4-1-1 Spring基础-Spring IoC容器与Bean管理
IoC控制反转
IoC控制反转,全称Inverse of Control,是一种设计理念
由代理人来创建与管理对象,消费者通过代理人来获取对象
IoC的目的是降低程序与程序之间直接耦合
为什么要IoC控制反转
对象直接引用导致对象硬性关联,程序难以维护
例如:顾客直接采购苹果
加入IoC对象统一管理,让对象关联变为弱耦合
例如:果商冷冻仓库批发苹果,然后快递给顾客
DI依赖注入
IoC是设计理念,是现代程序设计遵循的标准,是宏观目标
DI(Dependency Injection)是具体技术实现,是微观实现
DI在Java中利用反射技术实现对象注入(Injection)
Spring的含义
狭义的Spring是指Spring框架(Spring Fremework)
广义的Spring是指Spring生态体系
狭义的Spring框架
Spring框架是企业开发复杂性的一站式解决方案
Spring框架的核心是IoC容器与AOP面向切面编程
Spring IoC负责创建与管理系统对象,并在此基础上扩展功能
Spring IoC容器职责
对象的控制权交由第三方统一管理(IoC)控制反转
利用Java反射技术实现运行时对象创建与关联(DI依赖注入)
基于配置提高应用程序的可维护性与扩展性
Spring IoC的简单Demo
工程目录
pom.xml文件如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 7 <groupId>com.mingm.spring</groupId> 8 <artifactId>ioc</artifactId> 9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> 10 <repositories> 11 <repository> 12 <id>aliyun</id> 13 <name>aliyun</name> 14 <url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public</url> 15 </repository> 16 </repositories> 17 <dependencies> 18 <dependency> 19 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 20 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> 21 <version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version> 22 </dependency> 23 </dependencies> 24 25 </project>
applicationContext.xml文件如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 6 <!-- 在IoC容器启动时,自动由Spring实例化Apple对象,取名sweetApple放入到容器中 --> 7 <bean id="sweetApple" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 8 <property name="title" value="红富士"></property> 9 <property name="origin" value="欧洲"></property> 10 <property name="color" value="红色"></property> 11 </bean> 12 13 <bean id="sourApple" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 14 <property name="title" value="青苹果"></property> 15 <property name="origin" value="中亚"></property> 16 <property name="color" value="绿色"></property> 17 </bean> 18 19 <bean id="softApple" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 20 <property name="title" value="金帅"></property> 21 <property name="origin" value="中国"></property> 22 <property name="color" value="黄色"></property> 23 </bean> 24 25 <bean id="rdApple" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 26 <property name="title" value="蛇果"></property> 27 <property name="origin" value="美国"></property> 28 <property name="color" value="红色"></property> 29 </bean> 30 31 <bean id="lily" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Child"> 32 <property name="name" value="莉莉"/> 33 <property name="apple" ref="softApple"/> 34 </bean> 35 36 <bean id="andy" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Child"> 37 <property name="name" value="安迪"/> 38 <property name="apple" ref="rdApple"/> 39 </bean> 40 41 <bean id="luna" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Child"> 42 <property name="name" value="露娜"/> 43 <property name="apple" ref="sweetApple"/> 44 </bean> 45 </beans>
SpringApplication.java用于启动Spring IoC容器
1 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple; 2 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Child; 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class SpringApplication { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 //创建Spring IoC容器,并根据配置文件在容器中实例化对象 9 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); 10 Apple sweetApple = context.getBean("sweetApple" , Apple.class); 11 System.out.println(sweetApple.getTitle()); 12 //从IoC容器中提取beanId=lily的对象 13 Child lily = context.getBean("lily", Child.class); 14 lily.eat(); 15 Child andy = context.getBean("andy", Child.class); 16 andy.eat(); 17 Child luna = context.getBean("luna", Child.class); 18 luna.eat(); 19 20 } 21 }
初始化IoC容器
三种配置方式
基于XML配置Bean
基于注解配置Bean
基于Java代码配置Bean
Xml方式创建IoC容器
核心代码如下:
1 //创建Spring IoC容器,并根据配置文件在容器中实例化对象 2 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
实例化Bean的三种方式
基于构造方法对象实例化
基于静态工厂实例化
基于工厂实例方法实例化
示例工程
工程目录
实体类
1 package com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity; 2 3 public class Apple { 4 private String title; 5 private String color; 6 private String origin; 7 private Float price; 8 9 public Apple() { 10 System.out.println("Apple对象已创建," + this); 11 } 12 13 public Apple(String title, String color, String origin) { 14 System.out.println("通过带参构造方法创建对象, " + this); 15 this.title = title; 16 this.color = color; 17 this.origin = origin; 18 } 19 20 public Apple(String title, String origin ,String color, Float price) { 21 System.out.println("通过带参构造方法创建对象, " + this); 22 this.title = title; 23 this.color = color; 24 this.origin = origin; 25 this.price = price; 26 } 27 28 public String getTitle() { 29 return title; 30 } 31 32 public void setTitle(String title) { 33 this.title = title; 34 } 35 36 public String getColor() { 37 return color; 38 } 39 40 public void setColor(String color) { 41 this.color = color; 42 } 43 44 public String getOrigin() { 45 return origin; 46 } 47 48 public void setOrigin(String origin) { 49 this.origin = origin; 50 } 51 }
1 package com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity; 2 3 public class Child { 4 private String name; 5 private Apple apple; 6 7 public Child(){ 8 9 } 10 11 public Child(String name, Apple apple) { 12 this.name = name; 13 this.apple = apple; 14 } 15 16 public String getName() { 17 return name; 18 } 19 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 24 public Apple getApple() { 25 return apple; 26 } 27 28 public void setApple(Apple apple) { 29 this.apple = apple; 30 } 31 32 public void eat(){ 33 System.out.println(name + "吃到了" + apple.getOrigin() + "种植的" + apple.getTitle()); 34 } 35 }
工厂方法对象
1 package com.mingm.spring.ioc.factory; 2 3 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple; 4 5 /** 6 * 静态工厂通过静态方法创建对象,隐藏创建对象的细节 7 */ 8 public class AppleStaticFactory { 9 public static Apple createSweetApple(){ 10 //logger.info("") 11 Apple apple = new Apple(); 12 apple.setTitle("红富士"); 13 apple.setOrigin("欧洲"); 14 apple.setColor("红色"); 15 return apple; 16 } 17 }
1 package com.mingm.spring.ioc.factory; 2 3 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple; 4 5 /** 6 * 工厂实例方法创建对象是指IoC容器对工厂类进行实例化并调用对应的实例方法创建对象的过程 7 */ 8 public class AppleFactoryInstance { 9 public Apple createSweetApple(){ 10 Apple apple = new Apple(); 11 apple.setTitle("红富士"); 12 apple.setOrigin("欧洲"); 13 apple.setColor("红色"); 14 return apple; 15 } 16 }
applicationContext.xml文件配置
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 6 <!--bean标签默认通过默认构造方法创建对象--> 7 <bean id="apple1" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 8 9 </bean> 10 <!--使用带参构造方法实例化对象--> 11 <bean name="apple2" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 12 <constructor-arg name="title" value="红富士"/> 13 <constructor-arg name="color" value="红色"/> 14 <constructor-arg name="origin" value="欧洲"/> 15 <constructor-arg name="price" value="19.8"/> 16 </bean> 17 18 <bean id="apple3" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 19 <constructor-arg index="0" value="红富士"/> 20 <constructor-arg index="1" value="欧洲"/> 21 <constructor-arg index="2" value="红色"/> 22 <constructor-arg index="3" value="19.8"/> 23 </bean> 24 25 <!--利用静态工厂获取对象--> 26 <bean id="apple4" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.factory.AppleStaticFactory" 27 factory-method="createSweetApple"/> 28 29 <!--利用工厂实例方法获取对象--> 30 <bean id="factoryInstance" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.factory.AppleFactoryInstance"/> 31 <bean id="apple5" factory-bean="factoryInstance" factory-method="createSweetApple"/> 32 </beans>
从IoC容器获取Bean
1 //第一种方法 推荐,符合现在java编码规范 2 Apple apple1 = context.getBean("apple1", Apple.class); 3 //第二种方法 4 Apple apple2 = (Apple)context.getBean("apple2");
id与name属性相同点和区别
相同点:
1.bean id与name都是设置对象在IoC容器的唯一标识
2.两者在同一配置文件中都不允许重复
3.两者允许在多个配置文件中出现重复,新对象覆盖旧对象
1 //初始化多个配置文件,如果两个配置文件有共同的id或name,那么获取bean会从后一个配置文件中获取,新对象覆盖旧对象 2 String[] configLocations = new String[]{"classpath:applicationContext.xml","classpath:applicationContext-1.xml"}; 3 //初始化IoC容器并实例化对象 4 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configLocations);
区别:
1.id更为严格,一次只能定义一个对象标识
2.name更为宽松,一次允许定义多个对象标识
1 <bean name="apple2,apple7" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 2 <constructor-arg name="title" value="红富士2号"/> 3 <constructor-arg name="color" value="红色"/> 4 <constructor-arg name="origin" value="欧洲"/> 5 <constructor-arg name="price" value="29.8"/> 6 </bean>
3.id与name命名要有意义,按驼峰命名书写
路径表达式
加载单个配置文件
1 //创建Spring IoC容器,并根据配置文件在容器中实例化对象 2 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
classpath指的就是类路径
| 表达式实例 | 说明 |
| classpath:config.xml | 扫描classpath根路径下(不包含jar)的config.xml |
| classpath:com/mingm/config.xml | 扫描classpath根路径下(不包含jar)com.mingm包中的config.xml |
| classpath*:com/mingm/config.xml | 扫描classpath根路径下(包含jar)com.mingm包中的config.xml |
| classpath:config-*.xml | 扫描classpath根路径下(不包含jar)所有以config-开头的xml文件 |
| classpath:com/**/config.xml | 扫描classpath根路径下(不包含jar)com包(包含任何子包)的config.xml |
| file:c/config.xml | 扫描c盘根路径下的config.xml |
对象依赖注入
依赖注入是指运行时将容器内对象利用反射赋值给其他对象的操作
基于setter方法注入对象
基于构造方法注入对象(前文已经说明)
基于setter方法注入对象
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 6 <bean id="sweetApple" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 7 <!-- IoC容器自动利用反射机制运行时调用setXXX方法为属性赋值 --> 8 <property name="title" value="红富士"/> 9 <property name="color" value="红色"/> 10 <property name="origin" value="欧洲"/> 11 <property name="price" value="19.8"/> 12 </bean> 13 14 <bean id="lily" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Child"> 15 <property name="name" value="莉莉"/> 16 <!-- 利用ref注入依赖对象 --> 17 <property name="apple" ref="sweetApple"/> 18 </bean> 19 20 <bean id="sourApple" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Apple"> 21 <property name="title" value="青苹果"/> 22 <property name="color" value="绿色"/> 23 <property name="origin" value="中亚"/> 24 <property name="price" value="9.8"/> 25 </bean> 26 27 <bean id="andy" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Child"> 28 <constructor-arg name="name" value="安迪"/> 29 <constructor-arg name="apple" ref="sourApple"/> 30 </bean> 31 32 </beans>
注入集合对象
注入List
1 <bean id="company" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Company"> 2 <property name="rooms"> 3 <list> 4 <!-- 注入引用对象用ref --> 5 <value>2001-总裁办</value> 6 <value>2003-总经理办公室</value> 7 <value>2010-研发部会议室</value> 8 <value>2010-研发部会议室</value> 9 </list> 10 </property> 11 </bean>
注入Set
1 <bean id="company" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Company"> 2 <property name="rooms"> 3 <set> 4 <!-- 注入引用对象用ref --> 5 <value>2001-总裁办</value> 6 <value>2003-总经理办公室</value> 7 <value>2010-研发部会议室</value> 8 <value>2010-研发部会议室</value> 9 </set> 10 </property> 11 </bean>
注入Map
1 <bean id="company" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Company"> 2 <property name="computers"> 3 <map> 4 <entry key="dev-88172" value-ref="c1"/> 5 <entry key="dev-88173"> 6 <bean class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Computer"> 7 <constructor-arg name="brand" value="联想"/> 8 <constructor-arg name="type" value="笔记本"/> 9 <constructor-arg name="sn" value="1280258012"/> 10 <constructor-arg name="price" value="5060"/> 11 </bean> 12 </entry> 13 </map> 14 </property> 15 </bean>
注入Properties
1 <bean id="company" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Company"> 2 <property name="info"> 3 <props> 4 <prop key="phone">010-12345678</prop> 5 <prop key="address">北京市朝阳区XX路XX大厦</prop> 6 <prop key="website">http://www.xxx.com</prop> 7 </props> 8 </property> 9 </bean>
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); Company company = context.getBean("company", Company.class); System.out.println(company); String website = company.getInfo().getProperty("website"); System.out.println(website);
查看容器内对象
1 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Company; 2 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Computer; 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class SpringApplication { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); 9 //获取容器内所有beanId数组 10 String[] beanNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames(); 11 for (String beanName:beanNames){ 12 System.out.println(beanName); 13 System.out.println("类型:" + context.getBean(beanName).getClass().getName()); 14 System.out.println("内容:" + context.getBean(beanName)); 15 } 16 17 Computer computer = context.getBean("com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Computer", Computer.class); 18 System.out.println(computer.getBrand()); 19 Computer computer1 = context.getBean("com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Computer#1", Computer.class); 20 System.out.println(computer1.getBrand()); 21 } 22 }
bean对象的作用域
bean scope属性
bean scope属性用于决定对象何时被创建与作用范围
bean scope配置将影响容器内对象的数量
默认情况下bean会在IoC容器创建后自动实例化,全局唯一
scope用法
1 <bean id="userDao" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.dao.UserDao" scope="prototype"/>
bean scope属性清单
| scope属性 | 说明 |
| singleton | 单例(默认值),每一个容器有且只有唯一的实例,实例被全局共享 |
| prototype | 多例,每次使用都是创建一个实例 |
| request | web环境下,每一次独立请求存在唯一实例 |
| session | web环境下,每一个session存在唯一实例 |
| application | web环境下,ServletContext存在唯一实例 |
| websocket | web环境下,WebSocket连接中存在唯一实例 |
singleton与prototype
singleton:
1.在容器中是单例多线程执行,存在线程安全风险,所以该实例不能存在有状态的对象
2.被singleton修饰的bean会在IoC容器启动时实例化
protoytype:
1.在容器中多实例,占用更多资源,不存在线程安全问题
2.被prototype修饰的bean会在getBean()或者对象注入时实例化
bean生命周期

注意:对象执行构造方法时,该对象没有注入属性值,只有IoC容器为对象注入属性,对象调用init-method初始化方法对象才完成初始化
代码举例
对象实例
1 package com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity; 2 3 public class Order { 4 private Float price; 5 private Integer quantity; 6 private Float total; 7 8 public Order(){ 9 System.out.println("创建Order对象," + this); 10 } 11 12 public void init(){ 13 System.out.println("执行init()方法"); 14 total = price * quantity; 15 } 16 public void pay(){ 17 System.out.println("订单金额为:" + total); 18 } 19 public Float getPrice() { 20 return price; 21 } 22 23 public void setPrice(Float price) { 24 System.out.println("设置price:" + price); 25 this.price = price; 26 } 27 28 public Integer getQuantity() { 29 return quantity; 30 } 31 32 public void setQuantity(Integer quantity) { 33 System.out.println("设置quantity:" + quantity); 34 this.quantity = quantity; 35 } 36 37 public Float getTotal() { 38 return total; 39 } 40 41 public void setTotal(Float total) { 42 this.total = total; 43 } 44 45 public void destroy(){ 46 System.out.println("释放与订单对象相关的资源"); 47 } 48 }
在applicationContext.xml文件中配置
1 <bean id="order1" class="com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Order" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> 2 <property name="price" value="19.8"/> 3 <property name="quantity" value="1000"/> 4 </bean>
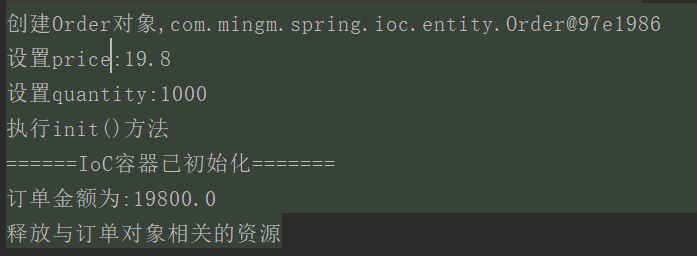
主方法
1 package com.mingm.spring.ioc; 2 3 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.entity.Order; 4 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.service.UserService; 5 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 7 8 public class SpringApplication { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); 11 System.out.println("======IoC容器已初始化======="); 12 13 Order order1 = context.getBean("order1", Order.class); 14 order1.pay(); 15 //销毁IoC容器 16 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).registerShutdownHook(); 17 } 18 }
运行结果
其他细节
prototype时对象创建与init-method延迟至执行业务代码阶段
prototype时对象不再受IoC对象管理,不再触发destory-method
延迟加载lazy-init属性可让对象创建与初始化延迟到执行代码阶段
基于注解配置IoC容器
基于注解的优势
摆脱繁琐的XML形式的bean与依赖注入
基于声明式的原则,更适合轻量级的现代企业应用
让代码可读性变得更好,研发人员拥有更好的开发体验
开启组件扫描
1 <!-- XML配置开启组件扫描,才能使用注解 --> 2 <context:component-scan base-package="com.mingm"> 3 <!-- 排除不需要扫描的包 --> 4 <context:exclude-filter type="regex" expression="com.mingm.exl.*"/> 5 </context:component-scan>
三类注解
组件类型注解 - 声明当前类的功能与职责
自动装配注解 - 根据属性特征自动注入对象
元数据注解 - 更细化的辅助IoC容器管理对象的注解
四种组件类型注解
| 注解 | 说明 |
| @Component | 组件注解,通用注解,被该注解描述的类将被IoC容器管理并实例化 |
| @Controller | 语义注解,说明当前类是MVC应用中的控制器类 |
| @Service | 语义注解,说明当前类是Service业务服务类 |
| @Repository | 语义注解,说明当前类用于业务持久层,通常描述对应Dao类 |
两类自动装配注解
| 分类 | 注解 | 说明 |
| 按类型装配 | @Autowored | 按容器内对象类型动态注入属性,由Spring机构提供 |
| @Inject | 基于JSR-330(Dependency Injection for java)标准,其他同@AutoWired,但不支持required属性 | |
| 按名称装配 | @Named | 与@Inject配合使用,JSR-330规范,按属性名自动装配属性 |
| @Resource | 基于JSR-250规范,优先按名称,再按类型匹配 |
元数据注解
| 注解 | 说明 |
| @Primary | 按类型装配时出现多个相同类型对象,拥有此注解对象优先被注入 |
| @PostConstruct | 描述方法,相当于XNL中init-method配置的注解版本 |
| @PreDestory | 描述方法,相当于XML中destory-method配置的注解版本 |
| @Scope | 设置对象的scope属性 |
| @Value | 为属性注入静态数据 |
演示@Value
config.properties文件
1 metaData=mingm.com 2 connection.driver=xxxxx 3 connection.url=xxx 4 connection.username=xxx 5 connection.password=xxx
applicationContext.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 6 https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 8 https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> 9 <!--通知Spring IoC容器初始化时加载属性文件--> 10 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config.properties"/> 11 <!-- 在IoC容器初始化时自动扫描四种组件类型注解并完成实例化 12 @Repository 13 @Service 14 @Controller 15 @Component 16 --> 17 <context:component-scan base-package="com.mingm"/> 18 </beans>
UserService.java
1 package com.mingm.spring.ioc.service; 2 3 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.dao.IUserDao; 4 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 5 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; 6 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; 7 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 8 9 import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; 10 11 @Service 12 @Scope("prototype")//设置单例/多例,XML中 bean scope完全相同 13 public class UserService { 14 @Value("${metaData}")//读取config.properties的metaData属性值 15 private String metaData ; 16 @Value("${connection.password}") 17 private String password; 18 19 public UserService(){ 20 System.out.println("正在创建UserService:" + this); 21 } 22 23 @PostConstruct //XML中bean init-method完全相同 24 public void init(){ 25 System.out.println("初始化UserService对象,metaData=" + metaData); 26 } 27 28 //Spring IoC容器会自动通过反射技术将属性private修饰符自动改为public,直接进行赋值 29 //不再执行set方法 30 @Autowired 31 private IUserDao udao ; 32 33 public IUserDao getUdao() { 34 return udao; 35 } 36 37 38 /*@Autowired 39 //如果装配注解放在set方法上,则自动按类型/名称对set方法参数进行注入 40 public void setUdao(UserDao udao) { 41 System.out.println("setUdao:" + udao); 42 this.udao = udao; 43 }*/ 44 }
使用Java Config方式实现Spring IoC
Java Config核心注解
| 注解 | 说明 |
| @Configuration | 描述类,说明当前类是Java Config配置类,完全替代XML文件 |
| @Bean | 描述方法,方法返回对象将被IoC容器管理,beanI默认方法名 |
| @ImportResource | 描述类,加载静态文件,可以使用@Value注解获取 |
| @ComponentScan | 描述类,同XML的<context:compoment-scan>标签 |
例如:
1 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.controller.UserController; 2 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.dao.EmployeeDao; 3 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.dao.UserDao; 4 import com.mingm.spring.ioc.service.UserService; 5 import org.springframework.context.annotation.*; 6 7 @Configuration //当前类是一个配置类,用于替代applicationContext.xml 8 @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.mingm") 9 public class Config { 10 @Bean //Java Config利用方法创建对象,将方法返回对象放入容器,beanId=方法名 11 public UserDao userDao(){ 12 UserDao userDao = new UserDao(); 13 System.out.println("已创建" + userDao); 14 return userDao; 15 } 16 17 @Bean //Java Config利用方法创建对象,将方法返回对象放入容器,beanId=方法名 18 @Primary 19 public UserDao userDao1(){ 20 UserDao userDao = new UserDao(); 21 System.out.println("已创建" + userDao); 22 return userDao; 23 } 24 25 @Bean 26 //先按name尝试注入,name不存在则按类型注入 27 public UserService userService(UserDao udao , EmployeeDao employeeDao){ 28 UserService userService = new UserService(); 29 System.out.println("已创建" + userService); 30 userService.setUserDao(udao); 31 System.out.println("调用setUserDao:" + udao); 32 userService.setEmployeeDao(employeeDao); 33 return userService; 34 } 35 36 @Bean //<bean id="xxx" clas="xxx"> 37 @Scope("prototype") 38 public UserController userController(UserService userService){ 39 UserController userController = new UserController(); 40 System.out.println("已创建" + userController); 41 userController.setUserService(userService); 42 System.out.println("调用setUserService:" + userService); 43 return userController; 44 } 45 }
启动类
1 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 2 import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; 3 4 public class SpringApplication { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 //基于Java Config配置IoC容器的初始化 7 ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class); 8 System.out.println("========================="); 9 String[] ids = context.getBeanDefinitionNames(); 10 for(String id : ids){ 11 System.out.println(id + ":" + context.getBean(id)); 12 } 13 } 14 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号