【SpringBoot】Spring Boot 中 AOP 的内部调用问题详解
在 Spring Boot 中使用 AOP 时,确实存在一个常见问题:在同一个类内部的方法调用中,AOP 切面不会生效。这是因为 Spring AOP 的实现机制导致的限制。
问题原因分析
1. AOP 代理机制
Spring AOP 是基于代理实现的:
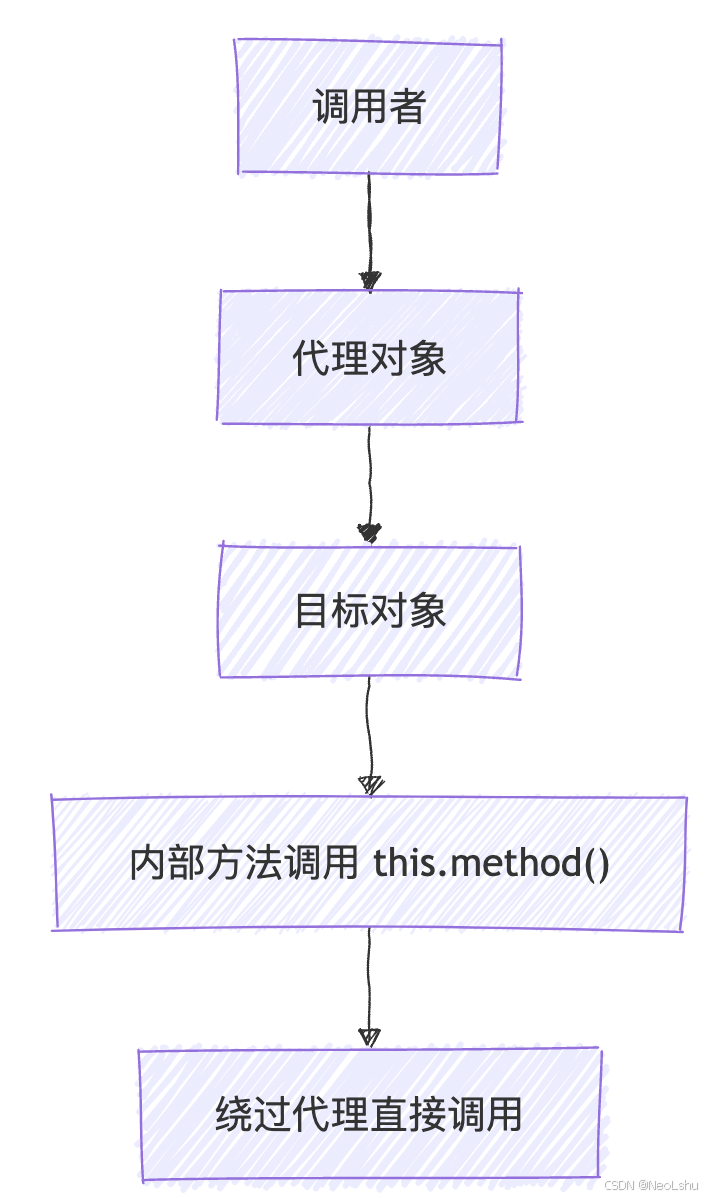
- 当调用被代理对象的方法时,会经过代理对象
- 代理对象负责执行切面逻辑
- 但在同一个类内部的方法调用时,调用是通过
this引用进行的,而不是通过代理对象
@Service
public class MyService {
public void methodA() {
// 这里调用 methodB 是通过 this.methodB(),而不是代理对象
methodB(); // AOP 不会生效
}
@MyAnnotation // 自定义切点
public void methodB() {
// 业务逻辑
}
}
2. 代理类型差异
Spring 支持两种代理方式:
- JDK 动态代理:基于接口实现
- CGLIB 代理:基于类继承实现
但无论哪种代理方式,都存在相同的内部调用限制:
解决方案
1. 使用 ApplicationContext 获取代理对象(推荐)
@Service
public class MyService implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public void methodA() {
// 从容器中获取当前类的代理对象
MyService proxy = applicationContext.getBean(MyService.class);
proxy.methodB(); // 通过代理对象调用,AOP 生效
}
@MyAnnotation
public void methodB() {
// 业务逻辑
}
}
2. 使用 AopContext 获取当前代理对象
@Service
public class MyService {
public void methodA() {
// 启用暴露代理(需要在配置中设置)
MyService proxy = (MyService) AopContext.currentProxy();
proxy.methodB(); // 通过代理对象调用
}
@MyAnnotation
public void methodB() {
// 业务逻辑
}
}
// 配置类中启用暴露代理
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)
public class AppConfig {
}
3. 重构代码结构(最佳实践)
将需要切面支持的方法拆分到不同的服务类中:
@Service
public class ServiceA {
@Autowired
private ServiceB serviceB;
public void methodA() {
serviceB.methodB(); // 跨类调用,AOP 生效
}
}
@Service
public class ServiceB {
@MyAnnotation
public void methodB() {
// 业务逻辑
}
}
4. 使用 AspectJ 编译时织入(高级方案)
在 pom.xml 中添加 AspectJ 依赖和插件:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectj-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.14.0</version>
<configuration>
<complianceLevel>11</complianceLevel>
<source>11</source>
<target>11</target>
<showWeaveInfo>true</showWeaveInfo>
<verbose>true</verbose>
<Xlint>ignore</Xlint>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>test-compile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
在配置中启用 LTW(Load-Time Weaving):
@Configuration
@EnableLoadTimeWeaving
public class AspectJConfig {
}
性能与设计考量
| 方案 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApplicationContext | 简单直接 | 依赖容器 | 一般业务场景 |
| AopContext | 无需依赖注入 | 需额外配置 | 工具类方法 |
| 代码重构 | 符合单一职责 | 增加类数量 | 大型项目 |
| AspectJ | 无内部调用问题 | 配置复杂 | 高性能要求系统 |
最佳实践建议
-
优先考虑代码重构:
- 遵循单一职责原则
- 避免过大的服务类
- 合理划分服务边界
-
谨慎使用 AOP:
// 明确切点表达式,避免过度拦截 @Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..)) && @annotation(MyAnnotation)") public void myPointcut() {} -
性能敏感场景:
- 使用编译时织入(AspectJ)
- 避免在切面中执行耗时操作
- 使用条件切点减少不必要的拦截
-
测试策略:
@SpringBootTest public class AopTest { @Autowired private MyService myService; @Test public void testAop() { // 验证切面是否生效 myService.methodA(); // 断言切面逻辑执行结果 } }
常见问题排查
-
切面完全不生效:
- 检查是否添加了
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy - 确认切面类被 Spring 管理(有
@Component注解) - 检查切点表达式是否匹配目标方法
- 检查是否添加了
-
内部调用部分生效:
- 使用上述解决方案之一
- 优先考虑代码重构方案
-
循环依赖问题:
- 当使用 ApplicationContext 方案时可能出现
- 使用
@Lazy注解解决:@Autowired @Lazy private MyService myService;
理解 Spring AOP 的代理机制是解决这类问题的关键。在大多数情况下,通过合理的代码结构设计和适当的解决方案,可以有效地规避内部调用导致的 AOP 失效问题。
本文来自博客园,作者:NeoLshu,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/neolshu/p/19513660


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号