选择排序
选择排序是一种更加简单直观的排序方法。
需求:
- 排序前:
- 排序后:
排序原理:
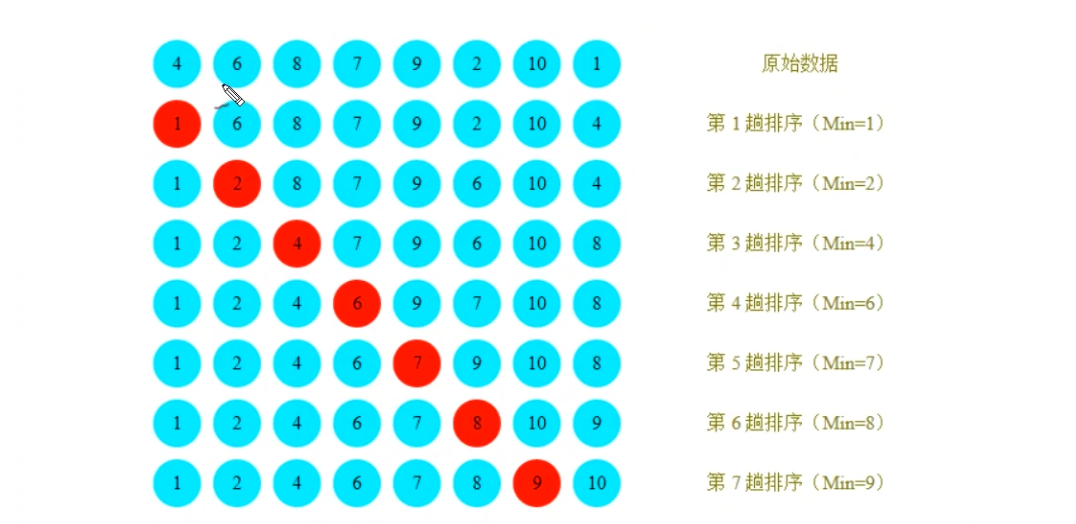
1.每一次遍历的过程中,都假定第一个索引处的元素是最小值,和其他索引处的值依次进行比较,如果当前索引处的值大于其他某个索引处的值,则假定其他某个索引出的值为最小值,最后可以找到最小值所在的索引
2.交换第一个索引处和最小值所在的索引处的值
选择排序API设计:
| 类名 | Selection |
|---|---|
| 构造方法 | Selection():创建Selection对象 |
| 成员方法 | 1.public static void sort(Comparable[] a):对数组内的元素进行排序 |
| 2.private static boolean greater(Comparable v,Comparable w):判断v是否大于w | |
| 3.private static void exch(Comparable[] a,int i,int j):交换a数组中,索引i和索引j处的值 |
选择排序的代码实现:
//选择排序
public class Selection {
/*
对数组a中的元素进行排序
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (greater(a[minIndex], a[j])) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
exch(a, i, minIndex);
}
}
/*
比较v元素是否大于w元素
*/
private static boolean greater(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) > 0;
}
/*
数组元素i和j交换位置
*/
private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
Comparable temp;
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
// 测试代码
public class SelectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//原始数据
Integer[] a = {4, 6, 8, 7, 9, 2, 10, 1};
Selection.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//{1,2,4,5,7,8,9,10}
}
}
选择排序的时间复杂度分析
-
选择排序使用了双层for循环,其中外层循环完成了数据交换,内层循环完成了数据比较,所以我们分别统计数据
-
交换次数和数据比较次数:
-
数据比较次数:(N-1)+(N-2)+(N-3)+...+2+1=((N-1)+1)*(N-1)/2=N^2/2-N/2
-
数据交换次数:N-1
-
时间复杂度:N2/2-N/2+(N-1)=N2/2+N/2-1;
-
根据大O推导法则,保留最高阶项,去除常数因子,时间复杂度为O(N^2);




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号