Test1
任务一
源代码
// 现代C++标准库、算法库体验
// 本例用到以下内容:
// 1. 字符串string, 动态数组容器类vector、迭代器
// 2. 算法库:反转元素次序、旋转元素
// 3. 函数模板、const引用作为形参
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
// 模板函数声明
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c);
void test1();
void test2();
void test3();
int main()
{
std::cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
std::cout << "\n测试3: \n";
test3();
}
// 输出容器对象c中的元素
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c)
{
for (auto &i : c)
std::cout << i << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
}
// 测试1:组合使用算法库、迭代器、string反转字符串
void test1()
{
using namespace std;
string s0{"0123456789"};
cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl;
string s1(s0);
// 反转s1自身
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
string s2(s0.size(), ' ');
// 将s0反转后结果拷贝到s2, s0自身不变
reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin());
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
}
// 测试2:组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector反转动态数组对象vector内数据
void test2()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end());
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin());
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
}
// 测试3:组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector实现元素旋转移位
void test3()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
// 将[v1.begin(), v1.end())区间内元素循环左移1位
rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin() + 1, v1.end());
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
// 将[v1.begin(), v1.end())区间内元素循环左移2位
rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin() + 2, v2.end());
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
vector<int> v3{v0};
// 将[v1.begin(), v1.end())区间内元素循环右移1位
rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end() - 1, v3.end());
cout << "v3: ";
output(v3);
vector<int> v4{v0};
// 将[v1.begin(), v1.end())区间内元素循环右移2位
rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end() - 2, v4.end());
cout << "v4: ";
output(v4);
}
测试结果
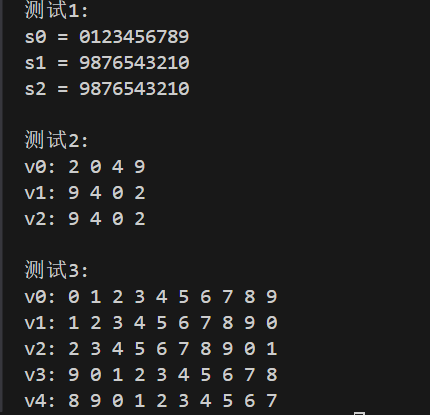
测试结论
问题1:reverse和reverse_copy有什么区别?
答:reserve是不需要新的容器而实现反转,reserve_copy需要新的容器放新反转的数据。
问题2:rotate算法是如何改变元素顺序的?它的三个参数分别代表什么?
答:采用循环置换的方法,将元素进行“环”循环搬运。三个参数分别是循环区间的起点,循环的切分点,循环区间的终点。
任务二
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
// 模板函数声明
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c);
int generate_random_number();
void test1();
void test2();
int main()
{
std::srand(std::time(0)); // 添加随机种子
std::cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
}
// 输出容器对象c中的元素
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c)
{
for (auto &i : c)
std::cout << i << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
}
// 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数
int generate_random_number()
{
return std::rand() % 101;
}
// 测试1:对容器类对象指定迭代器区间赋值、排序
void test1()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number); // 生成随机数填充v0
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对整个vector排序
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
sort(v2.begin() + 1, v2.end() - 1); // 只对中间部分排序,不包含首尾元素
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
}
// 测试2:对容器类对象指定迭代器区间赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值
void test2()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0(10);
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number);
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
// 求最大值和最小值
auto min_iter = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
auto max_iter = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *min_iter << endl;
cout << "最大值: " << *max_iter << endl;
// 同时求最大值和最小值
auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl;
cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl;
// 求平均值
double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0.0) / v0.size();
cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl;
sort(v0.begin(), v0.end());
double avg2 = accumulate(v0.begin() + 1, v0.end() - 1, 0.0) / (v0.size() - 2);
cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl;
}
测试结果
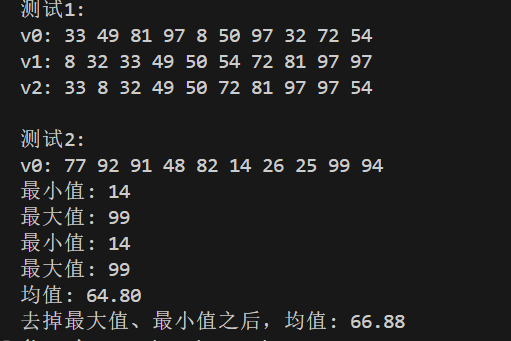
实验结论
问题1:generate算法的作用是什么?
答:对数组对象用随机生成数进行填充,随机生成的数可以用generate_random_number()来约束。
问题2:minmax_element 和min_element 、max_element 相比,有什么优势?
答:minmax_element在遍历一次可以找到最大值和最小值,而用min_element和max_element需要遍历两次,时间复杂度相对较小。
问题3:查询generate 第3个参数[](){return std::rand()%101;}用法,与使用自定义函数generate_random_number相比,lambda表达式适用场景是什么?
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), [](){return std::rand()%101;});
答:适用于当前语境使用,不会被多次调用。
任务三
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
unsigned char func(unsigned char c);
void test1();
void test2();
int main()
{
std::cout << "测试1: 字符串大小写转换\n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: 字符变换\n";
test2();
}
unsigned char func(unsigned char c)
{
if (c == 'z')
return 'a';
if (c == 'Z')
return 'A';
if (std::isalpha(c))
return static_cast<unsigned char>(c + 1);
return c;
}
void test1()
{
std::string s1{"Hello World 2049!"};
std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n';
std::string s2;
for (auto c : s1)
s2 += std::tolower(c);
std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n';
std::string s3;
for (auto c : s1)
s3 += std::toupper(c);
std::cout << "s3 = " << s3 << '\n';
}
void test2()
{
std::string s1{"I love cosmos!"};
std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n';
std::string s2(s1.size(), ' ');
std::transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(),
s2.begin(),
func);
std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n';
}
测试结果
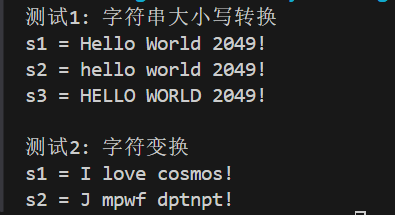
实验结论
问题1:自定义函数func功能是什么?
答:使得字母‘z’变成‘a’,‘Z’变成‘A’,其他字母向后变换,不是字母原样返回。
问题2:tolower和toupper功能分别是什么?
答:分别是将大写字母转小写和小写字母转大写。
问题3:transform的4个参数意义分别是什么?如果把第3个参数s2.begin()改成s1.begin(),有何区别?
答: 转换的开始,转换的结尾,转换放置的容器,转换规则。把转换后的字符串又放到了s1,这时s2为空。
任务四
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s);
bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string s;
// 多组输入,直到按下Ctrl+Z结束测试
while (cin >> s)
{
cout << boolalpha
<< "区分大小写: " << is_palindrome(s) << "\n"
<< "不区分大小写: " << is_palindrome_ignore_case(s) << "\n\n";
}
}
// 函数is_palindrome定义
bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s)
{
std::string s1(s.size(), ' ');
std::reverse_copy(s.begin(), s.end(), s1.begin());
return s == s1;
}
// 函数is_palindrome_ignore_case定义
bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s)
{
std::string s1(s.size(), ' ');
std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), s1.begin(), ::tolower);
std::string s2(s.size(), ' ');
std::reverse_copy(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s2.begin());
return s2 == s1;
}
测试结果
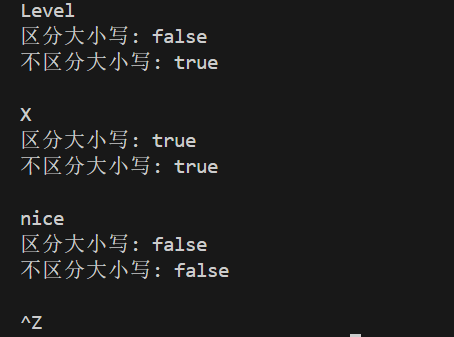
实验结论
问题1:用cin >> s输入时,输入的字符串中不能包含空格。如果希望测试字符串包含空格(如hello oop),代码应如何调整?
答:
std::string s;
std::getline(std::cin, s);
任务五
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2);
int main()
{
int x;
while (std::cin >> x)
{
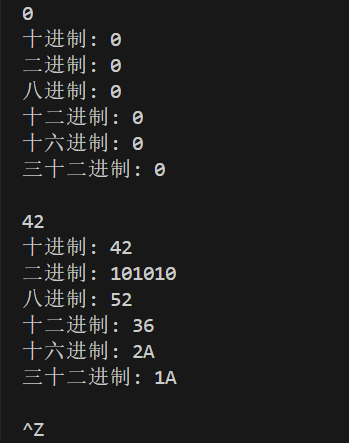
std::cout << "十进制: " << x << '\n'
<< "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << '\n'
<< "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << '\n'
<< "十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 12) << '\n'
<< "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << '\n'
<< "三十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 32) << "\n\n";
}
}
// 函数dec2n定义
std::string dec2n(int x, int n)
{
const char *digits = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
if (n < 2 || n > 36)
return "没有实现" + std::to_string(n) + "进制转换";
if (x == 0)
return "0";
std::string result;
while (x > 0)
{
int t = x % n;
result += digits[t];
x /= n;
}
std::reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
测试结果
任务六
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
void test()
{
std::string s = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
std::cout << " ";
for (auto &c : s)
std::cout << ' ' << c;
std::cout << '\n';
std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), s.begin(), ::toupper);
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; ++i)
{
std::rotate(s.begin(), s.begin() + 1, s.end());
std::cout << std::setw(2) << i;
for (auto &c : s)
std::cout << ' ' << c;
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
测试结果
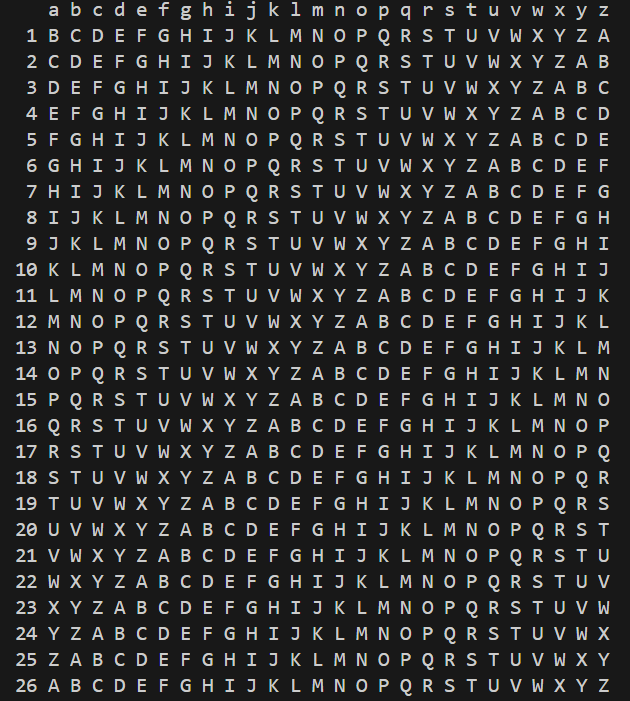
任务七
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
class Question
{
public:
Question(int x, int y);
~Question() = default;
void print() const
{
std::cout << a << ' ' << op << ' ' << b << " = ";
}
bool check(int user_answer) const
{
return user_answer == answer;
}
private:
int a, b, answer;
char op;
static const char ops[4];
};
const char Question::ops[4] = {'+', '-', '*', '/'};
Question::Question(int x, int y) : a(x), b(y)
{
int op_index = rand() % 4;
op = ops[op_index];
if (op == '+')
{
answer = a + b;
}
else if (op == '-')
{
if (a < b)
std::swap(a, b);
answer = a - b;
}
else if (op == '*')
{
answer = a * b;
}
else
{
if (b == 0)
b = rand() % 10 + 1;
while (a % b != 0)
{
a = rand() % 11;
b = rand() % 10 + 1;
}
answer = a / b;
}
}
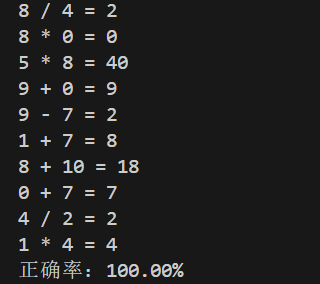
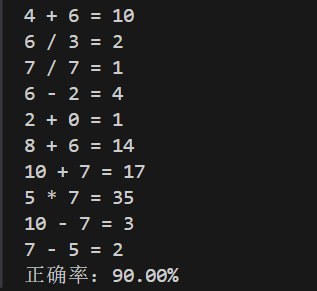
int main()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 10;
int correct_count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
int a = rand() % 11;
int b = rand() % 11;
Question q(a, b);
q.print();
int user_answer;
std::cin >> user_answer;
if (q.check(user_answer))
{
++correct_count;
}
}
double rate = 100.0 * correct_count / N;
std::cout << "正确率:" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rate << "%";
return 0;
}
测试结果



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号