heapprofd
一. Heapprofd 工具如何抓取内存信息
环境配置:
1.需要安装 python3
2.下载 heap_profile 工具,下载链接:
https://github.com/google/perfetto
工具目录: perfetto\tools\heap_profile
3.如果系统是userdebug版本,则可以抓取所有应用以及系统进程的内存信息,如果系统是user版本,则需要抓取的应用是userdebug版本,或者是应用在 manifest 中开启了 profileable 标记
抓取步骤:
执行命令: python d:\code\perfetto-master\tools\heap_profile -n 进程名
第一次执行的时候,工具会去google的网站下载 traceconv.exe 工具,但是这个下载需要FQ下载,建议手动使用如下地址下载好这个工具,下载地址为:
https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/perfetto-luci-artifacts/v32.1/windows-amd64/traceconv.exe
然后将 traceconv.exe 放到 C:\Users\huanghan3\.local\share\perfetto\prebuilts 目录下面即可
连续抓取步骤:
方式一:执行命令: python d:\code\perfetto-master\tools\heap_profile -c 5000 -n 进程名
方式二:执行命令: python d:\code\perfetto-master\tools\heap_profile -n 进程名,开启另一个窗口执行如下 命令,每执行一次就可以抓取一次内存信息
adb shell killall -USR1 heapprofd
备注:还有其他两种方式抓取 heapprofd,一个是使用纯命令方式,类似如用命令方式抓取trace的方式;另一个是使用 https://ui.perfetto.dev/ 网站方式来抓取 heapprofd 来抓取信息
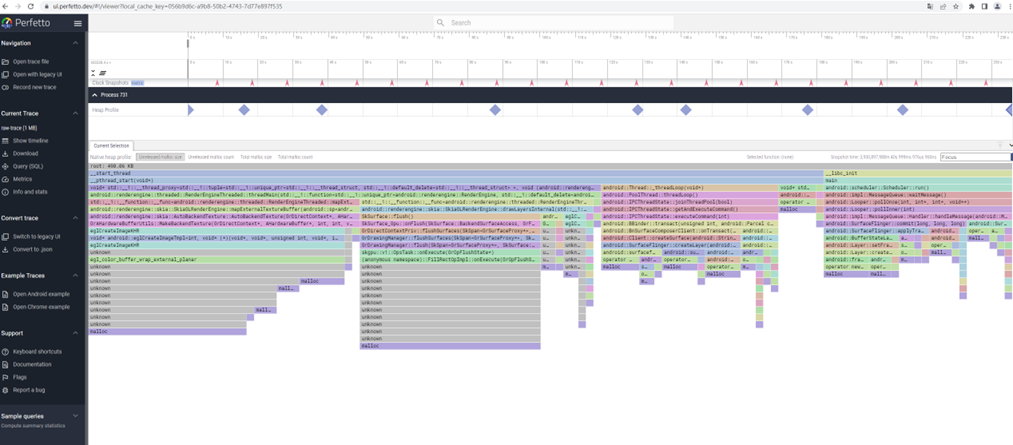
使用 https://ui.perfetto.dev/ 打开raw-trace文件即可,显示界面如下:
二. Heapprofd 工具特性及其实现原理
heapprofd具有如下特性:
1.不用特别设置,只需要一个命令就可以生成需要的信息
2.可以抓取正在运行的进程,在抓取时,进程不需要重启
3.可以抓取应用进程的native的内存信息
4.在不抓取信息时,对系统性能完全没有影响
5.可以抓取系统上所有的进程信息
6.没有或者极少的额外进程内存开销
7.对系统性能影响极小
heapprofd 实现原理:
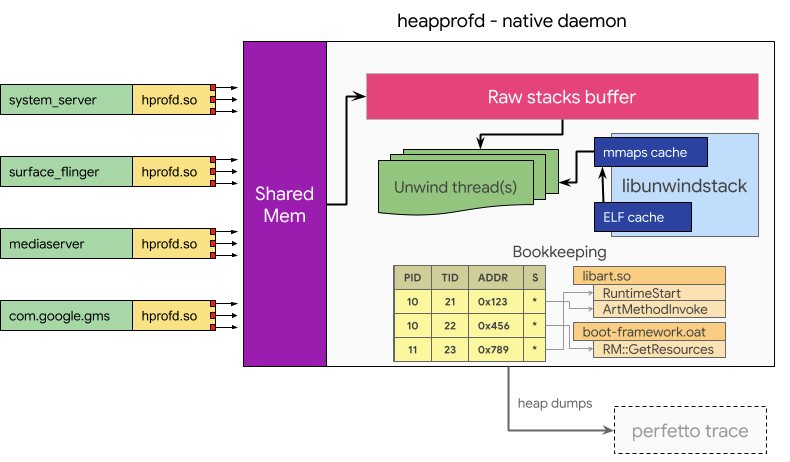
heapprofd既然也是一款监控内存的工具,那么也是需要代理-堆栈回溯-缓存记录三个模块的
heapprofd的代理部分采用的是hook malloc、calloc、realloc、free 等内存分配相关的函数,在系统中
建立一块共享内存buffer,然后按照百分比例进行采样,将进程中的内存申请堆栈复制到共享内存buffer里面,接着使用 libunwindstack 进行堆栈的回溯,最后根据回溯的信息构建一个 Bookkeeping 来跟踪内存分配
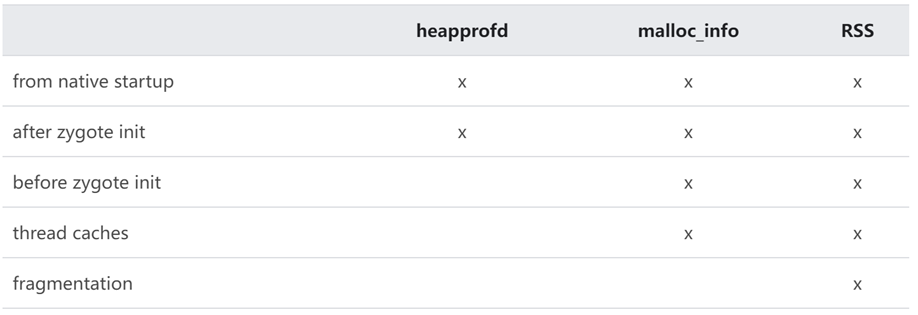
heapprofd vs malloc_info() vs RSS
heapprofd 能够提供从默认C/C++分配器请求的内存具体大小值。对于java应用程序启动时早期的初始化发生的分配是不会记录的,另外从Zygote fork的native 服务也是不会记录的。
malloc_info 是一个 libc 函数,它为您提供有关分配器的信息,在 userdebug 版本中通过使用命令:
am dumpheap -m <PID> /data/local/tmp/heap.txt
可以获取heap信息, 这种记录的数据通常会比 heapprofd 看到的内存多,多的部分一个是 before zygote init,另一个是 thread caches 保留的部分free 内存
Heap RSS 是分配器从操作系统申请的内存量。 这比前两个数字大,因为只能以页面大小的块获取内存,有些申请的内存没有页面大,也是按页进行申请的, 这可以通过运行 adb shell dumpsys meminfo <PID> 并查看"Private Dirty"列来获得。 如果设备内核使用ZRAM,并且进程的内存换出到 ZRAM,RSS 最终也可能比其他两个小。
三者统计内存的总结如下表:
二. Heapprofd 源码分析
heapprofd 的初始化有两条线路,一条是在 libc 初始化的时候进行 heapprofd 初始化, 如果要抓取的进程还没启动,则使用这条线路, 另一条是在收到要初始化的信号时,在下一次malloc的时候进行heapprofd的初始化,如果进程已经起来了,则使用的是这条线路。 两条线路最终都是通过 CommonInstallHooks 去做 heapprofd 的代理 hook 操作
线路1:
在 libc malloc 初始化时会去判断需要加载哪些 hook 模块,这里有malloc debug, heapprofd等模块的加载判断
// Initializes memory allocation framework once per process.
static void MallocInitImpl(libc_globals* globals) {
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
char* options = prop;
MaybeInitGwpAsanFromLibc(globals);
#if defined(USE_SCUDO)
__libc_shared_globals()->scudo_stack_depot = __scudo_get_stack_depot_addr();
__libc_shared_globals()->scudo_region_info = __scudo_get_region_info_addr();
__libc_shared_globals()->scudo_ring_buffer = __scudo_get_ring_buffer_addr();
__libc_shared_globals()->scudo_ring_buffer_size = __scudo_get_ring_buffer_size();
#endif
// Prefer malloc debug since it existed first and is a more complete
// malloc interceptor than the hooks.
bool hook_installed = false;
// 如果有设置环境选项 LIBC_DEBUG_MALLOC_OPTIONS 或者有设置 libc.debug.malloc.options 则表示malloc debug功能开启,
// 加载 libc_malloc_debug.so 库
if (CheckLoadMallocDebug(&options)) {
hook_installed = InstallHooks(globals, options, kDebugPrefix, kDebugSharedLib);
// 如果有设置环境选项 LIBC_HOOKS_ENABLE 或者有设置 libc.debug.hooks.enable 则表示需要 hook 相关的函数
} else if (CheckLoadMallocHooks(&options)) {
hook_installed = InstallHooks(globals, options, kHooksPrefix, kHooksSharedLib);
}
// 如果 hook_installed 为 false,则需要判断是否需要加载 heapprofd
if (!hook_installed) {
if (HeapprofdShouldLoad()) { // 如果返回值为true,则加载 heapprofd_client.so
HeapprofdInstallHooksAtInit(globals);
}
} else {
// Record the fact that incompatible hooks are active, to skip any later
// heapprofd signal handler invocations.
HeapprofdRememberHookConflict();
}
}
判断是否要加载 heapprofd 模块
bool HeapprofdShouldLoad() {
// First check for heapprofd.enable. If it is set to "all", enable
// heapprofd for all processes. Otherwise, check heapprofd.enable.${prog},
// if it is set and not 0, enable heap profiling for this process.
char property_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
// 如果没有读取到 heapprofd.enable 属性值,则返回 false, 系统默认是没有 heapprofd.enable 属性的,在使用工具抓取heaprofd后,
// 就会设置 heapprofd.enable 为1,抓取完后,就会设置 heapprofd.enable 为空
if (__system_property_get(kHeapprofdPropertyEnable, property_value) == 0) {
return false;
}
// 如果读取 heapprofd.enable 的属性值为 all , 则返回 true
if (strcmp(property_value, "all") == 0) {
return true;
}
char program_property[kHeapprofdProgramPropertyPrefixSize + kMaxCmdlineSize];
// 根据 /proc/self/cmdline 读取的信息来获取监控的进程名,比如我在cmd中输入的命令是监控的 surfaceflinger,
// 则获取到的属性是 heapprofd.enable.surfaceflinger
if (!GetHeapprofdProgramProperty(program_property,
sizeof(program_property))) {
return false;
}
// 在 heapprofd 获取进程的时候,会将 heapprofd.enable.surfaceflinger 置为 1
if (__system_property_get(program_property, property_value) == 0) {
return false;
}
// 返回 true
return property_value[0] != '\0';
}
加载 heapprofd_client.so
static void CommonInstallHooks(libc_globals* globals) {
void* impl_handle = atomic_load(&gHeapprofdHandle);
// gHeapprofdHandle 初始化值为 nullptr,也就是第一次需要加载 heapprofd_client.so
if (impl_handle == nullptr) {
impl_handle = LoadSharedLibrary(kHeapprofdSharedLib, kHeapprofdPrefix, &globals->malloc_dispatch_table);
if (impl_handle == nullptr) {
return;
}
atomic_store(&gHeapprofdHandle, impl_handle);
} else if (!InitSharedLibrary(impl_handle, kHeapprofdSharedLib, kHeapprofdPrefix, &globals->malloc_dispatch_table)) {
return;
}
FinishInstallHooks(globals, nullptr, kHeapprofdPrefix);
}
线路2:
__attribute__((constructor(1))) static void __libc_preinit() {
// The linker has initialized its copy of the global stack_chk_guard, and filled in the main
// thread's TLS slot with that value. Initialize the local global stack guard with its value.
__stack_chk_guard = reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(__get_tls()[TLS_SLOT_STACK_GUARD]);
__libc_preinit_impl();
}
__attribute__((noinline))
static void __libc_preinit_impl() {
#if defined(__i386__)
__libc_init_sysinfo();
#endif
// Register libc.so's copy of the TLS generation variable so the linker can
// update it when it loads or unloads a shared object.
TlsModules& tls_modules = __libc_shared_globals()->tls_modules;
tls_modules.generation_libc_so = &__libc_tls_generation_copy;
__libc_tls_generation_copy = tls_modules.generation;
__libc_init_globals();
__libc_init_common();
__libc_init_scudo();
#if __has_feature(hwaddress_sanitizer)
// Notify the HWASan runtime library whenever a library is loaded or unloaded
// so that it can update its shadow memory.
// This has to happen before _libc_init_malloc which might dlopen to load
// profiler libraries.
__libc_shared_globals()->load_hook = __hwasan_library_loaded;
__libc_shared_globals()->unload_hook = __hwasan_library_unloaded;
#endif
// Hooks for various libraries to let them know that we're starting up.
__libc_globals.mutate(__libc_init_malloc);
// Install reserved signal handlers for assisting the platform's profilers.
// libc 初始化 profiling
__libc_init_profiling_handlers();
__libc_init_fork_handler();
__libc_shared_globals()->set_target_sdk_version_hook = __libc_set_target_sdk_version;
netdClientInit();
}
// 注册信号监听函数 HandleProfilingSignal
__LIBC_HIDDEN__ void __libc_init_profiling_handlers() {
struct sigaction action = {};
action.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO | SA_RESTART;
action.sa_sigaction = HandleProfilingSignal;
sigaction(BIONIC_SIGNAL_PROFILER, &action, nullptr);
// The perfetto_hprof ART plugin installs a signal handler to handle this signal. That plugin
// does not get loaded for a) non-apps, b) non-profilable apps on user. The default signal
// disposition is to crash. We do not want the target to crash if we accidentally target a
// non-app or non-profilable process.
signal(BIONIC_SIGNAL_ART_PROFILER, SIG_IGN);
}
// 收到 perfetto 端发送的 BIONIC_SIGNAL_PROFILER 信号后,执行 HandleProfilingSignal ,
// 如果信号传递过来的值为0, 则进一步执行 HandleHeapprofdSignal
static void HandleProfilingSignal(int /*signal_number*/, siginfo_t* info, void* /*ucontext*/) {
ErrnoRestorer errno_restorer;
if (info->si_code != SI_QUEUE) {
return;
}
int signal_value = info->si_value.sival_int;
async_safe_format_log(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, "libc", "%s: received profiling signal with si_value: %d",
getprogname(), signal_value);
// Proceed only if the process is considered profileable.
bool profileable = false;
android_mallopt(M_GET_PROCESS_PROFILEABLE, &profileable, sizeof(profileable));
if (!profileable) {
async_safe_write_log(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR, "libc", "profiling signal rejected (not profileable)");
return;
}
// Temporarily override SIGSYS handling, in a best-effort attempt at not
// crashing if we happen to be running in a process with a seccomp filter that
// disallows some of the syscalls done by this signal handler. This protects
// against SECCOMP_RET_TRAP with a crashing SIGSYS handler (typical of android
// minijails). Won't help if the filter is using SECCOMP_RET_KILL_*.
// Note: the override is process-wide, but short-lived. The syscalls are still
// blocked, but the overridden handler recovers from SIGSYS, and fakes the
// syscall return value as ENOSYS.
struct sigaction sigsys_override = {};
sigsys_override.sa_sigaction = &HandleSigsysSeccompOverride;
sigsys_override.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
struct sigaction old_act = {};
// 注册监听信号 SIGSYS
sigaction(SIGSYS, &sigsys_override, &old_act);
// 如果信号值为 0,则需要调用 HandleHeapprofdSignal
if (signal_value == kHeapprofdSignalValue) {
HandleHeapprofdSignal();
} else if (signal_value == kTracedPerfSignalValue) {
HandleTracedPerfSignal();
} else {
async_safe_format_log(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR, "libc", "unrecognized profiling signal si_value: %d",
signal_value);
}
sigaction(SIGSYS, &old_act, nullptr);
}
// 此函数主要作用是处理 malloc 替换过程中出现的各种情况
void HandleHeapprofdSignal() {
if (atomic_load(&gHeapprofdState) == kIncompatibleHooks) {
error_log("%s: not enabling heapprofd, malloc_debug/malloc_hooks are enabled.", getprogname());
return;
}
// We cannot grab the mutex here, as this is used in a signal handler.
MaybeModifyGlobals(kWithoutLock, [] {
// ...........
// 此处省略大量代码
// Now, replace the malloc function so that the next call to malloc() will
// initialize heapprofd.
// 此处将 gEphemeralDispatch 的 malloc 替换成 MallocInitHeapprofdHook , 在 MallocInitHeapprofdHook 中会初始化 heapprofd,
// 并调用 native 的 malloc
gEphemeralDispatch.malloc = MallocInitHeapprofdHook;
// And finally, install these new malloc-family interceptors.
__libc_globals.mutate([](libc_globals* globals) {
atomic_store(&globals->default_dispatch_table, &gEphemeralDispatch);
if (!MallocLimitInstalled()) {
atomic_store(&globals->current_dispatch_table, &gEphemeralDispatch);
}
});
atomic_store(&gHeapprofdState, kEphemeralHookInstalled);
});
// Otherwise, we're racing against malloc_limit's enable logic (at most once
// per process, and a niche feature). This is highly unlikely, so simply give
// up if it does happen.
}
// 创建线程调用 InitHeapprofd , 初始化 heapprofd,返回 malloc 的结果
extern "C" void* MallocInitHeapprofdHook(size_t bytes) {
MaybeModifyGlobals(kWithLock, [] {
MallocHeapprofdState expected = kEphemeralHookInstalled;
// 如果 gHeapprofdState 和 kEphemeralHookInstalled 一致,则将 gHeapprofdState 改为 kRemovingEphemeralHook ,返回true;
// 否则将 gHeapprofdState 的值赋值给 expected,返回false
if (atomic_compare_exchange_strong(&gHeapprofdState, &expected, kRemovingEphemeralHook)) {
__libc_globals.mutate([](libc_globals* globals) {
// 读取 heapprofd hook 之前的 default_dispatch_table
const MallocDispatch* previous_dispatch = atomic_load(&gPreviousDefaultDispatchTable);
// 修改 default_dispatch_table 为之前保存的值
atomic_store(&globals->default_dispatch_table, previous_dispatch);
if (!MallocLimitInstalled()) {
atomic_store(&globals->current_dispatch_table, previous_dispatch);
}
});
// 将 gHeapprofdState 的状态改为 kInitialState
atomic_store(&gHeapprofdState, kInitialState);
pthread_t thread_id;
if (pthread_create(&thread_id, nullptr, InitHeapprofd, nullptr) != 0) {
error_log("%s: heapprofd: failed to pthread_create.", getprogname());
} else if (pthread_setname_np(thread_id, "heapprofdinit") != 0) {
error_log("%s: heapprod: failed to pthread_setname_np", getprogname());
} else if (pthread_detach(thread_id) != 0) {
error_log("%s: heapprofd: failed to pthread_detach", getprogname());
}
} else {
warning_log("%s: heapprofd: could not transition kEphemeralHookInstalled -> "
"kRemovingEphemeralHook. current state (possible race): %d. this can be benign "
"if two threads try this transition at the same time", getprogname(),
expected);
}
});
// If we had a previous dispatch table, use that to service the allocation,
// otherwise fall back to the native allocator.
// This could be modified by a concurrent HandleHeapprofdSignal, but that is
// benign as we will dispatch to the ephemeral handler, which will then dispatch
// to the underlying one.
const MallocDispatch* previous_dispatch = atomic_load(&gPreviousDefaultDispatchTable);
if (previous_dispatch) {
return previous_dispatch->malloc(bytes);
}
return NativeAllocatorDispatch()->malloc(bytes);
}
static void* InitHeapprofd(void*) {
MaybeModifyGlobals(kWithLock, [] {
MallocHeapprofdState expected = kInitialState;
// 如果 gHeapprofdState 和 kInitialState 一致,则将 gHeapprofdState 改为 kInstallingHook ,返回true;
// 否则将 gHeapprofdState 的值赋值给 expected,返回false
if (atomic_compare_exchange_strong(&gHeapprofdState, &expected, kInstallingHook)) {
__libc_globals.mutate([](libc_globals* globals) {
CommonInstallHooks(globals);
});
// 将 gHeapprofdState 的状态改为 kHookInstalled
atomic_store(&gHeapprofdState, kHookInstalled);
} else {
error_log("%s: heapprofd: failed to transition kInitialState -> kInstallingHook. "
"current state (possible race): %d", getprogname(), expected);
}
});
return nullptr;
}
// 加载 heapprofd_client.so
static void CommonInstallHooks(libc_globals* globals) {
void* impl_handle = atomic_load(&gHeapprofdHandle);
// gHeapprofdHandle 初始化值为 nullptr,也就是第一次需要加载 heapprofd_client.so
if (impl_handle == nullptr) {
impl_handle = LoadSharedLibrary(kHeapprofdSharedLib, kHeapprofdPrefix, &globals->malloc_dispatch_table);
if (impl_handle == nullptr) {
return;
}
atomic_store(&gHeapprofdHandle, impl_handle);
} else if (!InitSharedLibrary(impl_handle, kHeapprofdSharedLib, kHeapprofdPrefix, &globals->malloc_dispatch_table)) {
return;
}
FinishInstallHooks(globals, nullptr, kHeapprofdPrefix);
}
两条线路最终都是调用到 CommonInstallHooks 用来加载 heapprofd_client.so , 并使用 heapprofd 里面的内存申请函数来替换 libc 里面的函数
void* LoadSharedLibrary(const char* shared_lib, const char* prefix, MallocDispatch* dispatch_table) {
void* impl_handle = nullptr;
// Try to load the libc_malloc_* libs from the "runtime" namespace and then
// fall back to dlopen() to load them from the default namespace.
//
// The libraries are packaged in the runtime APEX together with libc.so.
// However, since the libc.so is searched via the symlink in the system
// partition (/system/lib/libc.so -> /apex/com.android.runtime/bionic/libc.so)
// libc.so is loaded into the default namespace. If we just dlopen() here, the
// linker will load the libs found in /system/lib which might be incompatible
// with libc.so in the runtime APEX. Use android_dlopen_ext to explicitly load
// the ones in the runtime APEX.
// 加载 lib 库,如果直接用 dlopen 加载的是 /system/lib/libc.so, 如果是 runtime 环境,则会出现不兼容情况,
// 这里需要在 runtime 环境下加载 runtime 下的 libc.so
struct android_namespace_t* runtime_ns = android_get_exported_namespace("com_android_runtime");
if (runtime_ns != nullptr) {
const android_dlextinfo dlextinfo = {
.flags = ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_NAMESPACE,
.library_namespace = runtime_ns,
};
impl_handle = android_dlopen_ext(shared_lib, RTLD_NOW | RTLD_LOCAL, &dlextinfo);
}
if (impl_handle == nullptr) {
impl_handle = dlopen(shared_lib, RTLD_NOW | RTLD_LOCAL);
}
if (impl_handle == nullptr) {
error_log("%s: Unable to open shared library %s: %s", getprogname(), shared_lib, dlerror());
return nullptr;
}
// 在加载 so 库,则需要将函数指针表进行初始化
if (!InitSharedLibrary(impl_handle, shared_lib, prefix, dispatch_table)) {
dlclose(impl_handle);
impl_handle = nullptr;
}
return impl_handle;
}
bool InitSharedLibrary(void* impl_handle, const char* shared_lib, const char* prefix, MallocDispatch* dispatch_table) {
static constexpr const char* names[] = {
"initialize",
"finalize",
"get_malloc_leak_info",
"free_malloc_leak_info",
"malloc_backtrace",
"write_malloc_leak_info",
};
// 先使用 for 循环对 gFunctions 进行初始化 , 后面会用到这个 gFunctions 做初始化,获取泄露信息,结束等动作
for (size_t i = 0; i < FUNC_LAST; i++) {
char symbol[128];
snprintf(symbol, sizeof(symbol), "%s_%s", prefix, names[i]);
gFunctions[i] = dlsym(impl_handle, symbol);
if (gFunctions[i] == nullptr) {
error_log("%s: %s routine not found in %s", getprogname(), symbol, shared_lib);
ClearGlobalFunctions();
return false;
}
}
// 然后初始化 globals->malloc_dispatch_table, 也就是将 malloc , free 等函数指针指向 heapprofd 里面对应的函数 heaprofd_malloc
if (!InitMallocFunctions(impl_handle, dispatch_table, prefix)) {
ClearGlobalFunctions();
return false;
}
return true;
}
然后在 FinishInstallHooks 里面调用 heapprofd_initialize 来初始化 heapprofd 。
bool FinishInstallHooks(libc_globals* globals, const char* options, const char* prefix) {
// init_func 指向的是 perfetto 端的 heapprofd_initialize
init_func_t init_func = reinterpret_cast<init_func_t>(gFunctions[FUNC_INITIALIZE]);
// If GWP-ASan was initialised, we should use it as the dispatch table for
// heapprofd/malloc_debug/malloc_debug.
const MallocDispatch* prev_dispatch = GetDefaultDispatchTable();
if (prev_dispatch == nullptr) {
prev_dispatch = NativeAllocatorDispatch();
}
// 调用 perfetto 端的初始化函数 heapprofd_initialize , 其中 options 为 null
if (!init_func(prev_dispatch, &gZygoteChild, options)) {
error_log("%s: failed to enable malloc %s", getprogname(), prefix);
ClearGlobalFunctions();
return false;
}
// Do a pointer swap so that all of the functions become valid at once to
// avoid any initialization order problems.
atomic_store(&globals->default_dispatch_table, &globals->malloc_dispatch_table);
if (!MallocLimitInstalled()) {
atomic_store(&globals->current_dispatch_table, &globals->malloc_dispatch_table);
}
// Use atexit to trigger the cleanup function. This avoids a problem
// where another atexit function is used to cleanup allocated memory,
// but the finalize function was already called. This particular error
// seems to be triggered by a zygote spawned process calling exit.
int ret_value = __cxa_atexit(MallocFiniImpl, nullptr, nullptr);
if (ret_value != 0) {
// We don't consider this a fatal error.
warning_log("failed to set atexit cleanup function: %d", ret_value);
}
return true;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号