003 Django request请求对象
目录
1 django 的wsgi的功能就是接收响应http的
wsgi文件: 封装了socket,功能是
1 解析请求数据,并且把解析的数据封装成request 以实际参数的形式传给urls ,触发视图函数,传入参数到函数内
2.接收到响应数据后,封装成http的响应体,响应头,用socker 转发给请求端
wsgi相当于 网络7层协议中 封包解包的功能
无论任何的客户端(游览器、postman )去请求服务的地址,必须是满足条件的
1、请求头(请求方式 请求路径 请求的connet-type 编码格式 时间等)
2、请求体(数据)
content-type = application/x-www-form-urlencoded 简称url_encoded
django request.post 只能处理 请求头的 connect-type= urlencoded 的类型 <也就是 user=123&pwd=456 这种类型>
# 所有的请求数据 会被 request的接收,那么request的属性和功能就能取出所有的请求数据。
2、 get 请求
一 游览器客户端
游览器地址栏 127.0.0.1:8000 回车
使用 请求类型是 url-encoded (默认)
get 请求携带参数 , 或者使用postman
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/?name="test"&password="123"
在游览器的地址栏中 把参数拼接到uri的地址中发送的。
使用from表单携带参数
<form action="http://127.0.0.1:8000/xx/" method="get" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" >
<input type="text" name="user" >
<input type="password" name="pwd" >
<input type="submit" >
# method 修改请求方式
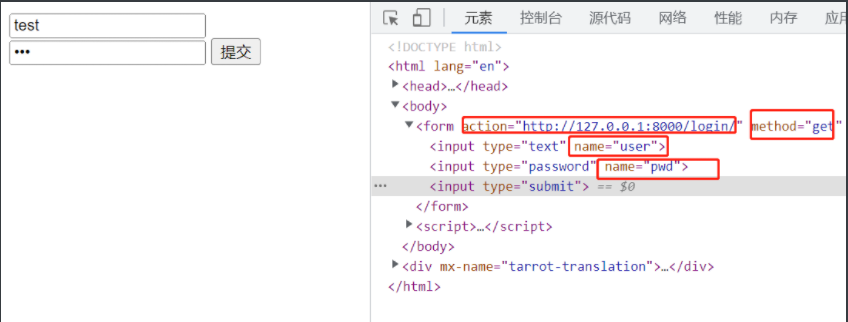
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/?user=test&pwd=123 # 拼接了get请求
request.get 字典信息也存进去了。
<QueryDict: {'user': ['test'], 'pwd': ['123']}>
3、 post 请求
post请求
结论:get请求 地址栏中有参数。
post请求 地址栏中没有参数 使用 form表单 或者 postman 进行发送数据
通过form表单提交
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://127.0.0.1:8000/xx/" method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" >
/* form 表单中enctype 的编码格式默认就是 url_encoded 的格式 */
<input type="text" name="user" >
<input type="password" name="pwd" >
<input type="submit" >
</form>
</body>
</html>
print(request.POST) # 打印POST请求的字典
[17/May/2022 15:25:49] "POST /xx/ HTTP/1.1" 200 8
<QueryDict: {'user': ['123'], 'pwd': ['4444']}>
postman 提交 json 格式的数据 ,request 取值操作。
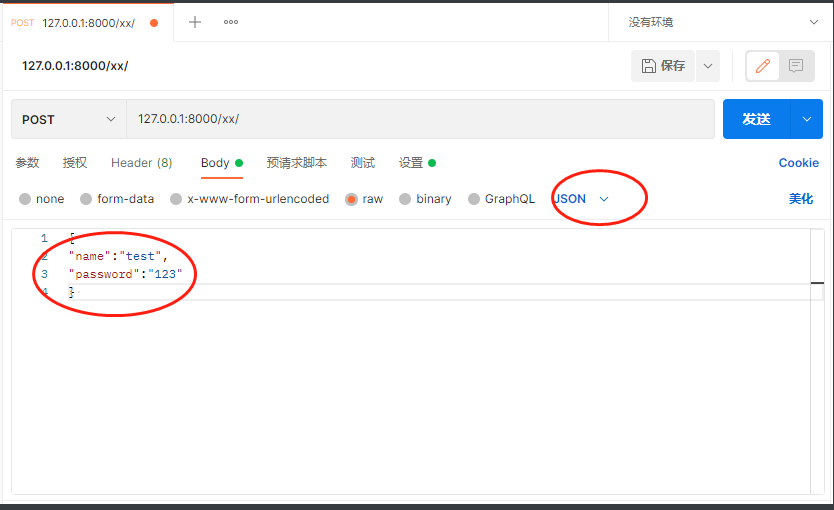
注意 字典的的元素是使用的 双引号 和 : 不要写等号
'''
print(request.method)
print(request.POST)
print(request.body)
'''
[17/May/2022 15:37:17] "POST /xx/ HTTP/1.1" 200 8
POST
<QueryDict: {}> #post 的字典里是没有数据的,无法取出
b'{\r\n"name"="tets",\r\n"password"="123"\r\n} ' #body 体内是有数据的 字节数据 需要转码
总结 请求方法 和取值方式
print(request.GET) 打印get请求的请求体
print(request.POST) 打印POST请求的请求体
get请求 encoded类型 body有值 字节型 POST 没有数据
POST 请求 encoded类型 body有值 字节型 ,POST也有值
get请求 json类型 POST 没有数据 ,body有值 字节型
POST请求 json类型 POST 没有数据 ,body有值 字节型
POST取值 <QueryDict: {'name': ['tets'], 'pwd': ['123']}>
print(request.POST.get("name")) # value 是列表,如果是一个值,就取值第一个元素
如果列表多个值 ,getlist 取多个值。
print(request.POST.get("pwd"))
现在需要把 request.body 的源数据,转成字典,提供使用。一般都是使用在请求端发出的json数据
data = json.loads(request.body.decode())
print(data["name"])这样 调用data 这个字典即可。
# request.GET.get('name'),
# request.POST.get('name') 效果是一样的。
4、django request的属性和方法
print(request.method) # 游览器的请求方式 get 还是 post
print(request.path) # 游览器的请求的url路径/
print(request.get_full_path()) # 能拿到全部的路径,且能拿到数据体的内容
# 请求 http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/?a=1 可以获取到 /login/?a=1
print(request.META) # 游览器的信息和系统信息,django 把他封装到一个字典中去了。、
print(request.META.get('HTTP_HOST')) # 可以通过get key值取出vlaue
# 后台代码 取到到的前台的数据全部都是通过字典里的key 取到的。
print(request.GET)
# 对应着Get 请求体的数据, 所以get请求(使用postman) ,
# request 会把数据体封装到字典内 <QueryDict: {'name ': ['test'], 'password': ['1233']}>
print(request.POST)
# 对应着POST 请求体的数据 ,所以post请求的类型是url-encoded
# request 才会把数据体封装到字典内 <QueryDict: {'a': ['1']}>
# 所以request.POST 只处理url-encoded的编码格式,其他类型忽略
print(request.body) # 请求体的源数据 ,所以无论哪种请求方式或者请求的数据体的编码格式 request.body 都能捕获到。
二 request 响应对象
1、响应基础类 Httpresponse
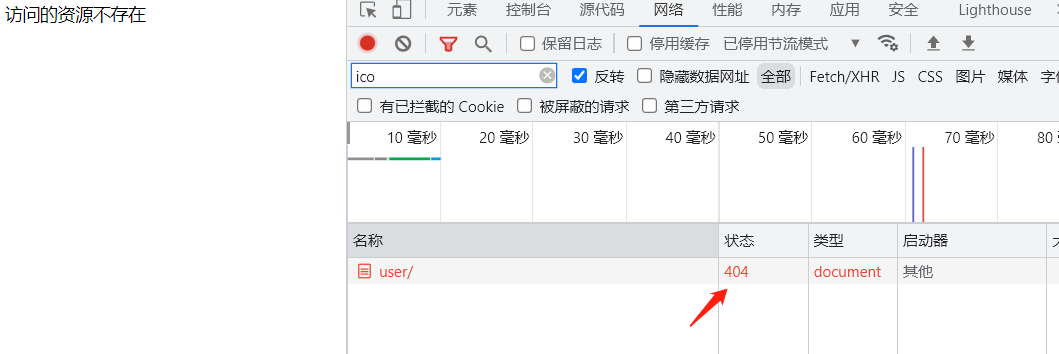
响应状态码
def index(request):
return HttpResponse('访问的资源不存在',status=404)
# 响应状态码 更改成404
响应类型
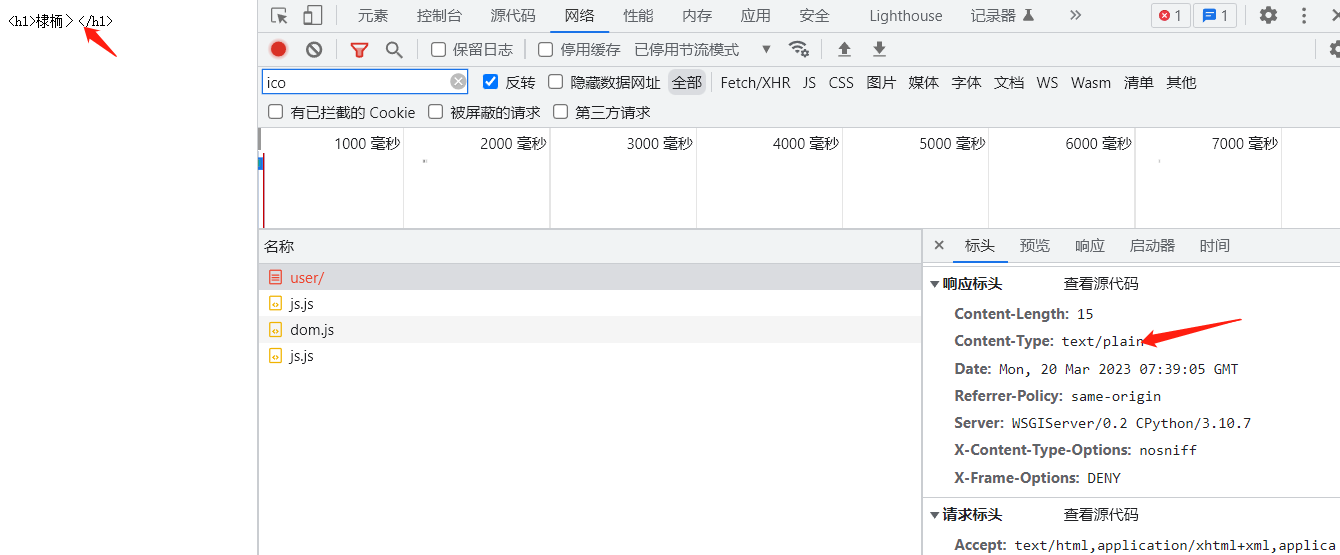
响应类型 默认是content-type html/text
如果更改响应的类型是 text/plain,就不会渲染html了
def index(request):
return HttpResponse('<h1>首页</h1>',status=404,content_type='text/plain')
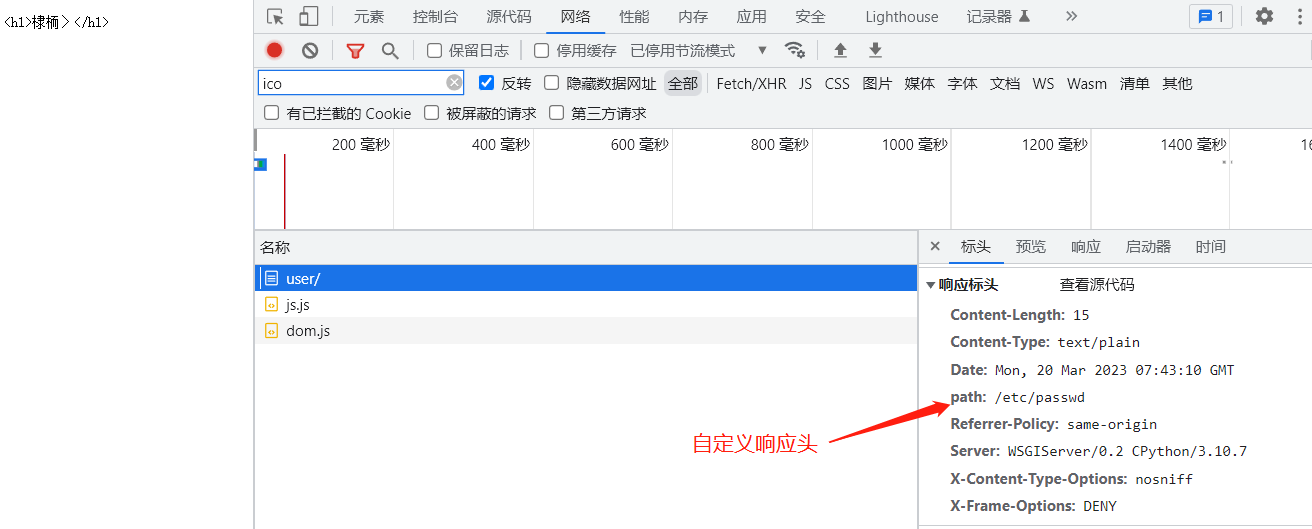
响应头
def index(request):
res = HttpResponse('<h1>首页</h1>',content_type='text/plain')
res["path"]='/etc/passwd'
return res
2 request jsonResponse
book = {"title":"世界简史","moneny":"500"}
'''
{
"title": "世界简史",
"moneny": "500"
}
'''
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(book,ensure_ascii=False),content_type="application/json")
默认情况下,响应数据数据体是的content-type:text/html,服务端返回给客户端的是json格式的数据的话,需要序列化成字符串。指定响应类型为json,请求端才能解析成json,
使用JsonResponse 封装了json的序列化功能,直接把字典作为参数,传给函数执行即可,django封装好响应json数据的方式
同时列表的响应数据也支持,使用一个safe的布尔值,来执行不同的方法
# JsonResponse 解析一个列表,
s = [{"1":"1"},{"1":"1"}]
return JsonResponse(s,safe=False)
3 render 响应模板文件
def index(request):
import time
date = time.strftime('%X')
return render(request, "app01/index.html", {"html_date":date})
# request 响应体 ,模板文件,和变量字典
客户端请求一个路径, 服务端响应一个数据,模板文件中嵌套了动态的数据,redner函数做了数据和html文件中变量的映射。
4 readirect 重定向
def index(request):
import time
date = time.strftime('%X')
return render(request, "app01/index.html", {"html_date":date})
def login(request):
return render(request,"app01/login.html")
def auth(request):
name = request.POST.get('user')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
print(name,pwd)
if name == 'root' and pwd =='123':
# return HttpResponse('登录成功')
return redirect('/user/')
return redirect('/user/login')
'''
重定向的含义就是
1.客户端的请求,服务端校验完数据后,让客户端重新发起新的请求的过程,请求的地址放在响应头的location中,默认请求的IP和端口号不变,uri是location的内容。重定向过程中,客户端实际发起了2次请求,接收了2次请求,服务端同样响应了2次,给用户的感觉是一次请求。
'''
重定向 返回阈值
1、 返回location目录,让游览器再发一次请求 --- 如果页面有动态数据的情况下,直接重定向
2、 直接返回一个html页面 --- 如果是静态页面的情况下,返回页面
def auth(request):
'''
登录验证的函数
登录成功 重定向到首页
登录失败 返回登录页面 添加登录报错信息,render
:param request:
:return:
'''
name = request.POST.get('user')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
print(name, pwd)
if name == 'root' and pwd == '123':
# return HttpResponse('登录成功')
return redirect('/user/')
msg = "用户名或者密码错误"
# 返回页面中嵌入自定义信息
return render(request, "app01/login.html", {'html_result':msg})
form 优化
<form action="/user/auth" method="post">
用户名: <input type="text" name="user">
密码: <input type="password" name="pwd">
<input type="submit"><span>{{ html_result }}</span>
action="http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/auth" 可以简写成 :action="/user/auth"
如果当前的页面的路径是http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/login ,action='/user/auth'
action可以根据当前路径的相对路径拼接地址,action="auth",那么自动拼接成"/user/auth",
有/根路径,那么访问的是绝对路径,
没有/ 路径,以当前页面的相对路径拼接
url 路径 排除故障问题
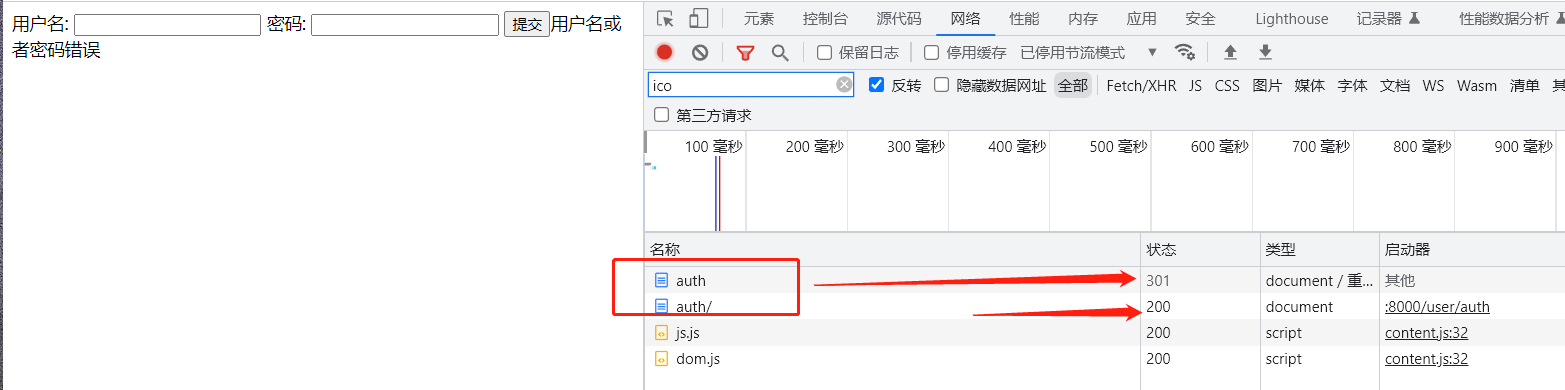
APPEND_SLASH=False : 开启重定向 ,url自动拼接 / 的功能
如果服务端有/, path('auth/',views.auth), 那么客户端访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/auth 客户端访问的路径缺失/ 时 ,不报错,重定向添加一个/ ,http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/auth/ 继续访问。
但是服务端 path('auth',views.auth) 没有/ 时 , http://127.0.0.1:8000/user/auth/ 访问报错。
生产环境,所有的配置路径必须加 /
urlpatterns = [
# path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include(app01.urls)),
path('user/', include(app01.urls)),
]
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.login),
path('auth/',views.auth),
path('index/',views.index),
]
def auth(request):
return redirect('/user/index/') # 重定向也要加/
# 自动补充/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号