(一)熟悉常用的Linux操作
请按要求上机实践如下linux基本命令。
cd命令:切换目录
(1)切换到目录 /usr/local
:~$ cd /usr/local
(2)去到目前的上层目录
:/usr/local$ cd ..
(3)回到自己的主文件夹
:/usr$ cd ~
ls命令:查看文件与目录
(4)查看目录/usr下所有的文件
:~$ ls /usr
bin games include lib local locale sbin share src
mkdir命令:新建新目录
(5)进入/tmp目录,创建一个名为a的目录,并查看有多少目录存在
:/$ cd /tmp
:/tmp$ mkdir a/
:/tmp$ ls
a
(6)创建目录a1/a2/a3/a4
:/tmp$ mkdir -p a1/a2/a3/a4
rmdir命令:删除空的目录
(7)将上例创建的目录a(/tmp下面)删除
:/tmp$ rmdir a/
(8)删除目录a1/a2/a3/a4,查看有多少目录存在
:/tmp$ rmdir -p a1/a2/a3/a4
:/tmp$ ls -l
总用量 12
srw------- 1 joneyzheng joneyzheng 0 9月 19 20:24 fcitx-socket-:0
-rw------- 1 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4 9月 19 20:25 indicator-china-weather-1000.pid
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 9月 19 20:24 systemd-private-8542a57250884708820706eed97c6794-colord.service-53zsDO
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 9月 19 20:24 systemd-private-8542a57250884708820706eed97c6794-rtkit-daemon.service-pM1Rp8
-rw-rw-r-- 1 joneyzheng joneyzheng 0 9月 19 20:24 unity_support_test.1
cp命令:复制文件或目录
(9)将主文件夹下的.bashrc复制到/usr下,命名为bashrc1
:~$ sudo cp .bashrc /usr/bashrc1
(10)在/tmp下新建目录test,再复制这个目录内容到/usr
:~$ cd /tmp
:/tmp$ mkdir test/
:/tmp$ sudo cp -r test/ /usr/test
mv命令:移动文件与目录,或更名
(11)将上例文件bashrc1移动到目录/usr/test
:/$ cd /usr
:/usr$ sudo mv bashrc1 test/
(12)将上例test目录重命名为test2
:/usr$ sudo mv test test2
rm命令:移除文件或目录
(13)将上例复制的bashrc1文件删除
:/usr$ cd test2
:/usr/test2$ sudo rm bashrc1
(14)将上例的test2目录删除
:/usr/test2$ cd ..
:/usr$ sudo rm -r test2
cat命令:查看文件内容
(15)查看主文件夹下的.bashrc文件内容
:~$ cat .bashrc
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
# See bash(1) for more options
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
shopt -s histappend
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
shopt -s checkwinsize
# If set, the pattern "**" used in a pathname expansion context will
# match all files and zero or more directories and subdirectories.
#shopt -s globstar
# make less more friendly for non-text input files, see lesspipe(1)
[ -x /usr/bin/lesspipe ] && eval "$(SHELL=/bin/sh lesspipe)"
# set variable identifying the chroot you work in (used in the prompt below)
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
fi
# set a fancy prompt (non-color, unless we know we "want" color)
case "$TERM" in
xterm-color|*-256color) color_prompt=yes;;
esac
# uncomment for a colored prompt, if the terminal has the capability; turned
# off by default to not distract the user: the focus in a terminal window
# should be on the output of commands, not on the prompt
#force_color_prompt=yes
if [ -n "$force_color_prompt" ]; then
if [ -x /usr/bin/tput ] && tput setaf 1 >&/dev/null; then
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
color_prompt=yes
else
color_prompt=
fi
fi
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
case "$TERM" in
xterm*|rxvt*)
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
;;
*)
;;
esac
# enable color support of ls and also add handy aliases
if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dircolors -b)"
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
#alias dir='dir --color=auto'
#alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
fi
# colored GCC warnings and errors
#export GCC_COLORS='error=01;31:warning=01;35:note=01;36:caret=01;32:locus=01:quote=01'
# some more ls aliases
alias ll='ls -alF'
alias la='ls -A'
alias l='ls -CF'
# Add an "alert" alias for long running commands. Use like so:
# sleep 10; alert
alias alert='notify-send --urgency=low -i "$([ $? = 0 ] && echo terminal || echo error)" "$(history|tail -n1|sed -e '\''s/^\s*[0-9]\+\s*//;s/[;&|]\s*alert$//'\'')"'
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
fi
tac命令:反向列示
(16)反向查看主文件夹下.bashrc文件内容
:~$ tac .bashrc
fi
fi
. /etc/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
fi
. ~/.bash_aliases
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# Alias definitions.
alias alert='notify-send --urgency=low -i "$([ $? = 0 ] && echo terminal || echo error)" "$(history|tail -n1|sed -e '\''s/^\s*[0-9]\+\s*//;s/[;&|]\s*alert$//'\'')"'
# sleep 10; alert
# Add an "alert" alias for long running commands. Use like so:
alias l='ls -CF'
alias la='ls -A'
alias ll='ls -alF'
# some more ls aliases
#export GCC_COLORS='error=01;31:warning=01;35:note=01;36:caret=01;32:locus=01:quote=01'
# colored GCC warnings and errors
fi
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
#alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
#alias dir='dir --color=auto'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dircolors -b)"
if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
# enable color support of ls and also add handy aliases
esac
;;
*)
;;
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
xterm*|rxvt*)
case "$TERM" in
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
fi
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
fi
fi
color_prompt=
else
color_prompt=yes
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
if [ -x /usr/bin/tput ] && tput setaf 1 >&/dev/null; then
if [ -n "$force_color_prompt" ]; then
#force_color_prompt=yes
# should be on the output of commands, not on the prompt
# off by default to not distract the user: the focus in a terminal window
# uncomment for a colored prompt, if the terminal has the capability; turned
esac
xterm-color|*-256color) color_prompt=yes;;
case "$TERM" in
# set a fancy prompt (non-color, unless we know we "want" color)
fi
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
# set variable identifying the chroot you work in (used in the prompt below)
[ -x /usr/bin/lesspipe ] && eval "$(SHELL=/bin/sh lesspipe)"
# make less more friendly for non-text input files, see lesspipe(1)
#shopt -s globstar
# match all files and zero or more directories and subdirectories.
# If set, the pattern "**" used in a pathname expansion context will
shopt -s checkwinsize
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
HISTFILESIZE=2000
HISTSIZE=1000
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
shopt -s histappend
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# See bash(1) for more options
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
esac
*) return;;
*i*) ;;
case $- in
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
# for examples
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
more命令:一页一页翻动查看
(17)翻页查看主文件夹下.bashrc文件内容
:~$ more .bashrc
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
# See bash(1) for more options
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
shopt -s histappend
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
--更多--(17%)
head命令:取出前面几行
(18)查看主文件夹下.bashrc文件内容前20行
:~$ head -n 20 .bashrc
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
# See bash(1) for more options
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
shopt -s histappend
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
(19)查看主文件夹下.bashrc文件内容,后面50行不显示,只显示前面几行
# 如果在number前面加加号,则不显示文件最前面相应的行数
:~$ head -n -50 .bashrc
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
# See bash(1) for more options
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
shopt -s histappend
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
shopt -s checkwinsize
# If set, the pattern "**" used in a pathname expansion context will
# match all files and zero or more directories and subdirectories.
#shopt -s globstar
# make less more friendly for non-text input files, see lesspipe(1)
[ -x /usr/bin/lesspipe ] && eval "$(SHELL=/bin/sh lesspipe)"
# set variable identifying the chroot you work in (used in the prompt below)
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
fi
# set a fancy prompt (non-color, unless we know we "want" color)
case "$TERM" in
xterm-color|*-256color) color_prompt=yes;;
esac
# uncomment for a colored prompt, if the terminal has the capability; turned
# off by default to not distract the user: the focus in a terminal window
# should be on the output of commands, not on the prompt
#force_color_prompt=yes
if [ -n "$force_color_prompt" ]; then
if [ -x /usr/bin/tput ] && tput setaf 1 >&/dev/null; then
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
color_prompt=yes
else
color_prompt=
fi
fi
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
case "$TERM" in
tail命令:取出后面几行
(20)查看主文件夹下.bashrc文件内容最后20行
:~$ tail -n 20 .bashrc
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
fi
(21)查看主文件夹下.bashrc文件内容,只列出50行以后的数据
# 如果在number前面加加号,则不显示文件最前面相应的行数
:~$ tail -n +50 .bashrc
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
color_prompt=yes
else
color_prompt=
fi
fi
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
case "$TERM" in
xterm*|rxvt*)
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
;;
*)
;;
esac
# enable color support of ls and also add handy aliases
if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dircolors -b)"
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
#alias dir='dir --color=auto'
#alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
fi
# colored GCC warnings and errors
#export GCC_COLORS='error=01;31:warning=01;35:note=01;36:caret=01;32:locus=01:quote=01'
# some more ls aliases
alias ll='ls -alF'
alias la='ls -A'
alias l='ls -CF'
# Add an "alert" alias for long running commands. Use like so:
# sleep 10; alert
alias alert='notify-send --urgency=low -i "$([ $? = 0 ] && echo terminal || echo error)" "$(history|tail -n1|sed -e '\''s/^\s*[0-9]\+\s*//;s/[;&|]\s*alert$//'\'')"'
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
fi
chown命令:修改文件所有者权限
(22)将hello文件所有者改为root帐号,并查看属性
:~$ sudo chown root hello
:~$ ls -l
总用量 32
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root joneyzheng 0 9月 20 02:51 hello
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 公共的
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 模板
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 视频
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 图片
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 文档
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 下载
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 音乐
drwxr-xr-x 2 joneyzheng joneyzheng 4096 9月 19 19:45 桌面
Vim/gedit/文本编辑器:新建文件
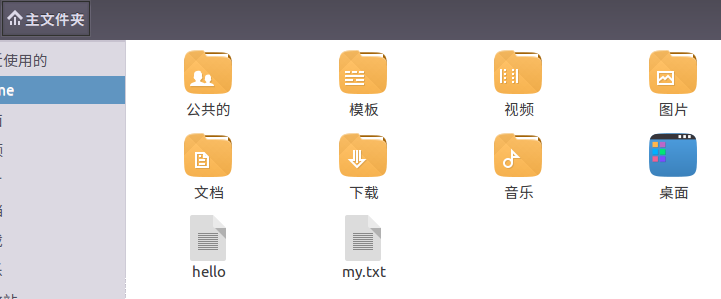
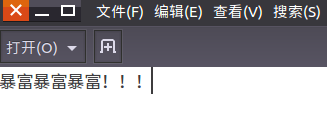
(23)在主文件夹下创建文本文件my.txt,输入文本保存退出。
tar命令:压缩命令
(24)将my.txt打包成test.tar.gz
:~$ tar -czvf test.tar.gz my.txt
(25)解压缩到~/tmp目录
:~$ tar zxvf test.tar.gz -C /tmp
(二)熟悉使用MySQL shell操作
(26)显示库:show databases;

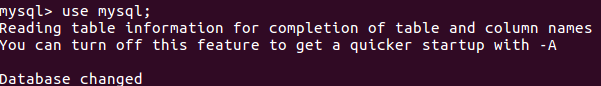
(27)进入到库:use 库名;
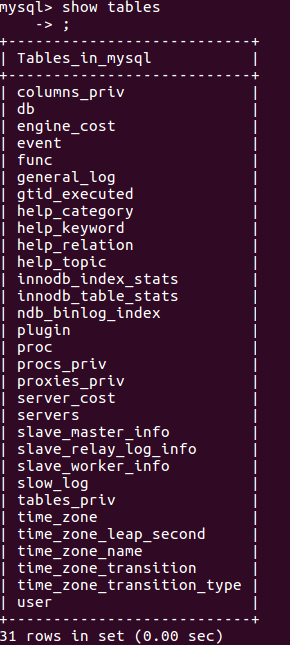
(28)展示库里表格:show tables;
(29)显示某一个表格属性:desc 表格名;
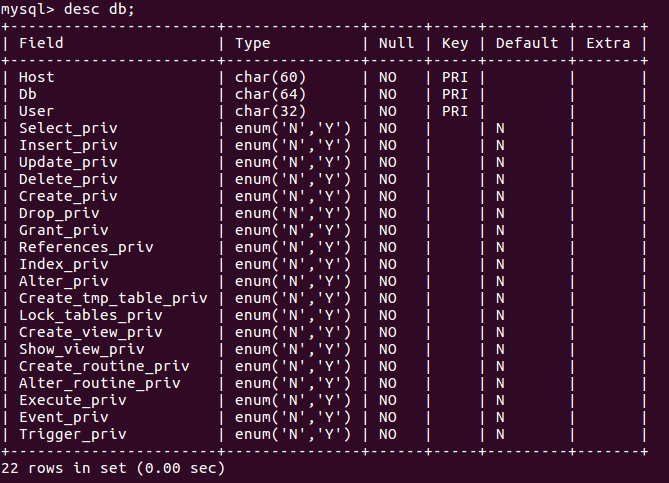
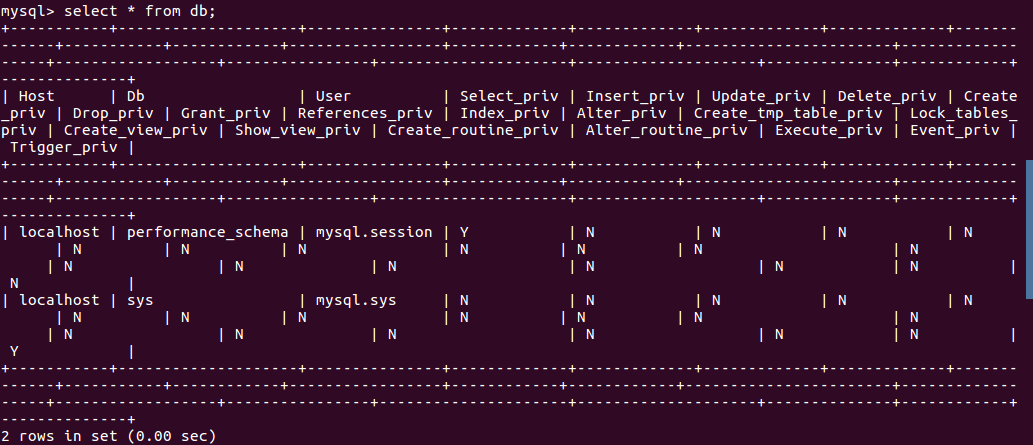
(30)显示某一个表格内的具体内容:select *form 表格名;
(31)创建一个表格:create table if not exists 表格名(名);

(32)向某一个表格中插入具体内容:insert into 表格名(名)values(value);
插入记录包含自己的学号姓名。
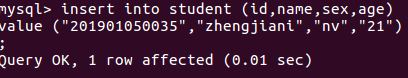
(33)显示表的内容。

(三)熟悉Hadoop及其操作
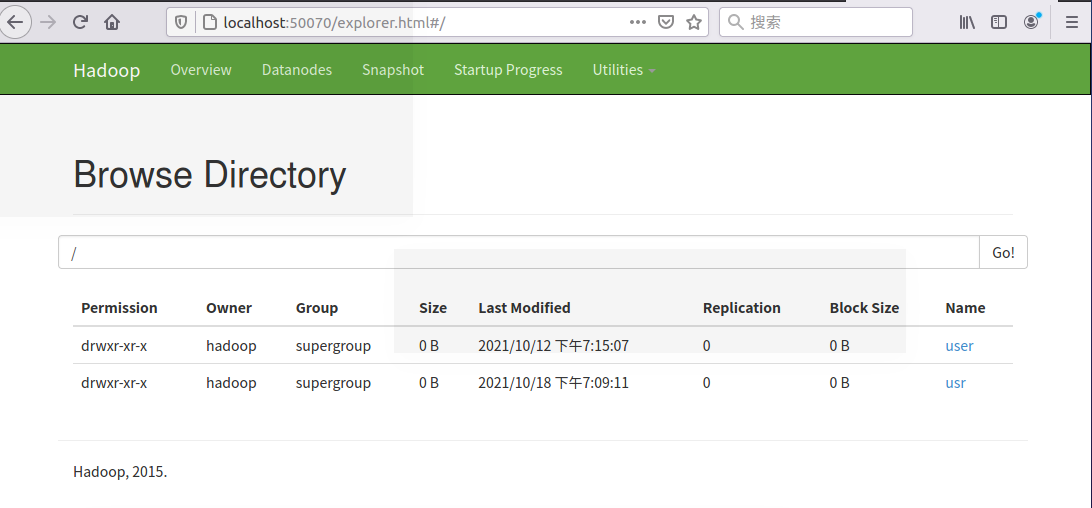
34.对比操作三个文件系统:分别用命令行与窗口方式查看windows,Linux和Hadoop文件系统的用户主目录。
用hadoop用户登录系统
localhost:50070
hdfs dfs -ls
命令行查看用户主目录
windows:
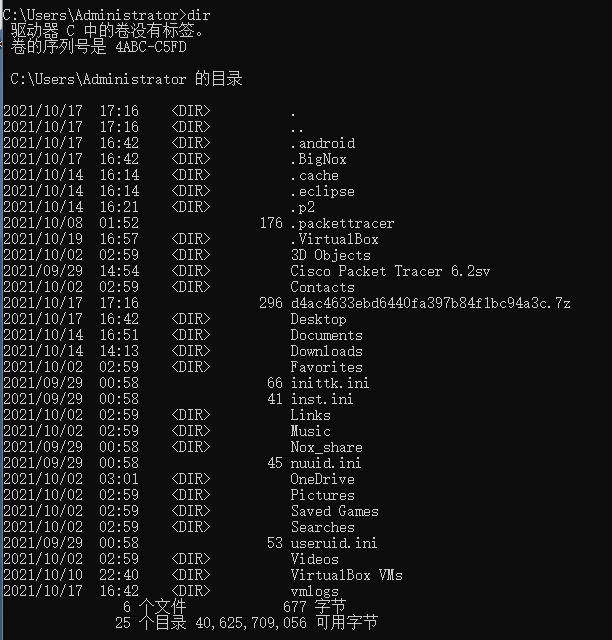
Linux:
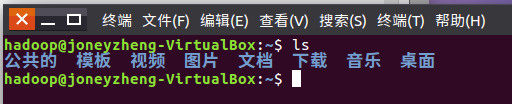
Hadoop:
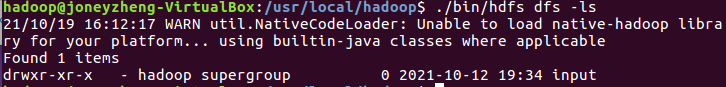
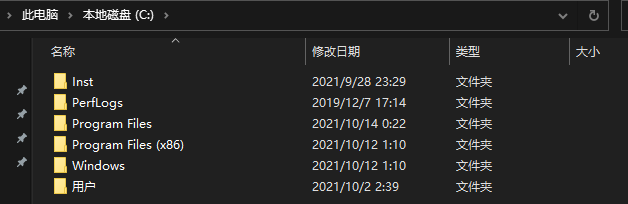
窗口查看用户主目录
windows:
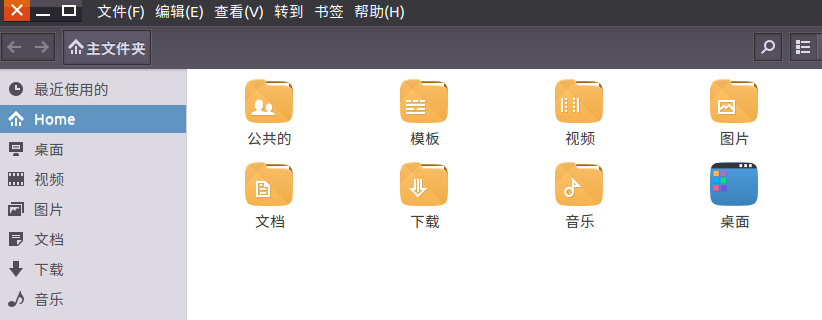
Linux:
Hadoop:
35.一个操作案例:
- 启动hdfs
![]()
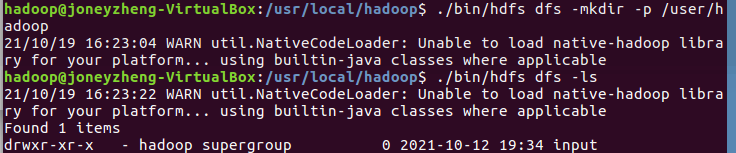
- 查看与创建hadoop用户目录。
![]()
- 在用户目录下创建与查看input目录。
![]()
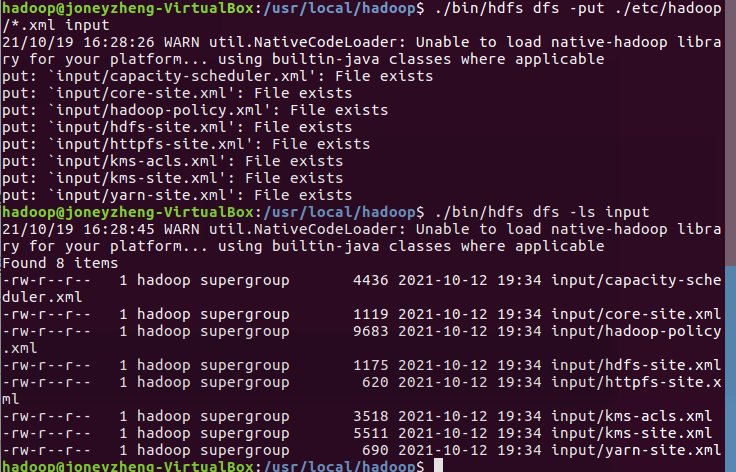
- 将hadoop的配置文件上传到hdfs上的input目录下。
![]()
- 运行MapReduce示例作业,输出结果放在output目录下。
![]()
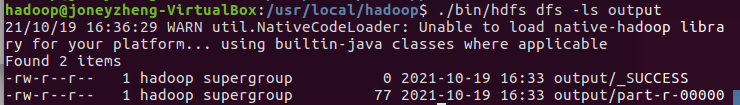
- 查看output目录下的文件。
![]()
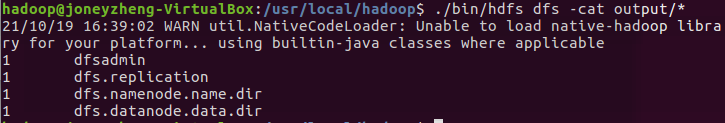
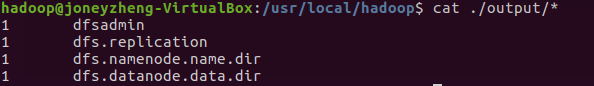
- 查看输出结果
![]()
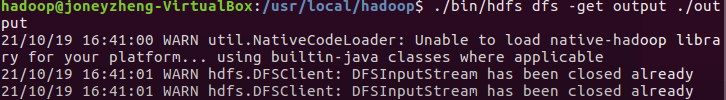
- 将输出结果文件下载到本地。
![]()
- 查看下载的本地文件。
![]()
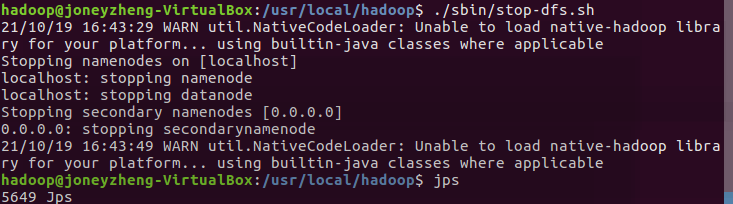
- 停止hdfs
![]()
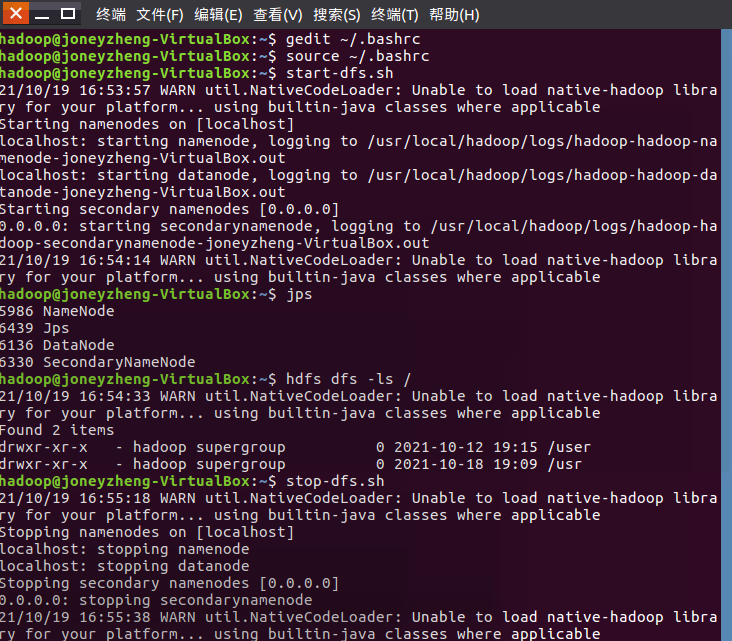
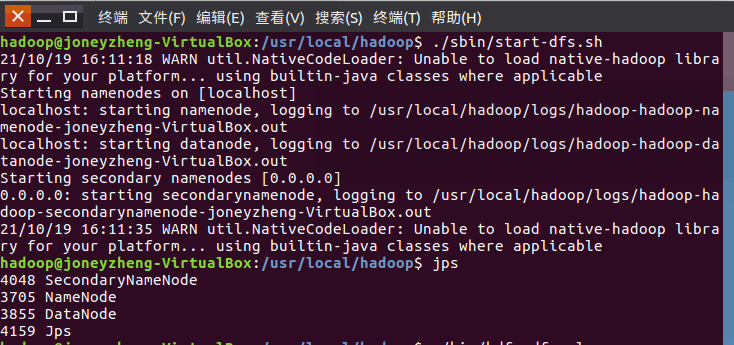
36.设置Hadoop环境变量,在本地用户主目录下启动hdfs,查看hdfs用户主目录,停止hdfs。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号