CS61B srping 2018 disc02 sol https://sp18.datastructur.es/
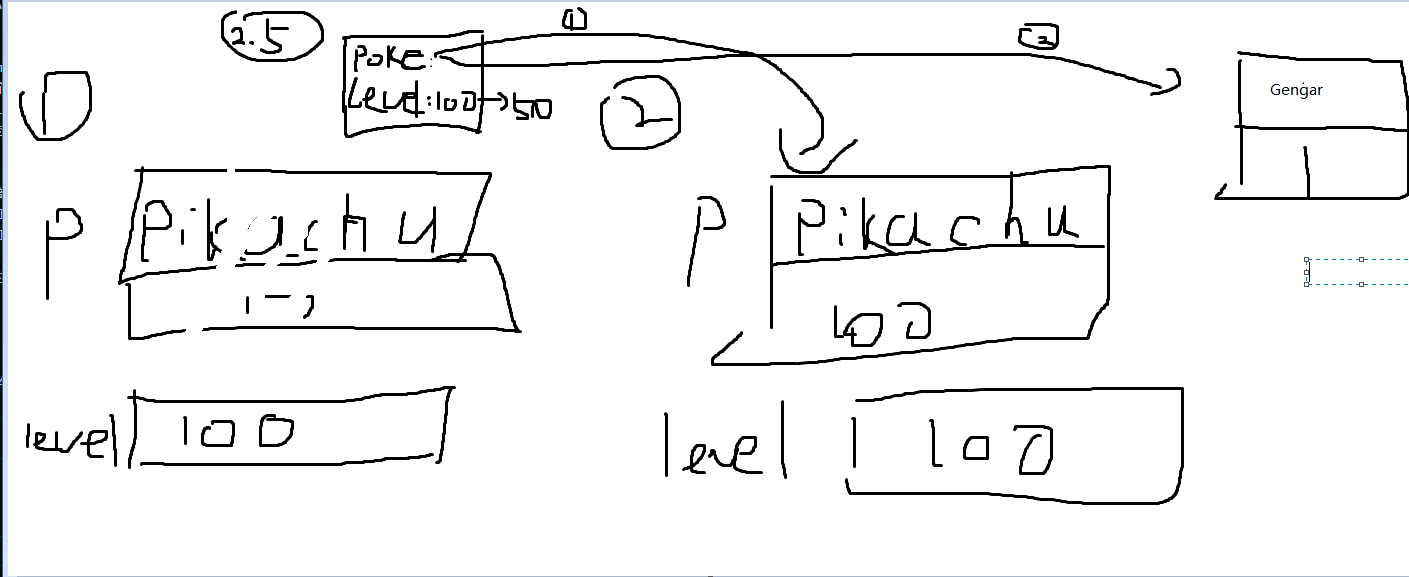
第19行的变量 level是 静态方法change方法内部的本地变量,他对main方法里的level或者是实例变量level没什么影响。
public class Pokemon {// 一个名为Pokemon的类
public String name;// 实例变量name
public int level;// 实例变量level
public Pokemon(String name, int level) { //实例方法 接受String类型的name和int类型的level
this.name = name;// 把实例变量name赋值为传入的name
this.level = level;//把实例变量level赋值为传入的level
}
public static void main(String[] args) { // Pokemon的 main方法
Pokemon p = new Pokemon("Pikachu", 17); //声明一个 Pokemon类型的实例p,生成一个新的Pokemon实例 传入"Pikachu",17两个参数 赋值给p
int level = 100;// 在main 方法内部声明一个本地变量level,赋值为100
change(p, level);// 调用静态方法change, 会把实例变量p的level变成传入的level也就是100的值。
System.out.println("Name: " + p.name + ", Level: " + p.level);// **Name: Pikachu, Level: 100 **
}
//change 方法会把接受的poke实例的实例变量level变成接收的level的值
public static void change(Pokemon poke, int level) {// 静态方法,接收一个Pokemon类型的实例poke ,一个int整形level
poke.level = level;// 把 接受的实例poke的实例变量 level变成接收的int整形level的值
//下面是第19行
level = 50;//把接收的 level值变成50 ;
poke = new Pokemon("Gengar", 1);//把接收的poke(的指向)变成一个新的Pokemon实例, ("Gengar", 1) 。
}
}
2.静态方法和变量 Static Methods and Variables
public class Cat {
public String name;
public static String noise; // 注意noise是静态变量
public Cat(String name, String noise) {
this.name = name;
this.noise = noise;
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(noise + " I'm " + name + " the cat!");
}
public static void anger() {//anger是静态方法
noise = noise.toUpperCase();
}
public static void calm() {
noise = noise.toLowerCase();
}
}
运行下列程序,写出每一次play方法被调用的结果
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat a = new Cat("Cream", "Meow!"); // 实例 a Cream ,Meow
Cat b = new Cat("Tubbs", "Nyan!"); // 实例 b Tubbs,Nyan;实例 a Cream ,Nyan
a.play(); //Nyan! I'm Cream the cat
b.play(); //Nyan! I'm Tubbs the cat
Cat.anger(); //实例 a Cream ,NYAN;实例 b Tubbs,NYAN
a.calm(); // 实例 a Cream ,nyan; 实例 b Tubbs,nyan;
a.play();//nyan! I'm Cream the cat
b.play();//nyan! I'm Tubbs the cat
}
链表的一些介绍Practice with Linked Lists
为下面程序的运行过程画出对应的 box-and-pointer 图,StringList类似IntList,有rest和first两个实例变量
StringList L = new StringList("eat", null);
L = new StringList("shouldn't", L);
L = new StringList("you", L);
L = new StringList("sometimes", L);
StringList M = L.rest;
StringList R = new StringList("many", null);
R = new StringList("potatoes", R);
R.rest.rest = R;
M.rest.rest.rest = R.rest;
L.rest.rest = L.rest.rest.rest;
L = M.rest;
- 如下两个平方列表元素的方法
public static IntList square(IntList L) {
if (L == null) {
return L;
} else {
IntList rest = square(L.rest);
IntList M = new IntList(L.first * L.first, rest);
return M;
}
}
public static IntList squareMutative(IntList L) {
IntList B = L;
while (B != null) {
B.first *= B.first;
B = B.rest
}
return L;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号