组合模式(学习笔记)
1. 意图
讲对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分——整体”的层次结构。Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性
2. 动机
如果应用的核心模型能用树状结构表示,在应用中使用组合模式才有价值
假如,有两类对象:产品和盒子。一个盒子可以包含几个产品或多个较小的盒子。这些小盒子也可以包含一些产品或更小的盒子,以此类推
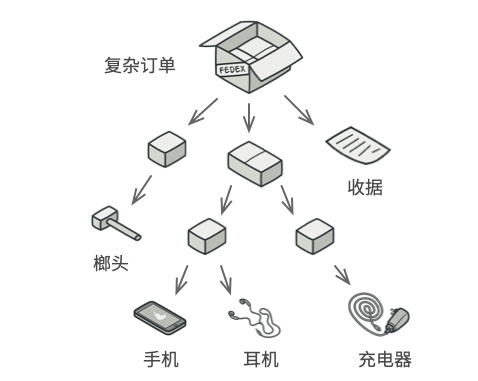
在此基础上开发一个订购系统。订单中可能包含无包装的产品,也可能包含装满产品的盒子....该如何计算每张订单的总价格呢?
组合模式使用一个通用的接口来与产品和盒子进行交互,并且在接口中声明一个计算总价的方法。对于一个产品, 该方法直接返回其价格; 对于一个盒子, 该方法遍历盒子中的所有项目, 询问每个项目的价格, 然后返回该盒子的总价格。 如果其中某个项目是小一号的盒子, 那么当前盒子也会遍历其中的所有项目, 以此类推, 直到计算出所有内部组成部分的价格。 该方式的最大优点在于你无需了解构成树状结构的对象的具体类。 你也无需了解对象是简单的产品还是复杂的盒子。 你只需调用通用接口以相同的方式对其进行处理即可。 当你调用该方法后, 对象会将请求沿着树结构传递下去
3. 适用性
- 如果希望实现树状对象结构
- 希望客户端代码以相同的方式处理简单和复杂元素
4. 结构
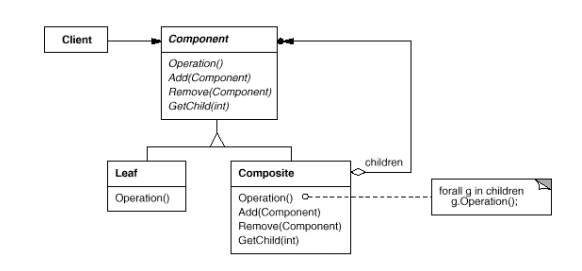
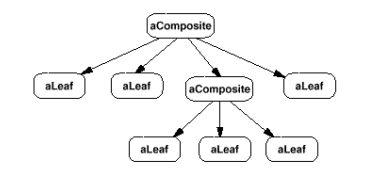
5. 效果
1) 可以利用多态和递归机制更方便地使用复杂树结构
2) 开闭原则。 无需更改现有代码, 你就可以在应用中添加新元素, 使其成为对象树的一部分
3) 简化客户代码
4) 对于功能差异较大的类, 提供公共接口或许会有困难。 在特定情况下, 你需要过度一般化组件接口, 使其变得令人难以理解
6. 代码实现
shapes/Shape.java: 通用形状接口
package composite.shapes; import java.awt.*; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 14:16 */ public interface Shape { int getX(); int getY(); int getWidth(); int getHeight(); void move(int x, int y); boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y); void select(); void unSelect(); boolean isSelected(); void paint(Graphics graphics); }
shapes/BaseShape.java: 提供基本功能的抽象形状
package composite.shapes; import java.awt.*; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 14:17 */ public class BaseShape implements Shape{ public int x; public int y; public Color color; private boolean selected = false; BaseShape(int x, int y, Color color) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.color = color; } @Override public int getX() { return x; } @Override public int getY() { return y; } @Override public int getWidth() { return 0; } @Override public int getHeight() { return 0; } @Override public void move(int x, int y) { this.x += x; this.y += y; } @Override public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) { return x > getX() && x < (getX() + getWidth()) && y > getY() && y < (getY() + getHeight()); } @Override public void select() { selected = true; } @Override public void unSelect() { selected = false; } @Override public boolean isSelected() { return selected; } void enableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) { graphics.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY); Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics; float dash1[] = {2.0f}; g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(1.0f, BasicStroke.CAP_BUTT, BasicStroke.JOIN_MITER, 2.0f, dash1, 0.0f)); } void disableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) { graphics.setColor(color); Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics; g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke()); } @Override public void paint(Graphics graphics) { if (isSelected()) { enableSelectionStyle(graphics); } else { disableSelectionStyle(graphics); } // ... } }
shapes/Dot.java: 点
package composite.shapes; import java.awt.*; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 14:35 */ public class Dot extends BaseShape{ private final int DOT_SIZE = 3; public Dot(int x, int y, Color color) { super(x, y, color); } @Override public int getWidth() { return DOT_SIZE; } @Override public int getHeight() { return DOT_SIZE; } @Override public void paint(Graphics graphics) { super.paint(graphics); graphics.fillRect(x - 1, y - 1, getWidth(), getHeight()); } }
shapes/Circle.java: 圆形
package composite.shapes; import java.awt.*; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 14:38 */ public class Circle extends BaseShape{ public int radius; public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, Color color) { super(x, y, color); this.radius = radius; } @Override public int getWidth() { return radius * 2; } @Override public int getHeight() { return radius * 2; } public void paint(Graphics graphics) { super.paint(graphics); graphics.drawOval(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1); } }
shapes/Rectangle.java: 长方形
package composite.shapes; import java.awt.*; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 14:39 */ public class Rectangle extends BaseShape{ public int width; public int height; public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height, Color color) { super(x, y, color); this.width = width; this.height = height; } @Override public int getWidth() { return width; } @Override public int getHeight() { return height; } @Override public void paint(Graphics graphics) { super.paint(graphics); graphics.drawRect(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1); } }
shapes/CompoundShape.java: 由其他形状对象组成的复合形状

package composite.shapes; import java.awt.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 14:40 */ public class CompoundShape extends BaseShape{ protected List<Shape> children = new ArrayList<>(); public CompoundShape(Shape... components) { super(0, 0, Color.BLACK); add(components); } public void add(Shape component) { children.add(component); } public void add(Shape... components) { children.addAll(Arrays.asList(components)); } public void remove(Shape child) { children.remove(child); } public void remove(Shape... components) { children.removeAll(Arrays.asList(components)); } public void clear() { children.clear(); } @Override public int getX() { if (children.size() == 0) { return 0; } int x = children.get(0).getX(); for (Shape child : children) { if (child.getX() < x) { x = child.getX(); } } return x; } @Override public int getY() { if (children.size() == 0) { return 0; } int y = children.get(0).getY(); for (Shape child : children) { if (child.getY() < y) { y = child.getY(); } } return y; } @Override public int getWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; int x = getX(); for (Shape child : children) { int childsRelativeX = child.getX() - x; int childWidth = childsRelativeX + child.getWidth(); if (childWidth > maxWidth) { maxWidth = childWidth; } } return maxWidth; } @Override public int getHeight() { int maxHeight = 0; int y = getY(); for (Shape child : children) { int childsRelativeY = child.getY() - y; int childHeight = childsRelativeY + child.getHeight(); if (childHeight > maxHeight) { maxHeight = childHeight; } } return maxHeight; } @Override public void move(int x, int y) { for (Shape child : children) { child.move(x, y); } } @Override public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) { for (Shape child : children) { if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) { return true; } } return false; } @Override public void unSelect() { super.unSelect(); for (Shape child : children) { child.unSelect(); } } public boolean selectChildAt(int x, int y) { for (Shape child : children) { if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) { child.select(); return true; } } return false; } @Override public void paint(Graphics graphics) { if (isSelected()) { enableSelectionStyle(graphics); graphics.drawRect(getX() - 1, getY() - 1, getWidth() + 1, getHeight() + 1); disableSelectionStyle(graphics); } for (composite.shapes.Shape child : children) { child.paint(graphics); } } }
editor/ImageEditor.java: 形状编辑器
package composite.editor; import composite.shapes.CompoundShape; import composite.shapes.Shape; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.border.Border; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter; import java.awt.event.MouseEvent; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 15:10 */ public class ImageEditor { private EditorCanvas canvas; private CompoundShape allShapes = new CompoundShape(); public ImageEditor() { canvas = new EditorCanvas(); } // 使用shapes.shape 类型的对象 public void loadShapes(Shape... shapes) { allShapes.clear(); allShapes.add(shapes); canvas.refresh(); } private class EditorCanvas extends Canvas { JFrame frame; private static final int PADDING = 10; EditorCanvas() { createFrame(); refresh(); addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() { @Override public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) { allShapes.unSelect(); allShapes.selectChildAt(e.getX(), e.getY()); e.getComponent().repaint(); } }); } void createFrame() { frame = new JFrame(); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel(); Border padding = BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(PADDING, PADDING, PADDING, PADDING); contentPanel.setBorder(padding); frame.setContentPane(contentPanel); frame.add(this); frame.setVisible(true); frame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY); } public int getWidth() { return allShapes.getX() + allShapes.getWidth() + PADDING; } public int getHeight() { return allShapes.getY() + allShapes.getHeight() + PADDING; } void refresh() { this.setSize(getWidth(), getHeight()); frame.pack(); } public void paint(Graphics graphics) { allShapes.paint(graphics); } } }
Demo.java: 客户端代码
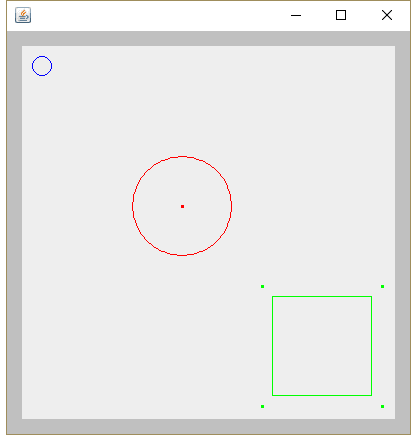
package composite; import composite.editor.ImageEditor; import composite.shapes.CompoundShape; import composite.shapes.Dot; import composite.shapes.Circle; import composite.shapes.Rectangle; import java.awt.*; /** * @author GaoMing * @date 2021/7/12 - 14:16 */ public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { ImageEditor editor = new ImageEditor(); editor.loadShapes( new Circle(10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE), new CompoundShape( new Circle(110, 110, 50, Color.RED), new Dot(160, 160, Color.RED) ), new CompoundShape( new Rectangle(250, 250, 100, 100, Color.GREEN), new Dot(240, 240, Color.GREEN), new Dot(240, 360, Color.GREEN), new Dot(360, 360, Color.GREEN), new Dot(360, 240, Color.GREEN) ) ); } }
执行结果
7. 与其他模式的关系
- 可以在创建复杂组合树时使用生成器模式, 因为这可使其构造步骤以递归的方式运行
- 责任链模式通常和组合模式结合使用。 在这种情况下, 叶组件接收到请求后, 可以将请求沿包含全体父组件的链一直传递至对象树的底部
- 可以使用迭代器模式来遍历组合树
- 可以使用访问者模式对整个组合树执行操作
- 可以使用享元模式实现组合树的共享叶节点以节省内存
-
组合和装饰模式的结构图很相似, 因为两者都依赖递归组合来组织无限数量的对象
装饰类似于组合, 但其只有一个子组件。 此外还有一个明显不同: 装饰为被封装对象添加了额外的职责, 组合仅对其子节点的结果进行了 “求和”
但是, 模式也可以相互合作: 你可以使用装饰来扩展组合树中特定对象的行为 -
大量使用组合和装饰的设计通常可从对于原型模式的使用中获益。 你可以通过该模式来复制复杂结构, 而非从零开始重新构造
8. 已知应用
一些 Java 标准程序库中的组合示例:
java.awt.Container#add(Component) (几乎广泛存在于 Swing 组件中)
javax.faces.component.UIComponent#getChildren() (几乎广泛存在于 JSF UI 组件中)
识别方法: 组合可以通过将同一抽象或接口类型的实例放入树状结构的行为方法来轻松识别
9. 关于组合模式安全性和透明性的讨论
- 在类层次结构的根部定义子节点管理接口的方法具有良好的透明性,因为可以一致的使用所有的组件,但是这一方法是以安全性为代价的,因为客户可能会做一些无意义的事情,例如在leaf中增加和删除对象
- 在composite类中定义和管理子部件的方法具有良好的安全性。但是这样又损失了透明性,因为leaf和composite具有不同的接口



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号