算法与数据结构 图论(二)割点与割边
割点集合
在一个无向连通图中,如果有一个顶点集合,删除这个顶点集合,以及这个集合中所有顶点相关联的边以后,原图变成多个连通块,就称这个点集为割点集合。(一般是有多个顶点组成)
割边集合
在一个无向连通图中,如果有一个边集合,删除这个边集合以后,原图变成多个连通块,就称这个点集为割边集合。(一般有多个边组成)
点连通度
一个图的点连通度的定义为,最小割点集合中的顶点数
边连通度
一个图的边连通度的定义为,最小割边集合中的边数。
双连通图
如果一个无向连通图的点/边连通度大于1,则称该图是点/边双连通的(biconnected),简称双连通或重连通
割点
一个图有割点,当且仅当这个图的点连通度为1,则割点集合的唯一元素被称为割点(cut point),又叫关节点(articulation point)。
桥
一个图有桥,当且仅当这个图的边连通度为1,则割边集合的唯一元素被称为桥(bridge),又叫关节边(articulation edge)。(也有人称为割边….)
割点:依次删除每一个顶点,然后用深度优先搜索或者广度优先搜索来检查图是否依然连通。如果删除某个顶点后,导致图不再连通,那么刚才删除的顶点就是割点。
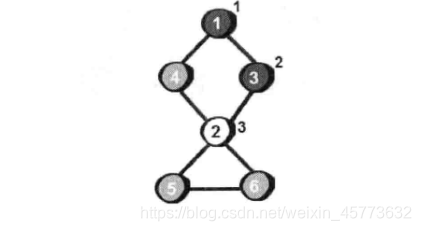
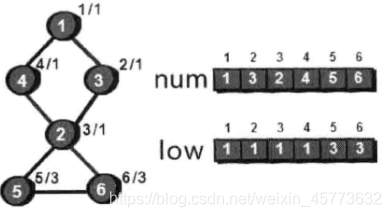
import java.util.Scanner;
//对一个图进行深度优先遍历将会得到这个图的一个生成树(并不一定是最小生成树)
public class gedian {
static int n,m,root;
static int [][] e = new int[9][9];
static int [] num = new int[9];
static int [] low = new int[9];
static int [] flag = new int[9];
static int index;//index用来进行时间戳的递增
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int x,y;
n = scan.nextInt();
m = scan.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
e[i][j]=0;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
x = scan.nextInt();
y = scan.nextInt();
e[x][y] = 1;
e[y][x] = 1;
}
root = 1;
dfs(1,root);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (flag[i] == 1)
System.out.print(i);
}
}
public static void dfs(int cur,int father){//传入当前顶点编号和父顶点的编号
int child = 0;//用来记录在生成树中当前顶点cur的儿子个数
index++;
num[cur] = index;//当前顶点cur的时间戳
low[cur] = index;//当前顶点cur能访问到最早顶点的时间戳,刚开始是自己
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {//枚举与当前顶点cur有边相连的顶点i
if (e[cur][i] == 1){
if (num[i] == 0){//说明i点还没有被访问过,就对该点进行dfs
child++;
dfs(i,cur);
low[cur] = Math.min(low[cur],low[i]);//检测以cur进为父节点进行dfs时,cur是否绕过父顶点回到之前的点
//即,
if (cur != root && low[i] >= num[cur])
flag[cur]=1;
if (cur == root && child == 2) //如果与起始点连通的点有两个,则该起始点也肯定是一个割点
flag[cur] = 1;
}
else if (i != father){//i点曾经被访问过,并且这个顶点不是当前顶点cur的父亲,则需要更新
//当前节点cur能否访问到更早顶点的时间戳
low[cur] = Math.min(low[cur],num[i]);
}
}
}
}
}

import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class gebian {
static int n,m,root;
static int [][] e = new int[9][9];
static int [] num = new int[9];
static int [] low = new int[9];
static int index;//index用来进行时间戳的递增
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int x,y;
n = scan.nextInt();
m = scan.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
e[i][j]=0;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
x = scan.nextInt();
y = scan.nextInt();
e[x][y] = 1;
e[y][x] = 1;
}
root = 1;
dfs(1,root);
}
public static void dfs(int cur,int father){//传入当前顶点编号和父顶点的编号
int child = 0;//用来记录在生成树中当前顶点cur的儿子个数
index++;
num[cur] = index;//当前顶点cur的时间戳
low[cur] = index;//当前顶点cur能访问到最早顶点的时间戳,刚开始是自己
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {//枚举与当前顶点cur有边相连的顶点i
if (e[cur][i] == 1){
if (num[i] == 0){//说明i点还没有被访问过,就对该点进行dfs
child++;
dfs(i,cur);
low[cur] = Math.min(low[cur],low[i]);//检测对cur进行dfs时,cur是否绕过父顶点回到之前的点
if (low[i] > num[cur])//low[i]>=num[cur]表示的是点i不可能在不经过父节点u而回到祖先(包括父亲)的,
//而low[i] > num[cur]表示连父亲都回不到了。倘若顶点i不能回到祖先,也没有另外一条路能回到父亲,那么
//i-cur这条边就是割边
System.out.println(String.format("%d-%d",cur,i));
}
else if (i != father){//i点曾经被访问过,并且这个顶点不是当前顶点cur的父亲,则需要更新
//当前节点cur能否访问到更早顶点的时间戳
low[cur] = Math.min(low[cur],num[i]);
}
}
}
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号