c++第四次作业继承
2019-10-13 19:50 myself914 阅读(176) 评论(0) 收藏 举报类的继承
所谓继承就是从先辈处得到属性和行为特征,类的继承,是新的类从已有类那里得到已有的特性。原有的类称为基类或父类,产生的新类称为派生类或子类。
一:公有继承
基类的公有成员和保护成员的访问属性在派生类中不变,派生类的其他成员可以直接访问它们,而基类的私有成员不可直接访问,无论是派生类的成员还是派生类的对象都无法直接访问基类的私有成员。
用以下例子证明:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
void initP(float xx,float yy);
void Move(float xOff,float yOff);
float GetX();
float GetY();
private:
float x;
float y;
};
void Point::initP(float xx,float yy)
{
x=xx;
y=yy;
}
void Point::Move(float xOff,float yOff)
{
x=x+xOff;
y=y+yOff;
}
float Point::GetX()
{
return x;
}
float Point::GetY()
{
return y;
}
class Rectangle:public Point
{
public:
void initR(float x,float y,float w,float h)
{
initP(x,y);//派生类中的成员可以访问基类中的公有成员
W=w;
H=h;
}
float GetH()
{
return H;
}
float GetW()
{
return W;
}
private:
float W,H;
};
int main()
{
Rectangle B;
B.initR(1,2,3,4);
cout<<"输出前为:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
B.Move(4,5);//派生类的对象访问基类中的公有成员
cout<<"输出值:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
从实验中可以看出公有继承中派生类的对象和成员可以访问基类的公有成员。
那么当访问基类的私有成员呢?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
void initP(float xx,float yy);
void Move(float xOff,float yOff);
float GetX();
float GetY();
private:
float x;
float y;
};
void Point::initP(float xx,float yy)
{
x=xx;
y=yy;
}
void Point::Move(float xOff,float yOff)
{
x=x+xOff;
y=y+yOff;
}
float Point::GetX()
{
return x;
}
float Point::GetY()
{
return y;
}
class Rectangle:public Point
{
public:
void initR(float X,float Y,float w,float h)
{
x=X;
y=Y;//派生类的成员可否访问基类的私有成员?
W=w;
H=h;
}
float GetH()
{
return H;
}
float GetW()
{
return W;
}
private:
float W,H;
};
int main()
{
Rectangle B;
B.initR(1,2,3,4);
cout<<"输出前为:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
B.Move(4,5);
B.x=7;//派生类的对象可否访问基类的私有成员?
cout<<"输出值:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果是失败的: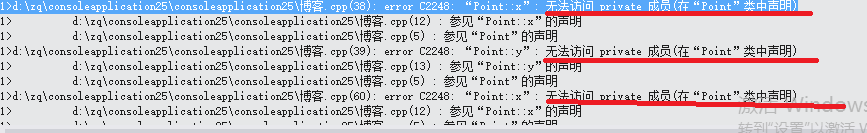
可见无论是派生类的成员还是派生类的对象都无法直接访问基类的私有成员。
二:私有继承
基类中的公有成员和保护成员都以私有成员身份出现在派生类中,而基类的私有成员在派生类中不可直接访问。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
void initP(float xx,float yy);
void Move(float xOff,float yOff);
float GetX();
float GetY();
private:
float x;
float y;
};
void Point::initP(float xx,float yy)
{
x=xx;
y=yy;
}
void Point::Move(float xOff,float yOff)
{
x=x+xOff;
y=y+yOff;
}
float Point::GetX()
{
return x;
}
float Point::GetY()
{
return y;
}
class Rectangle:private Point
{
public:
void initR(float x,float y,float w,float h)
{
initP(x,y);//派生类中的成员可以访问基类中的公有成员?
W=w;
H=h;
}
float GetH()
{
return H;
}
float GetW()
{
return W;
}
private:
float W,H;
};
int main()
{
Rectangle B;
B.initR(1,2,3,4);
cout<<"输出前为:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
B.Move(4,5);//派生类的对象可否访问基类的公有成员?
cout<<"输出值:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
return 0;
}
结果是失败的:

由此可得在私有继承中派生类的成员可以访问基类的公有和保护成员,而派生类的对象却不能访问。而无论是派生类的对象还是成员都无法访问基类的私有成员。
怎样可以使派生类的对象访问基类的公有成员和保护成员?可以通过在派生类中重新声明同名的成员,可以保证基类的一部分外部接口特征能够在派生类中也存在,如以下例子:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
void initP(float xx,float yy);
void Move(float xOff,float yOff);
float GetX();
float GetY();
private:
float x;
float y;
};
void Point::initP(float xx,float yy)
{
x=xx;
y=yy;
}
void Point::Move(float xOff,float yOff)
{
x=x+xOff;
y=y+yOff;
}
float Point::GetX()
{
return x;
}
float Point::GetY()
{
return y;
}
class Rectangle:private Point
{
public:
void initR(float x,float y,float w,float h)
{
initP(x,y);
W=w;
H=h;
}
float GetH()
{
return H;
}
float GetW()
{
return W;
}
void Move(float xOff,float yOff)
{
Point::Move( xOff,yOff);
} //声明同名成员
float GetX()
{
return Point::GetX();
} //声明同名成员
float GetY()
{
return Point::GetY();
} //声明同名成员
private:
float W,H;
};
int main()
{
Rectangle B;
B.initR(1,2,3,4);
cout<<"输出前为:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
B.Move(4,5);
cout<<"输出值:"<<B.GetX()<<B.GetY()<<B.GetH()<<B.GetW()<<endl;
return 0;
}
结果成功运行:
三:保护继承:
基类的公有成员和保护成员都以保护成员的身份出现在派生类中,而基类的私有成员不可直接访问。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
int x;
};
class B:protected A
{
public:
void function()
{
x=7;//派生类的成员可否访问基类的公有成员?
y=6;//派生类的成员可否访问基类的私有成员?
}
};
int main()
{
B b;
b.x=5;//派生类的对象可否访问基类的公有成员?
b.y=8;//派生类的对象可否访问基类的私有成员?
return 0;
}
结果: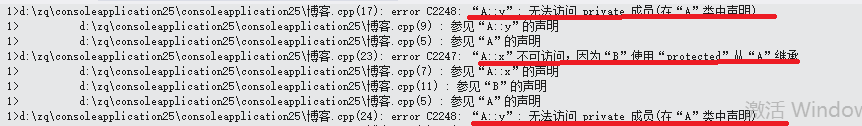
可以得出:在保护继承中派生类的成员可以访问基类的公有和保护成员,而派生类的对象却不能访问,而无论是派生类的对象还是成员都无法访问基类的私有成员。
比较保护继承和私有继承可以发现,在直接派生类中,所有的成员访问属性都是完全相同的,但是如果派生类作为基类继续派生时,二者则不同,私有继承会让所有成员都无法再被访问,而保护继承则基类成员有可能被间接访问。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号