Python读写Excel文件的实例
最近由于经常要用到Excel,需要根据Excel表格中的内容对一些apk进行处理,手动处理很麻烦,于是决定写脚本来处理。首先贴出网上找来的读写Excel的脚本。 1.读取Excel(需要安装xlrd):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
#-*- coding: utf8 -*-import xlrd fname = "reflect.xls"bk = xlrd.open_workbook(fname)shxrange = range(bk.nsheets)try: sh = bk.sheet_by_name("Sheet1")except: print "no sheet in %s named Sheet1" % fname#获取行数nrows = sh.nrows#获取列数ncols = sh.ncolsprint "nrows %d, ncols %d" % (nrows,ncols)#获取第一行第一列数据 cell_value = sh.cell_value(1,1)#print cell_value row_list = []#获取各行数据for i in range(1,nrows): row_data = sh.row_values(i) row_list.append(row_data) |
2.写入Excel(需安装pyExcelerator)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
from pyExcelerator import *w = Workbook() #创建一个工作簿ws = w.add_sheet('Hey, Hades') #创建一个工作表ws.write(0,0,'bit') #在1行1列写入bitws.write(0,1,'huang') #在1行2列写入huangws.write(1,0,'xuan') #在2行1列写入xuanw.save('mini.xls') #保存 |
3.再举个自己写的读写Excel的例子 读取reflect.xls中的某些信息进行处理后写入mini.xls文件中。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
#-*- coding: utf8 -*-import xlrdfrom pyExcelerator import * w = Workbook() ws = w.add_sheet('Sheet1') fname = "reflect.xls"bk = xlrd.open_workbook(fname)shxrange = range(bk.nsheets)try: sh = bk.sheet_by_name("Sheet1")except: print "no sheet in %s named Sheet1" % fnamenrows = sh.nrowsncols = sh.ncolsprint "nrows %d, ncols %d" % (nrows,ncols) cell_value = sh.cell_value(1,1)#print cell_value row_list = []mydata = []for i in range(1,nrows): row_data = sh.row_values(i) pkgdatas = row_data[3].split(',') #pkgdatas.split(',') #获取每个包的前两个字段 for pkgdata in pkgdatas: pkgdata = '.'.join((pkgdata.split('.'))[:2]) mydata.append(pkgdata) #将列表排序 mydata = list(set(mydata)) print mydata #将列表转化为字符串 mydata = ','.join(mydata) #写入数据到每行的第一列 ws.write(i,0,mydata) mydata = [] row_list.append(row_data[3])#print row_listw.save('mini.xls') |
4.现在我需要根据Excel文件中满足特定要求的apk的md5值来从服务器获取相应的apk样本,就需要这样做:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#-*-coding:utf8-*-import xlrdimport osimport shutil fname = "./excelname.xls"bk = xlrd.open_workbook(fname)shxrange = range(bk.nsheets)try: #打开Sheet1工作表 sh = bk.sheet_by_name("Sheet1")except: print "no sheet in %s named Sheet1" % fname#获取行数nrows = sh.nrows#获取列数ncols = sh.ncols#print "nrows %d, ncols %d" % (nrows,ncols)#获取第一行第一列数据cell_value = sh.cell_value(1,1)#print cell_value row_list = []#range(起始行,结束行)for i in range(1,nrows): row_data = sh.row_values(i) if row_data[6] == "HXB": filename = row_data[3]+".apk" #print "%s %s %s" %(i,row_data[3],filename) filepath = r"./1/"+filename print "%s %s %s" %(i,row_data[3],filepath) if os.path.exists(filepath): shutil.copy(filepath, r"./myapk/") |
补充一个使用xlwt3进行Excel文件的写操作。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
import xlwt3if __name__ == '__main__': datas = [['a', 'b', 'c'], ['d', 'e', 'f'], ['g', 'h']]#二维数组 file_path = 'D:\\test.xlsx' wb = xlwt3.Workbook() sheet = wb.add_sheet('test')#sheet的名称为test #单元格的格式 style = 'pattern: pattern solid, fore_colour yellow; '#背景颜色为黄色 style += 'font: bold on; '#粗体字 style += 'align: horz centre, vert center; '#居中 header_style = xlwt3.easyxf(style) row_count = len(datas) col_count = len(datas[0]) for row in range(0, row_count): col_count = len(datas[row]) for col in range(0, col_count): if row == 0:#设置表头单元格的格式 sheet.write(row, col, datas[row][col], header_style) else: sheet.write(row, col, datas[row][col]) wb.save(file_path) |
输出的文件内容如下图:
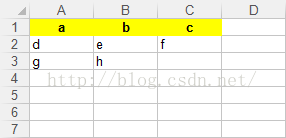
注:以上代码在Python 3.x版本测试通过。
好了,python操作Excel就这么!些了,简单吧




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号