dls的数论-阶与原根,指数方程
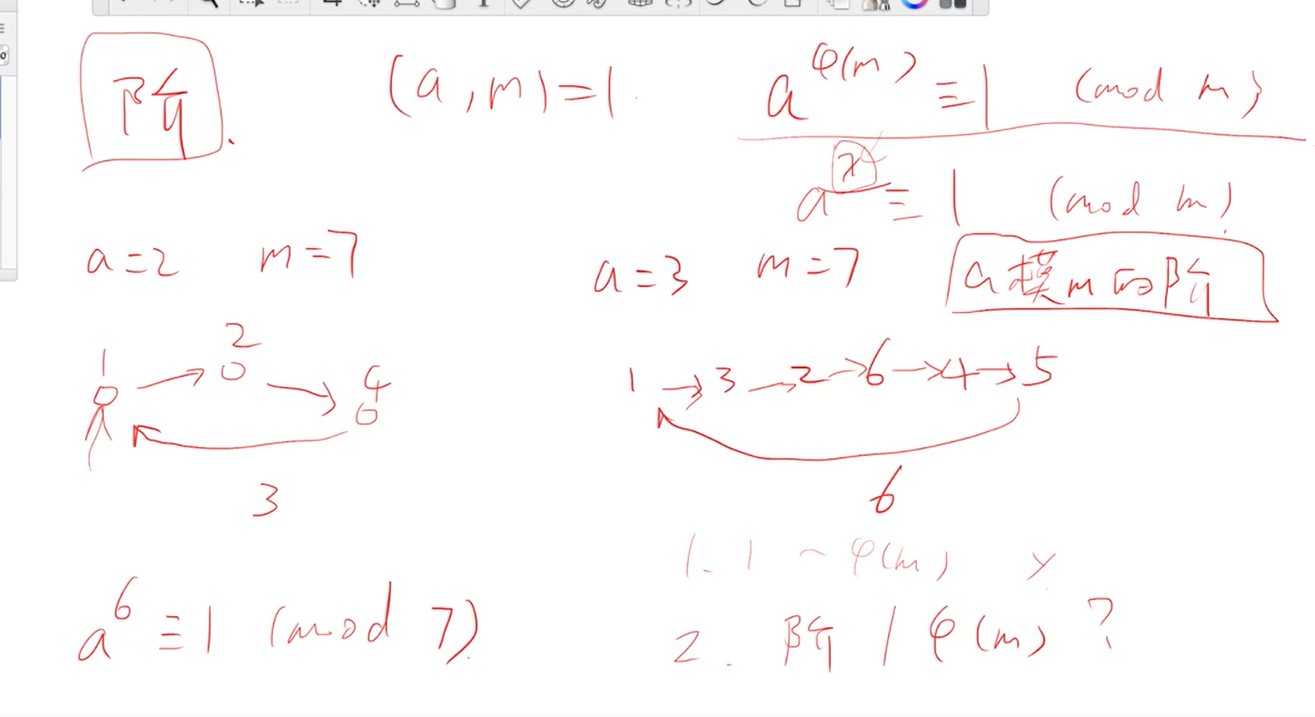
阶


#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
vector<int> pf;
LL qmi(LL a, LL b, LL mod){
LL res = 1 % mod;
while(b){
if(b&1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
int p, T; scanf("%d %d", &p, &T);
int m = p - 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= m / i; i ++){
if(m % i == 0){
pf.push_back(i);
while(m % i == 0) m /= i;
}
}
if(m != 1) pf.push_back(m);
while(T--){
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
int res = p - 1;
for(auto pp : pf){
while(res % pp == 0 && qmi(x, res / pp, p) == 1) res /= pp;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
原根

循环节的长度是f(m),1-m之间与m互质的数是f(m)个,这些数是一样
g是一个原根,g^i 1-f(m)能表示上面所有的数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int pf[100010];
LL qmi(LL a, LL b, LL mod){
LL res = 1 % mod;
while(b){
if(b&1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
int T; scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--){
int p; scanf("%d", &p);
int m = p - 1;
int t = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= m / i; i ++){
if(m % i == 0){
pf[t ++] = i;
while(m % i == 0) m /= i;
}
}
if(m != 1) pf[t ++] = m;
for(int g = 1; ; g ++){
int suc = true;
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++ ){
int pp = pf[i];
if(qmi(g, (p - 1) / pp, p) == 1){
suc = false;
break;
}
}
if(suc){
printf("%d\n", g);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
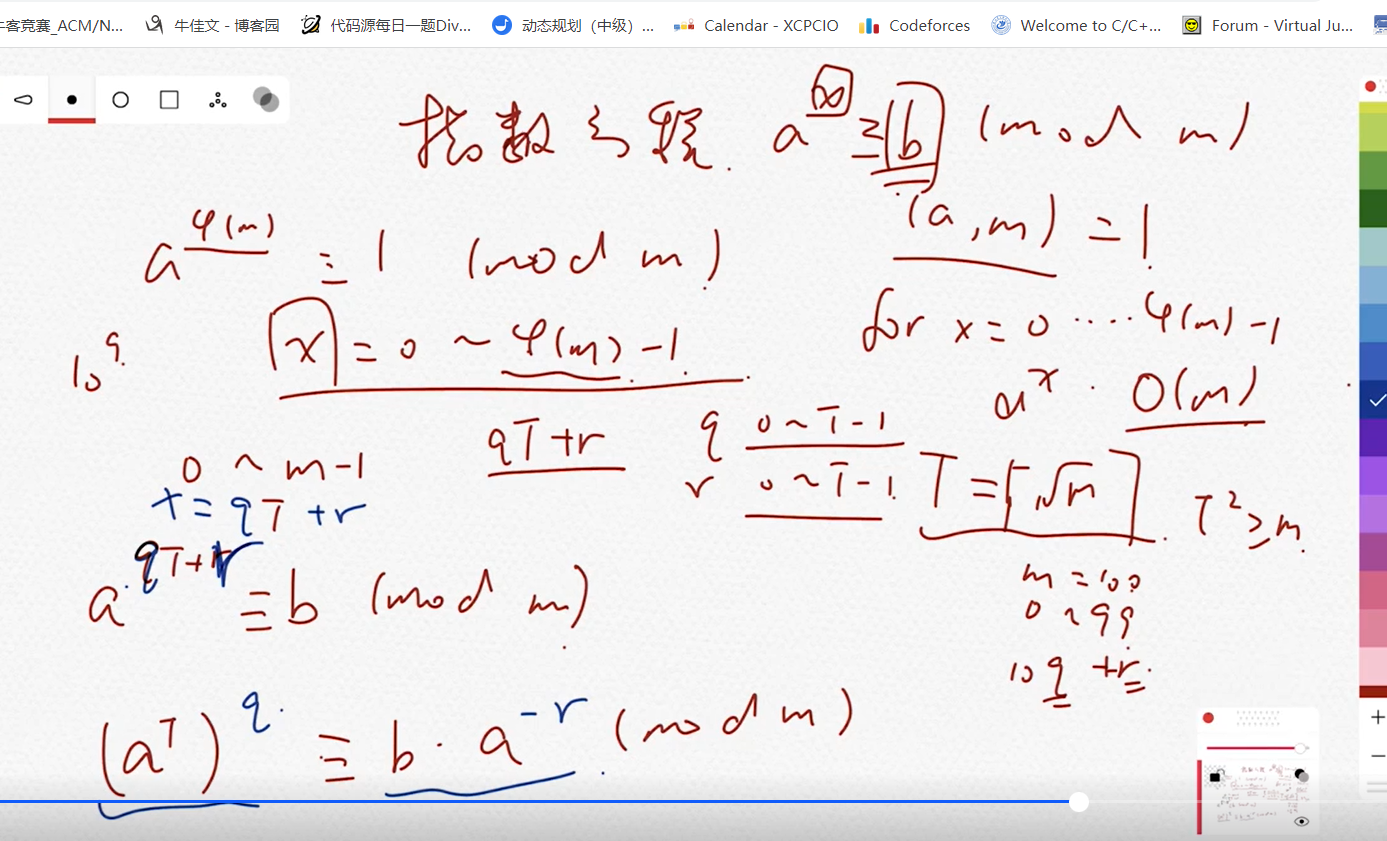
int bsgs(int a, int b, int p){
if(1 % p == b % p) return 0;
unordered_map<int, int> h;
int k = sqrt(p) + 2;
int B = b % p;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i ++){
h[B] = i;
B = (LL)B* a % p;
}
int Ak = 1, A = 1;
for(int i=1; i<=k; i++) Ak = (LL)Ak * a % p;
A = Ak;
for(int i=1; i<=k; i++){
if(h.count(A)) return i * k - h[A];
A = (LL) A * Ak % p;
}
return -1;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号