java中的重写和重载
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/fenglee594/p/6425980.html
-
重写
在java中有很多的继承,继承下来的有变量、方法。在有一些子类要实现的方法中,方法名、传的参数、返回值跟父类中的方法一样,但具体实现又跟父类的不一样,这时候我们就需要重写父类的方法,就比如我们有一个类叫做Animals,Animals类中有一个叫做Call,然后我们继承Animals又生成了Cat类和Dog类,Cat和Dog也分别有自己特别的叫声,程序如下:
1 class Animals {
2 public void call() {
3 System.out.println("啊啊啊啊啊啊啊");
4 }
5 }
6
7
8 public class Cat extends Animals {
9 @Override
10 public void call() {
11
12 System.out.println("喵喵喵喵喵");
13 }
14 }
15
16
17 public class Dog extends Animals {
18
19 @Override
20 public void call() {
21 System.out.println("汪汪汪汪汪汪");
22 }
23
24 public static void main(String[] args) {
25 Animals animals = new Animals();
26 animals.call();
27
28 Cat cat = new Cat();
29 cat.call();
30
31 Dog dog = new Dog();
32 dog.call();
33 }
34
35 }
打印结果如下:

-
重载
重载是在一个类中实现的,有多个同名方法,但参数不一样,包括参数类型、参数个数、还可以没有参数,总之每个重载的方法的参数必须不一样。
现在我写一个小程序,用来进行比较两个数值大小的,代码块如下:
1 public class Compare {
2
3 public void max(int a, int b) {
4 System.out.println(a>b?a:b);
5 }
6
7 public void max(float a, float b) {
8 System.out.println(a>b?a:b);
9 }
10
11
12 public void max() {
13 /**
14 * 无参重载
15 * */
16 System.out.println("Coding...");
17 }
18 public static void main(String[] args) {
19 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
20 Compare compare = new Compare();
21 compare.max(102, 23);
22 compare.max(2.0f, 3.0f);
23 compare.max();
24 }
25
26 }
打印结果如下图:
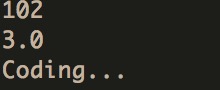
-
总结
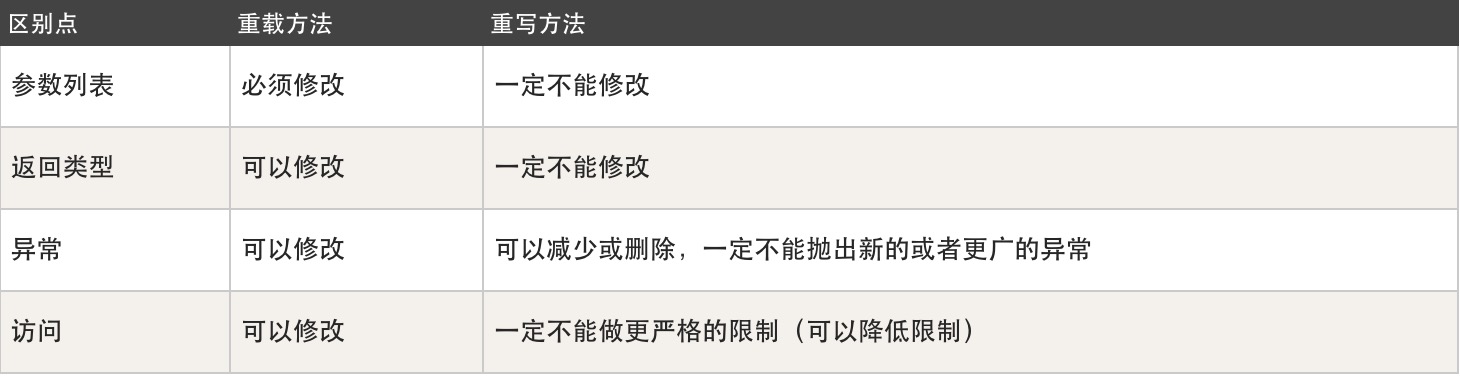
重写是外壳不变,核心变。也就是说方法名不变,参数不变,具体实现可以改变。一般是在父类中声明方法,在子类中重写。
重载是方法名不变,但参数一定要变。而且重载的方法一般都写在一个类中。用一张图来表示区别如下:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号