机试用
计算定长数组的大小
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); // 计算数组的大小
记得使用函数:
max() min()
max一般会用在贪心算法?
sort排序用法
定长:a[n]
sort(a,a+n);
vector
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
vector
队尾删除元素:使用 pop_back 函数删除向量的最后一个元素。
队尾添加元素:使用 push_back 函数将元素添加到向量的末尾。
删除元素:使用 erase 函数,传递 vec.begin() 作为要删除元素的位置的参数,删除向量的第一个元素。
添加元素:使用 insert 函数,传递 vec.begin() 作为插入位置的参数,将元素插入到向量的开头。
vec.end() 返回的是指向向量末尾的迭代器,而不是向量中最后一个元素的迭代器。
另一种方法是使用 vec.end() - 1,这也可以得到指向向量最后一个元素的迭代器。
但是如果我想获取最后一个元素不如直接用下面的:
获取第一个/最后一个函数的引用:back() front()
复写数组:assign 是 vector 类的一个成员函数,用于将一个新的元素序列分配给向量,替换其当前内容。
// 使用迭代器范围将新元素分配给向量
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::vector<int> new_elements = {6, 7, 8};
vec.assign(new_elements.begin(), new_elements.end());
// 使用重复元素进行分配
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
vec.assign(3, 100); // 将向量清空,然后填充三个值为 100 的元素
map用法:
说到动态数组,我们C++有一个成熟且靠谱的工具,叫做vector。
说到哈希表,直接unordered_map<int,int> hashtable。
统计出现次数最多的元素!
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int,int> count;
int times = 0,value = 0;
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
count[nums[i]]++;
if(count[nums[i]] > times){
value = nums[i];
times = count[nums[i]];
}
}
return value;
}
};
主要用法
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个 unordered_map
unordered_map<int, string> myMap;
// 插入元素到 map 中
myMap.insert(make_pair(1, "One"));
myMap.insert(make_pair(2, "Two"));
myMap.insert(make_pair(3, "Three"));
// 构造并插入元素到 map 中
myMap.emplace(4, "Four");
// 使用 operator[] 访问元素
cout << "Value for key 1: " << myMap[1] << endl;
// 使用 at 访问元素
cout << "Value for key 2: " << myMap.at(2) << endl;
// 查找元素
auto it = myMap.find(3);
if (it != myMap.end()) {
cout << "Element found: " << it->second << endl;
} else {
cout << "Element not found" << endl;
}
// 返回指定元素的个数
cout << "Number of elements with key 1: " << myMap.count(1) << endl;
// 移除元素
myMap.erase(4);
// 再次使用 count 检查是否成功移除
cout << "Number of elements with key 4 after erasing: " << myMap.count(4) << endl;
return 0;
}
随机数种子
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
获取随机数:
int randomIndex = rand() %nums.size();
return nums[randomIndex];
SET 集合
常见用法
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
int main() {
std::set<int> mySet;
// 插入元素到 set 中
mySet.insert(10);
mySet.insert(20);
mySet.insert(30);
// 使用 insert 返回值查看插入是否成功
auto result = mySet.insert(20);
if (result.second) {
std::cout << "Element 20 inserted successfully" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Element 20 already exists in the set" << std::endl;
}
// 使用 erase 移除元素
mySet.erase(20);
// 查找元素
auto it = mySet.find(30);
if (it != mySet.end()) {
std::cout << "Element 30 found in the set" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Element 30 not found in the set" << std::endl;
}
// 返回指定元素的个数
std::cout << "Number of occurrences of 10 in the set: " << mySet.count(10) << std::endl;
// 输出 set 中的元素
std::cout << "Set contains:";
for (const auto& elem : mySet) {
std::cout << " " << elem;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
用途:判断重复字符
记得有序查找使用二分
int low = 0;
int high = n-1;
while(low < high){
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target) return mid;
else if(nums[mid] < target) low = mid+1;
else high = mid-1;
}
return -1;
string 用法
stack用法
push(const T& value):将元素压入栈顶。pop():弹出栈顶元素。top():返回栈顶元素的引用,但不会将其从栈中移除。empty():检查栈是否为空。size():返回栈中元素的数量。
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个整型栈
stack<int> myStack;
// 将元素压入栈顶
cout << "Pushing elements onto the stack: 10, 20, 30" << endl;
myStack.push(10);
myStack.push(20);
myStack.push(30);
// 输出栈顶元素
cout << "Top element of the stack: " << myStack.top() << endl;
// 弹出栈顶元素
cout << "Popping the top element" << endl;
myStack.pop();
// 输出栈顶元素
cout << "Top element of the stack after popping: " << myStack.top() << endl;
// 检查栈是否为空
if (myStack.empty()) {
cout << "The stack is empty" << endl;
} else {
cout << "The stack is not empty" << endl;
}
// 输出栈的大小
cout << "Size of the stack: " << myStack.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
链表
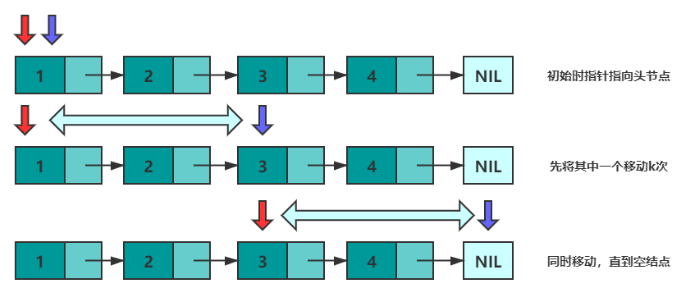
获取倒数第k个元素
设有两个指针 p 和 q,初始时均指向头结点。首先,先让 p 沿着 next 移动 k 次。此时,p 指向第 k+1个结点,q 指向头节点,两个指针的距离为 k 。然后,同时移动 p 和 q,直到 p 指向空,此时 q 即指向倒数第 k 个结点。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *p = head, *q = head; //初始化
while(k--) { //将 p指针移动 k 次
p = p->next;
}
while(p != nullptr) {//同时移动,直到 p == nullptr
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
return q;
}
};
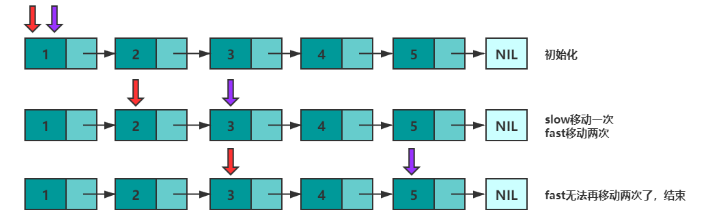
,获取中间位置的元素,
获取中间元素的问题。设有两个指针 fast 和 slow,初始时指向头节点。每次移动时,fast向后走两次,slow向后走一次,直到 fast 无法向后走两次。这使得在每轮移动之后。fast 和 slow 的距离就会增加一。设链表有 n 个元素,那么最多移动 n/2 轮。当 n 为奇数时,slow 恰好指向中间结点,当 n 为 偶数时,slow 恰好指向中间两个结点的靠前一个(可以考虑下如何使其指向后一个结点呢?)。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *p = head, *q = head;
while(q != nullptr && q->next != nullptr) {
p = p->next;
q = q->next->next;
}
return p;
}
};
判断链表是否存在环
如果一个链表存在环,那么快慢指针必然会相遇。
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while(fast != NULL){
fast = fast->next;
if(fast != NULL){
fast = fast->next;
}
if(fast == slow)return true;
slow = slow->next;
}
return false;
}
};
,判断环的长度
最后一个问题,如果存在环,如何判断环的长度呢?方法是,快慢指针相遇后继续移动,直到第二次相遇。两次相遇间的移动次数即为环的长度。
queue队列
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个整数队列
queue<int> myQueue;
// 向队列中插入元素
myQueue.push(10);
myQueue.push(20);
myQueue.push(30);
// 访问队首元素
cout << "Front element of queue: " << myQueue.front() << endl;
// 移除队首元素
myQueue.pop();
// 再次访问队首元素
cout << "Front element of queue after popping: " << myQueue.front() << endl;
// 输出队列的大小
cout << "Size of queue: " << myQueue.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
priority_queue
#include <iostream>
#include <queue> // 包含优先队列的头文件
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个优先队列(堆),存储整数类型
priority_queue<int> myPriorityQueue;
// 向优先队列中插入元素,实际上是向堆中添加元素
myPriorityQueue.push(30);
myPriorityQueue.push(10);
myPriorityQueue.push(20);
// 输出堆顶元素,即优先队列的最大元素
cout << "Top element of priority queue (max element of heap): " << myPriorityQueue.top() << endl;
// 弹出堆顶元素
myPriorityQueue.pop();
// 再次输出堆顶元素,此时堆中的最大元素已被弹出
cout << "Top element of priority queue after popping: " << myPriorityQueue.top() << endl;
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号