Mysql源码学习——Thread Manager
2011-08-27 15:18 心中无码 阅读(1936) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报一、前言
上篇的Connection Manager中,曾提及对于一个新到来的Connection,服务器会创建一个新的线程来处理这个连接。
其实没那么简单,为了提高系统效率,减少频繁创建线程和中止线程的系统消耗,Mysql使用了线程缓冲区的概念,即如果
一个连接断开,则并不销毁承载其的线程,而是将此线程放入线程缓冲区,并处于挂起状态,当下一个新的Connection到来
时,首先去线程缓冲区去查找是否有空闲的线程,如果有,则使用之,如果没有则新建线程。本问主要介绍这个线程缓冲区,
首先介绍下基本的概念。
二、基本概念
1.线程创建函数
大家知道,Mysql现在是插件式的存储引擎,只要实现规定的接口,就可实现自己的存储引擎。故Mysql的线程创建除了
出现在主服务器框架外,存储引擎也可能会进行线程的创建。通过设置断点,在我调试的版本中,发现了两个创建线程的函数。
pthread_create:Mysql自用的创建线程函数 os_thread_create:存储引擎innobase的创建线程的函数
os_thread_create是存储引擎innobase的线程函数,先搁浅不研究了,重点看下pthread_create,首先看下其源码。
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread_id, pthread_attr_t *attr,
pthread_handler func, void *param)
{
HANDLE hThread;
struct pthread_map *map;
DBUG_ENTER("pthread_create");
if (!(map=malloc(sizeof(*map))))
DBUG_RETURN(-1);
map->func=func; map->param=param;
pthread_mutex_lock(&THR_LOCK_thread); #ifdef __BORLANDC__ hThread=(HANDLE)_beginthread((void(_USERENTRY *)(void *)) pthread_start, attr->dwStackSize ? attr->dwStackSize : 65535, (void*) map); #else
hThread=(HANDLE)_beginthread((void( __cdecl *)(void *)) pthread_start, attr->dwStackSize ? attr->dwStackSize : 65535, (void*) map);
#endif
DBUG_PRINT("info", ("hThread=%lu",(long) hThread));
*thread_id=map->pthreadself=hThread;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&THR_LOCK_thread);
if (hThread == (HANDLE) -1)
{
int error=errno;
DBUG_PRINT("error",
("Can't create thread to handle request (error %d)",error));
DBUG_RETURN(error ? error : -1);
}
VOID(SetThreadPriority(hThread, attr->priority)) ;
DBUG_RETURN(0);
}
上面代码首先构造了一个map结构体,成员分别是函数地址和传入参数。然后调用操作系统的接口,_beginthread,但是执行函数并不是传入的函数——func,而是pthread_start,参数为map。继续跟踪pthread_start。
pthread_handler_t pthread_start(void *param)
{
pthread_handler
func=((struct pthread_map *) param)->func
; void *func_param=((struct pthread_map *) param)->param; my_thread_init(); /* Will always succeed in windows */ pthread_mutex_lock(&THR_LOCK_thread); /* Wait for beginthread to return */ win_pthread_self=((struct pthread_map *) param)->pthreadself; pthread_mutex_unlock(&THR_LOCK_thread); free((char*) param); /* Free param from create */ pthread_exit((void*) (*func)(func_param)); return 0; /* Safety */ }
可以看出,pthread_start中调用了map的func元素,作为真正执行的函数体。OK,创建线程的函数跟踪到此!
2.服务器启动时创建了哪些函数?
通过在两个创建线程的地方设置断点,总结了下,在服务器启动时,创建了如下的线程。
pthread_create创建的线程:
| 创建线程函数 | 线程执行函数 |
|
create_shutdown_thread |
handle_shutdown |
|
start_handle_manager |
handle_manager |
|
handle_connections_methods |
handle_connections_sockets |
innobase的os_thread_create创建的线程:
| 创建线程函数 | 线程执行函数 |
|
innobase_start_or_create_for_mysql |
io_handler_thread(4个) |
|
recv_recovery_from_checkpoint_finish |
trx_rollback_or_clean_all_without_sess |
|
innobase_start_or_create_for_mysql |
srv_lock_timeout_thread |
|
srv_error_monitor_thread |
|
|
srv_monitor_thread |
|
|
srv_master_thread |
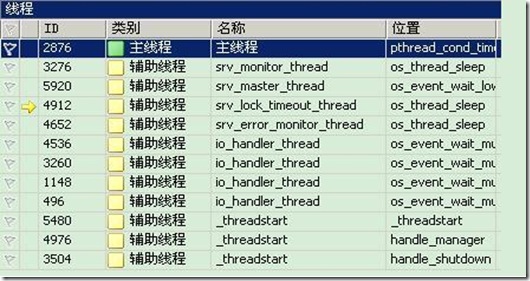
还可以在调试过程中,通过暂停来看此时服务器中的线程,如下图:
三、线程缓冲池
Mysql支持线程缓存,在多线程连接模式下,如果连接断开后,将这个线程放入空闲线程缓冲区,在下次有连接到来时,
先去缓冲池中查找是否有空闲线程,有则用之,无则创建。启动时可以设置线程缓冲池的数目:
Mysqld.exe --thread_cache_size=10
在一个连接断开时,会调用cache_thread函数,将空闲的线程加入到cache中,以备后用。源码如下:
static bool cache_thread()
{
safe_mutex_assert_owner(&LOCK_thread_count);
if (
cached_thread_count < thread_cache_size
&&
! abort_loop && !kill_cached_threads)
{
/* Don't kill the thread, just put it in cache for reuse */
DBUG_PRINT("info", ("Adding thread to cache"));
cached_thread_count++;
while (!abort_loop && ! wake_thread && ! kill_cached_threads)
(void) pthread_cond_wait(&COND_thread_cache, &LOCK_thread_count);
cached_thread_count--;
if (kill_cached_threads)
pthread_cond_signal(&COND_flush_thread_cache);
if (wake_thread)
{
THD *thd;
wake_thread--;
thd= thread_cache.get();
thd->thread_stack= (char*) &thd; // For store_globals
(void) thd->store_globals();
/*
THD::mysys_var::abort is associated with physical thread rather
than with THD object. So we need to reset this flag before using
this thread for handling of new THD object/connection.
*/
thd->mysys_var->abort= 0;
thd->thr_create_utime= my_micro_time();
threads.append(thd);
return(1);
}
}
return(0);
}
上面我们的启动参数设置线程缓冲区为10,此时对应代码里面的thread_cache_size = 10,cached_thread_count记录
了此刻cache中的空闲线程数目,只有在cache未满的情况下,才会将新的空闲线程加入缓冲池中。加入到缓冲区其实就是将线
程挂起,pthread_cond_wait函数便是线程等待函数,在此函数中,会调用WaitForMultipleObjects进行事件等待。具体源码
如下:
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex,
struct timespec *abstime)
{
int result;
long timeout;
union ft64 now;
if( abstime != NULL )
{
GetSystemTimeAsFileTime(&now.ft);
/*
Calculate time left to abstime
- subtract start time from current time(values are in 100ns units)
- convert to millisec by dividing with 10000
*/
timeout= (long)((abstime->tv.i64 - now.i64) / 10000);
/* Don't allow the timeout to be negative */
if (timeout < 0)
timeout= 0L;
/*
Make sure the calucated timeout does not exceed original timeout
value which could cause "wait for ever" if system time changes
*/
if (timeout > abstime->max_timeout_msec)
timeout= abstime->max_timeout_msec;
}
else
{
/* No time specified; don't expire */
timeout= INFINITE;
}
/*
Block access if previous broadcast hasn't finished.
This is just for safety and should normally not
affect the total time spent in this function.
*/
WaitForSingleObject(cond->broadcast_block_event, INFINITE);
EnterCriticalSection(&cond->lock_waiting);
cond->waiting++;
LeaveCriticalSection(&cond->lock_waiting);
LeaveCriticalSection(mutex);
result= WaitForMultipleObjects(2, cond->events, FALSE, timeout);
EnterCriticalSection(&cond->lock_waiting);
cond->waiting--;
if (cond->waiting == 0)
{
/*
We're the last waiter to be notified or to stop waiting, so
reset the manual event.
*/
/* Close broadcast gate */
ResetEvent(cond->events[BROADCAST]);
/* Open block gate */
SetEvent(cond->broadcast_block_event);
}
LeaveCriticalSection(&cond->lock_waiting);
EnterCriticalSection(mutex);
return result == WAIT_TIMEOUT ? ETIMEDOUT : 0;
}
此处是等待时间,何处进行事件通知呢?我们再次来到上篇所提及的为新的连接创建线程的代码中:
void create_thread_to_handle_connection(THD *thd)
{
if (cached_thread_count > wake_thread)
{
/* Get thread from cache */
thread_cache.append(thd);
wake_thread++;
pthread_cond_signal(&COND_thread_cache);
} Else ... }
上篇文章我们其实只讲了ELSE分支,而忽略了IF分支。wake_thread代表了唤醒的线程数,即在线程缓冲区中被再次使用的
线程,如果cache中的总数>被重新使用的数目,说明还有空闲的线程,此时进入if分支,调用phtread_cond_signal唤醒上面挂起
的空闲线程。
线程管理就到此为止了,这里只是介绍了下线程缓冲区的工作原理,并没有具体去介绍如何利用EVENT进行线程的挂起和唤醒,这些都是借助了操作系统的特性,有兴趣的可以自己研究下。这篇就到此为止,下节会介绍Mysql的用户身份认证原理和实现。
PS. 男怕入错行,夜半三更忙,一行又一行