c++中的继承关系
1 什么是继承
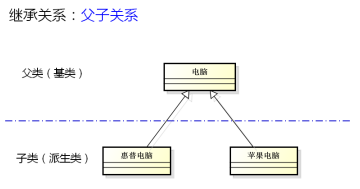
面向对象的继承关系指类之间的父子关系。用类图表示如下:
2 为什么要有继承?/ 继承的意义?
因为继承是面向对象中代码复用的一种手段。通过继承,可以获取父类的所有功能,也可以在子类中重写父类已有的功能 以及 添加父类中没有的功能。
3 如何理解 子类是特殊的父类?
因为子类不仅继承了父类所有的属性与行为,而且在子类中还可以重写父类已有的功能,以及添加自己的新属性与新方法。这也就是说子类对象可以当作父类对象使用。
4 继承的规则
1) 子类是特殊的父类
2) 子类对象可以直接初始化父类对象
3) 子类对象可以直接赋值给父类对象
5 继承中的访问级别
1)public:在类的内部和外部都可以访问。
2)protected::可以在类的内部使用,不可以在类的外部直接使用。,但是存在继承关系时,可以在子类中使用父类的protected的成员。
3)private:只可以在类的内部使用,不可以在类的外部使用。
注:类的内部:在当前类的作用域中(不包括子类的作用域);类的外部:类内部之外的作用域(包括子类的作用域)
问题1:子类是否可以直接访问父类中的private成员(非公有成员)吗?(No)
1)从面向对象理论的角度分析,可知子类拥有父类一切的属性与行为,得出的结论:Yes
2)从c++的语法角度分析,可知外界不能访问类的private成员,得出的结论:No
问题2:谈谈 protected关键字的存在的意义?
protected关键字是为继承而存在的,这样就可以在子类中访问父类的protected成员,同时还不允许外界直接访问父类中的protected成员。
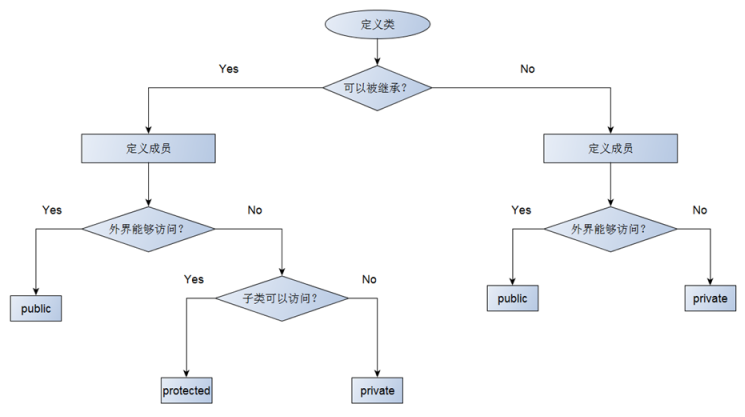
问题3:在类中如何选择类的访问级别?--- 见下图
6 继承中的继承方式
1)public 继承方式 --- 父类成员在子类中保持原有的访问级别。
2)protected 继承方式 --- 父类中的公有成员在子类中变成了protected成员,其它不变。
3)private 继承方式(默认) --- 父类成员在子类中变成了private成员
可归纳为: 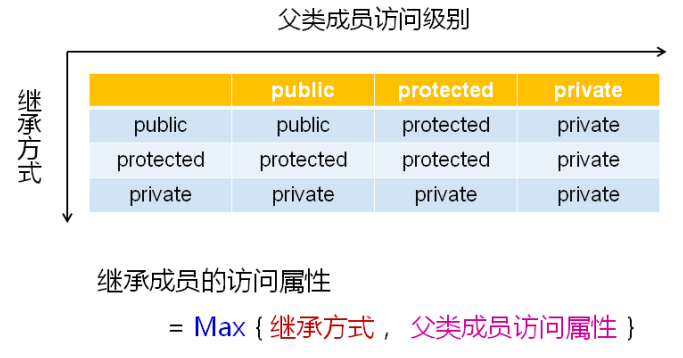
结论:无论选择哪种继承方式,都不会影响子类访问父类成员的级别
注:1) c++ 工程项目中只使用 public 继承方式;
2) c++ 派生语言(jave,c#)只支持 public继承方式;
3)protected、private 继承方式带来的复杂性远大于其实用性;(舍弃不用)
用代码实现类图中的功能: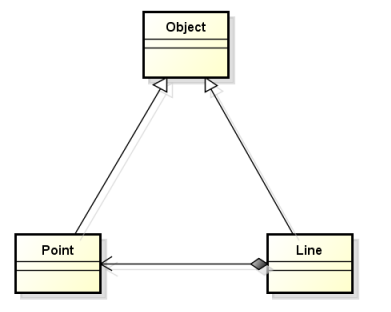
代码如下:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <sstream> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Object 8 { 9 protected: 10 string mName; 11 string mInfo; 12 public: 13 Object() 14 { 15 mName = "Object"; 16 mInfo = ""; 17 } 18 inline string getName() 19 { 20 return mName; 21 } 22 inline string getInfo() 23 { 24 return mInfo; 25 } 26 }; 27 28 class Point : public Object 29 { 30 private: 31 int mX; 32 int mY; 33 public: 34 Point(int x = 0, int y = 0) 35 { 36 ostringstream oss; 37 38 mX = x; 39 mY = y; 40 mName = "Point"; 41 42 oss << "Point(" << mX << ", " << mY << ")"; 43 mInfo = oss.str(); 44 } 45 inline int getX() 46 { 47 return mX; 48 } 49 inline int getY() 50 { 51 return mY; 52 } 53 }; 54 55 class Line : public Object 56 { 57 private: 58 Point mP1; 59 Point mP2; 60 public: 61 Line(Point p1, Point p2) 62 { 63 mP1 = p1; 64 mP2 = p2; 65 mName = "Line"; 66 mInfo = "Line from " + p1.getInfo() + " to " + p2.getInfo(); 67 } 68 inline Point getStartPoint() 69 { 70 return mP1; 71 } 72 inline Point getEndPoint() 73 { 74 return mP2; 75 } 76 }; 77 78 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 79 { 80 Object obj; 81 cout << obj.getName() << endl; 82 cout << obj.getInfo() << endl << endl; 83 84 Point p1(1, 2); 85 Point p2(3, 4); 86 cout << p1.getName() << endl; 87 cout << p1.getInfo() << endl; 88 cout << p2.getName() << endl; 89 cout << p2.getInfo() << endl << endl; 90 91 Line line(p1, p2); 92 cout << line.getName() << endl; 93 cout << line.getInfo() << endl << endl; 94 95 return 0; 96 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号