最短路
一、单源最短路
1.\(Bellman-ford(O(nm))\)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m,k;
int dist[10010];
struct Edge
{ss
int x,y,z;
}edge[20010];
void Bellman(int s,int t)
{
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
while(1)
{
bool ok = false;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x = edge[i].x,y = edge[i].y,z = edge[i].z;
if(dist[x]<(1<<30))
{
if(dist[x]+z<dist[y])
{
dist[y] = dist[x]+z;
ok = true;
}
}
}
if(!ok)break;
}
if(dist[t]<(1<<30))cout<<dist[t]<<endl;
else cout<<-1<<endl;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)cin>>edge[i].x>>edge[i].y>>edge[i].z;
while(k--)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
Bellman(x,y);
}
return 0;
}
Bellman_ford算法解决有边数限制最短路(打印路径)
// AC one more times
// nndbk
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1010,M = 4e5+10;
ll n, m, k, dist[N], backup[N],cnt = 0;
struct EDGES
{
ll a, b, w;
}edge[M];
ll f[N][N],pre[N];
void bellman_ford(int s)
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(f));
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));
dist[s] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < k; i++)//经过i条边
{
memcpy(backup, dist, sizeof dist);
for(int j = 0; j < m*2; j++)
{
auto e = edge[j];
int a = e.a,b = e.b,w = e.w;
if(dist[b] > backup[a] + w)
{
dist[b] = backup[a] + w;
pre[b] = a;
}
}
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)//经过i条边到j的最短路径
f[i][j] = dist[j];
}
}
vector<int>get_path(int t)
{
vector<int>path;
while(t != -1)
{
path.push_back(t);
t = pre[t];
}
reverse(path.begin(),path.end());
return path;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
ll u,v,w; cin>>u>>v>>w;
edge[cnt++] = {u,v,w};
edge[cnt++] = {v,u,w};
}
bellman_ford(1);
vector<int>path;
path = get_path(n);
for(auto x : path)
cout<<x<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
return 0;
}
解释:其中\(backup[]\)是用来避免串联的,其他最短路径问题都是通过一个已知的最短路的点去更新到其他点的最短距离,这就属于串联,在本题如果产生串联,就无法满足最多经过k条边的限制,所以构造一个backup[],存储上一次迭代的距离。
例题:2022女生赛H
// AC one more times
// nndbk
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1010,M = 4e5+10;
ll n, m, k, dist[N], backup[N],cnt = 0;
struct EDGES
{
ll a, b, w;
}edge[M];
ll f[N][N],pre[N];
void bellman_ford()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof f);
dist[1] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)//经过i条边
{
memcpy(backup, dist, sizeof dist);
for(int j = 0; j < m*2; j++)
{
auto e = edge[j];
dist[e.b] = min(dist[e.b], backup[e.a] + e.w);
}
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
f[i][j] = dist[j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
ll u,v,w; cin>>u>>v>>w;
edge[cnt++] = {u,v,w};
edge[cnt++] = {v,u,w};
}
bellman_ford();
int q;
cin>>q;
while(q--)
{
int t; cin>>t;
for(int i = 1;i <= n-1; i++)
{
ll w; cin>>w;
pre[i] = pre[i-1]+w;
}
ll res = 1e18;
for(int i = 1;i < n; i++)
{
if(f[i][t]!=0)
res = min(res,f[i][t] + pre[i]);
}
cout<<res<<"\n";
}
cout<<"\n";
return 0;
}
2.\(SPFA(O(nm))\)
- 用dis数组记录点到有向图的任意一点距离,初始化起点距离为0,其余点均为INF,起点入队。
- 判断该点是否存在。(未存在就入队,标记)
- 队首出队,并将该点标记为没有访问过,方便下次入队。
- 遍历以对首为起点的有向边(t,i),如果dis[i]>dis[t]+w(t,i),则更新dis[i]。
- 如果i不在队列中,则入队标记,一直到循环为空。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//edge[x]存x连出去的边及其边权
vector<pair<int,int>>edge[5001];
int n,m,k,dist[5001],c[5001];
queue<int>q;
bool in[5001];//是否在队列里面
inline void spfa(int s,int t)
{
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
memset(in,false,sizeof(in));
dist[s] = 0;
in[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
in[x] = false;
for(auto i:edge[x]){//x连出去的边i
if(dist[x]+i.second < dist[i.first]){
dist[i.first] = dist[x]+i.second;
if(!in[i.first]){
q.push(i.first);
in[i.first]=true;
}
}
}
}
if(dist[t]<(1<<30))cout<<dist[t]<<"\n";
else cout<<-1<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++){
int x,y,v;
cin>>x>>y>>v;
edge[x].push_back({y,v});
}
for(int i = 1;i<=k;i++)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
spfa(x,y);
}
return 0;
}
虽然在大多数情况下 SPFA 跑得很快,但其最坏情况下的时间复杂度为\(O(nm)\),将其卡到这个复杂度也是不难的,所以考试时要谨慎使用(在没有负权边时最好使用 Dijkstra 算法,在有负权边且题目中的图没有特殊性质时,若 SPFA 是标算的一部分,题目不应当给出 Bellman–Ford 算法无法通过的数据范围)
(SPFA)判负环
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<pair<int,int>>edge[5001];
int n,m,k,dist[5001],c[5001],cnt[5001];
bool in[5001];//是否在队列里面
int sum;//边数
inline void spfa(int s)
{
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
memset(in,false,sizeof(in));
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
queue<int>q;
dist[s] = 0;
in[s] = true;
cnt[s] = 1;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
in[x] = false;
for(auto i:edge[x]){//x连出去的边i
if(dist[x]+i.second < dist[i.first]){
dist[i.first] = dist[x]+i.second;
if(!in[i.first]){
cnt[i.first]++;
q.push(i.first);
in[i.first]=true;
if(cnt[i.first]>=sum)
{
cout<<"YES\n";
return;
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<"NO\n";
return;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
sum = 0;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
edge[i].clear();
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++)
{
int x,y,v;
cin>>x>>y>>v;
if(v>=0)
{
edge[x].push_back({y,v});
edge[y].push_back({x,v});
sum += 2;
}
else
{
edge[x].push_back({y,v});
sum++;
}
}
spfa(1);
}
return 0;
}
注意:\(spfa\)不能直接判断非联通图的负环,如果要判,需要先加入一个虚拟源点,向每个点连一条边权为0的边就可以判断了。
板子
const int N = 4e5 + 10, M = 1e4 + 10;
bool in[N];
int cnt[N],h[N];
inline bool spfa_check_negative_ring(int s, int n)
{
memset(h, 127, sizeof(h));
memset(in, false, sizeof(in));
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));
queue<int> q;
h[s] = 0;
in[s] = true;
cnt[s] = 1;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
in[u] = false;
for(auto [v, w]: edge[u])
{
if(h[u] + w < h[v])
{
h[v] = h[u] + w;
if(!in[v])
{
q.push(v);
cnt[v]++;
in[v]=true;
if(cnt[v]>=n)
{
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
(SPFA)次短路
[P2865 USACO06NOV] Roadblocks G
- 更新了最小距离,要把上次的最小距离先拿给次小距离,因为上次的最小距离就是比当前距离大且最小的距离(即为次短距离)。
- 虽然可能当前路径无法更新最小距离,但可能更新次小距离,要加判断
- 从上一个点的次短距离更新这一个点的次短距离
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 10100;
int n,m;
vector<pair<int,int>>edge[N];
int dist[2][N],c[N];
bool in[5001];//是否在队列里面
int sum;
inline void spfa(int s)
{
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
memset(in,false,sizeof(in));
queue<int>q;
dist[0][s] = 0;
dist[1][s] = 0;
in[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
in[x] = false;
for(auto i:edge[x]){//x连出去的边i
if(dist[0][x]+i.second < dist[0][i.first]){//更新最短路
dist[1][i.first] = dist[0][i.first];
dist[0][i.first] = dist[0][x]+i.second;
if(!in[i.first]){
q.push(i.first);
in[i.first]=true;
}
}
if((dist[1][i.first]>dist[0][x]+i.second&&dist[0][x]+i.second>dist[0][i.first])||
dist[1][i.first]==dist[0][i.first])//当前不能更新最短路,但可以更新次短路
{
dist[1][i.first] = dist[0][x] + i.second;
if(!in[i.first]){
q.push(i.first);
in[i.first] = true;
}
}
if(dist[1][i.first]>dist[1][x]+i.second&&dist[1][x]+i.second>dist[0][i.first])//用次短路更新次短路
{
dist[1][i.first] = dist[1][x] + i.second;
if(!in[i.first]){
q.push(i.first);
in[i.first] = true;
}
}
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,v;
cin>>x>>y>>v;
edge[x].push_back({y,v});
edge[y].push_back({x,v});
}
spfa(1);
cout<<dist[1][n]<<"\n";
return 0;
}
3.\(Dijkstra(O(n\log n + m))\)
裸的\(Dijkstra\)
//裸的Dijkstra
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int y,v;
Node(int _y,int _v){y = _y;v = _v;};
};
vector<Node>edge[5001];
bool b[5001];
int n,m,k, dist[5001];
inline void dijistra(int s,int t)
{
memset(b,false,sizeof(b));
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
while(1)
{
int x = -1;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!b[i]&&dist[i]<(1<<30))
{
if(x==-1||dist[i]<dist[x])x = i;
}
}
if(x==t||x==-1)break;
b[x] = true;
for(auto i:edge[x])
{
dist[i.y] = min(dist[i.y],dist[x]+i.v);
}
}
if(dist[t]<(1<<30))cout<<dist[t]<<endl;
else cout<<-1<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++){
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
edge[x].push_back(Node(y,z));
}
for(int i = 1;i<=k;i++)
{
int s,t;
cin>>s>>t;
dijistra(s,t);
}
return 0;
}
\(set\)优化的\(Dijikstra\)
//set优化的Dijikstra
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int y,v;
Node(int _y,int _v){y = _y;v = _v;};
};
set<pair<int,int>>q;//记录的是不在c中的点的信息
vector<Node>edge[100001];
int n,m,k, dist[100001];
inline void dijkstra(int s,int t)
{
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
q.clear();
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
q.insert({dist[i],i});
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.begin()->second;//离起点最近的点的下标
if(x==t||dist[x]>(1<<30))break;
q.erase(q.begin());
for(auto i:edge[x])
{
if(dist[x]+i.v<dist[i.y])
{
q.erase({dist[i.y],i.y});
dist[i.y]= dist[x]+i.v;
q.insert({dist[i.y],i.y});
}
}
}
if(dist[t]<(1<<30))cout<<dist[t]<<endl;
else cout<<-1<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++){
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
edge[x].push_back(Node(y,z));
}
for(int i = 1;i<=k;i++)
{
int s,t;
cin>>s>>t;
dijkstra(s,t);
}
return 0;
}
缺点:Dijkstra 算法不能正确求解带负权边的最短路
一道有意思Dijkstra思想的题
题意:给你\(n\)种药水,告诉你这\(n\)种药水的价格。接下来告诉你某些药水的配制方法,比如:\(A+B = C\),即一份\(A\)加上一份\(B\)可以得到一份\(C\)。
问:得到\(0\)号药水的最小花费和方案个数。
做法:我们可以用Dijkstra的思想,用已知来更新未知。
这里是在已经确定最小药价的药水中去查找(先选出一个最便宜的且未被确定为最小值的,因为它也不可能被其他药水的价钱再更新,如果要更新,之前比它小的已经更新过它了,之后的再也更新不动了),再根据这个最小价值的点去更新别的点。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1010;
const int inf = 1e9;
int n;
int cost[N],ans[N];
int f[N][N];
bool vis[N];
void dijkstra()
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
int x = -1;
int t = inf;
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(!vis[j]&&cost[j]<t)
x = j,t = cost[j];
}
if(t==inf)break;
vis[x] = true;
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(!f[x][j])continue;//没有此类配制方法
if(!vis[j])continue;//最小价值已经确定
if(cost[f[x][j]]>cost[x]+cost[j])//更新
{
cost[f[x][j]] = cost[x]+cost[j];
ans[f[x][j]] = ans[x]*ans[j];
}
else if(cost[f[x][j]] == cost[x]+cost[j])
{
ans[f[x][j]] += ans[x]*ans[j];
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin>>cost[i],ans[i] = 1;
int x,y,z;
while(cin>>x>>y>>z)
{
x++,y++,z++;
f[x][y] = z;
f[y][x] = z;
}
dijkstra();
cout<<cost[1]<<" "<<ans[1]<<endl;
return 0;
}
二、多源最短路
1.\(Floyd(O(n^3))\)
时间复杂度:\(O(n^3)\)
能解决负权边,但不能解决负环。跑得慢
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m,q,f[301][301];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>q;
memset(f,127,sizeof(f));
for(int i= 1;i<=n;i++)f[i][i] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
f[x][y] = z;
}
for(int k = 1;k<=n;k++)
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(f[i][k]<(1<<30)&&f[k][j]<(1<<30))
{
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j],f[i][k]+f[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
for(int i = 1;i<=q;i++)
{
int s,t;
cin>>s>>t;
if(f[s][t]<(1<<30)) cout<<f[s][t]<<"\n";
else cout<<"impossible"<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
帮助你对Floyd有更好的理解的几个题
例题1:P6464 传送门
题意:给你\(n\)个点\(m\)条双向边,没有自环和重边。每条边都有一定长度,各个点之间可以之间或者间接到达。现可以在任意\(x\)和\(y\)之间设一个传送门,人话就是\(x\)到\(y\)的距离变为\(0\)。问:任意两点的距离和最小是多少?\(x\)到\(y\)和\(y\)到\(x\)只算一次。
思路:看范围,\(n\)只有\(100\),又要求的是两点间距离,显然\(Floyd\)。
那么现在要考虑的是在哪建立传送门最优?我们枚举\(x\)和\(y\),令\(f[x][y] = f[y][x] = 0\),再用\(x\)和\(y\)点去更新其他点。
我们总不能每次都重新求一次每个点的距离吧,那我们可以先把\(f\)复制一次到\(F\),每次变化完下一次再还原。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 110;
int n,m;
int f[N][N];
int F[N][N];
inline void recover()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
F[i][j]=f[i][j];
}
void update(int k) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if(F[i][k]<(1<<30)&&F[j][k]<(1<<30))
F[i][j] = min(F[i][j],F[i][k] + F[k][j]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
memset(f,127,sizeof(f));
for(int i= 1;i<=n;i++)f[i][i] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
if(f[x][y]>(1>>30)||f[x][y]>z){
f[x][y] = z;
f[y][x] = z;
}
}
for(int k = 1;k<=n;k++)
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(f[i][k]<(1<<30)&&f[k][j]<(1<<30))
{
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j],f[i][k]+f[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
int ans = 1e9;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
recover();
F[i][j] = F[j][i] = 0;
update(i),update(j);
int res = 0;
for(int x = 1;x<=n;x++)
{
for(int y = x+1;y<=n;y++)
{
res += F[x][y];
}
}
ans = min(ans,res);
}
}
cout<<ans<<"\n";
return 0;
}
例题2:P1119 灾后重建
题意:给你\(n\)个点,编号\(0\)到\(n-1\)。给你\(m\)条双向边,并给出第\(i\)个村庄重建完成时候的时间\(t_i\)。之后有\(q\)个询问,问你第\(t\)天\(x,y\)的距离是多少,若还没重建完成,输出\(-1\)。
思路:\(Floyd\)的本质思想是两个点之间利用其他点进行中转,达到求最短路的目的。如何中转?让我们来看看\(Floyd\)的核心代码先:
for(int k = 1;k<=n;k++)
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(f[i][k]<(1<<30)&&f[k][j]<(1<<30))
{
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j],f[i][k]+f[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
代码用人话来说它在干什么事情就是:最外层循环的\(for(1..k)\)表示,一开始只用\(1\)号点进行中转,如然后接下来是允许\(1\)和\(2\)进行中转,以此类推就是到允许\(1..n\)个点进行中转来求任意两点的最短路。即:从\(i\)到\(j\)只用\(1\)到\(k\)到点进行中转的最短路。
由于题目很人性化,点按照重建的时间顺序给出,我们只需要按照这个顺序去更新每一个可以用的点。即:用当前可以用的点去更新所有点的最短路。和我们\(Floyd\)用前\(k\)个点去更新的思想是一样的。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 5e5+10;
int n,m,q;
int t[N];
int f[210][210];
void update(int k) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(f[i][k]<(1<<30)&&f[j][k]<(1<<30))
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j],f[i][k] + f[k][j]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>t[i];
memset(f,127,sizeof(f));
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)f[i][i] = 0;
for(int i =1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,v;
cin>>x>>y>>v;
x++,y++;
if(f[x][y]>(1>>30)||f[x][y]>v)
{
f[x][y] = v;
f[y][x] = v;
}
}
cin>>q;
int cur = 1;
while(q--)
{
int x,y,tt;
cin>>x>>y>>tt;
x++,y++;
while(t[cur]<=tt&&cur<=n)
{
update(cur);
cur++;
}
if(t[x]>tt||t[y]>tt||f[x][y]>(1<<30))cout<<-1<<"\n";
else cout<<f[x][y]<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
2.\(Johnson(O(nm\log m))\)
用于解决存在负权重边图里面最短路问题的。它主要是结合了\(Dijkstra\)和\(Bellman-Ford\).
\(Johnson\)算法是通过另一种方法来给每条边重新标注权值的。
做法:
- 我们先新建一个虚拟源点\(0\),从这个点向其他所有点连一条边权为\(0\)的边。
- 接下来,用\(Bellman-Ford\)求出从\(0\)号结点到其他所有点的最短路,记为\(h_i\)
- 重新标注权值:假设存在一条\(u->v\),边权为\(w\)的边,我们将边权重置为\(w+h_u-h_v\)
- 以每个点为起点跑\(n\)轮\(Dijkstra\)得到任意两点最短路
不难看出,\(Johnson\)算法的时间复杂度\(O(nm\log m)\)
那那那这么说:\(Dijkstra\)也可以解决负权(不含负环)的单源最短路了?
答案是:确实,当时没必要。因为如果要跑,那还得先用\(Bellman\)预处理,不如直接\(Bellman\)😂。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e3+10,M = 1e4+10;
const int INF = 1e9;
set<pair<int,int>>q;
vector<pair<int,int>>edge[M];
int n,m,k;
ll dist[N],h[N];
int c[N],cnt[N];
bool in[N];
bool vis[N];
void dijkstra(int start)
{
priority_queue<pair<ll,int>, vector<pair<ll, int>>, greater<pair<ll, int>>> q;
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
for(int i = 0;i<=n;i++)
dist[i] = 1e9;
dist[start] = 0;
q.push({0, start});
while(q.size() >= 1)
{
auto t = q.top(); q.pop();
int u = t.second;
if(vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = true;
for(auto [v, w] : edge[u])
{
if(dist[v] > dist[u] + w)
{
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
q.push({dist[v], v});
}
}
}
}
inline bool spfa_check_negative_ring(int s,int n)
{
memset(h,127,sizeof(h));
memset(in,false,sizeof(in));
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
queue<int>q;
h[s] = 0;
in[s] = true;
cnt[s] = 1;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
in[x] = false;
for(auto [y,v]:edge[x]){//x连出去的边i
if(h[x]+v < h[y]){
h[y] = h[x]+v;
if(!in[y]){
cnt[y]++;
q.push(y);
in[y]=true;
if(cnt[y]>=n)
{
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int u,v,w;
cin>>u>>v>>w;
edge[u].push_back({v,w});
}
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
edge[0].push_back({i,0});
if(spfa_check_negative_ring(0,n))
{
cout<<-1<<"\n";
return 0;
}
for(int u = 1;u<=n;u++)
{
for(auto& [v,w]:edge[u])
{
w += h[u]-h[v];
}
}
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
dijkstra(i);
ll ans = 0;
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(dist[j]==INF)
ans += (ll)j*INF;
else ans += j*(dist[j]+h[j]-h[i]);
}
cout<<ans<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
三、分层图最短路
分层图
一般模型:在图上,有\(k\)次机会可以直接通过一条边,问起点与终点之间的最短路径. 时间复杂度\(O(mklog(nk))\)。
1.模板题
做法:考虑把图分成\(k+1\)层,每往下一层,边权为\(0\)的边就增加\(1\)条。编号为\(i\)的点在第j层的编号是\(i+j*n\)。
每一层也都同样是\(n\)个点和\(m\)条边。
如何连边?
每次内部:对于\(u->v\)权值是\(w\),我们在\(0\)到\(k\)层连无向边\(u+i*n↔v+i*n(i\in[0,k])\)。
层与层之间:对于\(i-1\)层和\(i\)层之间我们连两条边权为\(0\)的有向边,且只能从上次到下层。\(u+(i-1)\times n->v+i\times n\)和\(v+(i-1)\times n->u+i\times n\)
建完图之后跑最短路就行了。
注意:
- 编号为i的点在第j层的编号是\(i+j*n\)
- 记得数组开\(4\)倍
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int n,m,k,s,t;
struct Node
{
int v,w;
Node(int _v,int _w){v = _v;w = _w;};
};
vector<Node>edge[N*4];
int dist[N*4];
vector<int>res;
void dijkstra(int s)
{
set<pair<int,int>>q;
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
q.insert({dist[i],i});
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.begin()->second;
q.erase(q.begin());
for(auto i:edge[x])
{
if(dist[i.v]>dist[x]+i.w)
{
q.erase({dist[i.v],i.v});
dist[i.v] = dist[x] + i.w;
q.insert({dist[i.v],i.v});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
cin>>s>>t;
s++,t++;
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
a++,b++;
edge[a].push_back({b,c});
edge[b].push_back({a,c});
for(int j = 1;j<=k;j++)
{
//层于层之间对应点连一条权值为0的边
edge[(a+(j-1)*n)].push_back({b+(j*n),0});
edge[(b+(j-1)*n)].push_back({a+(j*n),0});
//每一层对应点的连边
edge[(a+j*n)].push_back({b+j*n,c});
edge[(b+j*n)].push_back({a+j*n,c});
}
}
dijkstra(s);
int ans = 1e9;
for(int i = 0;i<=k;i++)
ans = min(ans,dist[t+i*n]);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
思路和上一题一样的,这里就不赘述啦QAQ...
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int n,m,k;
struct Node
{
int v,w;
Node(int _v,int _w){v = _v;w = _w;};
};
vector<Node>edge[N*4];
int dist[N*4];
vector<int>res;
void dijkstra(int s)
{
set<pair<int,int>>q;
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
q.insert({dist[i],i});
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.begin()->second;
q.erase(q.begin());
for(auto i:edge[x])
{
if(dist[i.v]>dist[x]+i.w)
{
q.erase({dist[i.v],i.v});
dist[i.v] = dist[x] + i.w;
q.insert({dist[i.v],i.v});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
edge[a].push_back({b,c});
edge[b].push_back({a,c});
for(int j = 1;j<=k;j++)
{
//层于层之间对应点连一条权值为0的边
edge[(a+(j-1)*n)].push_back({b+(j*n),0});
edge[(b+(j-1)*n)].push_back({a+(j*n),0});
//每一层对应点的连边
edge[(a+j*n)].push_back({b+j*n,c});
edge[(b+j*n)].push_back({a+j*n,c});
}
}
dijkstra(1);
cout<<dist[n+k*n]<<"\n";
return 0;
}
2.不那么模板的题
题意:有\(1\)到\(n\)个城市,每个城市水晶球的有不同的价格。给你\(m\)条路的信息。要你从一个城市购入水晶球,再到另一个城市卖出(该贸易只进行一次)。问最大的收益是多少?
思路:
做法一:分层图+\(SPFA\)
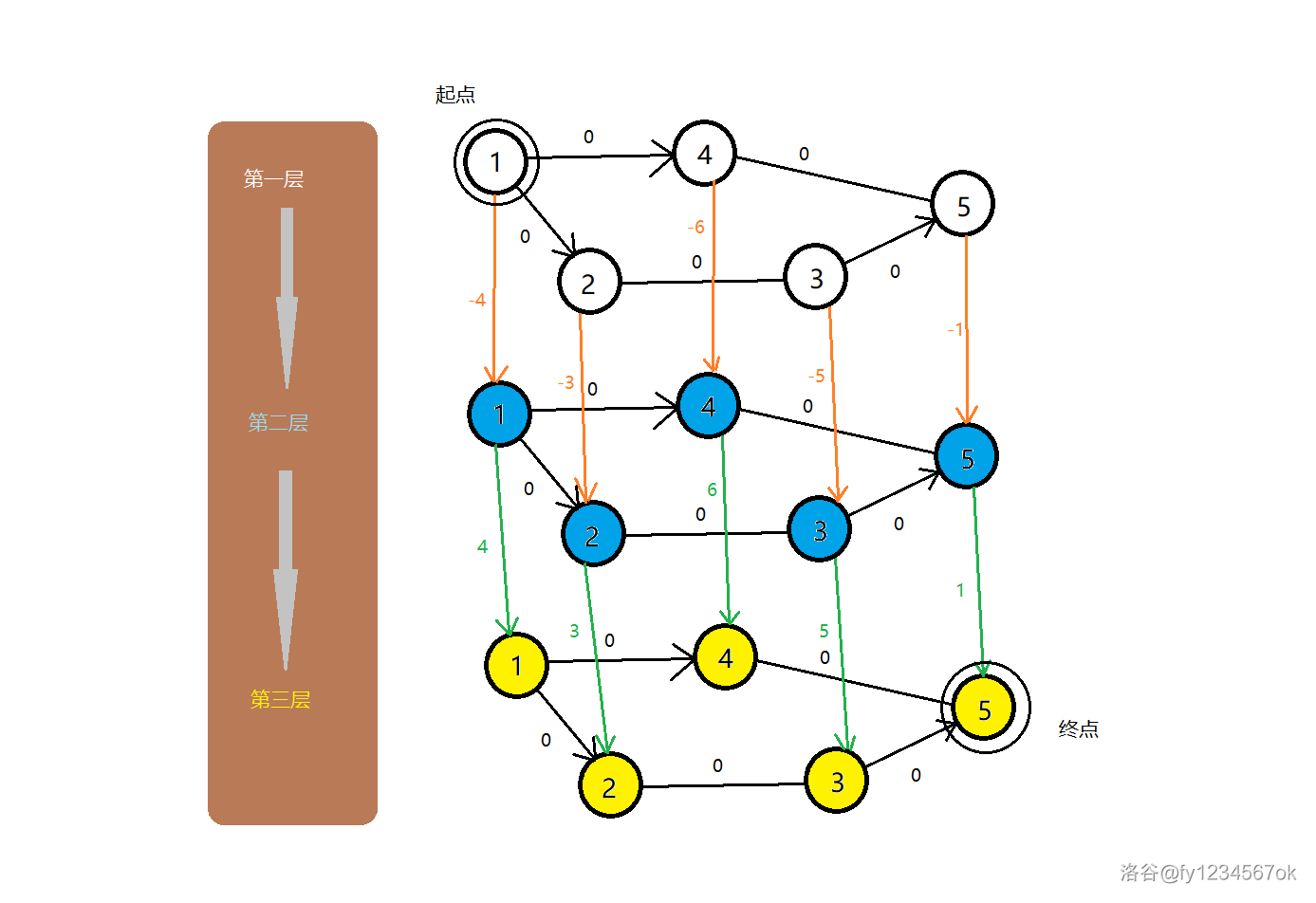
我们把图分为三层:第一层没买也没卖,第二层买,第三层买。每层之间我们连单向边,这个很好理解,我们肯定得先买才能卖出。
因为存在负权边,且求的是最大值,那用\(SPFA\)跑最长路即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 100100;
const int M = 500100;
int n,m;
int cost[N];
struct Node
{
int v,w;
Node(int _v,int _w){v = _v;w = _w;};
};
vector<pair<int,int>>edge[N*3];
int dist[N*3],c[N*3];
queue<int>q;
bool in[M*6+N*2];//是否在队列里面
inline void spfa(int s)
{
memset(dist,128,sizeof(dist));
memset(in,false,sizeof(in));
dist[s] = 0;
in[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
in[x] = false;
for(auto [y,v]:edge[x]){//x连出去的边i
if(dist[x]+v > dist[y]){
dist[y] = dist[x]+v;
if(!in[y]){
q.push(y);
in[y]=true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>cost[i];
edge[i].push_back({i+n,-cost[i]});
edge[i+n].push_back({i+2*n,cost[i]});
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
edge[x].push_back({y,0});
edge[x+n].push_back({y+n,0});
edge[x+2*n].push_back({y+2*n,0});
if(z==2)
{
edge[y].push_back({x,0});
edge[y+n].push_back({x+n,0});
edge[y+2*n].push_back({x+2*n,0});
}
}
spfa(1);
cout<<max(dist[n],dist[n*3])<<"\n";
return 0;
}
做法二:\(Tarjan\)缩点+\(Topo\)+\(DP\)
这个题其实很容易想到\(DP\),但是原图是有环的,不能直接DP。但是我们可以缩点,缩完点之后变成一个\(DAG\)(新图),再\(Tpop\)排序确定遍历顺序,再跑\(DP\)。
因为每个\(SCC\)内部我们都可以互相到达,我们记录每个\(SCC\)可达的最大值\(mx\)和最小值\(mn\)。那么在一个强连通分量里面的最大利益就是\(mx-mn\)。
\(dp[i]\)为新图中\(1\)对应的\(SCC\)编号 到 编号为\(i\)的\(SCC\)能获得的最大利润。
\(minc[i]\)为新图中1对应的\(SCC\)编号 到 编号为\(i\)的\(SCC\)能获得的最小花费。
考虑如何更新\(dp?\)
更新dp前,我们先更新\(minc\),假设从\(x\)走到\(y\):\(minc[y] = min(minc[x],mn[y])\)
之后再进行dp的状态转移:\(dp[y] = max(max(dp[x],dp[y]),max(maxx[y],mx[y]-minc[y]))\);
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 100100;
const int M = 500100;
int n,m;
int cost[N];
vector<int>edge[M*2];
int dfn[N],low[N],ins[N],idx,bel[N],cnt,sz[N];
stack<int>stk;
ll ans;
int a[N];
vector<int>cc[N];
int ind[N],mx[N],mn[N],maxx[N],cntt,dep[N],minc[N];
queue<int>q;
int dp[N];
vector<int>edge2[M*2];
void dfs(int u)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++idx;
ins[u] = true;
stk.push(u);
for(auto v:edge[u])
{
if(!dfn[v])dfs(v);
if(ins[v])low[u] = min(low[u],low[v]);
}
if(dfn[u] == low[u]){
++cnt;
while(1)
{
int v = stk.top();
ins[v] = false;
bel[v] = cnt;
cc[cnt].push_back(v);
sz[cnt]++;
stk.pop();
if(u==v)break;
}
}
}
void tarjan()
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!dfn[i])dfs(i);
}
}
inline void topo()
{
for(int i = 1;i<=cnt;i++)
if(ind[i]==0&&i==bel[1])//注意这里要写i==bel[i],因为只能从1出发,题意并没有保证入度为0的点只有1
q.push(i);
/*
hack数据
3 2
100 1 100
2 1 1
1 3 1
输出 0
*/
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
dep[++cntt] = x;
for(auto y:edge2[x])
{
if(--ind[y]==0)
{
q.push(y);
}
}
}
}
inline void DP()
{
memset(minc,0x3f,sizeof(minc));
minc[dep[1]] = mn[dep[1]];
for(int i = 1;i<=cntt;i++)
{
int x = dep[i];
for(auto y:edge2[x])
{
minc[y] = min({minc[y],minc[x],mn[x]});
dp[y] = max(dp[y],max({dp[x],maxx[y],mx[y]-minc[y]}));
}
}
cout<<dp[bel[n]]<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin>>cost[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
if(x==y)continue;
edge[x].push_back(y);
if(z==2)
edge[y].push_back(x);
}
tarjan();
for(int u = 1;u<=n;u++)
{
for(auto v:edge[u])
{
if(bel[u] != bel[v])//建新图
{
ind[bel[v]]++;
edge2[bel[u]].push_back(bel[v]);
}
}
}
memset(mn,0x3f,sizeof(mn));
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
mx[bel[i]] = max(mx[bel[i]],cost[i]);
mn[bel[i]] = min(mn[bel[i]],cost[i]);
}
for(int i = 1;i<=cnt;i++)
maxx[i] = mx[i]-mn[i];
topo();
DP();
return 0;
}
做法三:$ 2\(次\)spfa\(
**明确是先买然后再卖的**
找到\)dist1[i]$:点\(1\)到\(i\)最便宜的买入
再找到\(dist2[i]\):点\(i\)到\(n\)最贵的卖出
\(Dijkstra\)不适合,因为第一次出队的不一定是最小的,我们只是想求路径上的最值
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 5e5+10;
vector<pair<int,int>>edge[N],edge2[N];
int n,m,k,dist[N],dist2[N],v[N];
queue<int>q;
bool in[N];//是否在队列里面
inline void spfa1(int s)
{
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
memset(in,false,sizeof(in));
dist[s] = v[s];
in[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
in[x] = false;
for(auto [y,c]:edge[x]){//x连出去的边i
if(min(dist[x],c) < dist[y]){
dist[y] = min(dist[x],c);
if(!in[y]){
q.push(y);
in[y]=true;
}
}
}
}
}
inline void spfa2(int s)
{
memset(dist2,128,sizeof(dist2));
memset(in,false,sizeof(in));
dist2[s] = v[s];
in[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
in[x] = false;
for(auto [y,c]:edge2[x]){//x连出去的边i
if(max(dist2[x],c) > dist2[y]){
dist2[y] = max(dist2[x],c);
if(!in[y]){
q.push(y);
in[y]=true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>v[i];
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
edge[x].push_back({y,v[y]});
edge2[y].push_back({x,v[x]});
if(z==2)
{
edge[y].push_back({x,v[x]});
edge2[x].push_back({y,v[y]});
}
}
spfa1(1);
spfa2(n);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
ans = max(dist2[i]-dist[i],ans);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
四、同余最短路
形如:
- 给你\(n\)个整数,求这\(n\)个整数能拼凑出多少的其他整数(这\(n\)个整数可以重复取)。
- 给你\(n\)个整数,求这\(n\)个整数不能拼凑出的最小(最大)的整数
- 给你\(n\)个整数,至少要拼几次才能拼出\(\mod k = p\)的数
此类问题可以考虑用同余最短路的方法。同余最短路转移方程通常是:\(f(i+y) = f(i)+y\)
1.模板题
P3403 跳楼机
题意:给你\(x,y,z,h\),\(k\in[1,h]\),问你有多少个\(k\)满足\(ax+by+cz = k\)。
思路:
不妨假设\(x<y<z\)。
令\(d_i\)是只通过操作\(2\)和操作\(3\),且满足\(p \mod x = i\)能够到达的最低楼层\(p\)。人话来说就是:只进行操作\(2\)和操作\(3\)后能得到的模\(x\)下与\(i\)同余的最小数(通常取最小的作为模数,可以减小时间复杂度)。
计算该同余类满足条件的个数。
- \(i -y->(i+y)\mod x\)
- \(i-z->(i+z)\mod x\)
对应的状态方程就是:
- \(f(i+y) = f(i)+y\)
- \(f(i+z) =f(i)+z\)
意义就是:\(f(i+y) = f(i)+y\)能到达\(\mod x = i+y\)的最低楼层等于能到达$ \mod x = i$的最低楼层的基础上再走一次操作2。下面那个柿子同理。
转化到图论里面相当于\(i->(i+y)\mod x\)连接一条权值为\(y\)的边和\(i->(i+z)\mod x\)连一条权值为\(z\)边。
接下来我们只要求出\(d_0,d_1...d_{x-1}\),答案就好求了。
那么答案就是\(\sum_{i = 0}^{x-1}\lfloor\dfrac{(h-d_i)}{x} \rfloor+1\)(+1是现处的楼层也要算一次)
为什么是这样?\(d_i\)是不进行操作\(1\)的情况下到达的\(\mod x\)的最低楼层,而每进行一次操作\(1\)就可以到达一个新楼层,答案数就是\(\lfloor\dfrac{(h-d_i)}{x} \rfloor\)的累加。
那么问题转化为如何求\(d_i\)?
\(d_i\)其实就是\(1->i\)的最短路。
(源点是1,因为dist[1] = 1在已知范围内最小,因此得到的也是一组最小解)。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5+10;
ll h,x,y,z;
struct Node
{
int v,w;
Node(int _v,int _w){v = _v;w = _w;};
};
vector<Node>edge[N];
ll dist[N];
void dijkstra(int s)
{
set<pair<int,int>>q;
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 1;//注意本身也有一层,设为1
for(int i = 0;i<x;i++)
q.insert({dist[i],i});
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.begin()->second;
q.erase(q.begin());
for(auto i:edge[x])
{
if(dist[i.v]>dist[x]+i.w)
{
q.erase({dist[i.v],i.v});
dist[i.v] = dist[x] + i.w;
q.insert({dist[i.v],i.v});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>h>>x>>y>>z;
if(x==1||y==1||z==1){
cout<<h<<"\n";
return 0;
}
for(int i = 0;i<x;i++)
{
edge[i].push_back(Node((i+y)%x,y));
edge[i].push_back(Node((i+z)%x,z));
}
dijkstra(1);
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < x; i++)
if(dist[i]<=h)
ans += (h-dist[i])/x+1;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
五、图上的DP
一、DAG上的DP
对于DAG上DP,我们一般套路有两种:拓扑序或者最短路算法(SPFA、Dijkstra..)。
拓扑序在图上DP的应用
对于\(DAG\)上的\(DP\),我们考虑用安装它的拓扑序来确定\(DP\)顺序。为什么呢?为什么我们不能直接随便选一个入度为0的点直接开始呢?理由如下:
\(DP\)是分阶段的,我们要保证阶段的正确性和无后效性。
拓扑序起到了什么作用呢?对于任意一条边\(u->v\),拓扑序保证\(u\)的出现顺序在\(v\)的前面。这样的话,保证了在\(DAG\)转移 时候,对于每个点,它先前的点(可以转移到它的点)我们都已经处理过了。这样就保证了阶段的正确性进而保证了\(DP\)的无后效性。
例题1:P4645 BICIKLI
题意:这个地方有 \(n\) 个城镇,从 \(1\sim n\) 编号,其中有 \(m\) 条单向道路连接它们。比赛将在 \(1\) 号城镇开始并在 \(2\) 号城镇结束。
主办方想知道,一共有多少条不同的路线?
如果有无数条不同的路线,则输出 inf。
思路:\(Darjan\)缩点+\(Topo\)+\(DP\)
先考虑什么时候有无数条路径?如果在从\(1\)到\(2\)的路径上存在环那么就有无数条。
怎么判环?我用的是强连通分量缩点变成一个\(DAG\),判断\(SCC\)的大小是不是\(\ge 2\)的,如果是则有环。但是如果一个强连通分量大小为\(2\)且包含终点,则没有影响。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5+10;
const int mod = 1e9;
int n,m;
vector<int>edge[N],edge2[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],ins[N],idx,bel[N],cnt,sz[N];
stack<int>stk;
vector<int>cc[N];
ll dp[N];
int ind[N];
queue<int>q;
int dep[N],wa[N];
int cntt;
struct edge{
int u,v;
}e[N];
void dfs(int u)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++idx;
ins[u] = true;
stk.push(u);
for(auto v:edge[u])
{
if(!dfn[v])dfs(v);
if(ins[v])low[u] = min(low[u],low[v]);
}
if(dfn[u] == low[u]){
++cnt;
while(1)
{
int v = stk.top();
ins[v] = false;
bel[v] = cnt;
sz[cnt]++;
stk.pop();
cc[cnt].push_back(v);
if(u==v)break;
}
}
}
void tarjan()
{
dfs(1);
}
inline void Topo()
{
for(int i = 1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
if(!ind[i])
{
q.push(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
dep[++cntt] = x;
for(auto y:edge2[x])
{
wa[y]|=wa[x];
if(--ind[y]==0)
{
q.push(y);
}
}
}
}
inline void DP()
{
dp[bel[1]] = 1;
for(int i = 1;i<=cntt;i++)
{
int x = dep[i];
for(auto y:edge2[x])
{
dp[y] += dp[x];
dp[y] %= mod;
}
}
cout<<dp[bel[2]]<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
edge[x].push_back(y);
e[i]={x,y};
}
tarjan();
for(int u = 1;u<=n;u++)
{
for(auto v:edge[u])
{
if(bel[u] != bel[v]&&bel[u]&&bel[v])//这里记得还要判bel[u]和bel[v]存不存在,否则不是路径上的点,呜呜呜之前wa了就是因为这里
{
ind[bel[v]]++;
edge2[bel[u]].push_back(bel[v]);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
if(sz[i]>1)wa[i] = 1;
if(i==bel[2]&&sz[i]==2)wa[i] = 0;
}
Topo();
if(wa[2])
{
cout<<"inf\n";
return 0;
}
DP();
return 0;
}
例题2:Journey
题意:给出一个\(n\)个点\(m\)条边的有向无环图。
问起点是\(1\),终点是\(n\),从\(1\)到\(n\)在距离不超过\(k\)的情况下最多经过多少点,并输出一个方案。
思路:求最多经过多少个点,显然可以用\(DP\)。而且是个\(DAG\)那么我们可以放心跑\(DP\)了。定义\(dp[i][j]\)为从\(1\)到\(n\)经过\(j\)个点的最短路。先对图跑\(Topo\)来确定\(dp\)的遍历顺序。考虑怎么转移?
考虑\(x->y\),\(dp[y][j]\)可以由\(dp[x][j-1]\)转移过来。
\(if(dp[x][j-1]+v(u,v)<dp[y][j])\)那么\(dp[y][j]= dp[x][j-1]+v(u,v)\)然后用\(pre\)记录一下路径。
注意:
- \(dp\)数组\(memset\)初始化成\(127\)会炸,这里初始化成\(0x3f\)即可。
- \(pre\)数组也要定义成二维的。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 5010;
int n,m,k,cnt;
vector<pair<int,int>>edge[N];
int dep[N],ind[N];
queue<int>q;
int pre[N][N];
int dp[N][N];
inline void Topo()
{
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
{
if(!ind[i])
{
q.push(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
dep[++cnt] = x;
for(auto [y,v]:edge[x])
{
if(--ind[y]==0)
{
q.push(y);
}
}
}
}
/*
dp[i][j]:从1到i经过j的点的最短路
*/
inline void DP()
{
memset(dp,0x3f,sizeof(dp));
memset(pre,-1,sizeof(pre));
dp[1][1] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
int x = dep[i];
for(auto [y,v]:edge[x])
{
for(int j = 2;j<=n;j++)
{
if(dp[x][j-1]+v<dp[y][j])
{
dp[y][j] = dp[x][j-1]+v;
pre[y][j] = x;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,v;
cin>>x>>y>>v;
edge[x].push_back({y,v});
ind[y]++;
}
Topo();
DP();
int maxx = 0;
for(int i = n;i>=1;i--)
{
if(dp[n][i]<=k)
{
maxx = i;
break;
}
}
int pos = n,d= maxx;
stack<int>path;
cout<<d<<"\n";
while(pos!=-1)
{
path.push(pos);
pos = pre[pos][d];
d--;
}
while(!path.empty())
{
cout<<path.top()<<" ";
path.pop();
}
cout<<"\n";
return 0;
}
二、普通图上的DP
对于一般的图,不是DAG的话,由于有环的存在,一部分DP存在后效性,需要用最短路算法解决。另一种可能是在图上DFS,记忆化搜索。
例题1:P3953 逛公园
思路:起点\(1\)号点,终点是\(n\)号点,从\(1\)到\(n\)的最短路是\(d\),问你长度不超过\(d+k\)的路径有多少条?有无穷多条输出\(-1\)。
思路:因为权值非负,要有无数条那就是有\(0\)环。
怎么判断\(0\)环?当\(dfs\)的时候,访问到了自己的祖先,说明有\(0\)环。
要求路径条数,很容易想到\(dp\)。问的是路径条数,那\(dp\)数组怎么定义呢?
考虑定义:\(dp[i][j]\)表示从\(1\)到\(i\)多出来的长度是\(j\)的路径条数。人话来说就是:\(1\)到\(i\)的距离为\(mindist[1][v]+j\)的路径条数。
考虑怎么转移?
不妨假设\(dp[u][k]\)可以由\(dp[v][x]\)转移而来。
那么:\(mindist[v]+x+w(u,v) = mindist[u]+k\)
移向得到:\(x = mindist[u]-mindist[v]+k-w(u,v)\)
那么转移方程就是:\(dp[u][k] = \sum_{(u,v)\in E}dp[v][x]\)
我们在正图上求出\(1\)到所有点的最短路,再对反图进行\(dfs\)。
为什么要对反图\(dfs\)?因为不是所有点都能到达\(n\),从反图开搜效率更高。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N =1e5+10;
ll n,m,k,mod;
struct Node
{
int v,w;
Node(int _v,int _w){v = _v;w = _w;};
};
vector<Node>edge[N],nedge[N];
ll dp[N][55];
ll dist[N];
bool flag;
void dijkstra(int s)
{
set<pair<int,int>>q;
memset(dist,127,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
q.insert({dist[i],i});
while(!q.empty())
{
int x = q.begin()->second;
q.erase(q.begin());
for(auto i:edge[x])
{
if(dist[i.v]>dist[x]+i.w)
{
q.erase({dist[i.v],i.v});
dist[i.v] = dist[x] + i.w;
q.insert({dist[i.v],i.v});
}
}
}
}
int dfs(int u,int ex)
{
if(~dp[u][ex])return dp[u][ex];
dp[u][ex] = -2;
ll res = (u==1&&ex==0);
for(auto i:nedge[u])
{
int v = i.v,w = i.w;
int tmp = (dist[u]+ex)-(dist[v]+w);
if(tmp<0)continue;
if(dp[v][tmp]==-2)
{
flag = 0;
return 0;
}
res += dfs(v,tmp);
res %= mod;
}
return dp[u][ex] = res;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>m>>k>>mod;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
edge[i].clear();
nedge[i].clear();
}
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,v;
cin>>x>>y>>v;
edge[x].push_back(Node(y,v));
nedge[y].push_back(Node(x,v));
}
dijkstra(1);
ll ans = 0;
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
flag = 1;
for(int i = 0;i<=k&&flag;i++)
{
ans += dfs(n,i);
ans %= mod;
}
cout<<(flag?ans:-1)<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号