NCHU-OOP-第二次工程级项目
一、 前言与概述
这次阶段迭代由两次作业组成,每次作业的题量适中,难度也还算适中,主要考察的知识点是面向对象设计原则,例如单一职责原则,里氏代换原则,开闭原则,合成复用原则,依赖倒转原则等。
二、题目描述
第一次需求
https://images.ptausercontent.com/499d204b-fcef-4610-a9ca-c8fbf5e346d9.pdf
第二次需求
https://images.ptausercontent.com/b9cec79b-8012-4901-843e-3d48f27d28a6.pdf
三、题目分析
此次的迭代程序主要考察了面向对象设计原则,接下来是对题目的具体分析:
-
单一职责原则(SRP)
要求:每个类只负责单一功能。
应用场景:Good类:仅负责货物属性(重量、体积、类型)和计费重量计算。Pay类:仅处理支付方式和金额展示。 -
里氏代换原则(LSP)
要求:子类可替换父类,且不改变程序正确性。
应用场景:Customer、StartPerson、EndPerson继承自Person,需确保子类show()方法不改变父类定义的行为(如参数类型、返回值)。WechatPay、AliPay等支付子类需正确实现Pay抽象类的show()方法。 -
开闭原则(OCP)
要求:对扩展开放,对修改封闭。
应用场景:新增货物类型(如 “贵重货物”)时,只需创建新子类继承Good,不修改原有费率逻辑。新增支付方式(如 “银联支付”)时,创建UnionPay子类继承Pay,不修改Agent类的支付逻辑。 -
合成复用原则(CRP)
要求:优先使用组合 / 聚合,而非继承。
应用场景:Order类可包含Good对象列表(组合关系),而非继承Good。Agent类通过持有Customer、Airport等对象引用实现功能,而非继承这些类。 -
依赖倒转原则(DIP)
要求:高层模块不依赖低层模块,依赖抽象接口。
应用场景:Agent类通过Pay抽象类处理支付,而非直接依赖WechatPay等具体子类。货物类型判断通过抽象方法(如Good.getRate())实现,而非在Agent中硬编码if-else。
四、程序展示
第一次的程序:
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Person{
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
public Person(){
super();
}
public Person(String address, String name, String phone){
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public abstract void show();
}
class Customer extends Person{
private int id;
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
public Customer(){
super();
}
public Customer(int id,String address, String name,String phone){
this.id = id;
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:\n",name,phone);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
}
}
class StartPerson extends Person{
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
public StartPerson(){
super();
}
public StartPerson(String address, String name,String phone){
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s\n发件人电话:%s\n发件人地址:%s\n",name,phone,address);
}
}
class EndPerson extends Person{
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
public EndPerson(){
super();
}
public EndPerson(String address, String name,String phone){
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s\n收件人电话:%s\n收件人地址:%s\n",name,phone,address);
}
}
class Good{
private int id;
private String name;
private int width;
private int length;
private int height;
private int weight;
public Good(){
}
public Good(int id,String name,int width,int length,int height,int weight){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight > width * length * height / 6000 ? weight : width * length * height / 6000;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public void show(){
System.out.printf("");
}
}
abstract class Pay{
private String wayOfPay;
private float sum;
public Pay(){
super();
}
public String getWayOfPay() {
return wayOfPay;
}
public void setWayOfPay(String wayOfPay) {
this.wayOfPay = wayOfPay;
}
public float getSum() {
return sum;
}
public void setSum(float sum) {
this.sum = sum;
}
public abstract void show();
}
class WechatPay extends Pay{
private String wayOfPay = "微信支付金额";
private float sum;
public WechatPay(){
super();
}
public WechatPay(float sum){
this.sum = sum;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("%s:%.1f",wayOfPay,sum);
}
}
class AliPay extends Pay{
private String wayOfPay = "支付宝支付金额";
private float sum;
public AliPay(){
super();
}
public AliPay(float sum){
this.sum = sum;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("%s:%.1f",wayOfPay,sum);
}
}
class Airport{
private String id;
private String startAirport;
private String endAirport;
private String date;
private float max;
public Airport(){}
public Airport(String id,String startAirport,String endAirport,String date,float max) {
this.id = id;
this.startAirport = startAirport;
this.endAirport = endAirport;
this.date =date;
this.max = max;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStartAirport() {
return startAirport;
}
public void setStartAirport(String startAirport) {
this.startAirport = startAirport;
}
public String getEndAirport() {
return endAirport;
}
public void setEndAirport(String endAirport) {
this.endAirport = endAirport;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public float getMax() {
return max;
}
public void setMax(float max) {
this.max = max;
}
public void show(){
System.out.printf("航班号:%s\n",id);
}
}
class Order{
private int id;
private String date;
private float weight;
public Order(){}
public Order(int id, String date, float weight){
this.id= id;
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public float getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(float weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public void show(){
System.out.printf("订单号:%d\n订单日期:%s\n",id,date);
}
}
class Agent{
private float weight = 0;
private float money = 0;
private float rate;
private float sumWeight = 0;
private float sumMoney = 0;
public Agent(){}
public void customerShow(Customer customer){
customer.show();
}
public void airportShow(Airport airport){
airport.show();
}
public void orderShow(Order order){
order.show();
}
public void startPersonShow(StartPerson startPerson){
startPerson.show();
}
public void endPersonShow(EndPerson endPerson){
endPerson.show();
}
public float calculateor(Good good[], int num){
for(int i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
weight = good[i].getWeight();
if(weight < 20)
rate = 35;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 30;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 25;
else
rate = 15;
sumWeight += weight;
sumMoney += rate * weight;
}
return sumWeight;
}
public void payShow(Good good[], int num){
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n微信支付金额:%.1f\n",sumWeight,sumMoney);
}
public void goodShow(Good[] good, int num){
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:\n" + "-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
for(int i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
weight = good[i].getWeight();
if(weight < 20)
rate = 35;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 30;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 25;
else
rate = 15;
money = rate * weight;
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n",i+1,good[i].getName(),(float)good[i].getWeight(),rate,money);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int customerId = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine(); // 清除nextInt()后残留的换行符!!!下面记得也要有
String customerName = input.nextLine();
String customerPhone = input.nextLine();
String customerAddress = input.nextLine();
int goodNum = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
int goodId[] = new int[goodNum];
String goodName[] = new String[goodNum];
int goodWidth[] = new int[goodNum];
int goodLength[] = new int[goodNum];
int goodHeight[] = new int[goodNum];
int goodWeight[] = new int[goodNum];
for (int i = 0; i < goodNum; ++i) {
goodId[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodName[i] = input.nextLine();
goodWidth[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodLength[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodHeight[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodWeight[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
}
String planeId = input.nextLine();
String airportStart = input.nextLine();
String airportEnd = input.nextLine();
String airportDate = input.nextLine();
int planeMax = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
int orderId = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
String orderDate = input.nextLine();
String startAddress = input.nextLine();
String startName = input.nextLine();
String startPhone = input.nextLine();
String endAddress = input.nextLine();
String endName = input.nextLine();
String endPhone = input.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(customerId, customerAddress, customerName, customerPhone);
StartPerson startPerson = new StartPerson(startAddress, startName, startPhone);
EndPerson endPerson = new EndPerson(endAddress, endName, endPhone);
Good[] good = new Good[goodNum];
for (int i = 0; i < goodNum; ++i) {
good[i] = new Good(goodId[i], goodName[i], goodWidth[i], goodLength[i], goodHeight[i], goodWeight[i]);
}
Order order = new Order(orderId, orderDate, 0);
Airport airport = new Airport(planeId, airportStart, airportEnd, airportDate, planeMax);
Agent agent = new Agent();
float sumWeight = agent.calculateor(good,goodNum);
if(sumWeight > planeMax)
{
System.out.print("The flight with flight number:"+ planeId +" has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.");
input.close();
return;
}
else
{
agent.customerShow(customer);
agent.airportShow(airport);
agent.orderShow(order);
agent.startPersonShow(startPerson);
agent.endPersonShow(endPerson);
agent.payShow(good, goodNum);
agent.goodShow(good, goodNum);
}
input.close();
}
}
第二次程序:
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Person{
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
public Person(){
super();
}
public Person(String address, String name, String phone){
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public abstract void show();
}
class Customer extends Person{
private int id;
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
private String type;
public Customer(){
super();
}
public Customer(String type, int id,String address, String name,String phone){
this.type = type;
this.id = id;
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:\n",name,phone);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
}
}
class StartPerson extends Person{
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
public StartPerson(){
super();
}
public StartPerson(String address, String name,String phone){
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s\n发件人电话:%s\n发件人地址:%s\n",name,phone,address);
}
}
class EndPerson extends Person{
private String address;
private String name;
private String phone;
public EndPerson(){
super();
}
public EndPerson(String address, String name,String phone){
this.address = address;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public void show(){
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s\n收件人电话:%s\n收件人地址:%s\n",name,phone,address);
}
}
class Good{
private int id;
private String name;
private int width;
private int length;
private int height;
private int weight;
private String type;
public Good(){
}
public Good(int id,String name,int width,int length,int height,int weight){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight > width * length * height / 6000 ? weight : width * length * height / 6000;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public void show(){
System.out.printf("");
}
}
abstract class Pay{
private String wayOfPay;
private float sum;
public Pay(){
super();
}
public String getWayOfPay() {
return wayOfPay;
}
public void setWayOfPay(String wayOfPay) {
this.wayOfPay = wayOfPay;
}
public float getSum() {
return sum;
}
public void setSum(float sum) {
this.sum = sum;
}
public void show(){
System.out.printf("%s:%.1f",wayOfPay,sum);
}
}
class WechatPay extends Pay{
private String wayOfPay = "微信支付金额";
private float sum;
public WechatPay(){
super();
}
public WechatPay(float sum){
this.sum = sum;
}
}
class ALiPay extends Pay{
private String wayOfPay = "支付宝支付金额";
private float sum;
public ALiPay(){
super();
}
public ALiPay(float sum){
this.sum = sum;
}
}
class CashPay extends Pay{
private String wayOfPay = "现金支付金额";
private float sum;
public CashPay(){
super();
}
public CashPay(float sum){
this.sum = sum;
}
}
class Airport{
private String id;
private String startAirport;
private String endAirport;
private String date;
private float max;
public Airport(){}
public Airport(String id,String startAirport,String endAirport,String date,float max) {
this.id = id;
this.startAirport = startAirport;
this.endAirport = endAirport;
this.date =date;
this.max = max;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStartAirport() {
return startAirport;
}
public void setStartAirport(String startAirport) {
this.startAirport = startAirport;
}
public String getEndAirport() {
return endAirport;
}
public void setEndAirport(String endAirport) {
this.endAirport = endAirport;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public float getMax() {
return max;
}
public void setMax(float max) {
this.max = max;
}
public void show(){
System.out.printf("航班号:%s\n",id);
}
}
class Order{
private int id;
private String date;
private float weight;
public Order(){}
public Order(int id, String date, float weight){
this.id= id;
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public float getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(float weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public void show(){
System.out.printf("订单号:%d\n订单日期:%s\n",id,date);
}
}
class Agent{
private float weight = 0;
private float money = 0;
private float rate;
private float sumWeight = 0;
private float sumMoney = 0;
public Agent(){}
public void customerShow(Customer customer){
customer.show();
}
public void airportShow(Airport airport){
airport.show();
}
public void orderShow(Order order){
order.show();
}
public void startPersonShow(StartPerson startPerson){
startPerson.show();
}
public void endPersonShow(EndPerson endPerson){
endPerson.show();
}
public float calculateor(Good good[], String goodType, String customerType){
double discount = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < good.length; ++i)
{
weight = good[i].getWeight();
if(goodType.equals("Normal"))
{
if(weight < 20)
rate = 35;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 30;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 25;
else
rate = 15;
}
else if(goodType.equals("Dangerous"))
{
if(weight < 20)
rate = 80;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 50;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 30;
else
rate = 20;
}
else
{
if(weight < 20)
rate = 60;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 50;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 40;
else
rate = 30;
}
if(customerType.equals("Individual"))
discount = 0.9;
else
discount = 0.8;
sumWeight += weight;
sumMoney += rate * weight * discount;
}
return sumWeight;
}
public void payShow(Pay pay){
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n%s:%.1f\n",sumWeight,pay.getWayOfPay(),sumMoney);
}
public void goodShow(Good[] good, String goodType, String customerType){
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:\n" + "-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
for(int i = 0; i < good.length; ++i)
{
weight = good[i].getWeight();
if(goodType.equals("Normal"))
{
if(weight < 20)
rate = 35;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 30;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 25;
else
rate = 15;
}
else if(goodType.equals("Dangerous"))
{
if(weight < 20)
rate = 80;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 50;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 30;
else
rate = 20;
}
else
{
if(weight < 20)
rate = 60;
else if(weight < 50)
rate = 50;
else if(weight < 100)
rate = 40;
else
rate = 30;
}
money = rate * weight;
// if(customerType.equals("Individual"))
// money *= 0.9;
// else
// money *= 0.8;
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n",i+1,good[i].getName(),(float)good[i].getWeight(),rate,money);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String customerType = input.nextLine();
int customerId = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine(); // 清除nextInt()后残留的换行符!!!下面记得也要有
String customerName = input.nextLine();
String customerPhone = input.nextLine();
String customerAddress = input.nextLine();
String goodType = input.nextLine();
int goodNum = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
int goodId[] = new int[goodNum];
String goodName[] = new String[goodNum];
int goodWidth[] = new int[goodNum];
int goodLength[] = new int[goodNum];
int goodHeight[] = new int[goodNum];
int goodWeight[] = new int[goodNum];
for (int i = 0; i < goodNum; ++i) {
goodId[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodName[i] = input.nextLine();
goodWidth[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodLength[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodHeight[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
goodWeight[i] = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
}
String planeId = input.nextLine();
String airportStart = input.nextLine();
String airportEnd = input.nextLine();
String airportDate = input.nextLine();
int planeMax = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
int orderId = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
String orderDate = input.nextLine();
String startAddress = input.nextLine();
String startName = input.nextLine();
String startPhone = input.nextLine();
String endAddress = input.nextLine();
String endName = input.nextLine();
String endPhone = input.nextLine();
String wayOfPay = input.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(customerType,customerId, customerAddress, customerName, customerPhone);
StartPerson startPerson = new StartPerson(startAddress, startName, startPhone);
EndPerson endPerson = new EndPerson(endAddress, endName, endPhone);
Good[] good = new Good[goodNum];
for (int i = 0; i < goodNum; ++i) {
good[i] = new Good(goodId[i], goodName[i], goodWidth[i], goodLength[i], goodHeight[i], goodWeight[i]);
good[i].setType(goodType);
}
Order order = new Order(orderId, orderDate, 0);
Airport airport = new Airport(planeId, airportStart, airportEnd, airportDate, planeMax);
Agent agent = new Agent();
float sumWeight = agent.calculateor(good,goodType,customerType);
Pay pay;
if(wayOfPay.equals("Wechat")){
pay = new WechatPay(sumWeight);
pay.setWayOfPay("微信支付金额");
}
else if(wayOfPay.equals("ALiPay")){
pay = new ALiPay(sumWeight);
pay.setWayOfPay("支付宝支付金额");
}
else{
pay = new CashPay(sumWeight);
pay.setWayOfPay("现金支付金额");
}
if(sumWeight > planeMax)
{
System.out.print("The flight with flight number:"+ planeId +" has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.");
input.close();
return;
}
else
{
agent.customerShow(customer);
agent.airportShow(airport);
agent.orderShow(order);
agent.startPersonShow(startPerson);
agent.endPersonShow(endPerson);
agent.payShow(pay);
agent.goodShow(good,goodType,customerType);
}
input.close();
}
}
五、代码分析
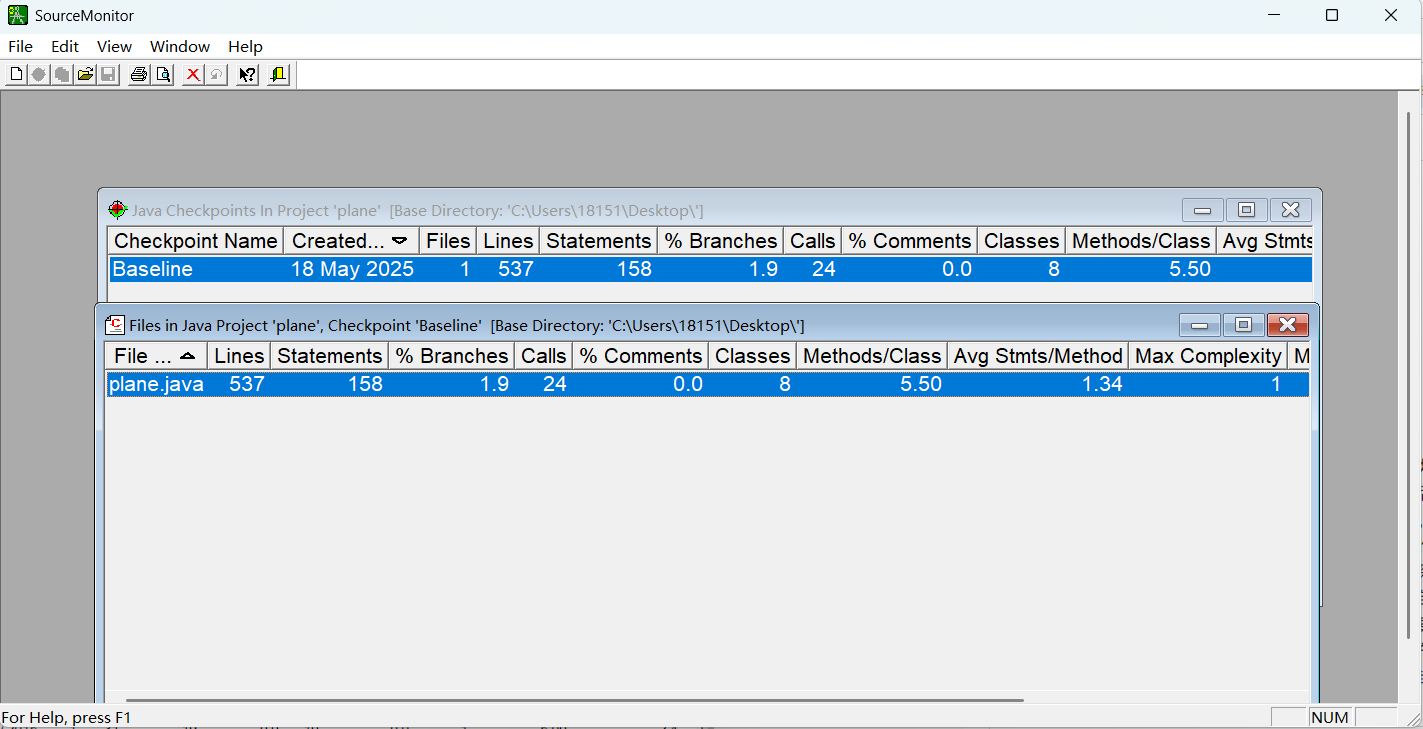
代码行数(Lines):537 行,这表明项目代码量相对不算特别少,有一定规模。
语句数(Statements):158 条,说明代码中执行性语句的数量情况。
分支百分比(% Branches):1.9 ,反映代码中分支结构(如 if - else、switch 等)占比相对较低。
调用数(Calls):24 ,表示方法之间的调用次数总计。
注释百分比(% Comments):0.0 ,意味着代码中完全没有添加注释,这不利于代码的可读性和可维护性,后续开发人员难以快速理解代码逻辑。
类数(Classes):8 ,说明项目中定义了 8 个类,体现了一定的模块化程度。
每个类的平均方法数(Methods/Class):5.50 ,即平均每个类包含 5.5 个方法,反映类的功能丰富度。
每个方法的平均语句数(Avg Stmts/Method):1.34 ,表示方法内部平均语句数量较少,从侧面说明方法相对比较简洁。
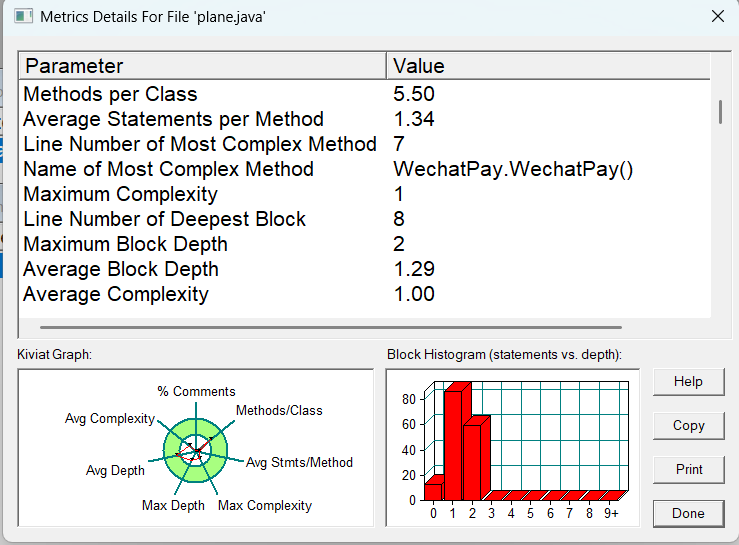
最深块的行号(Line Number of Deepest Block):8 ,最大块深度(Maximum Block Depth):2 ,平均块深度(Average Block Depth):1.29 ,平均复杂度(Average Complexity):1.00 ,这些指标表明代码中语句块嵌套深度较浅,整体复杂度较低。
第二张可视化图表解读
雷达图(Kiviat Graph):展示了多个指标的相对情况,从图中可以直观看到各项指标围绕中心分布情况,由于没有注释,“% Comments” 指标处于最内圈 ,其他指标分布也体现了前面分析的结果,如平均复杂度(Avg Complexity)、平均深度(Avg Depth)等都处于相对较优的位置。
块直方图(Block Histogram (statements vs. depth)):以直方图形式展示语句数量与块深度的关系,从图中可见,块深度为 1 和 2 时语句数量较多,再次说明代码中大部分语句块深度较浅,符合前面指标分析结果。
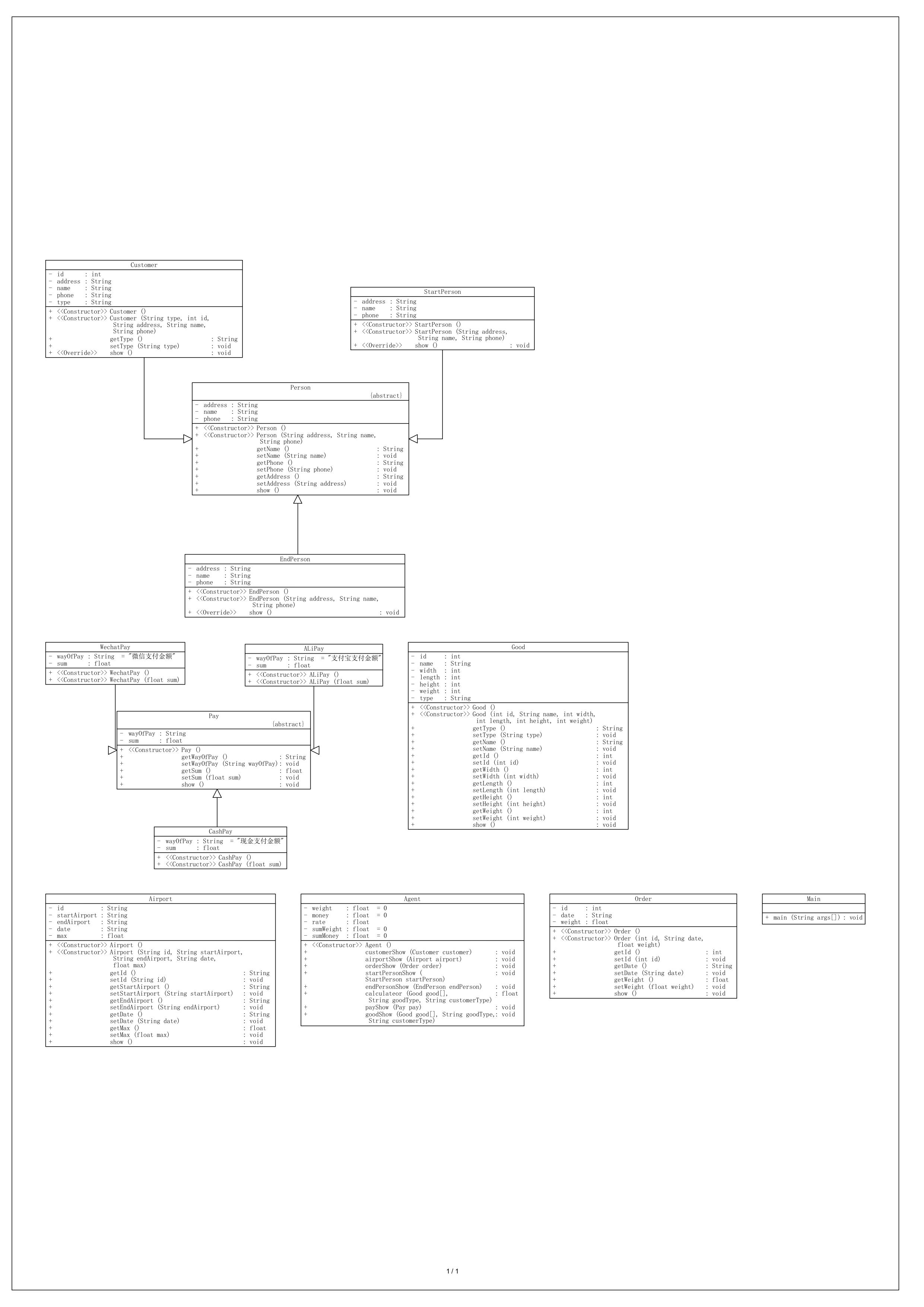
下面是对程序类图的分析:
一、类继承关系
-
Person抽象类()
属性:私有 address、name、phone(字符串类型)
方法:
构造方法Person()和Person(String address, String name, String phone)。
公开的getter/setter方法(getName()、setName()等)。
抽象方法show()(需子类实现)。
作用:定义客户、发件人、收件人的通用属性和行为,符合里氏代换原则。 -
子类继承 Person
Customer类()
新增属性:type(客户类型,字符串)、id(整数)。
方法:
构造方法Customer()和Customer(String type, int id, String address, String name, String phone)。
getType()、setType(String type)和重写的show()方法。StartPerson类()
方法:构造方法StartPerson(String address, String name, String phone)和重写的show()方法(打印发件人信息)。
EndPerson类()
方法:构造方法EndPerson(String address, String name, String phone)和重写的show()方法(打印收件人信息)。
二、其他核心类
-
Good类(货物)
属性:id、name、width、length、height、weight(整数),type(货物类型,字符串)。
方法:
构造方法Good()和Good(int id, String name, int width, int length, int height, int weight)。
getter/setter方法(如getWeight()计算体积重量与实际重量的较大值)。 -
Pay抽象类(支付)
子类:WechatPay、AliPay、CashPay
方法:show()方法打印支付信息,子类重写实现具体支付方式。
设计优点:通过抽象类实现支付方式扩展,符合开闭原则。 -
Airport类(航班)
属性:id、startAirport、endAirport、date(字符串),max(最大载重,浮点型)。
方法:构造方法和getter/setter,show()方法打印航班号。 -
Order类(订单)
属性:id、date(字符串),weight(总重量,浮点型)。
方法:构造方法和getter/setter,show()方法打印订单基本信息。 -
Agent类(业务逻辑)
属性:rate、sumWeight、sumMoney(浮点型,记录计算结果)。
方法:
展示方法(customerShow、airportShow等)。
计算方法calculateor()(根据货物类型和客户类型计算总重量和费用)。
goodShow()打印货物明细。
三、设计原则符合性分析
-
单一职责原则(SRP)
Good类专注于货物属性和计费重量计算()。
Pay类层次结构分离支付方式()。 -
开闭原则(OCP)
新增支付方式(如银联)只需创建Pay子类,无需修改现有代码()。 -
依赖倒转原则(DIP)
Agent通过Pay抽象类处理支付(),而非具体子类。 -
里氏代换原则(LSP)
对于抽象父类Person类,定义客户、发件人、收件人的通用属性和行为,符合里氏代换原则。 -
合成复用原则(CRP)
Order类与Good类通过组合关联(一个订单包含多件货物),而非继承。
六、 总结与反思
这个阶段的作业在算法思维难度上较上次的电梯模拟程序来说更简单一些,但是此阶段更加注重对于面向对象程序设计原则的考察,同时航空货物系统的程序没有给出类图,需要自己对需求进行详细的分析,根据需求设计程序的结构,设计类以及类与类之间关系。在这阶段的作业中,我通过联系更加深刻地理解了单一职责原则,里氏代换原则,合成复用原则,但是在复用的过程中对于继承复用和合成复用的理解选择还不够,还是局限于知道继承复用的耦合度较高而且要符合里氏代换原则但是可以实现多态,合成复用耦合度较低但是无法实现多态。同时对于依赖倒转原则也还是处在理论的阶段,还需要后续的勤加练习,在实践中体会。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号