1-5-5 Java工具类--多线程
进程与线程
进程:指在系统中正在运行的一个应用程序;程序一旦运行就是进程;进程——资源分配的最小单位。
线程:系统分配处理器时间资源的基本单元,或者说进程之内独立执行的一个单元执行流。线程——程序执行的最小单位。
创建线程的三种方法
1) 继承Thread类,重写run()方法,run()方法代表线程要执行的任务。
2) 实现Runnable接口,重写run()方法,run()方法代表线程要执行的任务。
3) 实现callable接口,重写call()方法,call()作为线程的执行体,具有返回值,并且可以对异常进行声明和抛出;使用start()方法来启动线程
第三种方法介绍
1、 创建Callable接口的实现类,并实现call()方法,该call()方法将作为线程执行体,并且有返回值。
2、 创建Callable实现类的实例,使用FutureTask类来包装Callable对象,该FutureTask对象封装了该Callable对象的call()方法的返回值。
3、 使用FutureTask对象作为Thread对象的target创建并启动新线程。
4、 调用FutureTask对象的get()方法来获得子线程执行结束后的返回值。
实例代码:
1 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 2 3 public class ThreeThread implements Callable<String> { 4 @Override 5 public String call() throws Exception { 6 String str = "多线程的第三种创建方式"; 7 return str; 8 } 9 }
1 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 2 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 3 import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; 4 5 public class ThreeThreadTest { 6 //测试方法 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Callable<String> call = new ThreeThread(); 9 FutureTask<String> ft = new FutureTask<>(call); 10 Thread t3 = new Thread(ft); 11 12 //启动线程 13 t3.start(); 14 15 try { 16 System.out.println(ft.get()); 17 } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 } 21 22 }
线程状态和生命周期

sleep方法的使用
public static void sleep(long millis)
在指定的毫秒数内让正在执行的线程休眠(暂停执行)
参数为休眠时间,单位是毫秒
join方法使用
public final void join()
等待调用该方法的线程结束才能执行
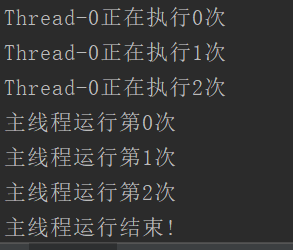
1 public class JoinDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyThread mt = new MyThread(); 4 mt.start(); 5 try { 6 mt.join(); 7 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 11 System.out.println("主线程运行第" + i + "次"); 12 } 13 System.out.println("主线程运行结束!"); 14 } 15 } 16 class MyThread extends Thread{ 17 @Override 18 public void run() { 19 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 20 System.out.println(getName() + "正在执行" + i + "次"); 21 } 22 } 23 }
运行结果:
public final void join(long millis)
等待该线程终止的最长时间为millis毫秒
线程优先级
优先级用1-10表示,超过范围会抛出异常
主线程优先级默认为5
优先级常量
MAX_PRIORITY:最高优先级10
MIN_PRIORITY:最低优先级1
NORM_PRIORITY:默认优先级5
相关方法
public int getPriority() 获取线程优先级的方法
public void setPriority(int newPriority) 设置线程优先级的方法
线程间同步与通信
同步:synchronized
通信:wait,notify,notifyAll
1 public class Queue { 2 3 private int n; 4 boolean flag = false; 5 6 public synchronized int get() { 7 if (!flag) { 8 try { 9 wait(); 10 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 System.out.println("消费:"+n); 15 flag = false; 16 notifyAll(); 17 return n; 18 } 19 20 public synchronized void set(int n) { 21 if(flag) { 22 try { 23 wait(); 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 System.out.println("生产:"+n); 29 this.n=n; 30 flag = true;//生产完毕,容器里面已经有数据 31 notifyAll(); 32 } 33 }
1 public class Consumer implements Runnable { 2 Queue queue; 3 Consumer(Queue queue) { 4 this.queue = queue; 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void run() { 9 while (true) { 10 queue.get(); 11 try { 12 Thread.sleep(1000); 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 }
1 public class Producer implements Runnable { 2 Queue queue; 3 Producer(Queue queue) { 4 this.queue = queue; 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public void run() { 9 int i=0; 10 while (true) { 11 queue.set(i++); 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(1000); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Queue queue=new Queue(); new Thread(new Producer(queue)).start(); new Thread(new Consumer(queue)).start(); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号