文件
一、 文件的基本操作
- 打开/关闭 文件
打开文件: f = open(file_path, mode='r') # 传入表示文件路径的字符串,会返回一个文件对象。
- 关闭文件: f.close() # 调用给定文件对象的close方法
f = open('/home/pyvip/py_case/a.py','r') # 相对路径或绝对路径 默认以读的方式打开文件
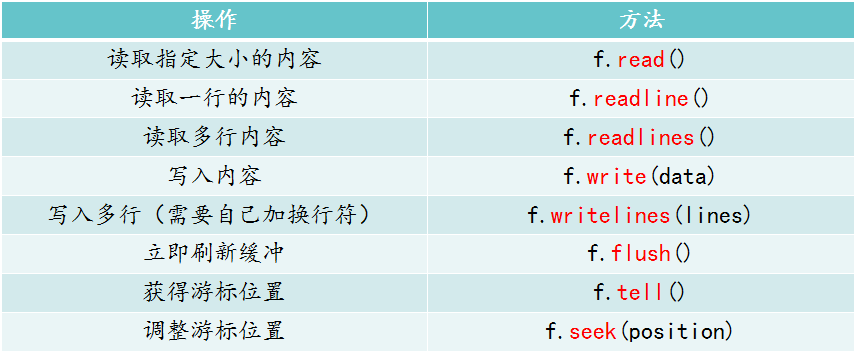
content = f.read() # 读取文件所有内容
print(f)
content = f.read(5) # 读取文件前5个位置的内容
print(content)
f.close() # 关闭文件
f.read() # 文件关闭了 再对其操作就会报错
- 文件对象 <_io.TextIOWrapper name='test.py' mode='r' encoding='UTF-8'>
# mode 什么方式打开 'r' read 读 'w' write 写 encoding 编码格式
- 文件的打开模式和方法
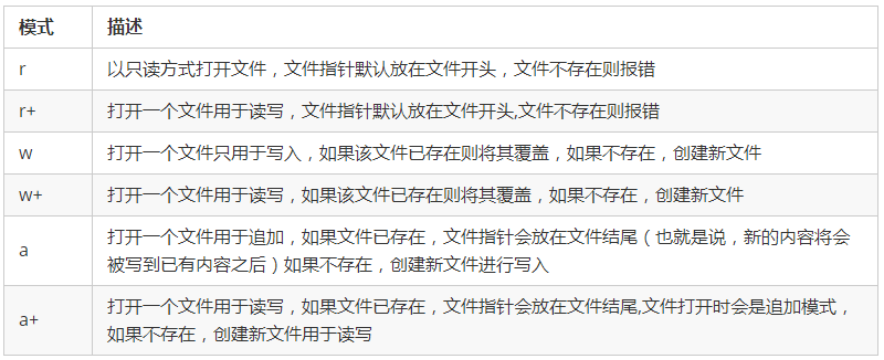
- 文本模式(默认)与二进制模式
- 文本模式:以str字符串形式写入 读取出来的也是str字符串
- 二进制模式:以bytes字符串形式写入 读取出来的也是bytes字符串
- 其他模式:rb rb+ wb wb+ ab ab+ 加个b的作用:以二进制的格式打开文件,进行上述操作 。
f = open('test.py') # 默认以读的方式打开
content3 = f.read() # 读取所有
print(content3)
print('->-'*30)
print(f.tell()) # 查看光标所在的位置
f.seek(0) # 调节光标所在的位置
content = f.readline() # 读取第一行
print(content)
content2 = f.readline() # 读取第二行
print(content2)
f.close()
f = open('b.py','w') # 以写方式打开文件 没有则创建 'a' 追加
f.write('啦啦啦6666666') # 覆盖掉原来的内容
f.flush() # 刷新一下
f.read() # 以写的模式打开 只能写 不能读
f.close()
# w+ 写的基础上,增加读的功能 r+ 读的基础上,增加写的功能 a+
f = open('test.py','r')
print(f.read(5)) # \n
f.close()
二、StringIO和BytesIO
内存假文件:内存假文件一旦关闭,数据消失 。优点:速度快,方便
import io
# f = io.StringIO() # 存在内存里面 不需要路径和什么方式打开
# f.write('hello world !') # 写完之后 光标在最后
# f.seek(0)
# print(f.read())
# f.close() # 假文件 一旦关闭 就会消失
f = io.BytesIO() # 对二进制文件操作
# f.write('dsadas') # 报错
f.write(b'dsds')
print(f.getvalue()) # 不需要你去调节光标
f.close()
# 1 速度快
# 2 方便
三、上下文管理
with … as … # 实现文件运行后自动关闭
with open(file_path, mode='r') as f:
# 对f进行一系列操作
# 也可以执行别的操作
# 跳出with语句快的时候自动执行f.close()
with open(file_path, mode='r') as f1,\
open(file_path, mode='r') as f2,\ … :
# 对f进行一系列操作
# 也可以执行别的操作
# 跳出with语句快的时候自动执行f.close()
with open('a.py','a+') as f,\
open('test.py') as f2: # 以追加的模式
f.seek(0)
content = f.read()
print(content)
print(f2.read(6))
f.read() # 文件关闭 报错
f2.read() # 文件关闭 报错
四、常见问题处理
- 文件访问编码:
f = open('a.py',encoding='gbk',errors='ignore') # ignore 忽略
print(f.read()) # 不同编码强行读取 乱码
f.close()
- os模块:
import os
print(os.getcwd()) # 相当于 pwd
print(os.listdir('/home/pyvip/py_case')) # 存放在列表
print(os.system('ls -a')) # 操作Linux命令
print(os.path.join(os.getcwd(),'A','B','a.py'))







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号