Linux input子系统
-
Input driver :主要实现对硬件设备的读写访问,中断设置,并把硬件产生的事件转换为核心层定义的规范提交给事件处理层。
-
Input core :承上启下。为设备驱动层提供了规范和接口;通知事件处理层对事件进行处理;
-
Event handler :提供用户编程的接口(设备节点),并处理驱动层提交的数据处理。
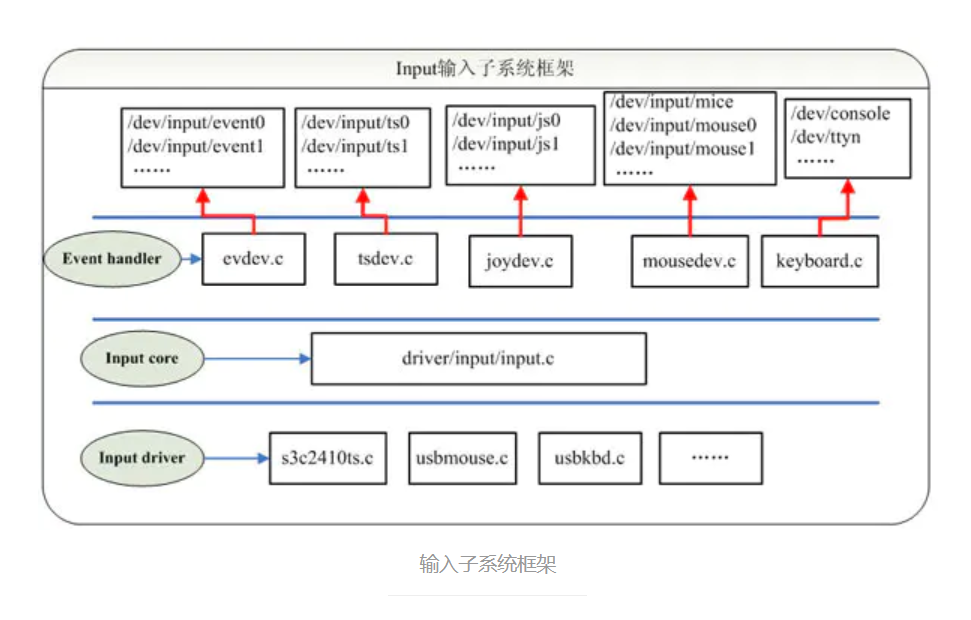
1输入子系统框架分析
1.1设备驱动层(Input driver)
- device是纯硬件操作层,包含不同的硬件接口处理,如gpio等
- 对于每种不同的具体硬件操作,都对应着不同的input_dev结构体
- 该结构体内部也包含着一个h_list,指向handle
1.2.系统核心层(Input core)
- 申请主设备号;
- 提供input_register_device跟input_register_handler函数分别用于注册device跟handler;
- 提供input_register_handle函数用于注册一个事件处理,代表一个成功配对的input_dev和input_handler;
1.3.事件处理层(Event handler)
- 不涉及硬件方面的具体操作,handler层是纯软件层,包含不同的解决方案,如键盘,鼠标,游戏手柄等;
- 对于不同的解决方案,都包含一个名为input_handler的结构体,该结构体内含的主要成员如下:
| 成员 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| .id_table | 一个存放该handler所支持的设备id的表(其实内部存放的是EV_xxx事件,用于判断device是否支持该事件) |
| .fops | 该handler的file_operation |
| .connect | 连接该handler跟所支持device的函数 |
| .disconnect | 断开该连接 |
| .event | 事件处理函数,让device调用 |
| h_list | 是一个链表,该链表保存着该handler到所支持的所有device的中间站:handle结构体的指针 |
2.两条链表连接dev和handler
#file pwd: drivers/input/input.c
MODULE_AUTHOR("Vojtech Pavlik <vojtech@suse.cz>"); MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Input core"); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");#define INPUT_MAX_CHAR_DEVICES 1024
#define INPUT_FIRST_DYNAMIC_DEV 256
static DEFINE_IDA(input_ida);static LIST_HEAD(input_dev_list);
static LIST_HEAD(input_handler_list);
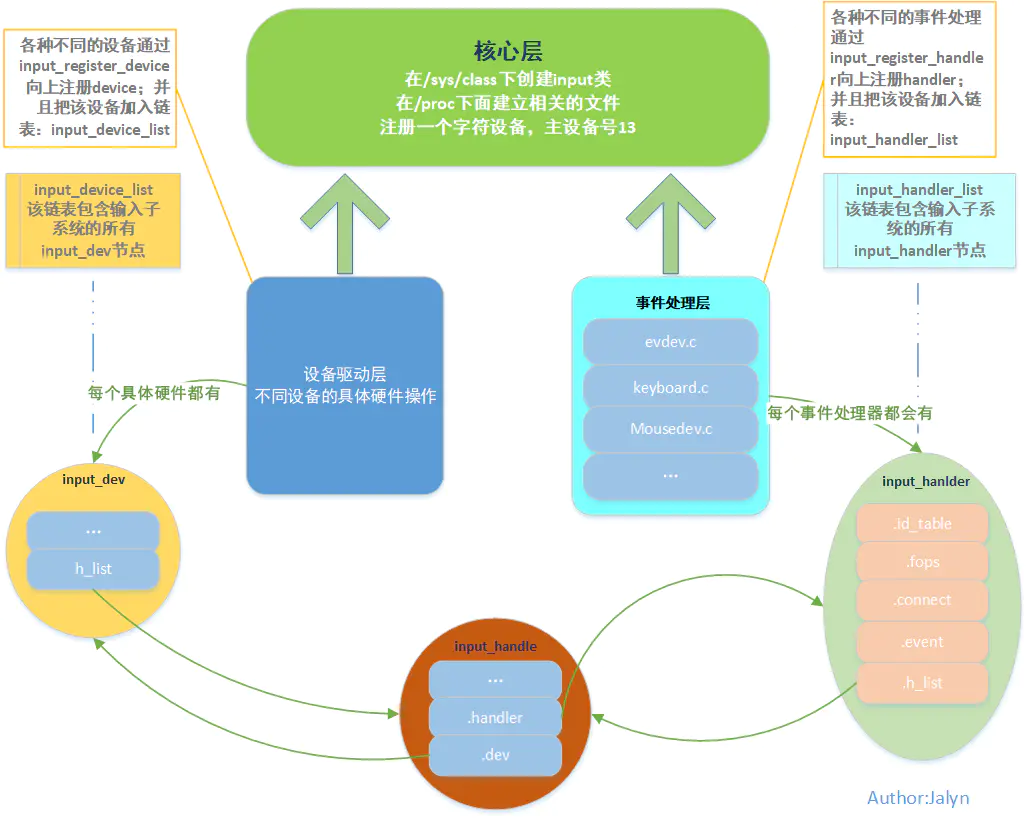
3.输入子系统代码分析
文件路径:driver/input/input.c (核心层)
1 static int __init input_init(void) 2 { 3 int err; 4 5 err = class_register(&input_class);//在/sys/class下创建逻辑(input)类,在类下面挂载input设备6 if (err) { 7 pr_err("unable to register input_dev class\n"); 8 return err; 9 } 10 11 err = input_proc_init();//在/proc下面建立相关的虚拟文件,proc下创建的文件可以看作是虚拟文件对内核读写的一种操作12 if (err) 13 goto fail1; 14 15 err = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, 0),//在/dev下创建input设备号 16 INPUT_MAX_CHAR_DEVICES, "input"); 17 if (err) { 18 pr_err("unable to register char major %d", INPUT_MAJOR); 19 goto fail2; 20 } 21 22 return 0; 23 24 fail2: input_proc_exit(); 25 fail1: class_unregister(&input_class); 26 return err; 27 } 28 29 static void __exit input_exit(void) 30 { 31 input_proc_exit(); 32 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, 0), 33 INPUT_MAX_CHAR_DEVICES); 34 class_unregister(&input_class); 35 } 36 37 subsys_initcall(input_init); 38 module_exit(input_exit);
现在基本框架已经建成,如何往input系统里面注册dev和hanlder呢?
3.1注册dev
1 /** 2 * struct input_dev - represents an input device 3 * @name: name of the device 4 * @phys: physical path to the device in the system hierarchy 5 * @uniq: unique identification code for the device (if device has it) 6 * @id: id of the device (struct input_id) 7 * @propbit: bitmap of device properties and quirks 8 * @evbit: bitmap of types of events supported by the device (EV_KEY, 9 * EV_REL, etc.) 10 * @keybit: bitmap of keys/buttons this device has 11 * @relbit: bitmap of relative axes for the device 12 * @absbit: bitmap of absolute axes for the device 13 * @mscbit: bitmap of miscellaneous events supported by the device 14 * @ledbit: bitmap of leds present on the device 15 * @sndbit: bitmap of sound effects supported by the device 16 * @ffbit: bitmap of force feedback effects supported by the device 17 * @swbit: bitmap of switches present on the device 18 * @hint_events_per_packet: average number of events generated by the 19 * device in a packet (between EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT events). Used by 20 * event handlers to estimate size of the buffer needed to hold 21 * events. 22 * @keycodemax: size of keycode table 23 * @keycodesize: size of elements in keycode table 24 * @keycode: map of scancodes to keycodes for this device 25 * @getkeycode: optional legacy method to retrieve current keymap. 26 * @setkeycode: optional method to alter current keymap, used to implement 27 * sparse keymaps. If not supplied default mechanism will be used. 28 * The method is being called while holding event_lock and thus must 29 * not sleep 30 * @ff: force feedback structure associated with the device if device 31 * supports force feedback effects 32 * @repeat_key: stores key code of the last key pressed; used to implement 33 * software autorepeat 34 * @timer: timer for software autorepeat 35 * @rep: current values for autorepeat parameters (delay, rate) 36 * @mt: pointer to multitouch state 37 * @absinfo: array of &struct input_absinfo elements holding information 38 * about absolute axes (current value, min, max, flat, fuzz, 39 * resolution) 40 * @key: reflects current state of device's keys/buttons 41 * @led: reflects current state of device's LEDs 42 * @snd: reflects current state of sound effects 43 * @sw: reflects current state of device's switches 44 * @open: this method is called when the very first user calls 45 * input_open_device(). The driver must prepare the device 46 * to start generating events (start polling thread, 47 * request an IRQ, submit URB, etc.) 48 * @close: this method is called when the very last user calls 49 * input_close_device(). 50 * @flush: purges the device. Most commonly used to get rid of force 51 * feedback effects loaded into the device when disconnecting 52 * from it 53 * @event: event handler for events sent _to_ the device, like EV_LED 54 * or EV_SND. The device is expected to carry out the requested 55 * action (turn on a LED, play sound, etc.) The call is protected 56 * by @event_lock and must not sleep 57 * @grab: input handle that currently has the device grabbed (via 58 * EVIOCGRAB ioctl). When a handle grabs a device it becomes sole 59 * recipient for all input events coming from the device 60 * @event_lock: this spinlock is is taken when input core receives 61 * and processes a new event for the device (in input_event()). 62 * Code that accesses and/or modifies parameters of a device 63 * (such as keymap or absmin, absmax, absfuzz, etc.) after device 64 * has been registered with input core must take this lock. 65 * @mutex: serializes calls to open(), close() and flush() methods 66 * @users: stores number of users (input handlers) that opened this 67 * device. It is used by input_open_device() and input_close_device() 68 * to make sure that dev->open() is only called when the first 69 * user opens device and dev->close() is called when the very 70 * last user closes the device 71 * @going_away: marks devices that are in a middle of unregistering and 72 * causes input_open_device*() fail with -ENODEV. 73 * @dev: driver model's view of this device 74 * @h_list: list of input handles associated with the device. When 75 * accessing the list dev->mutex must be held 76 * @node: used to place the device onto input_dev_list 77 * @num_vals: number of values queued in the current frame 78 * @max_vals: maximum number of values queued in a frame 79 * @vals: array of values queued in the current frame 80 * @devres_managed: indicates that devices is managed with devres framework 81 * and needs not be explicitly unregistered or freed. 82 */ 83 struct input_dev { 84 const char *name; 85 const char *phys; 86 const char *uniq; 87 struct input_id id; 88 89 unsigned long propbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(INPUT_PROP_CNT)]; 90 91 unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)]; 92 unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)]; 93 unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)]; 94 unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)]; 95 unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)]; 96 unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)]; 97 unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)]; 98 unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)]; 99 unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)]; 100 101 unsigned int hint_events_per_packet; 102 103 unsigned int keycodemax; 104 unsigned int keycodesize; 105 void *keycode; 106 107 int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, 108 const struct input_keymap_entry *ke, 109 unsigned int *old_keycode); 110 int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, 111 struct input_keymap_entry *ke); 112 113 struct ff_device *ff; 114 115 unsigned int repeat_key; 116 struct timer_list timer; 117 118 int rep[REP_CNT]; 119 120 struct input_mt *mt; 121 122 struct input_absinfo *absinfo; 123 124 unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)]; 125 unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)]; 126 unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)]; 127 unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)]; 128 129 int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev); 130 void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev); 131 int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file); 132 int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value); 133 134 struct input_handle __rcu *grab; 135 136 spinlock_t event_lock; 137 struct mutex mutex; 138 139 unsigned int users; 140 bool going_away; 141 142 struct device dev; 143 144 struct list_head h_list; 145 struct list_head node; 146 147 unsigned int num_vals; 148 unsigned int max_vals; 149 struct input_value *vals; 150 151 bool devres_managed; 152 }; 153 #define to_input_dev(d) container_of(d, struct input_dev, dev)
1 /** 2 * input_register_device - register device with input core 3 * @dev: device to be registered 4 * 5 * This function registers device with input core. The device must be 6 * allocated with input_allocate_device() and all it's capabilities 7 * set up before registering. 8 * If function fails the device must be freed with input_free_device(). 9 * Once device has been successfully registered it can be unregistered 10 * with input_unregister_device(); input_free_device() should not be 11 * called in this case. 12 * 13 * Note that this function is also used to register managed input devices 14 * (ones allocated with devm_input_allocate_device()). Such managed input 15 * devices need not be explicitly unregistered or freed, their tear down 16 * is controlled by the devres infrastructure. It is also worth noting 17 * that tear down of managed input devices is internally a 2-step process: 18 * registered managed input device is first unregistered, but stays in 19 * memory and can still handle input_event() calls (although events will 20 * not be delivered anywhere). The freeing of managed input device will 21 * happen later, when devres stack is unwound to the point where device 22 * allocation was made. 23 */ 24 int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev) 25 { 26 struct input_devres *devres = NULL; 27 /* 输入事件的处理接口指针,用于和设备的事件类型进行匹配 */ 28 struct input_handler *handler; 29 unsigned int packet_size; 30 const char *path; 31 int error; 32 33 if (dev->devres_managed) { 34 devres = devres_alloc(devm_input_device_unregister, 35 sizeof(struct input_devres), GFP_KERNEL); 36 if (!devres) 37 return -ENOMEM; 38 39 devres->input = dev; 40 } 41 42 /* Every input device generates EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT events. */ 43 __set_bit(EV_SYN, dev->evbit); 44 45 /* KEY_RESERVED is not supposed to be transmitted to userspace. */ 46 __clear_bit(KEY_RESERVED, dev->keybit); 47 48 /* Make sure that bitmasks not mentioned in dev->evbit are clean. */ 49 input_cleanse_bitmasks(dev); 50 51 packet_size = input_estimate_events_per_packet(dev); 52 if (dev->hint_events_per_packet < packet_size) 53 dev->hint_events_per_packet = packet_size; 54 55 dev->max_vals = dev->hint_events_per_packet + 2; 56 dev->vals = kcalloc(dev->max_vals, sizeof(*dev->vals), GFP_KERNEL); 57 if (!dev->vals) { 58 error = -ENOMEM; 59 goto err_devres_free; 60 } 61 62 /* 63 * If delay and period are pre-set by the driver, then autorepeating 64 * is handled by the driver itself and we don't do it in input.c. 65 */ 66 if (!dev->rep[REP_DELAY] && !dev->rep[REP_PERIOD]) { 67 dev->timer.data = (long) dev; 68 dev->timer.function = input_repeat_key; 69 dev->rep[REP_DELAY] = 250; 70 dev->rep[REP_PERIOD] = 33; 71 } 72 73 if (!dev->getkeycode) 74 dev->getkeycode = input_default_getkeycode; 75 76 if (!dev->setkeycode) 77 dev->setkeycode = input_default_setkeycode; 78 79 error = device_add(&dev->dev); 80 if (error) 81 goto err_free_vals; 82 83 path = kobject_get_path(&dev->dev.kobj, GFP_KERNEL); 84 pr_info("%s as %s\n", 85 dev->name ? dev->name : "Unspecified device", 86 path ? path : "N/A"); 87 kfree(path); 88 89 error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex); 90 if (error) 91 goto err_device_del; 92 93 /* 重要:把设备挂到全局的input子系统设备链表input_dev_list上 */ 94 list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list); 95 96 /* 核心重点,input设备在增加到input_dev_list链表上之后,会查找 97 * input_handler_list事件处理链表上的handler进行匹配,这里的匹配 98 * 方式与设备模型的device和driver匹配过程很相似*/ 99 list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node) 100 input_attach_handler(dev, handler);/*遍历input_handler_list,通过input_match_device试图与每一个handler进行匹配 匹配上了就使用connect连接*/ 101 /* 102 static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler) 103 { 104 const struct input_device_id *id; 105 int error; 106 107 id = input_match_device(handler, dev); 108 if (!id) 109 return -ENODEV; 110 111 error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id); 112 if (error && error != -ENODEV) 113 pr_err("failed to attach handler %s to device %s, error: %d\n", 114 handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error); 115 116 return error; 117 } 118 */ 119 120 input_wakeup_procfs_readers(); 121 122 mutex_unlock(&input_mutex); 123 124 if (dev->devres_managed) { 125 dev_dbg(dev->dev.parent, "%s: registering %s with devres.\n", 126 __func__, dev_name(&dev->dev)); 127 devres_add(dev->dev.parent, devres); 128 } 129 return 0; 130 131 err_device_del: 132 device_del(&dev->dev); 133 err_free_vals: 134 kfree(dev->vals); 135 dev->vals = NULL; 136 err_devres_free: 137 devres_free(devres); 138 return error; 139 } 140 EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_register_device);
3.2注册handler
一般handler不需要我们自己写 内核里面已经有了很多的hanlder基本够用
下面以Evdev为例,来分析事件处理层。vim drivers/input/evdev.c
1 static const struct input_device_id evdev_ids[] = { 2 { .driver_info = 1 }, /* Matches all devices */ 3 { }, /* Terminating zero entry */ 4 }; 5 6 MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(input, evdev_ids); 7 8 static struct input_handler evdev_handler = { 9 .event = evdev_event, 10 .events = evdev_events, 11 .connect = evdev_connect, 12 .disconnect = evdev_disconnect, 13 .legacy_minors = true, 14 .minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE, 15 .name = "evdev", 16 .id_table = evdev_ids, 17 }; 18 19 static int __init evdev_init(void) 20 { 21 return input_register_handler(&evdev_handler); 22 } 23 24 static void __exit evdev_exit(void) 25 { 26 input_unregister_handler(&evdev_handler); 27 } 28 29 module_init(evdev_init); 30 module_exit(evdev_exit); 31 32 MODULE_AUTHOR("Vojtech Pavlik <vojtech@ucw.cz>"); 33 MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Input driver event char devices"); 34 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
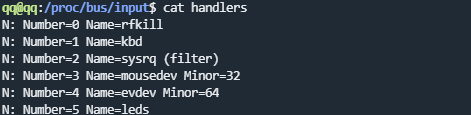
注册的handler可以在proc/bus/input/danlder中查看到
1 /** 2 * input_register_handler - register a new input handler 3 * @handler: handler to be registered 4 * 5 * This function registers a new input handler (interface) for input 6 * devices in the system and attaches it to all input devices that 7 * are compatible with the handler. 8 */ 9 int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler) 10 { 11 struct input_dev *dev; 12 int error; 13 14 error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex); 15 if (error) 16 return error; 17 18 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list); 19/* `重要`:把设备处理器挂到全局的input子系统设备链表input_handler_list上 */20 list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list); 21/*遍历input_dev_list,试图与每一个input_dev进行匹配*/22 list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node) 23 input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
/*static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler) { const struct input_device_id *id; int error;<span class="token comment">/* 利用handler->id_table和dev进行匹配*/ id <span class="token operator">= <span class="token function">input_match_device<span class="token punctuation">(handler<span class="token punctuation">, dev<span class="token punctuation">)<span class="token punctuation">; <span class="token keyword">if <span class="token punctuation">(<span class="token operator">!id<span class="token punctuation">) <span class="token keyword">return <span class="token operator">-ENODEV<span class="token punctuation">; <span class="token comment">/*匹配成功,则调用handler->connect函数进行连接*/ error <span class="token operator">= handler<span class="token operator">-><span class="token function">connect<span class="token punctuation">(handler<span class="token punctuation">, dev<span class="token punctuation">, id<span class="token punctuation">)<span class="token punctuation">; <span class="token keyword">if <span class="token punctuation">(error <span class="token operator">&& error <span class="token operator">!= <span class="token operator">-ENODEV<span class="token punctuation">) <span class="token function">pr_err<span class="token punctuation">(<span class="token string">"failed to attach handler %s to device %s, error: %d\n"<span class="token punctuation">, handler<span class="token operator">->name<span class="token punctuation">, <span class="token function">kobject_name<span class="token punctuation">(<span class="token operator">&dev<span class="token operator">->dev<span class="token punctuation">.kobj<span class="token punctuation">)<span class="token punctuation">, error<span class="token punctuation">)<span class="token punctuation">; <span class="token keyword">return error<span class="token punctuation">;
}
*/
24
25 input_wakeup_procfs_readers();
26
27 mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
28 return 0;
29 }
30 EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_register_handler);
这个过程和注册dev及其相似
3.3 handler的connect函数
1 static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, 2 const struct input_device_id *id) 3 { 4 struct evdev *evdev; 5 int minor; 6 int dev_no; 7 int error; 8 9 /*申请一个新的次设备号*/ 10 minor = input_get_new_minor(EVDEV_MINOR_BASE, EVDEV_MINORS, true); 11 12 /* 这说明内核已经没办法再分配这种类型的设备了 */ 13 if (minor < 0) { 14 error = minor; 15 pr_err("failed to reserve new minor: %d\n", error); 16 return error; 17 } 18 19 /* 开始给evdev事件层驱动分配空间了 */ 20 evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL); 21 if (!evdev) { 22 error = -ENOMEM; 23 goto err_free_minor; 24 } 25 26 /* 初始化client_list列表和evdev_wait队列 */ 27 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list); 28 spin_lock_init(&evdev->client_lock); 29 mutex_init(&evdev->mutex); 30 init_waitqueue_head(&evdev->wait); 31 evdev->exist = true; 32 33 dev_no = minor; 34 /* Normalize device number if it falls into legacy range */ 35 if (dev_no < EVDEV_MINOR_BASE + EVDEV_MINORS) 36 dev_no -= EVDEV_MINOR_BASE; 37 38 /*设置设备节点名称,/dev/eventX 就是在此时设置*/ 39 dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", dev_no); 40 41 /* 初始化evdev结构体,其中handle为输入设备和事件处理的关联接口 */ 42 evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev); 43 evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev); 44 evdev->handle.handler = handler; 45 evdev->handle.private = evdev; 46 47 /*设置设备号,应用层就是通过设备号,找到该设备的*/ 48 evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, minor); 49 evdev->dev.class = &input_class; 50 evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev; 51 evdev->dev.release = evdev_free; 52 device_initialize(&evdev->dev); 53 54 /* input_dev设备驱动和handler事件处理层的关联,就在这时由handle完成 */ 55 error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle); 56 if (error) 57 goto err_free_evdev; 58 59 cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops); 60 evdev->cdev.kobj.parent = &evdev->dev.kobj; 61 error = cdev_add(&evdev->cdev, evdev->dev.devt, 1); 62 if (error) 63 goto err_unregister_handle; 64 65 /*将设备加入到Linux设备模型,它的内部将找到它的bus,然后让它的bus 66 给它找到它的driver,在驱动或者总线的probe函数中,一般会在/dev/目录 67 先创建相应的设备节点,这样应用程序就可以通过该设备节点来使用设备了 68 ,/dev/eventX 设备节点就是在此时生成 69 */ 70 error = device_add(&evdev->dev); 71 if (error) 72 goto err_cleanup_evdev; 73 74 return 0; 75 76 err_cleanup_evdev: 77 evdev_cleanup(evdev); 78 err_unregister_handle: 79 input_unregister_handle(&evdev->handle); 80 err_free_evdev: 81 put_device(&evdev->dev); 82 err_free_minor: 83 input_free_minor(minor); 84 return error; 85 }
over
4.应用层的角度分析到底层
evdev_read()---------------------------》wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait,client->packet_head != client->tail || !evdev->exist || client->revoked);等待evdev->wait唤醒
evdev_pass_values-----------------------》wake_up_interruptible(&evdev->wait);
evdev_events---------------------------》evdev_pass_values(client, vals, count, ev_time);
evdev_event----------------------------》evdev_events(handle, vals, 1);
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.legacy_minors = true,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
input_to_handler-----------------------------》 if (handler->events)
handler->events(handle, vals, count);
else if (handler->event)
for (v = vals; v != vals + count; v++)
handler->event(handle, v->type, v->code, v->value);
input_pass_values--------------------------------》count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
input_handle_event----------------------------》input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
input_event----------------------------------------》input_handle_event(dev, type, code, value);
显然,就是input_dev通过输入核心为驱动层提供统一的接口,input_event,来向事件处理层上报数据并唤醒。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号