(四) 线程间的协作 wait() 、 notify() 、 notifyAll()
线程之间的协作
用一个手枪打弹和装弹的例子,废话不多,上代码
package com.monco.ch1.wn;
/**
* @author monco
* @date 2020/5/21
* @description: 给手枪装子弹 打子弹
*/
public class Gun {
private Integer zd = 0;
/**
* 装子弹
*/
public synchronized void put() {
while (zd >= 20) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 发现子弹已经装满了,当前子弹剩余=" + zd);
wait();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
zd++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 装入子弹一枚,当前子弹剩余=" + zd);
// 唤醒其他线程
notifyAll();
}
/**
* 打子弹
*/
public synchronized void get() {
while (zd <= 0) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 发现子弹已经射完了,当前子弹剩余=" + zd);
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
zd--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 发射一枚子弹,当前子弹剩余=" + zd);
notifyAll();
}
/**
* 消费者打枪
*/
static class Consumer implements Runnable {
Gun gun;
public Consumer(Gun gun) {
this.gun = gun;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
gun.get();
try {
Thread.sleep(6);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 生产者 装子弹
*/
static class Product implements Runnable {
Gun gun;
public Product(Gun gun) {
this.gun = gun;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
gun.put();
try {
Thread.sleep(6);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gun gun = new Gun();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
new Thread(new Product(gun), "生产者" + i).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
new Thread(new Consumer(gun), "消费者" + i).start();
}
}
}
测试结果
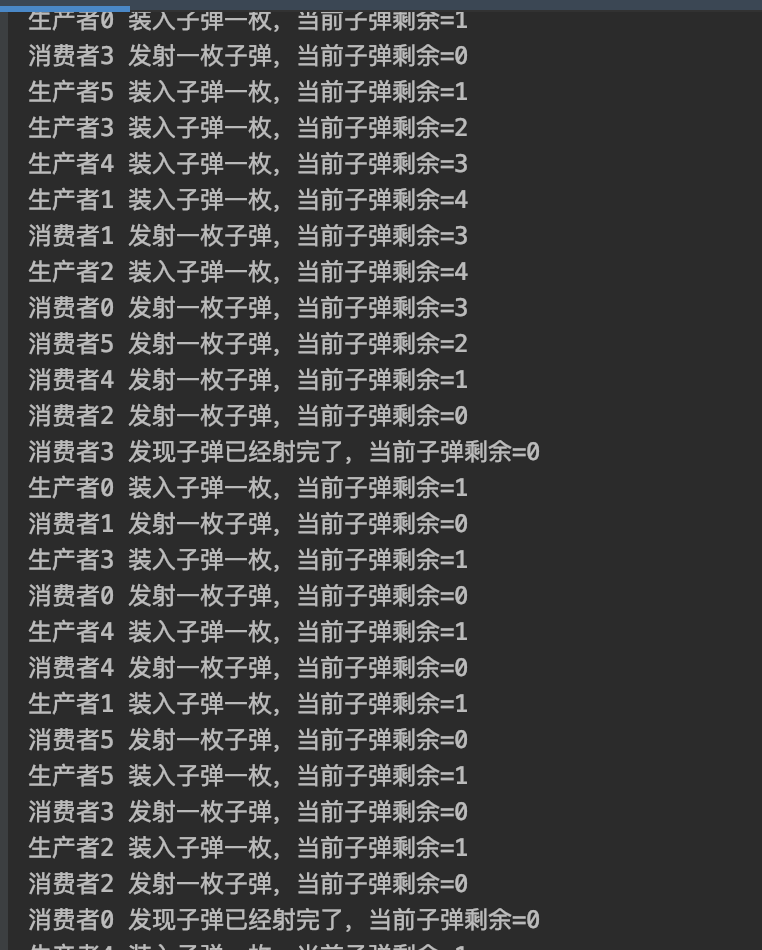
代码结论
我们都知道 wait() 、 notify() 、notifyAll() 是典型的等待通知机制,可以保证使多线程下的线程按照一定顺序执行。
等待/通知 遵循范式
synchronized(对象){
while(条件不满足){
对象.wait();
}
处理相应的业务逻辑
}
synchronized(对象){
改变条件
notifyAll();
}
方法总比困难多。
思想重于实现。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号