java博客作业(一)
一、前言
题目集一
知识点:if 判断、for 循环、双重循环、输入输出语句、数据计算处理、格式化输出(保留两位小数、四舍五入取整数等)、制表符 \t 的使用、字符串处理、String类查找重复字符、字符串删减、数组查重、判断素数、GPS数据处理、求定积分等。
题量:较多
难度:难易交叉
题目集二
知识点:数据类型的转换、基础语法、判断闰年、求下一天
题量:一般
难度:一般
题目集三
知识点:类与方法设计、封装、LocalDate类型运用、boolean型数据、使用数组存放信息、求下n天以及两日期间相差天数
题量:少
难度:较难
二、设计与分析
题目集一
7-6 统计一个子串在整串中出现的次数
最开始看到这道题人挺懵的,怎么统计字符串里面一部分出现的次数?我应该把它们分成一个个字符放到数组里面,然后判断计算吗?打开课本看到String类相关的内容,才发现Java已经为我们提供了诸多处理String类数据的方法,根据课本给出的方法,我想到以下思路:String类里面的indexOf( )方法使我可以轻松得到字符在字符串中的位置,也就是说我现在处理字符串就如同处理数组,只需要通过下标增加“遍历”字符串,从而算出子串在整串出现的次数即可。而String类里面还特别提供了substring( )方法以方便我们获取子串。所以我用indexOf( b, x)判断是否包含子串,并返回子串下标,之后用substring(x+b.length())截取整串后面的部分,循环判断,得到子串次数。
源码如下:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 5 String a = input.nextLine(); 6 String b = input.nextLine(); 7 int x=0; 8 int count=0; 9 while((x=a.indexOf(b,x))!=-1){ 10 a=a.substring(x+b.length()); 11 count++; 12 } 13 System.out.print(count); 14 } 15 }
7-7 有重复的数据
这题要求我们在一大堆数据中判断是否存在重复数据,返回“YES” or "No",看到此题第一眼当然是觉得小case,连重复次数都不需要计算,只要有一个数据重复一次便可以轻松结束,然而当我自信满满的掏出双重循环时,才被测试点狠狠的打了脸,“运行超时”,这意料之外却又情理之中,可我该如何将代码进行改进呢?怎样才能提高运行速度呢?对于此类大量数据的处理问题,我想到了曾经处理的判断素数问题,为了减少运行负担采用了二分法对数据进行处理。对于现在这道题,如果我想使用二分法,那就得先排序,可是之前在C语言学习的排序简直是复杂无比,想想应该会适得其反。于是便止步放弃了,我还需要一定的时间对此进行分析。因此最终还是提交了超时的二重循环代码。
二重循环源码如下:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 int i; 7 int j; 8 int k=0; 9 int n = input.nextInt(); 10 int[] number=new int[n]; 11 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 12 number[i]=input.nextInt(); 13 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 14 for(j=i+1;j<n;j++) 15 if(number[i]==number[j]){ 16 k++; 17 break; 18 } 19 } 20 if(k!=0) System.out.print("YES"); 21 if(k==0) System.out.print("NO"); 22 } 23 }
7-10 GPS数据处理
不会,写不来,长篇大论,不知道该如何处理,直接劝退。
附上题目:

7-10 GPS数据处理 分数 10 作者 翁恺 单位 浙江大学 NMEA-0183协议是为了在不同的GPS(全球定位系统)导航设备中建立统一的BTCM(海事无线电技术委员会)标准,由美国国家海洋电子协会(NMEA-The National Marine Electronics Associa-tion)制定的一套通讯协议。GPS接收机根据NMEA-0183协议的标准规范,将位置、速度等信息通过串口传送到PC机、PDA等设备。 NMEA-0183协议是GPS接收机应当遵守的标准协议,也是目前GPS接收机上使用最广泛的协议,大多数常见的GPS接收机、GPS数据处理软件、导航软件都遵守或者至少兼容这个协议。 NMEA-0183协议定义的语句非常多,但是常用的或者说兼容性最广的语句只有$GPGGA、$GPGSA、$GPGSV、$GPRMC、$GPVTG、$GPGLL等。 其中$GPRMC语句的格式如下: $GPRMC,024813.640,A,3158.4608,N,11848.3737,E,10.05,324.27,150706,,,A*50 这里整条语句是一个文本行,行中以逗号“,”隔开各个字段,每个字段的大小(长度)不一,这里的示例只是一种可能,并不能认为字段的大小就如上述例句一样。 字段0:$GPRMC,语句ID,表明该语句为Recommended Minimum Specific GPS/TRANSIT Data(RMC)推荐最小定位信息 字段1:UTC时间,hhmmss.sss格式 字段2:状态,A=定位,V=未定位 字段3:纬度ddmm.mmmm,度分格式(前导位数不足则补0) 字段4:纬度N(北纬)或S(南纬) 字段5:经度dddmm.mmmm,度分格式(前导位数不足则补0) 字段6:经度E(东经)或W(西经) 字段7:速度,节,Knots 字段8:方位角,度 字段9:UTC日期,DDMMYY格式 字段10:磁偏角,(000 - 180)度(前导位数不足则补0) 字段11:磁偏角方向,E=东W=西 字段16:校验值 这里,*为校验和识别符,其后面的两位数为校验和,代表了$和*之间所有字符(不包括这两个字符)的异或值的十六进制值。上面这条例句的校验和是十六进制的50,也就是十进制的80。 提示:^运算符的作用是异或。将$和*之间所有的字符做^运算(第一个字符和第二个字符异或,结果再和第三个字符异或,依此类推)之后的值对65536取余后的结果,应该和*后面的两个十六进制数字的值相等,否则的话说明这条语句在传输中发生了错误。注意这个十六进制值中是会出现A-F的大写字母的。另外,在Java语言中,如果你需要的话,可以用Integer.parseInt(s)从String变量s中得到其所表达的整数数字;而Integer.parseInt(s, 16)从String变量s中得到其所表达的十六进制数字 现在,你的程序要读入一系列GPS输出,其中包含$GPRMC,也包含其他语句。在数据的最后,有一行单独的 END 表示数据的结束。 你的程序要从中找出$GPRMC语句,计算校验和,找出其中校验正确,并且字段2表示已定位的语句,从中计算出时间,换算成北京时间。一次数据中会包含多条$GPRMC语句,以最后一条语句得到的北京时间作为结果输出。 你的程序一定会读到一条有效的$GPRMC语句。 输入格式: 多条GPS语句,每条均以回车换行结束。最后一行是END三个大写字母。 输出格式: 6位数时间,表达为: hh:mm:ss 其中,hh是两位数的小时,不足两位时前面补0;mm是两位数的分钟,不足两位时前面补0;ss是两位数的秒,不足两位时前面补0。 输入样例: $GPRMC,024813.640,A,3158.4608,N,11848.3737,E,10.05,324.27,150706,,,A*50 END 输出样例: 10:48:13
题目集二
7-5 学号识别
 题目
题目此题看起来比较简单,也就是基本的 if 语句的判断输出,但是其中的逻辑判断确实为难了我好一会,此处不多叙述,将在踩坑心得中细说。
源码如下:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String s=input.nextLine(); if(s.length()!=8||((s.charAt(2)!='0'&&s.charAt(2)!='2')||(s.charAt(2)=='2'&&s.charAt(3)!='0')||(s.charAt(2)=='0'&&(s.charAt(3)=='0'||s.charAt(3)=='4'||s.charAt(3)=='5'||s.charAt(3)=='6'||s.charAt(3)=='7'||s.charAt(3)=='8'||s.charAt(3)=='9')))){ System.out.print("Wrong Format"); } else{ System.out.println("入学年份:20"+s.substring(0,2)+"年"); if(s.charAt(2)=='0'){ if(s.charAt(3)=='1') System.out.println("学院:材料学院"); if(s.charAt(3)=='2') System.out.println("学院:机械学院"); if(s.charAt(3)=='3') System.out.println("学院:外语学院"); } else System.out.println("学院:软件学院"); System.out.println("班级:"+s.substring(4,6)); System.out.print("学号:"+s.substring(6,8)); } } }
7-8 判断三角形类型
此题繁琐但是简单,只需要根据题目给出的信息,逐个编写判断语句输出对应三角形类型即可。然而最后有个测试点迟迟过不了,最后老师课堂提醒了,计算机无法精确取等,直角三角形边长计算公式使用时不应该写“=”号,而是给予他一个小误差(我写了小于0.1)。
源码如下:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 6 double side1=input.nextDouble(); 7 double side2=input.nextDouble(); 8 double side3=input.nextDouble(); 9 double t; 10 if(side1>side2){ 11 t=side1; 12 side1=side2; 13 side2=t; 14 } 15 if(side2>side3){ 16 t=side2; 17 side2=side3; 18 side3=t; 19 } 20 if(side1>=1&&side1<=200&&side2>=1&&side2<=200&&side3>=1&&side3<=200){ 21 if(((side1+side2)<=side3)||((side3-side2)>=side1)){ 22 System.out.print("Not a triangle"); 23 } 24 else if((side1==side2)&&(side2==side3)){ 25 System.out.print("Equilateral triangle"); 26 } 27 else if((side1==side2)&&(2*side1*side1-side3*side3<0.1)){ 28 System.out.print("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); 29 } 30 else if(side1==side2||side2==side3){ 31 System.out.print("Isosceles triangle"); 32 } 33 else if(side1*side1+side2*side2-side3*side3<0.1){ 34 System.out.print("Right-angled triangle"); 35 } 36 else{ 37 System.out.print("General triangle"); 38 } 39 } 40 else{ 41 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 42 } 43 } 44 }
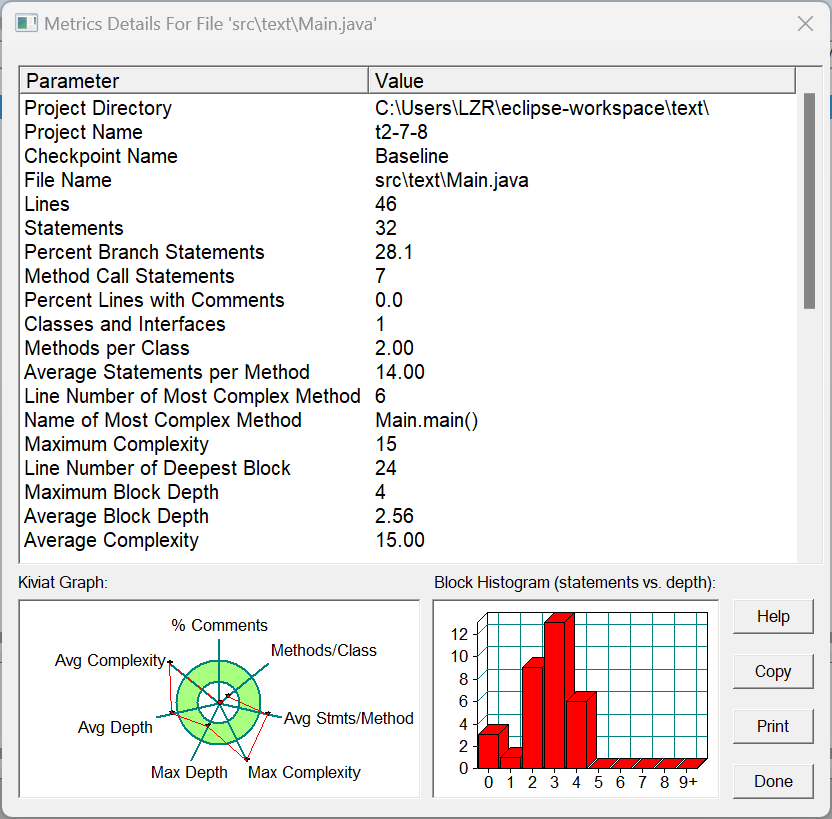
SourceMonitor生成的报表内容:
7-9 求下一天
第一道正式要求使用类、方法进行分块完成功能的题目,也是我第一次试着转变c语言的书写格式。题目要求求下一天,所以我只需要在当天天数+1,如果日超过了该月最大天数,便将日改为1,月份+1,月份为13时,将月份改为1,年份+1,期间注意对于闰年的判定。关于最大天数,我是用了 if 语句对月份进行判断,后来也是知道了这样写较为繁琐垃圾。这题并没有多大难度,挑战性最大的还是思维的转变,格式的书写以及理解。
源码如下:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int year=input.nextInt(); int month=input.nextInt(); int day=input.nextInt(); checkInputValidity(year,month,day); if(!checkInputValidity(year,month,day)){ System.out.print("Wrong Format"); } else{ nextDate(year,month,day); } } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year){ //判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型 if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||(year%400==0)) return true; else return false; } public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day){ //判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值 if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=31) return true; else return false; } public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day){ //求输入日期的下一天 int maxday=0; if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12) maxday=31; if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11) maxday=30; if(month==2){ if(!isLeapYear(year)) maxday=28; else maxday=29; } if(day<=maxday){ if(day==maxday){ day=1; month++; if(month==13){ month=1; year++; } } else if(day<maxday) day=day+1; System.out.print("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); } else System.out.print("Wrong Format"); } }
题目集三
这次题目全都对类与方法做了要求,不可以再用C语言的方法写Java了。
7-3 定义日期类
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。
注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法,否则按0分处理。
要求:Date类结构如下图所示:
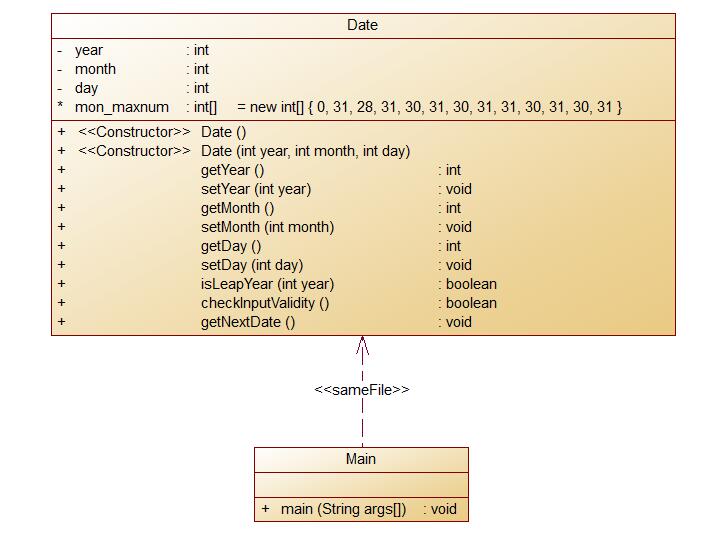
此题依旧是求下一天,也就是上次题目集二7-9的润色处理,将之前C语言版的代码转变为面向对象的Java,所以整体难度不大,毕竟大部分问题在上次都已经得到解决。此次题目中给出的类图中,对于月份最大天数的处理当属最有意识。一开始我并不能理解,不过老师课堂点拨过后便是豁然开朗了,使用数组存放每个月最大天数,月份对应各下标,比起之前冗长的 if 语句判断,面对大工程文件确实显得明智省事。其余不多加叙述。
源码如下:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 6 int year=input.nextInt(); 7 int month=input.nextInt(); 8 int day=input.nextInt(); 9 Date date=new Date(year,month,day); 10 if(!date.checkInputValidity()){ 11 System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong"); 12 } 13 else{ 14 date.getNextDate(); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 19 class Date{ 20 private int year; 21 private int month; 22 private int day; 23 private int mon_maxnum[]=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 24 public Date(){ 25 26 } 27 public Date(int year,int month,int day){ 28 this.year=year; 29 this.month=month; 30 this.day=day; 31 } 32 public int getYear(){ 33 return this.year; 34 } 35 public int getMonth(){ 36 return this.month; 37 } 38 public int getDay(){ 39 return this.day; 40 } 41 public boolean isLeapYear(int year){ 42 if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||(year%400==0)) 43 return true; 44 else return false; 45 } 46 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ 47 if(year>=1900&&year<=2000&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=31) 48 return true; 49 else return false; 50 } 51 public void getNextDate(){ 52 if(!isLeapYear(year)){ 53 this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 54 } 55 if(this.day<=this.mon_maxnum[this.month]){ 56 if(this.day==this.mon_maxnum[this.month]){ 57 this.day=1; 58 this.month++; 59 if(this.month==13){ 60 this.month=1; 61 this.year++; 62 } 63 } 64 else if(this.day<this.mon_maxnum[this.month]) this.day++; 65 System.out.println("Next day is:"+this.year+"-"+this.month+"-"+this.day); 66 } 67 else System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong"); 68 } 69 }
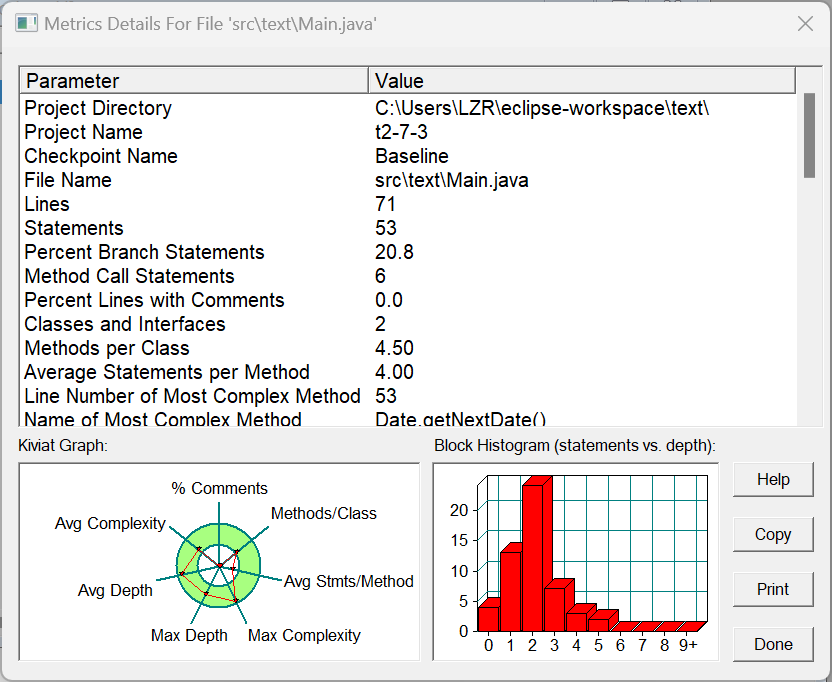
SourceMonitor生成的报表内容:
7-4 日期类设计
这题是7-3的promax版本,附上题目详情:

7-4 日期类设计 参考题目3和日期相关的程序,设计一个类DateUtil,该类有三个私有属性year、month、day(均为整型数),其中,year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 除了创建该类的构造方法、属性的getter及setter方法外,需要编写如下方法: public boolean checkInputValidity();//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法 public boolean isLeapYear(int year);//判断year是否为闰年 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的下n天日期 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的前n天日期 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date);//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后) public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date);//判断两个日期是否相等 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date);//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数 public String showDate();//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值 应用程序共测试三个功能: 求下n天 求前n天 求两个日期相差的天数 注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改) 程序主方法如下: import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print( date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } 输入格式: 有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]): 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数 输出格式: 当输入有误时,输出格式如下: Wrong Format 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下: year1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下: year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下: The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2-month2-day2 are:值 输入样例1: 在这里给出一组输入。例如: 3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14 输出样例1: 在这里给出相应的输出。例如: The days between 2014-2-14 and 2020-6-14 are:2312 输入样例2: 在这里给出一组输入。例如: 2 1834 2 17 7821 输出样例2: 在这里给出相应的输出。例如: 1834-2-17 previous 7821 days is:1812-9-19 输入样例3: 在这里给出一组输入。例如: 1 1999 3 28 6543 输出样例3: 在这里给出相应的输出。例如: 1999-3-28 next 6543 days is:2017-2-24 输入样例4: 在这里给出一组输入。例如: 0 2000 5 12 30 输出样例4: 在这里给出相应的输出。例如: Wrong Format
从题目给出的方法和主类就能知道这题可是个大工程了,不过还是万幸已经给出了主类和方法,这省去了很多分析设计的时间。题目要求实现三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
前两个功能想也知道如出一辙,且之前也有了求下一天的经验,所以我还是蛮自信的。然而下n 天可比下一天复杂多了,毕竟n可以取特别大。最初我想着从输入的 n 开始下手,直接计算下n 天是哪一天,可是每四年一次闰年,每个月最大天数又不一样,直接算实在复杂。于是我想将这个任务变得简单点,不如就写个循环,让计算机自己一天一天加吧!天数满了月份就进一位,月份满了天数就进一位,就像时钟一样。这样写代码量少了很多,思路也更加清晰简单。然而测试点中有一个极大的n ,一天一天加注定会使得系统运行超时。不过问题不大,很快我便想到,对于求下n 天的模块,我可以将天数一天一天加,一直加到下一年的1月1日,之后通过判断闰年与平年,直接加366天或365天,直到剩下的天数不足365天,再进行一天一天的加,如此便简单可行了。其余两个功能,也是在这个功能的基础上进行小小的改动,大致思路并没有多大变化。
源码如下:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 int year = 0; 7 int month = 0; 8 int day = 0; 9 10 int choice = input.nextInt(); 11 12 if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method 13 int m = 0; 14 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 15 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 16 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 17 18 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 19 20 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 21 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 22 System.exit(0); 23 } 24 25 m = input.nextInt(); 26 27 if (m < 0) { 28 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 29 System.exit(0); 30 } 31 32 System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:"); 33 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 34 } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method 35 int n = 0; 36 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 37 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 38 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 39 40 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 41 42 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 43 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 44 System.exit(0); 45 } 46 47 n = input.nextInt(); 48 49 if (n < 0) { 50 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 51 System.exit(0); 52 } 53 54 System.out.print( 55 date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); 56 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 57 } 58 else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method 59 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 60 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 61 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 62 63 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 64 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 65 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 66 67 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 68 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); 69 70 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { 71 System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + 72 " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" 73 + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 74 } else { 75 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 76 System.exit(0); 77 } 78 } 79 else{ 80 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 81 System.exit(0); 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 86 87 class DateUtil{ 88 private int year; 89 private int month; 90 private int day; 91 private int mon_maxnum[]=new int[]{31,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 92 public DateUtil(){ 93 94 } 95 public DateUtil(int year,int month,int day){ 96 this.year=year; 97 this.month=month; 98 this.day=day; 99 } 100 public int getYear(){ 101 return this.year; 102 } 103 public int getMonth(){ 104 return this.month; 105 } 106 public int getDay(){ 107 return this.day; 108 } 109 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ 110 if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=31) 111 return true; 112 else return false; 113 } 114 public boolean isLeapYear(int year){ 115 if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||(year%400==0)) 116 return true; 117 else return false; 118 } 119 120 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ 121 int i; 122 for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ 123 if(!isLeapYear(year)){ 124 this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 125 } 126 else{ 127 this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 128 } 129 day++; 130 if(day>mon_maxnum[month]){ 131 day=1; 132 month++; 133 } 134 if(month==13){ 135 month=1; 136 this.year++; 137 while(n-i>365){ 138 if(!isLeapYear(year)){ 139 n-=365; 140 year++; 141 } 142 else{ 143 n-=366; 144 year++; 145 } 146 } 147 } 148 } 149 DateUtil a=new DateUtil(year,month,day); 150 return a; 151 } 152 153 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ 154 int i; 155 for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ 156 if(!isLeapYear(year)){ 157 this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 158 } 159 else{ 160 this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 161 } 162 day--; 163 if(day<1){ 164 month--; 165 day=mon_maxnum[month]; 166 } 167 if(month==0){ 168 month=12; 169 this.year--; 170 while(n-i>365){ 171 if(!isLeapYear(year)){ 172 n-=365; 173 year--; 174 } 175 else{ 176 n-=366; 177 year--; 178 } 179 } 180 } 181 } 182 DateUtil a=new DateUtil(year,month,day); 183 return a; 184 } 185 186 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){ 187 if(this.year>date.getYear()) 188 return true; 189 else if(this.year==date.getYear()&&this.month>this.getMonth()) 190 return true; 191 else if(this.year==date.getYear()&&this.month==this.getMonth()&&this.day>date.getDay()) 192 return true; 193 else return false; 194 } 195 196 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ 197 //相等返回true 198 if(this.year==date.getYear()&&this.month==date.getMonth()&&this.day==date.getDay()) 199 return true; 200 else return false; 201 } 202 203 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ 204 int dif=0; 205 int i; 206 int n=0; 207 int x=0; 208 // System.out.println(this.year+"-"+date.getYear()); 209 if(compareDates(date)){ 210 //前大于后(this>date) 211 if(date.getYear()!=this.year){ 212 //不同年 213 n=this.year-date.getYear()-1; 214 for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ 215 if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear()+i)) 216 dif+=365; 217 else dif+=366; 218 } 219 for(i=1;i<date.getMonth();i++){ 220 if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear())){ 221 this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 222 } 223 else this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 224 x+=this.mon_maxnum[i]; 225 } 226 if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear())) 227 dif+=365-x-date.getDay(); 228 else dif+=366-x-date.getDay(); 229 for(i=1;i<this.month;i++){ 230 if(!isLeapYear(this.year)){ 231 this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 232 } 233 else this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 234 dif+=this.mon_maxnum[i]; 235 } 236 dif+=this.day; 237 } 238 else{ 239 //同一年 240 while(this.month!=date.getMonth()||this.day!=date.getDay()){ 241 dif++; 242 this.day--; 243 if(day<1){ 244 this.month--; 245 this.day=this.mon_maxnum[this.month]; 246 } 247 } 248 } 249 } 250 else{ 251 if(equalTwoDates(date)){ 252 //相等 253 dif=0; 254 } 255 256 else{ 257 //前小于后(this<date) 258 if(date.getYear()!=this.year){ 259 //不同年 260 n=date.getYear()-this.year-1; 261 for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ 262 if(!isLeapYear(this.year+i)) 263 dif+=365; 264 else dif+=366; 265 } 266 for(i=1;i<this.month;i++){ 267 if(!isLeapYear(this.year)){ 268 this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 269 } 270 else this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 271 x+=this.mon_maxnum[i]; 272 } 273 if(!isLeapYear(this.year)) 274 dif+=365-x-this.day; 275 else dif+=366-x-this.day; 276 for(i=1;i<date.getMonth();i++){ 277 if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear())){ 278 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 279 } 280 else date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 281 dif+=date.mon_maxnum[i]; 282 } 283 dif+=date.getDay(); 284 } 285 else{ 286 //同一年 287 while(this.month!=date.getMonth()||this.day!=date.getDay()){ 288 dif++; 289 this.day++; 290 if(day>mon_maxnum[month]){ 291 this.day=1; 292 this.month++; 293 } 294 } 295 } 296 } 297 } 298 return dif; 299 } 300 301 public String showDate(){ 302 return (year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 303 } 304 }
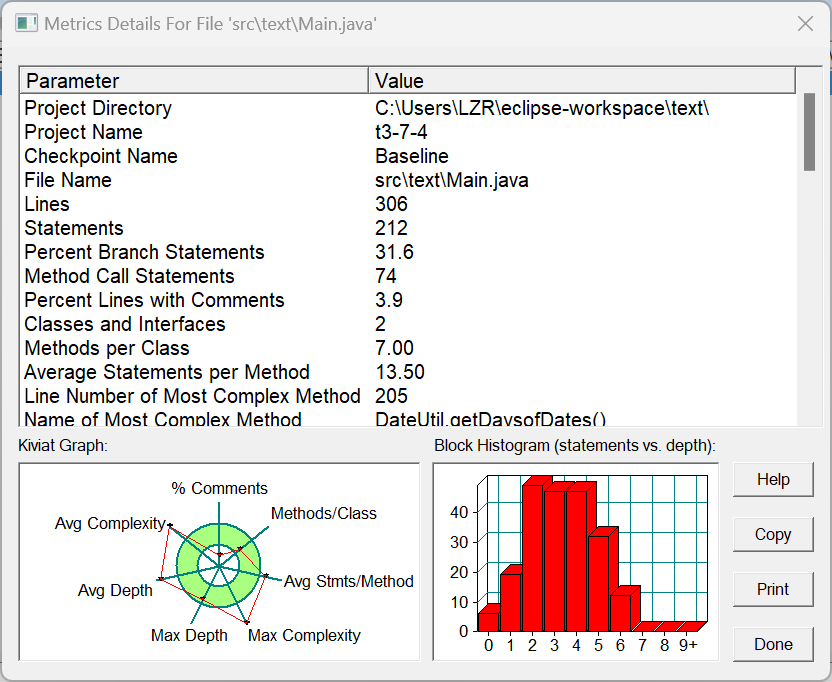
SourceMonitor生成的报表内容:
三、踩坑心得
题目集一
7-1 写题目时使用("实际利率="+(int)(basic*0.7*100)/100.0+"%")方法保留小数有问题,这样虽然能保留两位小数,但是当数据为71.0此类数据时,不会格式化为71.00。
7-4 题目要求最后四舍五入取整,使用 (int)(x) 的方法并不会四舍五入,可以改成 (int)(x+0.5) 达到四舍五入的效果。
(后来知道Java也有printf,格式和C一样,简直了...)
7-5 去掉重复的字符 字符串不能==,但是charAt()是取出单个字符,可以==;
思路是使用String类里的charAt()方法,二重循环遍历字符串,如果字符重复使k=0,否则k为1,输出k为1时的字符。最开始使用如下方法进行循环,导致重复的字符一次也无法输出,而题目要求去重,保留第一次出现。

最后调整了 j 的循环范围,使得 j < i ,如此便能保证只输出一次重复数据。

7-7 有重复的数据 运行超时的问题,想法过于单纯。
(笔者在写此篇博客时,已经想到了新的处理思路。通过与室友同学的讨论,我明白在java中Scanner非常占用运行时间,输入大量数据要大量调用Scanner,因此我最好能一次性输完,那么便是将int数据转换成String类型一次性输入,之后再对其进行处理。Java还为用户提供了自动排序的方法,那么我便可以轻松使用二分法查重了,想必问题应该可以得到解决。)
7-10 Gps信息处理 题目信息量确实大,加上当时任务确实繁杂,所以直接劝退了。踩了被题目直接吓倒的坑......
题目集二
7-1、7-3 要最后要输出float 类型数据,题目没有给出任何提示 。实在是离谱至极!!!!!!
7-5学号识别 由于题目要求设置非法输入的判断口,(输入学号不是8位或者学院编号不是01、02、03、20其中之一,属于非法输入),所以我使用 if 语句进行判断
if(s.length()!=8||((s.charAt(2)!='0'&&s.charAt(2)!='2')||(s.charAt(2)=='2'&&s.charAt(3)!='0')))
而测试报错,后来发现这样写是不全面的,漏写了学院编号是04、05等的判断条件,所以改成如下语句
if(s.length()!=8||((s.charAt(2)!='0'&&s.charAt(2)!='2')||(s.charAt(2)=='2'&&s.charAt(3)!='0')||(s.charAt(2)=='0'&&(s.charAt(3)!='1'||s.charAt(3)!='2'||s.charAt(3)!='3'))))
依旧报错,最后是这样的
if(s.length()!=8||((s.charAt(2)!='0'&&s.charAt(2)!='2')||(s.charAt(2)=='2'&&s.charAt(3)!='0')||(s.charAt(2)=='0'&&(s.charAt(3)=='0'||s.charAt(3)=='4'||s.charAt(3)=='5'||s.charAt(3)=='6'||s.charAt(3)=='7'||s.charAt(3)=='8'||s.charAt(3)=='9'))))
测试点通过的时候我是很开心的,但我也是意识到了这样写的弊端,实在是太麻烦,太容易出错了!!!
7-8 判断三角形类型 判断直角三角形时,一开始直接套用公式,写了以下代码

然而计算机无法对精确的数据取等,双精度数应给予其小范围误差,所以最后改成以下代码

题目集三
7-4 求前n天时,计算失误,让计算机自行累加结果超时,最后得到解决(见上文)
求两日期间天数时,最初想着先计算两日期间隔的整年,然后再计算起始年剩余天数,以及最终年的经过天数,最后进行相加

public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int dif=0; int i; int n=0; int x=0; if(compareDates(date)){ //前小于后(this<date) if(date.getYear()!=this.year){ n=date.getYear()-this.year-1; for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!isLeapYear(this.year+i)) dif+=365; else dif+=366; } for(i=1;i<this.month;i++){ if(!isLeapYear(this.year)){ this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; x+=this.mon_maxnum[i]; } if(!isLeapYear(this.year)) dif+=365-x; else dif+=366-x; for(i=1;i<date.getMonth();i++){ if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear())){ date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; dif+=date.mon_maxnum[i]; } dif+=date.getDay(); } }
然而没有考虑两日期同年的情况,导致差值n可以为负数,计算错误。改进后对年份进行了“同一年”和“非同一年”的区分

public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int dif=0; int i; int n=0; int x=0; // System.out.println(this.year+"-"+date.getYear()); if(compareDates(date)){ //前大于后(this>date) if(date.getYear()!=this.year){ //不同年 n=this.year-date.getYear()-1; for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear()+i)) dif+=365; else dif+=366; } for(i=1;i<date.getMonth();i++){ if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear())){ this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; x+=this.mon_maxnum[i]; } if(!isLeapYear(date.getYear())) dif+=365-x-date.getDay(); else dif+=366-x-date.getDay(); for(i=1;i<this.month;i++){ if(!isLeapYear(this.year)){ this.mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else this.mon_maxnum[2]=29; dif+=this.mon_maxnum[i]; } dif+=this.day; } else{ //同一年 while(this.month!=date.getMonth()||this.day!=date.getDay()){ dif++; this.day--; if(day<1){ this.month--; this.day=this.mon_maxnum[this.month]; } } } }
但是依旧错误,最后发现
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date);//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
此块方法出现了错误,原先样式:
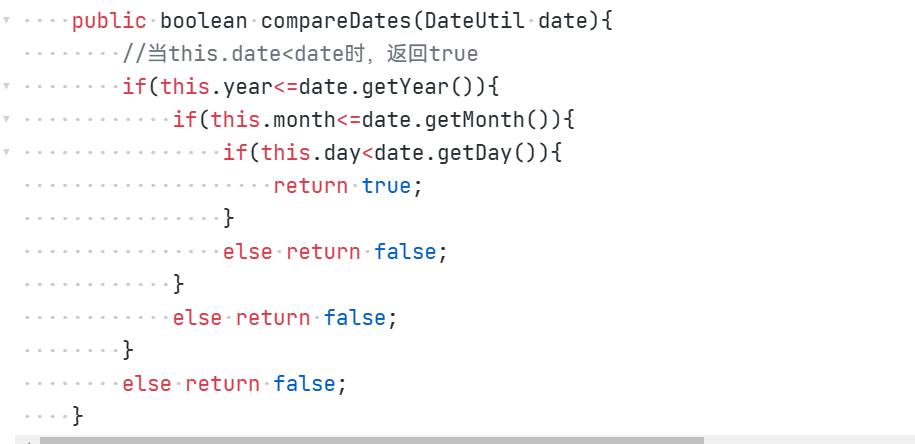
这样写看似没有问题,然而却是会在判断时出现各种不正确的情况
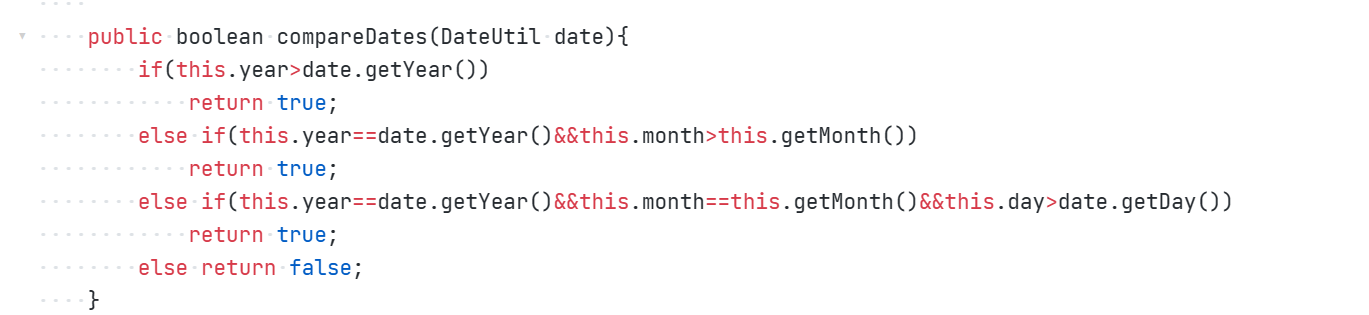
最后改成如下代码
四、改进建议
1、对于多个if 语句,可以尝试改成switch。
2、格式化输出时可以使用 printf 格式,方便好用(此方法会四舍五入)。
3、对于题目集二 7-7 有重复的数据 这题,放弃二循环这种老套方法,尝试在踩坑心得中得出的新方法。
4、对于长if 语句,想办法将其简化,而不是不断给其补全漏洞。
5、判断月份最大天数时,使用数组存放天数信息,放弃垃圾代码。
6、转变代码书写思路,切忌使用C语言思路写Java,要习惯Java的书写风格。
7、要减少代码的嵌套,使各方法各司其职。
五、总结
这三次题目集使我得到了非常好的锻炼,最初题目集并未对书写的格式进行要求,我仅仅是在用Java的语句书写C语言程序罢了,而慢慢地题目便给出了类、方法的要求,这段潜移默化使我更好接受一门新的语言。此外每次题目集中题目也是逐渐加深难度,就拿求前n天一题来说,带着我们逐步分析题目,一点一点拓宽维度,使我对这题的印象很深刻,也整体的、实打实的学到了许多知识,而不是碎片化学习。
三次的题目集也让我认识到了规划设计程序的重要性,拿到题目就上手做,尝试在不断的报错下不断修正BUG真的很愚笨。在最初就应该花时间设计规划类、方法等,而不是不断弥补之前一股脑写下的缺陷,补完之后才发现方法多么不合理,又直接推翻重来。
在达成相同目标的情况下,往往有诸多解决方法,不应该拘泥于最简单的、一想就通的方法,要试着综合多方面因素改进(比如运行效率、代码复杂度等)。
最后,要注意转变思维!要注意转变思维!要注意转变思维!要注意转变思维!要注意转变思维!要注意转变思维!要面向对象!要面向对象!要面向对象!要面向对象!要面向对象!要面向对象!要面向对象!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号