个人项目作业word-count
1,项目地址:
https://github.com/Next-world/word-count
2、题目描述
Word Count
1. 实现一个简单而完整的软件工具(源程序特征统计程序)。
2. 进行单元测试、回归测试、效能测试,在实现上述程序的过程中使用相关的工具。
3. 进行个人软件过程(PSP)的实践,逐步记录自己在每个软件工程环节花费的时间。
2.1 WC 项目要求
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
扩展功能:
-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”。
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。一个有趣的例子是有些程序员会在单字符后面加注释:
} //注释
在这种情况下,这一行属于注释行。
[file_name]: 文件或目录名,可以处理一般通配符。
高级功能:
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。
需求举例:
wc.exe -s -a *.c
返回当前目录及子目录中所有*.c 文件的代码行数、空行数、注释行数。
3,已实现功能
基本功能
- -c
- -w
- -l
扩展功能
- -s
- -a
4,psp
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
|
|
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
12*60 |
13*60 |
|
Development |
开发 |
|
|
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
5 |
4 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
10 |
8 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
5 |
3 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
2 |
2 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
15 |
10 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
3*60 |
5*60 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 |
60 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
30 |
25 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
|
|
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
45 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
15 |
20 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
10 |
10 |
|
合计 |
|
12*60 |
10*60 |
5,设计思路:
该程序主要是控制台统计文件相关信息的程序,主要需要的技术是对文件的操作和对文本信息的正则表达式匹配,由于对Java比较熟悉,所以选择Java来开发这个程序,并且使用maven进行包管理。
6,程序设计
6.1,具体分包结构
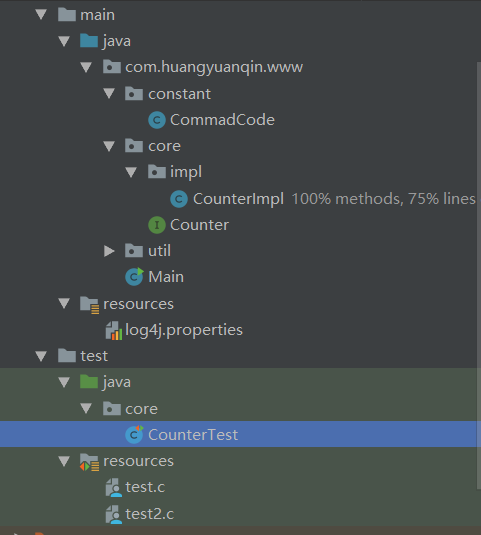
由于程序相对简单,就只进行了简单的分包处理。
core包主要是进行文件相关信息技术的包
util包是提供递归正则解析文件的工具包
constant包是参数的常量
test包是测试代码的包
resources是配置文件与测试文件存放的地方
6.2,主要接口:
1 public interface Counter { 2 3 /** 4 * 计算文件的字符数 5 * @param path 文件路径 6 * @return 字符数 7 */ 8 long countChar(String path); 9 10 /** 11 * 计算文件的字数 12 * @param path 文件路径 13 * @return 字数 14 */ 15 long countWord(String path); 16 17 /** 18 * 计算文件行数 19 * @param path 文件路径 20 * @return 行数 21 */ 22 long countLine(String path); 23 24 /** 25 * 计算多文件的字符数 26 * @param paths 多文件的路径 27 * @return 字符数 28 */ 29 long countChar(List<String> paths); 30 31 /** 32 * 计算多文件的字数 33 * @param paths 多文件的路径 34 * @return 字符数 35 */ 36 long countWord(List<String> paths); 37 38 /** 39 * 计算多文件的行数 40 * @param paths 多文件的路径 41 * @return 行数 42 */ 43 long countLine(List<String> paths); 44 45 /** 46 *计算空行 47 * @param path 路径 48 * @return 空行数量 49 */ 50 long countEmptyLine(String path); 51 52 /** 53 * 计算注释行 54 * @param path 路径 55 * @return 注释行数量 56 */ 57 long countAnnotationLine(String path); 58 59 /** 60 * 计算代码行 61 * @param path 路径 62 * @return 行数 63 */ 64 long countCodeLine(String path); 65 66 /** 67 *计算空行 68 * @param paths 路径 69 * @return 空行数量 70 */ 71 long countEmptyLine(List<String> paths); 72 73 /** 74 * 计算注释行 75 * @param paths 路径 76 * @return 注释行数量 77 */ 78 long countAnnotationLine(List<String> paths); 79 80 /** 81 * 计算代码行 82 * @param paths 路径 83 * @return 行数 84 */ 85 long countCodeLine(List<String> paths); 86 87 88 }
6.3,接口实现:
1 public class CounterImpl implements Counter { 2 3 private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CounterImpl.class); 4 5 public long countChar(String path){ 6 File file = new File(path); 7 if(!file.exists()){ 8 return -1L; 9 } 10 return file.length(); 11 } 12 13 public long countWord(String path) { 14 File file = new File(path); 15 if(!file.exists()){ 16 return -1L; 17 } 18 long count = 0L; 19 FileReader fileReader = null; 20 BufferedReader bufferedReader = null; 21 try { 22 fileReader = new FileReader(file); 23 bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader); 24 String[] words; 25 while (bufferedReader.read()>0){ 26 String s = bufferedReader.readLine(); 27 words = s.split("[\\W]+"); 28 for (String s1 : words){ 29 if(s1.matches("[\\w]+")){ 30 count++; 31 } 32 33 } 34 } 35 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 36 logger.warn("文件未找到"); 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 }finally { 41 42 try { 43 bufferedReader.close(); 44 } catch (IOException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 48 try { 49 fileReader.close(); 50 } catch (IOException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 54 } 55 return count; 56 } 57 58 public long countLine(String path){ 59 File file = new File(path); 60 if(!file.exists()){ 61 return -1L; 62 } 63 long count = 0L; 64 FileReader fileReader = null; 65 BufferedReader bufferedReader = null; 66 try { 67 68 fileReader = new FileReader(file); 69 bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader); 70 while (bufferedReader.readLine() != null){ 71 count++; 72 } 73 74 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 75 logger.warn("文件未找到"); 76 e.printStackTrace(); 77 } catch (IOException e) { 78 e.printStackTrace(); 79 }finally { 80 try { 81 82 fileReader.close(); 83 bufferedReader.close(); 84 85 } catch (IOException e) { 86 e.printStackTrace(); 87 } 88 89 } 90 91 return count; 92 } 93 94 public long countChar(List<String> paths) { 95 long total = 0L; 96 for(String s :paths){ 97 total += this.countChar(s); 98 } 99 return total; 100 } 101 102 public long countWord(List<String> paths) { 103 long total = 0L; 104 for(String s :paths){ 105 total += this.countWord(s); 106 } 107 return total; 108 } 109 110 public long countLine(List<String> paths) { 111 long total = 0L; 112 for(String s :paths){ 113 total += this.countLine(s); 114 } 115 return total; 116 } 117 118 public long countEmptyLine(String path) { 119 File file = new File(path); 120 if(!file.exists()){ 121 return -1L; 122 } 123 long count = 0L; 124 FileReader fileReader = null; 125 BufferedReader bufferedReader = null; 126 try { 127 128 fileReader = new FileReader(file); 129 bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader); 130 while (bufferedReader.read() > 0){ 131 String s = bufferedReader.readLine(); 132 s = s.trim(); 133 if ("".equals(s)){ 134 count++; 135 } 136 } 137 138 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 139 logger.warn("文件未找到"); 140 e.printStackTrace(); 141 } catch (IOException e) { 142 e.printStackTrace(); 143 }finally { 144 try { 145 146 fileReader.close(); 147 bufferedReader.close(); 148 149 } catch (IOException e) { 150 e.printStackTrace(); 151 } 152 153 } 154 155 return count; 156 } 157 158 public long countAnnotationLine(String path) { 159 File file = new File(path); 160 if(!file.exists()){ 161 return -1L; 162 } 163 //单行注释正则 164 String regexAnnotation = "\\s*/{2}.*"; 165 //多行注释正则 166 String regexAnnotationStart = "\\s*/\\x2A.*"; 167 String regexAnnotationEnd = "\\s*\\x2A/.*"; 168 169 Long count = 0L; 170 FileReader fileReader = null; 171 BufferedReader bufferedReader = null; 172 try { 173 174 fileReader = new FileReader(file); 175 bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader); 176 String line; 177 while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){ 178 if(line.matches(regexAnnotationStart)){ 179 count++; 180 line = bufferedReader.readLine(); 181 while (!line.matches(regexAnnotationEnd)){ 182 count++; 183 line = bufferedReader.readLine(); 184 } 185 count++; 186 } 187 if(line.matches(regexAnnotation)){ 188 count++; 189 } 190 } 191 192 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 193 logger.warn("文件未找到"); 194 e.printStackTrace(); 195 } catch (IOException e) { 196 e.printStackTrace(); 197 }finally { 198 try { 199 200 fileReader.close(); 201 bufferedReader.close(); 202 203 } catch (IOException e) { 204 e.printStackTrace(); 205 } 206 207 } 208 209 return count; 210 } 211 212 public long countCodeLine(String path) { 213 return countLine(path)-countEmptyLine(path)-countAnnotationLine(path); 214 } 215 216 public long countEmptyLine(List<String> paths) { 217 long total = 0L; 218 for(String s :paths){ 219 total += this.countEmptyLine(s); 220 } 221 return total; 222 } 223 224 public long countAnnotationLine(List<String> paths) { 225 long total = 0L; 226 for(String s :paths){ 227 total += this.countAnnotationLine(s); 228 } 229 return total; 230 } 231 232 public long countCodeLine(List<String> paths) { 233 long total = 0L; 234 for(String s :paths){ 235 total += this.countCodeLine(s); 236 } 237 return total; 238 } 239 }
递归查找匹配正则表达式的所有文件代码:
1 public class FileUtil { 2 private List<String> pathList; 3 4 private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FileUtil.class); 5 6 public List<String> getFiles(String path){ 7 String file = path.substring(0,path.lastIndexOf('\\')); 8 String re = path.substring(path.lastIndexOf('\\')+1); 9 10 logger.debug("file:"+file); 11 logger.debug("re:"+re); 12 13 File file1 = new File(file); 14 if(!file1.exists()){ 15 logger.warn("文件路径不存在"); 16 return null; 17 }else { 18 pathList = new LinkedList<String>(); 19 getFiles0(file1,re); 20 } 21 return this.pathList; 22 } 23 private void getFiles0(File file, String re){ 24 if (file.isDirectory()){ 25 File[] files = file.listFiles(); 26 for (File f : files){ 27 getFiles0(f,re); 28 } 29 }else { 30 String fileName = file.getName(); 31 if(fileName.matches(re)){ 32 fileName = file.getPath(); 33 logger.debug(fileName); 34 pathList.add(fileName); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 }
7,代码测试
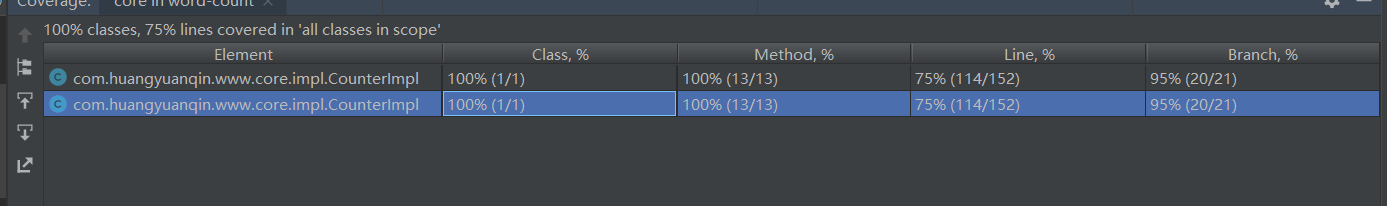
代码测试使用了Junit5进行测试
![]()
核心代码方法覆盖率100%,行覆盖率75%,分支覆盖率95%
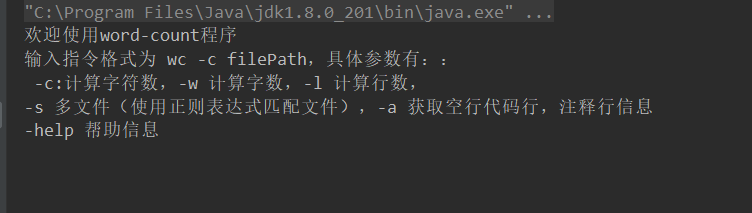
8,程序使用:
开始界面:
-c
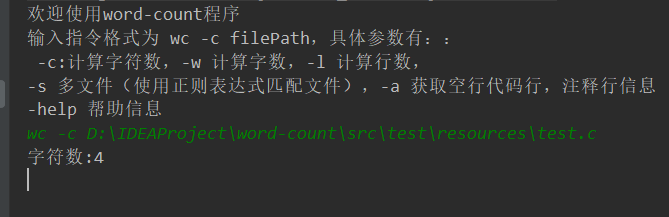
测试文件:
-w
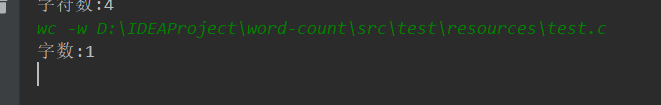
测试文件
-l
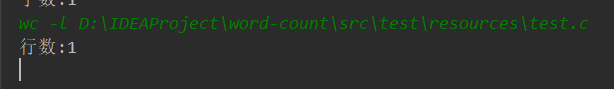
测试文件
-s

测试文件
test.c
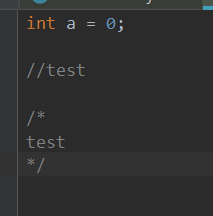
test2.c
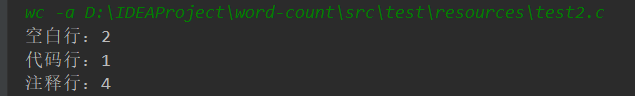
-a
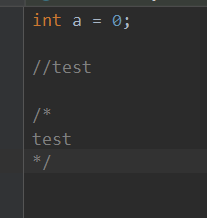
测试文件:
9,总结
缺点:整体开发比较仓促,导致一些细节问题没有注意好,代码注释也不够详细,代码一些地方可能不够规范,同时由于没有进行太多的普遍的测试,可能会有一些bug存在
优点:整体开发顺利,基本功能与扩展功能都实现了,代码逻辑也比较清晰,使用面向接口的开发思路,方便以后扩展,使用maven方便包管理
改进措施:进一步添加代码注释与思考代码具体实现细节,进行更多的实际例子的测试,修复内在可能存在的bug,更加深入的对程序功能进行更新迭代


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号