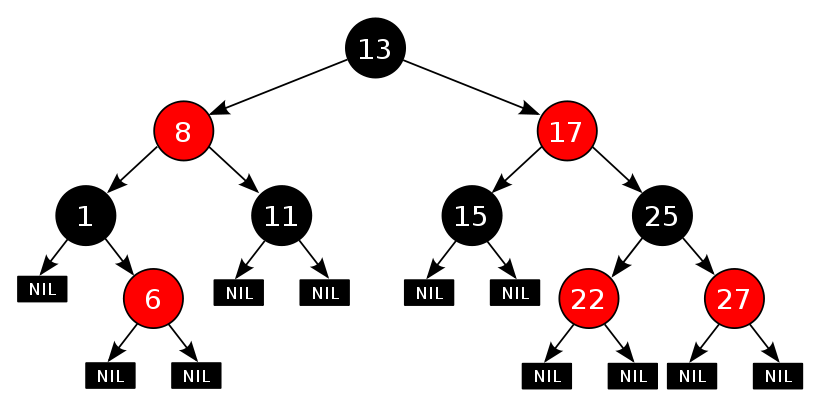
三、红黑树的基本操作
因为红黑树也是二叉查找树,因此红黑树上的查找操作与普通二叉查找树上的查找操作相同。然而,红黑树上的插入操作和删除操作会导致不再符合红黑树的性质。恢复红黑树的性质需要少量(O(log n))的颜色变更(实际是非常快速的)和不超过三次树旋转(对于插入操作是两次)。虽然插入和删除很复杂,但操作时间仍可以保持为 O(log n) 次。
3.1、红黑树数的着色
改变节点颜色比较容易理解,因为它违背了规则3。假设现在有个节点E,然后插入节点A和节点S,节点A在左子节点,S在右子节点,目前是平衡的。如果此时再插一个节点,那么就出现了不平衡了,因为红色节点的子节点必须为黑色,但是新插的节点是红色的。所以这时候就必须改变节点颜色了。所以我们将根的两个子节点从红色变为黑色(至于为什么都要变,下面插入的时候会详细介绍),将父节点会从黑色变成红色。可以用如下示意图表示一下:
3.2、红黑树的旋转
3.2.1 左旋
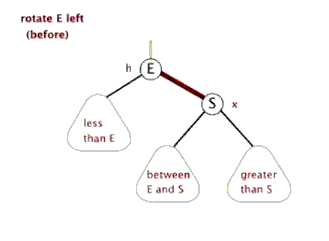
左旋的伪代码:

1 LeftRoate(T, x) 2 y ← x.right //定义y:y是x的右孩子 3 x.right ← y.left //y的左孩子成为x的右孩子 4 if y.left ≠ T.nil 5 y.left.p ← x 6 y.p ← x.p //x的父结点成为y的父结点 7 if x.p = T.nil 8 then T.root ← y 9 else if x = x.p.left 10 then x.p.left ← y 11 else x.p.right ← y 12 y.left ← x //x作为y的左孩子 13 x.p ← y
3.2.2、右旋
右旋与左旋差不多,再此不做详细介绍
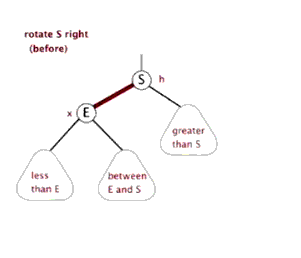

RIGHT-ROTATE(T, y) x ← left[y] // 前提:这里假设y的左孩子为x。下面开始正式操作 left[y] ← right[x] // 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”,即 将β设为y的左孩子 p[right[x]] ← y // 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”,即 将β的父亲设为y p[x] ← p[y] // 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲” if p[y] = nil[T] then root[T] ← x // 情况1:如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点 else if y = right[p[y]] then right[p[y]] ← x // 情况2:如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的左孩子” else left[p[y]] ← x // 情况3:(y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“y的父节点的左孩子” right[x] ← y // 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子” p[y] ← x // 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
至于有些书如《STL源码剖析》有对双旋的描述,其实双旋只是单旋的两次应用,并无新的内容,因此这里就不再介绍了,而且左右旋也是相互对称的,只要理解其中一种旋转就可以了。
3.3、红黑树的插入
插入操作可以概括为以下几个步骤:
(1) 查找要插入的位置,时间复杂度为:O(N)
(2) 将新节点的color赋为红色
(3) 自下而上重新调整该树为红黑树
插入伪代码:

1 TREE-INSERT(T, z) 2 y ← NIL 3 x ← T.root 4 while x ≠ NIL 5 do y ← x 6 if z.key < x.key 7 then x ← x.left 8 else x ← x.right 9 z.p ← y 10 if y == NIL 11 then T.root ← z 12 else if z.key < y.key 13 then y.left ← z 14 else y.right ← z
红黑树的插入和插入修复
现在我们了解了二叉查找树的插入,接下来,咱们便来具体了解下红黑树的插入操作。红黑树的插入相当于在二叉查找树插入的基础上,为了重新恢复平衡,继续做了插入修复操作。
其中,第(1)步的查找方法跟普通二叉查找树一样,第(2)步之所以将新插入的节点的颜色赋为红色,是因为:如果设为黑色,就会导致根到叶子的路径上有一条路上,多一个额外的黑节点,这个是很难调整的。但是设为红色节点后,可能会导致出现两个连续红色节点的冲突,那么可以通过颜色调换(color flips)和树旋转来调整,这样简单多了。下面讨论步骤(3)的一些细节:
设要插入的节点为N,其父节点为P,其父亲G的兄弟节点为U(即P和U是同一个节点的两个子节点)。
[1] 如果P是黑色的,则整棵树不必调整便是红黑树。
[2] 如果P是红色的(可知,其父节点G一定是黑色的),则插入z后,违背了性质4,需要进行调整。调整时分以下3种情况(需要旋转和变色):
-
1.插入节点的父节点和其叔叔节点(祖父节点的另一个子节点)均为红色的;
-
2.插入节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且插入节点是其父节点的右子节点;
-
3.插入节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且插入节点是其父节点的左子节点。
| 现象说明 |
处理策略 |
|
| Case 1 | 当前节点的父节点是红色,且当前节点的祖父节点的另一个子节点(叔叔节点)也是红色。 |
(01) 将“父节点”设为黑色。 |
| Case 2 | 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的右孩子 |
(01) 将“父节点”作为“新的当前节点”。 |
| Case 3 | 当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是其父节点的左孩子 |
(01) 将“父节点”设为“黑色”。 |
(1)N的叔叔U是红色的
如上图所示,我们将P和U重绘为黑色并重绘节点G为红色(用来保持性质5)。现在新节点N有了一个黑色的父节点P,因为通过父节点P或叔父节点U的任何路径都必定通过祖父节点G,在这些路径上的黑节点数目没有改变。但是,红色的祖父节点G的父节点也有可能是红色的,这就违反了性质4。为了解决这个问题,我们在祖父节点G上递归调整颜色。
(2)N的叔叔U是黑色的,且N是右孩子

如上图所示,我们对P进行一次左旋转调换新节点和其父节点的角色; 接着,按情形(c)处理以前的父节点P以解决仍然失效的性质4。
(3)N的叔叔U是黑色的,且N是左孩子

如上图所示,对祖父节点G 的一次右旋转; 在旋转产生的树中,以前的父节点P现在是新节点N和以前的祖父节点G 的父节点, 然后交换以前的父节点P和祖父节点G的颜色,结果的树满足性质4,同时性质5[4]也仍然保持满足。
3.4、红黑树的删除
将红黑树内的某一个节点删除。需要执行的操作依次是:首先,将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将该节点从二叉查找树中删除;然后,通过"旋转和重新着色"等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。详细描述如下:
第一步:将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点删除。
这和"删除常规二叉查找树中删除节点的方法是一样的"。分3种情况:
① 被删除节点没有儿子,即为叶节点。那么,直接将该节点删除就OK了。
② 被删除节点只有一个儿子。那么,直接删除该节点,并用该节点的唯一子节点顶替它的位置。
③ 被删除节点有两个儿子。那么,先找出它的后继节点;然后把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。在这里,后继节点相当于替身,在将后继节点的内容复制给"被删除节点"之后,再将后继节点删除。这样就巧妙的将问题转换为"删除后继节点"的情况了,下面就考虑后继节点。 在"被删除节点"有两个非空子节点的情况下,它的后继节点不可能是双子非空。既然"的后继节点"不可能双子都非空,就意味着"该节点的后继节点"要么没有儿子,要么只有一个儿子。若没有儿子,则按"情况① "进行处理;若只有一个儿子,则按"情况② "进行处理。
第二步:通过"旋转和重新着色"等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。
因为"第一步"中删除节点之后,可能会违背红黑树的特性。所以需要通过"旋转和重新着色"来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。
删除伪代码:

1 RB-DELETE(T, z) 2 if left[z] = nil[T] or right[z] = nil[T] 3 then y ← z // 若“z的左孩子” 或 “z的右孩子”为空,则将“z”赋值给 “y”; 4 else y ← TREE-SUCCESSOR(z) // 否则,将“z的后继节点”赋值给 “y”。 5 if left[y] ≠ nil[T] 6 then x ← left[y] // 若“y的左孩子” 不为空,则将“y的左孩子” 赋值给 “x”; 7 else x ← right[y] // 否则,“y的右孩子” 赋值给 “x”。 8 p[x] ← p[y] // 将“y的父节点” 设置为 “x的父节点” 9 if p[y] = nil[T] 10 then root[T] ← x // 情况1:若“y的父节点” 为空,则设置“x” 为 “根节点”。 11 else if y = left[p[y]] 12 then left[p[y]] ← x // 情况2:若“y是它父节点的左孩子”,则设置“x” 为 “y的父节点的左孩子” 13 else right[p[y]] ← x // 情况3:若“y是它父节点的右孩子”,则设置“x” 为 “y的父节点的右孩子” 14 if y ≠ z 15 then key[z] ← key[y] // 若“y的值” 赋值给 “z”。注意:这里只拷贝z的值给y,而没有拷贝z的颜色!!! 16 copy y's satellite data into z 17 if color[y] = BLACK 18 then RB-DELETE-FIXUP(T, x) // 若“y为黑节点”,则调用 19 return y

四、红黑树源代码
4.1、红黑树操作源代码

1 package tree; 2 /** 3 * @description implementation of Red-Black Tree by Java 4 * @author eson_15 5 * @param <T> 6 * @date 2016-4-18 19:27:28 7 */ 8 public class RBTree<T extends Comparable<T>> { 9 private RBNode<T> root; //根节点 10 private static final boolean RED = false; //定义红黑树标志 11 private static final boolean BLACK = true; 12 13 //内部类:节点类 14 public class RBNode<T extends Comparable<T>>{ 15 boolean color; //颜色 16 T key; //关键字(键值) 17 RBNode<T> left; //左子节点 18 RBNode<T> right; //右子节点 19 RBNode<T> parent; //父节点 20 21 public RBNode(T key, boolean color, RBNode<T> parent, RBNode<T> left, RBNode<T> right) { 22 this.key = key; 23 this.color = color; 24 this.parent = parent; 25 this.left = left; 26 this.right = right; 27 } 28 29 public T getKey() { 30 return key; 31 } 32 33 public String toString() { 34 return "" + key + (this.color == RED? "R" : "B"); 35 } 36 } 37 38 public RBTree() { 39 root = null; 40 } 41 42 public RBNode<T> parentOf(RBNode<T> node) { //获得父节点 43 return node != null? node.parent : null; 44 } 45 46 public void setParent(RBNode<T> node, RBNode<T> parent) { //设置父节点 47 if(node != null) 48 node.parent = parent; 49 } 50 51 public boolean colorOf(RBNode<T> node) { //获得节点的颜色 52 return node != null? node.color : BLACK; 53 } 54 55 public boolean isRed(RBNode<T> node) { //判断节点的颜色 56 return (node != null)&&(node.color == RED)? true : false; 57 } 58 59 public boolean isBlack(RBNode<T> node) { 60 return !isRed(node); 61 } 62 63 public void setRed(RBNode<T> node) { //设置节点的颜色 64 if(node != null) 65 node.color = RED; 66 } 67 68 public void setBlack(RBNode<T> node) { 69 if(node != null) { 70 node.color = BLACK; 71 } 72 } 73 74 public void setColor(RBNode<T> node, boolean color) { 75 if(node != null) 76 node.color = color; 77 } 78 79 /***************** 前序遍历红黑树 *********************/ 80 public void preOrder() { 81 preOrder(root); 82 } 83 84 private void preOrder(RBNode<T> tree) { 85 if(tree != null) { 86 System.out.print(tree.key + " "); 87 preOrder(tree.left); 88 preOrder(tree.right); 89 } 90 } 91 92 /***************** 中序遍历红黑树 *********************/ 93 public void inOrder() { 94 inOrder(root); 95 } 96 97 private void inOrder(RBNode<T> tree) { 98 if(tree != null) { 99 preOrder(tree.left); 100 System.out.print(tree.key + " "); 101 preOrder(tree.right); 102 } 103 } 104 105 /***************** 后序遍历红黑树 *********************/ 106 public void postOrder() { 107 postOrder(root); 108 } 109 110 private void postOrder(RBNode<T> tree) { 111 if(tree != null) { 112 preOrder(tree.left); 113 preOrder(tree.right); 114 System.out.print(tree.key + " "); 115 } 116 } 117 118 /**************** 查找红黑树中键值为key的节点 ***************/ 119 public RBNode<T> search(T key) { 120 return search(root, key); 121 // return search2(root, key); //使用递归的方法,本质一样的 122 } 123 124 private RBNode<T> search(RBNode<T> x, T key) { 125 while(x != null) { 126 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 127 if(cmp < 0) 128 x = x.left; 129 else if(cmp > 0) 130 x = x.right; 131 else 132 return x; 133 } 134 return x; 135 } 136 //使用递归 137 private RBNode<T> search2(RBNode<T> x, T key) { 138 if(x == null) 139 return x; 140 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 141 if(cmp < 0) 142 return search2(x.left, key); 143 else if(cmp > 0) 144 return search2(x.right, key); 145 else 146 return x; 147 } 148 149 /**************** 查找最小节点的值 **********************/ 150 public T minValue() { 151 RBNode<T> node = minNode(root); 152 if(node != null) 153 return node.key; 154 return null; 155 } 156 157 private RBNode<T> minNode(RBNode<T> tree) { 158 if(tree == null) 159 return null; 160 while(tree.left != null) { 161 tree = tree.left; 162 } 163 return tree; 164 } 165 166 /******************** 查找最大节点的值 *******************/ 167 public T maxValue() { 168 RBNode<T> node = maxNode(root); 169 if(node != null) 170 return node.key; 171 return null; 172 } 173 174 private RBNode<T> maxNode(RBNode<T> tree) { 175 if(tree == null) 176 return null; 177 while(tree.right != null) 178 tree = tree.right; 179 return tree; 180 } 181 182 /********* 查找节点x的后继节点,即大于节点x的最小节点 ***********/ 183 public RBNode<T> successor(RBNode<T> x) { 184 //如果x有右子节点,那么后继节点为“以右子节点为根的子树的最小节点” 185 if(x.right != null) 186 return minNode(x.right); 187 //如果x没有右子节点,会出现以下两种情况: 188 //1. x是其父节点的左子节点,则x的后继节点为它的父节点 189 //2. x是其父节点的右子节点,则先查找x的父节点p,然后对p再次进行这两个条件的判断 190 RBNode<T> p = x.parent; 191 while((p != null) && (x == p.right)) { //对应情况2 192 x = p; 193 p = x.parent; 194 } 195 return p; //对应情况1 196 197 } 198 199 /********* 查找节点x的前驱节点,即小于节点x的最大节点 ************/ 200 public RBNode<T> predecessor(RBNode<T> x) { 201 //如果x有左子节点,那么前驱结点为“左子节点为根的子树的最大节点” 202 if(x.left != null) 203 return maxNode(x.left); 204 //如果x没有左子节点,会出现以下两种情况: 205 //1. x是其父节点的右子节点,则x的前驱节点是它的父节点 206 //2. x是其父节点的左子节点,则先查找x的父节点p,然后对p再次进行这两个条件的判断 207 RBNode<T> p = x.parent; 208 while((p != null) && (x == p.left)) { //对应情况2 209 x = p; 210 p = x.parent; 211 } 212 return p; //对应情况1 213 } 214 215 /*************对红黑树节点x进行左旋操作 ******************/ 216 /* 217 * 左旋示意图:对节点x进行左旋 218 * p p 219 * / / 220 * x y 221 * / \ / \ 222 * lx y -----> x ry 223 * / \ / \ 224 * ly ry lx ly 225 * 左旋做了三件事: 226 * 1. 将y的左子节点赋给x的右子节点,并将x赋给y左子节点的父节点(y左子节点非空时) 227 * 2. 将x的父节点p(非空时)赋给y的父节点,同时更新p的子节点为y(左或右) 228 * 3. 将y的左子节点设为x,将x的父节点设为y 229 */ 230 private void leftRotate(RBNode<T> x) { 231 //1. 将y的左子节点赋给x的右子节点,并将x赋给y左子节点的父节点(y左子节点非空时) 232 RBNode<T> y = x.right; 233 x.right = y.left; 234 235 if(y.left != null) 236 y.left.parent = x; 237 238 //2. 将x的父节点p(非空时)赋给y的父节点,同时更新p的子节点为y(左或右) 239 y.parent = x.parent; 240 241 if(x.parent == null) { 242 this.root = y; //如果x的父节点为空,则将y设为父节点 243 } else { 244 if(x == x.parent.left) //如果x是左子节点 245 x.parent.left = y; //则也将y设为左子节点 246 else 247 x.parent.right = y;//否则将y设为右子节点 248 } 249 250 //3. 将y的左子节点设为x,将x的父节点设为y 251 y.left = x; 252 x.parent = y; 253 } 254 255 /*************对红黑树节点y进行右旋操作 ******************/ 256 /* 257 * 左旋示意图:对节点y进行右旋 258 * p p 259 * / / 260 * y x 261 * / \ / \ 262 * x ry -----> lx y 263 * / \ / \ 264 * lx rx rx ry 265 * 右旋做了三件事: 266 * 1. 将x的右子节点赋给y的左子节点,并将y赋给x右子节点的父节点(x右子节点非空时) 267 * 2. 将y的父节点p(非空时)赋给x的父节点,同时更新p的子节点为x(左或右) 268 * 3. 将x的右子节点设为y,将y的父节点设为x 269 */ 270 private void rightRotate(RBNode<T> y) { 271 //1. 将y的左子节点赋给x的右子节点,并将x赋给y左子节点的父节点(y左子节点非空时) 272 RBNode<T> x = y.left; 273 y.left = x.right; 274 275 if(x.right != null) 276 x.right.parent = y; 277 278 //2. 将x的父节点p(非空时)赋给y的父节点,同时更新p的子节点为y(左或右) 279 x.parent = y.parent; 280 281 if(y.parent == null) { 282 this.root = x; //如果x的父节点为空,则将y设为父节点 283 } else { 284 if(y == y.parent.right) //如果x是左子节点 285 y.parent.right = x; //则也将y设为左子节点 286 else 287 y.parent.left = x;//否则将y设为右子节点 288 } 289 290 //3. 将y的左子节点设为x,将x的父节点设为y 291 x.right = y; 292 y.parent = x; 293 } 294 295 /*********************** 向红黑树中插入节点 **********************/ 296 public void insert(T key) { 297 RBNode<T> node = new RBNode<T>(key, RED, null, null, null); 298 if(node != null) 299 insert(node); 300 } 301 302 //将节点插入到红黑树中,这个过程与二叉搜索树是一样的 303 private void insert(RBNode<T> node) { 304 RBNode<T> current = null; //表示最后node的父节点 305 RBNode<T> x = this.root; //用来向下搜索用的 306 307 //1. 找到插入的位置 308 while(x != null) { 309 current = x; 310 int cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key); 311 if(cmp < 0) 312 x = x.left; 313 else 314 x = x.right; 315 } 316 node.parent = current; //找到了位置,将当前current作为node的父节点 317 318 //2. 接下来判断node是插在左子节点还是右子节点 319 if(current != null) { 320 int cmp = node.key.compareTo(current.key); 321 if(cmp < 0) 322 current.left = node; 323 else 324 current.right = node; 325 } else { 326 this.root = node; 327 } 328 329 //3. 将它重新修整为一颗红黑树 330 insertFixUp(node); 331 } 332 333 private void insertFixUp(RBNode<T> node) { 334 RBNode<T> parent, gparent; //定义父节点和祖父节点 335 336 //需要修整的条件:父节点存在,且父节点的颜色是红色 337 while(((parent = parentOf(node)) != null) && isRed(parent)) { 338 gparent = parentOf(parent);//获得祖父节点 339 340 //若父节点是祖父节点的左子节点,下面else与其相反 341 if(parent == gparent.left) { 342 RBNode<T> uncle = gparent.right; //获得叔叔节点 343 344 //case1: 叔叔节点也是红色 345 if(uncle != null && isRed(uncle)) { 346 setBlack(parent); //把父节点和叔叔节点涂黑 347 setBlack(uncle); 348 setRed(gparent); //把祖父节点涂红 349 node = gparent; //将位置放到祖父节点处 350 continue; //继续while,重新判断 351 } 352 353 //case2: 叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是右子节点 354 if(node == parent.right) { 355 leftRotate(parent); //从父节点处左旋 356 RBNode<T> tmp = parent; //然后将父节点和自己调换一下,为下面右旋做准备 357 parent = node; 358 node = tmp; 359 } 360 361 //case3: 叔叔节点是黑色,且当前节点是左子节点 362 setBlack(parent); 363 setRed(gparent); 364 rightRotate(gparent); 365 } else { //若父节点是祖父节点的右子节点,与上面的完全相反,本质一样的 366 RBNode<T> uncle = gparent.left; 367 368 //case1: 叔叔节点也是红色 369 if(uncle != null & isRed(uncle)) { 370 setBlack(parent); 371 setBlack(uncle); 372 setRed(gparent); 373 node = gparent; 374 continue; 375 } 376 377 //case2: 叔叔节点是黑色的,且当前节点是左子节点 378 if(node == parent.left) { 379 rightRotate(parent); 380 RBNode<T> tmp = parent; 381 parent = node; 382 node = tmp; 383 } 384 385 //case3: 叔叔节点是黑色的,且当前节点是右子节点 386 setBlack(parent); 387 setRed(gparent); 388 leftRotate(gparent); 389 } 390 } 391 392 //将根节点设置为黑色 393 setBlack(this.root); 394 } 395 396 /*********************** 删除红黑树中的节点 **********************/ 397 public void remove(T key) { 398 RBNode<T> node; 399 if((node = search(root, key)) != null) 400 remove(node); 401 } 402 403 private void remove(RBNode<T> node) { 404 RBNode<T> child, parent; 405 boolean color; 406 407 //1. 被删除的节点“左右子节点都不为空”的情况 408 if((node.left != null) && (node.right != null)) { 409 //先找到被删除节点的后继节点,用它来取代被删除节点的位置 410 RBNode<T> replace = node; 411 // 1). 获取后继节点 412 replace = replace.right; 413 while(replace.left != null) 414 replace = replace.left; 415 416 // 2). 处理“后继节点”和“被删除节点的父节点”之间的关系 417 if(parentOf(node) != null) { //要删除的节点不是根节点 418 if(node == parentOf(node).left) 419 parentOf(node).left = replace; 420 else 421 parentOf(node).right = replace; 422 } else { //否则 423 this.root = replace; 424 } 425 426 // 3). 处理“后继节点的子节点”和“被删除节点的子节点”之间的关系 427 child = replace.right; //后继节点肯定不存在左子节点! 428 parent = parentOf(replace); 429 color = colorOf(replace);//保存后继节点的颜色 430 if(parent == node) { //后继节点是被删除节点的子节点 431 parent = replace; 432 } else { //否则 433 if(child != null) 434 setParent(child, parent); 435 parent.left = child; 436 replace.right = node.right; 437 setParent(node.right, replace); 438 } 439 replace.parent = node.parent; 440 replace.color = node.color; //保持原来位置的颜色 441 replace.left = node.left; 442 node.left.parent = replace; 443 444 if(color == BLACK) { //4. 如果移走的后继节点颜色是黑色,重新修整红黑树 445 removeFixUp(child, parent);//将后继节点的child和parent传进去 446 } 447 node = null; 448 return; 449 } 450 } 451 //node表示待修正的节点,即后继节点的子节点(因为后继节点被挪到删除节点的位置去了) 452 private void removeFixUp(RBNode<T> node, RBNode<T> parent) { 453 RBNode<T> other; 454 455 while((node == null || isBlack(node)) && (node != this.root)) { 456 if(parent.left == node) { //node是左子节点,下面else与这里的刚好相反 457 other = parent.right; //node的兄弟节点 458 if(isRed(other)) { //case1: node的兄弟节点other是红色的 459 setBlack(other); 460 setRed(parent); 461 leftRotate(parent); 462 other = parent.right; 463 } 464 465 //case2: node的兄弟节点other是黑色的,且other的两个子节点也都是黑色的 466 if((other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) && 467 (other.right == null || isBlack(other.right))) { 468 setRed(other); 469 node = parent; 470 parent = parentOf(node); 471 } else { 472 //case3: node的兄弟节点other是黑色的,且other的左子节点是红色,右子节点是黑色 473 if(other.right == null || isBlack(other.right)) { 474 setBlack(other.left); 475 setRed(other); 476 rightRotate(other); 477 other = parent.right; 478 } 479 480 //case4: node的兄弟节点other是黑色的,且other的右子节点是红色,左子节点任意颜色 481 setColor(other, colorOf(parent)); 482 setBlack(parent); 483 setBlack(other.right); 484 leftRotate(parent); 485 node = this.root; 486 break; 487 } 488 } else { //与上面的对称 489 other = parent.left; 490 491 if (isRed(other)) { 492 // Case 1: node的兄弟other是红色的 493 setBlack(other); 494 setRed(parent); 495 rightRotate(parent); 496 other = parent.left; 497 } 498 499 if ((other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) && 500 (other.right==null || isBlack(other.right))) { 501 // Case 2: node的兄弟other是黑色,且other的俩个子节点都是黑色的 502 setRed(other); 503 node = parent; 504 parent = parentOf(node); 505 } else { 506 507 if (other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) { 508 // Case 3: node的兄弟other是黑色的,并且other的左子节点是红色,右子节点为黑色。 509 setBlack(other.right); 510 setRed(other); 511 leftRotate(other); 512 other = parent.left; 513 } 514 515 // Case 4: node的兄弟other是黑色的;并且other的左子节点是红色的,右子节点任意颜色 516 setColor(other, colorOf(parent)); 517 setBlack(parent); 518 setBlack(other.left); 519 rightRotate(parent); 520 node = this.root; 521 break; 522 } 523 } 524 } 525 if (node!=null) 526 setBlack(node); 527 } 528 529 /****************** 销毁红黑树 *********************/ 530 public void clear() { 531 destroy(root); 532 root = null; 533 } 534 535 private void destroy(RBNode<T> tree) { 536 if(tree == null) 537 return; 538 if(tree.left != null) 539 destroy(tree.left); 540 if(tree.right != null) 541 destroy(tree.right); 542 tree = null; 543 } 544 545 /******************* 打印红黑树 *********************/ 546 public void print() { 547 if(root != null) { 548 print(root, root.key, 0); 549 } 550 } 551 /* 552 * key---节点的键值 553 * direction--- 0:表示该节点是根节点 554 * 1:表示该节点是它的父节点的左子节点 555 * 2:表示该节点是它的父节点的右子节点 556 */ 557 private void print(RBNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) { 558 if(tree != null) { 559 if(0 == direction) 560 System.out.printf("%2d(B) is root\n", tree.key); 561 else 562 System.out.printf("%2d(%s) is %2d's %6s child\n", 563 tree.key, isRed(tree)?"R":"b", key, direction == 1?"right":"left"); 564 print(tree.left, tree.key, -1); 565 print(tree.right, tree.key, 1); 566 } 567 } 568 } 569
4.2、测试程序

1 package test; 2 3 import tree.RBTree; 4 5 public class RBTreeTest { 6 7 private static final int a[] = {10, 40, 30, 60, 90, 70, 20, 50, 80}; 8 private static final boolean mDebugInsert = true; // "插入"动作的检测开关(false,关闭;true,打开) 9 private static final boolean mDebugDelete = true; // "删除"动作的检测开关(false,关闭;true,打开) 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 int i, ilen = a.length; 13 RBTree<Integer> tree = new RBTree<Integer>(); 14 15 System.out.printf("== 原始数据: "); 16 for(i=0; i<ilen; i++) 17 System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]); 18 System.out.printf("\n"); 19 20 for(i=0; i<ilen; i++) { 21 tree.insert(a[i]); 22 // 设置mDebugInsert=true,测试"添加函数" 23 if (mDebugInsert) { 24 System.out.printf("== 添加节点: %d\n", a[i]); 25 System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n"); 26 tree.print(); 27 System.out.printf("\n"); 28 } 29 } 30 31 System.out.printf("== 前序遍历: "); 32 tree.preOrder(); 33 34 System.out.printf("\n== 中序遍历: "); 35 tree.inOrder(); 36 37 System.out.printf("\n== 后序遍历: "); 38 tree.postOrder(); 39 System.out.printf("\n"); 40 41 System.out.printf("== 最小值: %s\n", tree.minValue()); 42 System.out.printf("== 最大值: %s\n", tree.maxValue()); 43 System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n"); 44 tree.print(); 45 System.out.printf("\n"); 46 47 // 设置mDebugDelete=true,测试"删除函数" 48 if (mDebugDelete) { 49 for(i=0; i<ilen; i++) 50 { 51 tree.remove(a[i]); 52 53 System.out.printf("== 删除节点: %d\n", a[i]); 54 System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n"); 55 tree.print(); 56 System.out.printf("\n"); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 }
五、总结
红黑树是一种重要的二叉树,应用广泛,红黑树还是有点难,因此在学习红黑树的时候一定要多画+多想,这样才能更好地理解红黑树的原理,尤其是旋转的原理。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号