Postman-Tests
用于postman断言
一、Postman断言
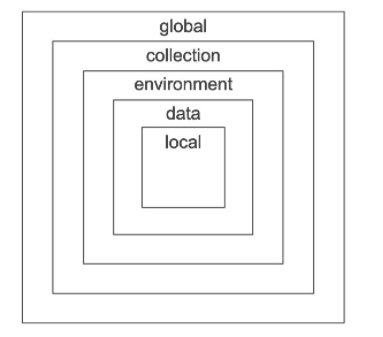
1.环境环境
获取环境变量--Get an enviroment variable
pm.environment.set("variable_key", "variable_value");
将嵌套对象设置为环境变量
var array = [1, 2, 3, 4];
pm.environment.set("array", JSON.stringify(array, null, 2));
var obj = { a: [1, 2, 3, 4], b: { c: 'val' } };
pm.environment.set("obj", JSON.stringify(obj));
获取环境变量
var value = pm.environment.get("variable_key");
如果值为字符串化JSON:
// These statements should be wrapped in a try-catch block if the data is coming from an unknown source.
var array = JSON.parse(pm.environment.get("array"));
var obj = JSON.parse(pm.environment.get("obj"));
清除环境变量
pm.environment.unset("variable_key");
2.集合
设置集合变量
pm.collectionVariables.set(variableName:String, variableValue:String);
获取集合变量
pm.collectionVariables.get(variableName:String);
清除集合变量
pm.collectionVariables.unset(variableName:String);
3.全局
设置全局变量
pm.globals.set("variable_key", "variable_value");
获取全局变量
pm.globals.get("variable_key");
清除全局变量
pm.globals.unset("variable_key");
4.变数
此函数在全局变量和活动环境中搜索变量。
var value = pm.variables.get("variable_key");
二、响应处理
检查响应主体是否包含字符串
pm.test("Body matches string", function () {
pm.expect(pm.response.text()).to.include("string_you_want_to_search");
});
检查响应主体是否等于字符串
pm.test("Body is correct", function () {
pm.response.to.have.body("response_body_string");
});
检查JSON值
pm.test("Your test name", function () {
var jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(jsonData.value).to.eql(100);
});
存在Content-Type标头
pm.test("Content-Type header is present", function () {
pm.response.to.have.header("Content-Type");
});
响应时间小于200ms
pm.test("Response time is less than 200ms", function () {
pm.expect(pm.response.responseTime).to.be.below(200);
});
状态码为200
pm.test("Status code is 200", function () {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
代号名称包含一个字符串
pm.test("Status code name has string", function () {
pm.response.to.have.status("Created");
});
成功的POST请求状态代码
pm.test("Successful POST request", function () {
pm.expect(pm.response.code).to.be.oneOf([201,202]);
});
三、验证响应结构
使用TV4进行JSON模式验证
var schema = {
"items": {
"type": "boolean"
}
};
var data1 = [true, false];
var data2 = [true, 123];
pm.test('Schema is valid', function() {
pm.expect(tv4.validate(data1, schema)).to.be.true;
pm.expect(tv4.validate(data2, schema)).to.be.true;
});
使用AJV进行JSON模式验证
var Ajv = require('ajv'),
ajv = new Ajv({logger: console}),
schema = {
"properties": {
"alpha": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
};
pm.test('Schema is valid', function() {
pm.expect(ajv.validate(schema, {alpha: true})).to.be.true;
pm.expect(ajv.validate(schema, {alpha: 123})).to.be.false;
});
1.编码/解码
解码base64数据
// Assume `base64Content` has a base64 encoded value
var rawContent = base64Content.slice('data:application/octet-stream;base64,'.length);
// CryptoJS is an inbuilt object, documented here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/crypto-js
var intermediate = CryptoJS.enc.Base64.parse(base64content);
pm.test('Contents are valid', function() {
pm.expect(CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.stringify(intermediate)).to.be.true; // a check for non-emptiness
});
将XML主体转换为JSON对象
var jsonObject = xml2Json(responseBody);
2.发送异步请求
此功能既可以作为预请求脚本也可以作为测试脚本使用。
pm.sendRequest("https://postman-echo.com/get", function (err, response) {
console.log(response.json());
});
3.样本数据文件
JSON文件由键/值对组成。
对于CSV文件,第一行需要包含变量名。
4.断言库示例
以下是Postman测试脚本中使用的一些最常见的断言测试的列表。
请注意,此列表并不详尽。有关完整的参考,请参见以下文档:ChaiJS Expect BDD库
断言目标中是否存在子字符串
pm.test("Check if pattern is in target string",function () {
pm.expect('foobar').to.have.string('bar');
});
严格比较
const TEN = 10;
pm.test('Check if number is equal to 10', function () {
pm.expect(TEN).to.equal(10);
});
比较宽松
pm.test("Our JSON is loosely equal to the provided JSON", function () {
pm.expect(data1).to.deep.equal(data2);
});
注意:
.deep导致所有.equal,.include,.members,.keys,和.property其按照使用深平等(松散平等),而不是严格(===)平等链断言。- 虽然
.eql还松散地进行了比较,但.deep.equal导致深度相等性比较也可用于链中后面的任何其他声明,而.eql没有使用。
主张回应的价值
pm.test("Check response value", function () {
var jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(jsonData.value).to.eql(100);
});
声明当前环境
pm.test("Check if environment is production", function () {
pm.expect(pm.environment.get('env')).to.equal('production');
});
断言目标的类型等于给定的字符串 **type**
pm.test("Check if target is string", function () {
pm.expect('Postman').to.be.a('string');
});
pm.test("Check if target is an object", function () {
pm.expect({a: 1}).to.be.an('object');
});
pm.test("Check if target is undefined", function () {
pm.expect(undefined).to.be.an('undefined');
});
注意:
- 通常最好在对同一目标进行更多断言之前先
.a检查目标的状态type。 - 类型不区分大小写。
断言目标是否为空
pm.test("Check if array is empty", function () {
expect([]).to.be.empty;
});
pm.test("Check if string is empty", function () {
pm.expect('').to.be.empty;
});
可以将其与.a检查目标是否为空但有一个type,例如an array或an一起使用object。
例:
pm.test("Check if array is empty", function () {
pm.expect([]).to.be.an('array').that.is.empty;
});
断言目标包含已传递的密钥
pm.test("Check if object contains all provided keys", function () {
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.have.all.keys('a', 'b');
});
pm.test("Checking if object contains any ONE of the keys", function () {
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.have.any.keys('a', 'b');
});
pm.test("Check if object contains any NONE of the provided keys", function () {
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.not.have.any.keys('c', 'd');
});
断言目标包含所述属性
pm.test("Check if object contains the property", function () {
pm.expect({a: 1}).to.have.property('a');
});
注意:
- 目标可以是
object,set,array或map。 - 如果
.keys在不使用.all或.any的情况下运行,则表达式默认为.all。 - 由于
.keys不根据目标的不同的东西type,建议检查目标的type使用之前.keys使用.a。
pm.test("Check if object contains all the keys", function () {
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.be.an('object').that.has.all.keys('a', 'b');
});
确认目标长度
pm.test("Check the length of the target", function () {
pm.expect('foo').to.have.lengthOf(3);
});
pm.test("Check the size of the target", function () {
pm.expect([1, 2, 3]).to.have.lengthOf(2);
});
断言目标数组具有与给定数组集相同的成员
pm.test("Check if the target has same members as the array set", function () {
pm.expect([1, 2, 3]).to.have.members([2, 1, 3]);
});
注意:
- 默认情况下,
.members进行严格比较。 - 成员的顺序无关紧要。
断言目标包含所提供的项目
pm.test("Check if the target array includes the number provided", function () {
pm.expect([1, 2, 3]).to.include(2);
});
pm.test("Check if the target object includes the properties provided", function () {
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}).to.include({a: 1, b: 2});
});
注意: 建议先声明目标的类型,因为要.include对各种类型进行操作。因此,建议.a在使用时进行连锁.include。
例:
pm.test("Check if the target is an array that includes the number specified", function () {
pm.expect([1, 2, 3]).to.be.an('array').that.includes(2);
});
5.较旧的Postman测试写作风格(已弃用)
注意:本节涉及在较早版本的Postman中使用的不赞成使用的脚本语法。如果现在正在编写脚本,请使用上述语法。
Postman测试的较早编写风格依赖于为特殊tests对象设置值。您可以为对象中的元素设置一个描述键,然后说出它是对还是错。例如,tests["Body contains user_id"] = responsebody.has("user_id");将检查响应正文是否包含user_id字符串。
您可以根据需要添加多少密钥,具体取决于要测试的内容。您可以在“ 测试”选项卡下的响应查看器中查看测试结果。选项卡标题显示了通过了多少测试,并且在此处列出了您在tests变量中设置的键。如果该值评估为true,则测试通过。
设置环境变量(不建议使用)
postman.setEnvironmentVariable("key", "value");
将嵌套对象设置为环境变量(不建议使用)
var array = [1, 2, 3, 4];
postman.setEnvironmentVariable("array", JSON.stringify(array, null, 2));
var obj = { a: [1, 2, 3, 4], b: { c: 'val' } };
postman.setEnvironmentVariable("obj", JSON.stringify(obj));
获取环境变量(不建议使用)
postman.getEnvironmentVariable("key");
获取环境变量(其值为字符串对象)(不建议使用)
// These statements should be wrapped in a try-catch block if the data is coming from an unknown source.
var array = JSON.parse(postman.getEnvironmentVariable("array"));
var obj = JSON.parse(postman.getEnvironmentVariable("obj"));
清除环境变量(不建议使用)
postman.clearEnvironmentVariable("key");
设置全局变量(不建议使用)
postman.setGlobalVariable("key", "value");
获取全局变量(不建议使用)
postman.getGlobalVariable("key");
清除全局变量(不建议使用)
postman.clearGlobalVariable("key");
检查响应主体是否包含字符串(不建议使用)
tests["Body matches string"] = responseBody.has("string_you_want_to_search");
将XML主体转换为JSON对象(不建议使用)
var jsonObject = xml2Json(responseBody);
检查响应主体是否等于字符串(不建议使用)
tests["Body is correct"] = responseBody === "response_body_string";
检查JSON值(不建议使用)
var data = JSON.parse(responseBody);
tests["Your test name"] = data.value === 100;
存在Content-Type(不区分大小写的检查)(不建议使用)
tests["Content-Type is present"] = postman.getResponseHeader("Content-Type"); //Note: the getResponseHeader() method returns the header value, if it exists.
存在Content-Type(区分大小写)(不建议使用)
tests["Content-Type is present"] = responseHeaders.hasOwnProperty("Content-Type");
响应时间小于200ms(不建议使用)
tests["Response time is less than 200ms"] = responseTime < 200;
响应时间在特定范围内(包括下限,包括上限)(不建议使用)
tests["Response time is acceptable"] = _.inRange(responseTime, 100, 1001); // _ is the inbuilt Lodash v3.10.1 object, documented at https://lodash.com/docs/3.10.1
状态码为200(已弃用)
tests["Status code is 200"] = responseCode.code === 200;
代号名称包含字符串(不建议使用)
tests["Status code name has string"] = responseCode.name.has("Created");
成功的POST请求状态代码(不建议使用)
tests["Successful POST request"] = responseCode.code === 201 || responseCode.code === 202;
对TinyValidator使用JSON数据(不建议使用)
var schema = {
"items": {
"type": "boolean"
}
};
var data1 = [true, false];
var data2 = [true, 123];
tests["Valid Data1"] = tv4.validate(data1, schema);
tests["Valid Data2"] = tv4.validate(data2, schema);
console.log("Validation failed: ", tv4.error);
解码base64编码的数据(不建议使用)
var intermediate,
base64Content, // assume this has a base64 encoded value
rawContent = base64Content.slice('data:application/octet-stream;base64,'.length);
intermediate = CryptoJS.enc.Base64.parse(base64content); // CryptoJS is an inbuilt object, documented here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/crypto-js
tests["Contents are valid"] = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.stringify(intermediate); // a check for non-emptiness


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号