java并发编程(更新)
概念理解:①串行程序②并发程序;
线程安全问题:
同一进程中的所有线程共享进程中的内存地址空间。如果没有明确的同步机制来管理共享数据,那么当一个线程正在使用某个变量时,另一个线程可能同时访问这个变量,造成不可预测的结果。
同步(Synchronous):
异步(Asynchronous):
并发(Concurrency):
并行(Parallelism):
临界区:临界区表示一种公共资源或公共数据,可以被多个线程交替使用。
阻塞(Blocking):一个线程占用了临界区资源,其他所有需要这个资源的线程必须在这个临界区中等待;
非阻塞(Non-Blocking):
java的内存模型JMM:
①原子性:一个线程进行操作,不该被其他线程干扰。
②可见性:当一个线程修改了某一个共享变量的值,其他线程能否立即知道这个共享变量已被修改。
③有序性:
进程:进程是线程的容器。程序是指令、数据及其组织形式的描述,进程是程序的实体。
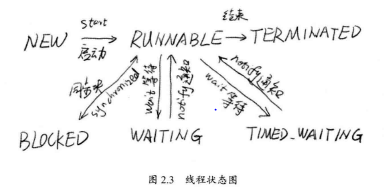
线程状态:

线程操作API:
创建线程的方式:
new Thread(){//匿名内部类的方式,重载了run方法,run方法结束自动回收线程。
public void run(){
System.out.println("线程1");
}}.start();
new Thread(new Runnable(){//构造方法:Thread(Runnable target)
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程2");
}
}).start();
线程的终止:
Thread.stop()已废弃,stop强行终止线程,并且会立即释放这个线程所持有的锁(如果这些锁恰恰是用来维持对象的一致性的,其他线程就会读到不一致的对象):
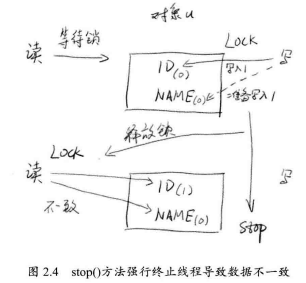
线程的终止应该由程序员自己决定。
(volatile关键字解释:)
线程中断:
interrupt()中断线程
isInterrupted()判断是否被中断
interrupted()判断是否被中断,并清除当前中断状态
等待(wait)和通知(notify、notifyAll):
public class waitTest { final static Object obj=new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(){ public void run(){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } synchronized(obj){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" T2:start! notify one thread"); obj.notify(); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" T2:end!"); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }.start(); new Thread(){ public void run(){ synchronized(obj){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" T1:start!"); try { System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" T1 wait for obj!"); obj.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" T1:end!"); } } }.start(); } }
wait、notify、notifyAll是Object类的方法(由锁对象object调用),sleep、yeild是Thread类的方法;
obj.wait()和Thread.sleep()都能让线程等待若干时间。wait()可以被唤醒,并且释放目标对象的锁,而Thread.sleep()不会释放任何资源。
等待线程结束(join)和谦让(yield):
public class joinTest { public volatile static int i=0; public static class AddThread extends Thread{ public void run(){ for(;i<10000000;i++);//相当于for(i=0;i<100000;i++); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { AddThread t1=new AddThread(); t1.start(); t1.join(); //主线程将等待t1线程执行完,再执行主线程; //如果没有join(),t1未执行完就切换到主线程,输出0-10000000的值; Thread.sleep(2); System.out.println(i); } }
join内部是调用了wait:
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
join代码理解:
public class myJoinTest { public volatile static int i=0; public volatile static int j=0; public static class AddThread extends Thread{ Thread b= new Thread(new Runnable(){ public void run() {//B线程run方法; for(;j<20;j++){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("B线程"+"---:j="+j); } System.out.println("B线程结束!"); } }); public void run(){//A线程run方法; for(;i<20;i++){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("A线程"+"---:i="+i); if(i==10){ try { b.join(); /* i<10,总共有三个线程争夺资源,当i=10时,线程A中调用了线程B的join()方法,此时CPU被A占用,引入B并被B占用,此后只有main线程和B争夺CPU执行权, B结束后,才有A和main争夺执行权; (当前线程中有其他线程执行join方法,则当前线程无权再争夺CPU,直到join调用者执行完,但join调用者在执行过程中仍会和别的线程争夺资源) */ } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } System.out.println("A线程结束!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { AddThread a = new AddThread(); a.b.start(); a.start(); for(int k=0;k<50;k++){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("main线程"+":k="+k); } System.out.println("main线程结束!"); } }
三、JDK并发包
使用重入锁可以替代synchronized、Object.wait()、Object.notify();
重入锁:
重入锁使用java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock类实现。
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class ReenterLock implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock(); //重入锁(reentrant-可重入); public static int i=0; public void run() { for(int j=0;j<10;j++){ try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } lock.lock(); //重入锁:在一个线程内,这种锁可以反复进入(一个线程连续两次获得同一把锁)。 lock.lock(); try{ i++; }finally{ lock.unlock(); lock.unlock(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" i="+i); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ReenterLock tl=new ReenterLock(); Thread t1=new Thread(tl); Thread t2=new Thread(tl); t1.start(); t2.start(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Thread.sleep(200); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); t1.join();//join保证调用者在main线程之前执行完 t2.join(); } System.out.println(i); } }
中断响应Page72:
请求锁时使用lockInterruptibly()替代lock(),这是一个可以对中断进行响应的锁申请,即在等待锁的过程中可以响应中断(死锁情况)。thread.interrupt()可以中断线程的锁等待,放弃在等待的锁申请,并且释放已经获得的锁(交叉死锁的另一个线程就可以获得被释放的锁,而继续执行下去);
interrupt代码:
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class IntLock implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock lock1=new ReentrantLock(); public static ReentrantLock lock2=new ReentrantLock(); int lock; public IntLock(int lock){ this.lock=lock; } public void run() { try { if(lock==1){ lock1.lockInterruptibly();//区别于lock(); // (interruptibly-可中断) Thread.sleep(500); lock2.lockInterruptibly(); System.out.println("lock==1"); }else{ lock2.lockInterruptibly(); Thread.sleep(500); lock1.lockInterruptibly(); System.out.println("lock!=1"); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally{ if(lock1.isHeldByCurrentThread())//held-握住 lock1.unlock(); if(lock2.isHeldByCurrentThread()) lock2.unlock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":线程退出!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { IntLock r1=new IntLock(1); IntLock r2=new IntLock(2); Thread t1=new Thread(r1); Thread t2=new Thread(r2); t1.start(); t2.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); t2.interrupt(); } }
限时等待申请锁:
使用tryLock(parm1,parm2)方法:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class TimeLock implements Runnable{ public static ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock(); public void run() { try { if(lock.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){ //当前线程请求锁lock,最多等待5秒,成功获得锁返回true,超过5秒没有得到锁就会返回false Thread.sleep(2000); }else{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get lock failed"); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally{ if(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { TimeLock t=new TimeLock(); Thread t1=new Thread(t); Thread t2=new Thread(t); t1.start(); t2.start(); //两者之一获得锁并会睡眠2s,另一个线程只会等待1s会返回false; } }
公平锁与非公平锁:
ReentrantLock(boolean fair)
重入锁的Condition接口Page81:
await()
awaitUninterruptibly()
awaitNanos(Long nanosTimeout)
signal()
signalAll()
//await和signal
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class ReenterLockCondition implements Runnable { public static ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock(); public static Condition condition=lock.newCondition(); @Override public void run() { try { lock.lock(); condition.await(); System.out.println("Thread is going on!"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally{ lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ReenterLockCondition t = new ReenterLockCondition(); Thread t1 = new Thread(t); t1.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); lock.lock();//? condition.signal(); lock.unlock();//? } }
阻塞队列源码中应用了重入锁和Condition对象。
信号量(Semaphore),可以指定多个线程同时访问一个资源。
public class SemapDemo implements Runnable{ final Semaphore semp=new Semaphore(5); public void run() { try { semp.acquire();//申请信号量 Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":done!"); semp.release();//释放信号量 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20); final SemapDemo demo=new SemapDemo(); for(int i=0;i<20;i++){ exec.submit(demo); } } }
读写锁ReadWriteLock(多操作次数远大于写操作次数时应用)Page87:
import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; public class ReadWirterLockDemo { private static Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();//重入锁 private static ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock=new ReentrantReadWriteLock();//可重入读写锁 private static Lock readLock=readWriteLock.readLock(); private static Lock writeLock=readWriteLock.writeLock(); private int value; public Object handleRead(Lock lock) throws InterruptedException { try { lock.lock(); Thread.sleep(1000); return value; } finally{ lock.unlock(); } } public void handleWrite(Lock lock,int index) throws InterruptedException{ try { lock.lock(); Thread.sleep(1000); value = index; } finally{ lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { final ReadWirterLockDemo demo = new ReadWirterLockDemo(); Runnable readRunnable=new Runnable(){ public void run(){ try { demo.handleRead(readLock); demo.handleRead(lock); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; Runnable writeRunnable=new Runnable(){ public void run(){ try { demo.handleWrite(writeLock, new Random().nextInt()); demo.handleWrite(lock, new Random().nextInt()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; for(int i=0;i<18;i++){ new Thread(readRunnable).start(); } for(int i=18;i<20;i++){ new Thread(writeRunnable).start(); } } }
线程阻塞工具类:LockSupport
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport; public class LockSupportDemo { public static Object u=new Object(); static ChangeObjectThread t1=new ChangeObjectThread("线程t1"); static ChangeObjectThread t2=new ChangeObjectThread("线程t2"); public static class ChangeObjectThread extends Thread{ public ChangeObjectThread(String name){ super.setName(name); } public void run(){ synchronized(u){ System.out.println("in "+getName()); LockSupport.park(); /* 为当前线程准备一个许可,线程运行到该代码就会消费这个许可,并将许可变为 * 不可用,线程阻塞(其他线程无法进入)。LockSupport.unpark(当前线程)可以使得许可变为可用。 */ System.out.println("代码片"); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { t1.start();Thread.sleep(100); t2.start(); LockSupport.unpark(t1); LockSupport.unpark(t2); t1.join(); t2.join(); } }
LockSupport.park()支持中断影响,不会抛出InterruptedException异常。

1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport; 2 public class LockSupportDemo { 3 public static Object u=new Object(); 4 static ChangeObjectThread t1=new ChangeObjectThread("线程t1"); 5 static ChangeObjectThread t2=new ChangeObjectThread("线程t2"); 6 public static class ChangeObjectThread extends Thread{ 7 public ChangeObjectThread(String name){ 8 super.setName(name); 9 } 10 public void run(){ 11 synchronized(u){ 12 System.out.println("in "+getName()); 13 LockSupport.park(); 14 /* 为当前线程准备一个许可,线程运行到该代码就会消费这个许可,并将许可变为 15 * 不可用,线程阻塞(其他线程无法进入)。LockSupport.unpark(当前线程)可以使得许可变为可用。 16 */ 17 if(Thread.interrupted()){ 18 System.out.println(getName()+" 被中断了!"); 19 } 20 } 21 System.out.println(getName()+"执行结束!"); 22 } 23 } 24 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 25 t1.start();Thread.sleep(100); 26 t2.start(); 27 t1.interrupt(); 28 LockSupport.unpark(t2); 29 } 30 }
线程池的作用:避免系统频繁地创建和销毁线程,让创建的线程进行复用。
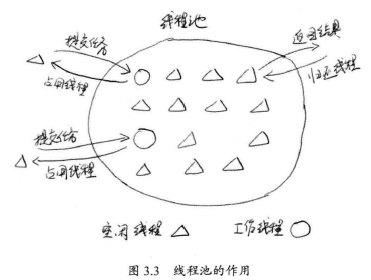
JDK提供了一套Executor框架用于线程控制(java.util.concurrent并发包核心类),ThreadPoolExecutor表示为一个线程池。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(
int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)


①newFixedThreadPool(int capacity)有界线程池

1 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 2 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 3 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 4 public class ThreadPoolDemo { 5 public static class MyTask implements Runnable{ 6 public void run() { 7 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+":Thread ID:" 8 +Thread.currentThread().getId()); 9 try { 10 Thread.sleep(1000); 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 MyTask task = new MyTask(); 18 ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); 19 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 20 es.submit(task); 21 } 22 } 23 }
newFixedThreadPool(int capacity,ThreadFactory tf)
②newCachedThreadPool();
newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadfactory)定制线程工厂;

public static class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory{ //根据需要自定义线程工厂类 @Override public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { Thread thread=new Thread(r); thread.setName("定制池中的线程对象的名称:["+Math.random()+"]"); return thread; } } @Test public void test(){ MyThreadFactory threadFactory = new MyThreadFactory(); ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(threadFactory); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ es.execute(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("正在运行:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }); } }
③newSingleThreadExecutor()单一线程池
newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory tf)
自定义线程创建:ThreadFactory
线程池中线程的创建来自于ThreadFactory接口。Thread newThread(Runnable r);
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class ThreadFactoryTest { public static class MyTask implements Runnable{ public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyTask task = new MyTask(); ExecutorService es =new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,5, 0L,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), new ThreadFactory(){ public Thread newThread(Runnable r){ Thread t=new Thread(r); t.setDaemon(true); //将所有线程都设为守护线程,当主线程退出后,将会强制销毁线程池; System.out.println("create "+t); return t; } }); for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ es.submit(task); } Thread.sleep(2000); } }
线程池扩展:beforeExecute()、afterExecute()、terminated()
重写以上方法可以对线程池中执行的线程对象实现监控。
Page112
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class ExtThreadPool { public static class MyTask implements Runnable{ public String name; public MyTask(String name) { this.name = name; } public void run() { System.out.println("正在执行"+"Thread ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getName() +",Task Name="+name); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ExecutorService es=new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,5,0L,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()){ @Override protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) { System.out.println("准备执行:"+((MyTask)r).name); } @Override protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) { System.out.println("执行完成:"+((MyTask)r).name); } @Override protected void terminated() { System.out.println("线程池退出!"); } }; for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ MyTask task = new MyTask("TASK-GEYM-"+i); es.execute(task); Thread.sleep(10); } es.shutdown(); } }
在线程池中寻找堆栈:
public class DivTask implements Runnable{ int a,b; public DivTask(int a,int b){ this.a=a; this.b=b; } public void run() { double re=a/b; System.out.println(re); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ThreadPoolExecutor pools=new ThreadPoolExecutor(0,Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0L,TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()){ protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) { System.out.println("准备执行:"+t.getName()); } }; for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ // pools.submit(new DivTask(100, i)); // pools.execute(new DivTask(100, i)); //改用execute(),可以看到异常堆栈 Future re = pools.submit(new DivTask(100, i)); re.get();//或者获取Future,get方法可以抛出异常; } } }
Fork/Join框架,ForkJoinPool线程池Page117:

public class CountTask extends RecursiveTask<Long> { private static final int THRESHOLD=10000; private long start; private long end; public CountTask(long start, long end) { this.start = start; this.end = end; } protected Long compute() { long sum=0; boolean canCompute=(end-start)<THRESHOLD; if(canCompute){ for(long i=start;i<=end;i++){ sum+=i; } }else{ long step=(start+end)/100; ArrayList<CountTask> subTasks=new ArrayList<CountTask>(); long pos=start; for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ long lastOne=pos+step; if(lastOne>end)lastOne=end; CountTask subTask=new CountTask(pos,lastOne); pos+=step+1; subTasks.add(subTask); subTask.fork(); } for(CountTask t:subTasks){ sum+=t.join(); } } return sum; } public static void main(String[] args) { ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(); CountTask task=new CountTask(0,200000L); ForkJoinTask<Long> result=forkJoinPool.submit(task); try { long res=result.get(); System.out.println("sum="+res); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
JDK的并发容器:
程序就是“算法+数据结构”,容器类就是JDK准备好的线程数据结构(可以找到链表、HashMap、队列);
并发集合:


Collections工具类具有将任意集合包装成线程安全的方法,多线程环境下的性能较低,使用java.util.concurrent包中的并发集合效率较高(优化了锁机制);
public static Map map=Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap());
BlockingQueue:适合做数据共享的通道,当队列为空时,服务线程进行等待(Blocking-阻塞),当有新的消息进入队列后,自动将线程唤醒。(用于解耦生产者和消费者)
随机数据结构:跳表(SkipList):
锁的优化及注意事项Page138
减少线程持有锁的时间,提高系统的吞吐量;
ThreadLocal的应用:线程的局部变量。
public class ThreadLocalTest { private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> t1=new ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>(); public static class ParseDate implements Runnable{ int i=0; public ParseDate(int i){ this.i=i; } public void run() { try { if(t1.get()==null){ t1.set(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); } Date t=t1.get().parse("2015-03-29 19:29:"+i%60); System.out.println(i+":"+t); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ es.execute(new ParseDate(i)); } } }
单例模式:
public class Singleton { private Singleton() { //构造函数设为私有,防止类外创建实例; System.out.println("Singleton is create!"); } private static Singleton instance=new Singleton(); //instance设为私有,类外无法修改,getInstance为静态的,instance也要设为静态的; public static Singleton getInstance(){ return instance; } }
不变模式:
public final class Product {//无法被继承,其方法也不会被重载而修改 private final String no;//属性私有,不会被其他对象获取 private final String name; //使用final修饰,其值可以在构造函数中初始化,不能再二次赋值 private final double price; public Product(String no, String name, double price) { //构造函数必须全参,保证final变量赋初值 super(); this.no = no; this.name = name; this.price = price; } //没有setter方法,保证属性不会被修改 public String getNo() { return no; } public String getName() { return name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } }
JDK中的java.lang.String类和元数据包装类都是不变模式实现的(Boolean、Byte、Character、Double、Float、Integer、Long、Short)。
生产者-消费者模式:

import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; final class PCData{ private final int intData; public PCData(int intData) { super(); this.intData = intData; } public PCData(String d){ intData=Integer.valueOf(d); } public int getData(){ return intData; } public String toString() { return "data:" + intData; } } public class Producer implements Runnable { private volatile boolean isRunning =true; private BlockingQueue<PCData> queue; private static AtomicInteger count=new AtomicInteger(); private static final int SLEEPTIME=1000; public Producer(BlockingQueue<PCData> queue){ this.queue=queue; } public void run() { PCData data=null; Random r=new Random(); System.out.println("start producer id="+Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { while(isRunning){ Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEPTIME)); data=new PCData(count.incrementAndGet()); System.out.println(data+" is put into queue"); if(!queue.offer(data,2,TimeUnit.SECONDS)){ System.err.println("failed to put data: "+data); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } public void stop(){ isRunning=false; } }

import java.text.MessageFormat; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; public class Consumer implements Runnable{ private BlockingQueue<PCData> queue; private static final int SLEEPTIME=1000; public Consumer(BlockingQueue<PCData> queue) { this.queue = queue; } public void run() { System.out.println("start Consumer id="+Thread.currentThread().getName()); Random r=new Random(); try{ while(true){ PCData data=queue.take(); if(null!=data){ int re=data.getData()*data.getData(); System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("{0}*{1}={2}",data.getData(),data.getData(),re)); Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEPTIME)); } } }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } }

import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; public class ProCusTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { BlockingQueue<PCData> queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue<PCData>(10); Producer producer1 = new Producer(queue); Producer producer2 = new Producer(queue); Producer producer3= new Producer(queue); Consumer consumer1=new Consumer(queue); Consumer consumer2=new Consumer(queue); Consumer consumer3=new Consumer(queue); ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); service.execute(producer1); service.execute(producer2); service.execute(producer3); service.execute(consumer1); service.execute(consumer2); service.execute(consumer3); Thread.sleep(10*1000); producer1.stop(); producer2.stop(); producer3.stop(); Thread.sleep(3000); service.shutdown(); } }
参考:http://ifeve.com/





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号