JavaScript
JavaScript
概述

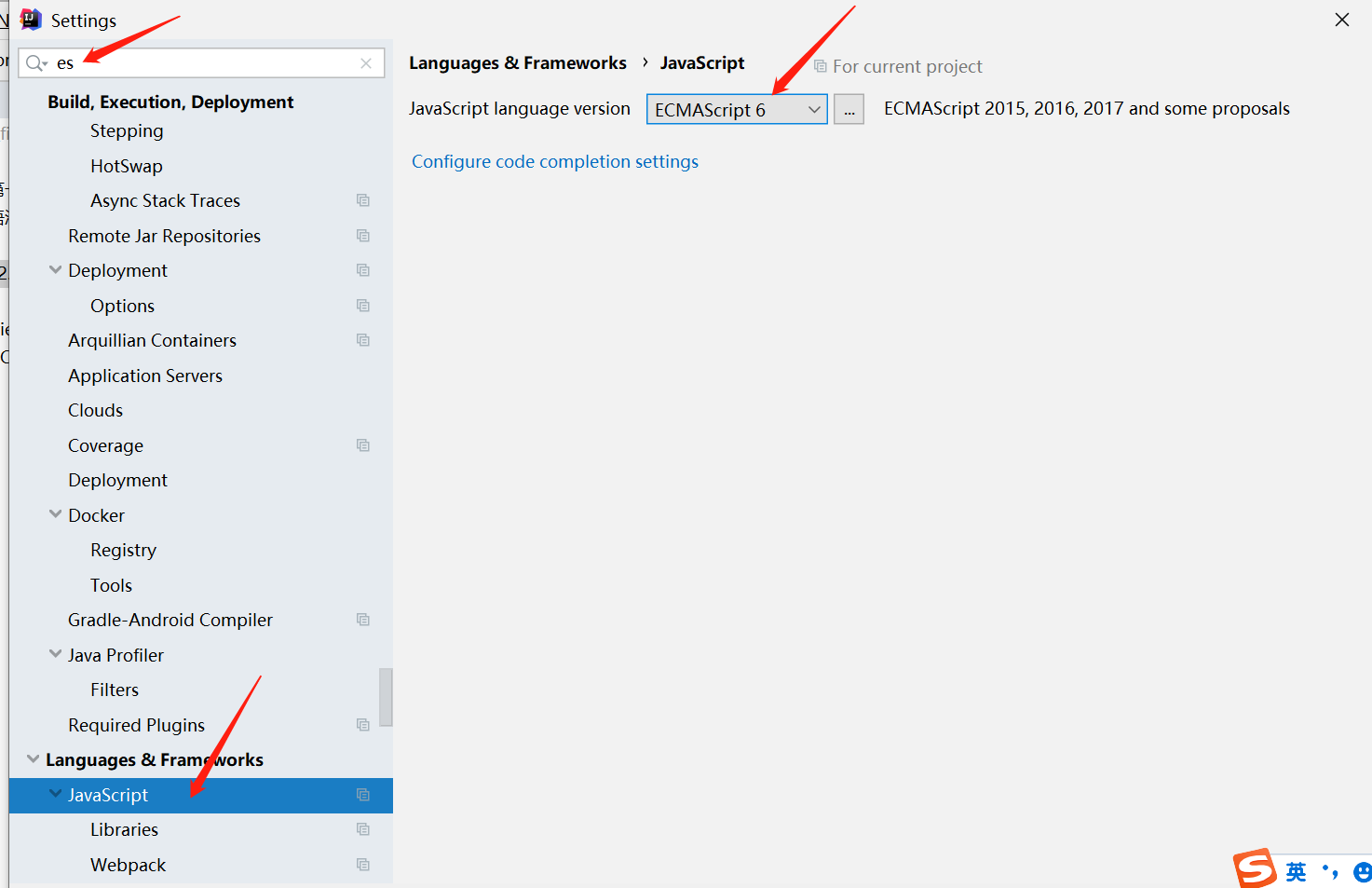
helloworld
方式一
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- 方式一:
js程序,可以写在head
alert('hello world'); 弹出hello world
-->
<script>
alert('hello world');
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
方式二:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 方式二:
js程序,可以写在body
alert('hello world'); 弹出hello world
-->
<script>
alert('hello world');
</script>
</body>
</html>
方式三
/* 方式三:
js程序,可以写在bjs文件中
alert('hello world'); 弹出hello world
*/
alert('hello world');
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/qj.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
浏览器控制台使用
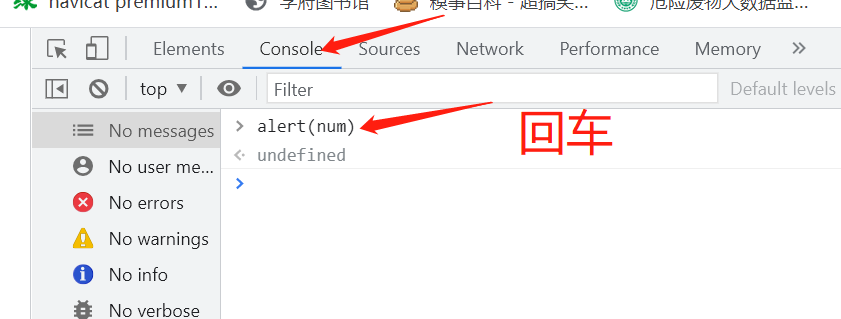
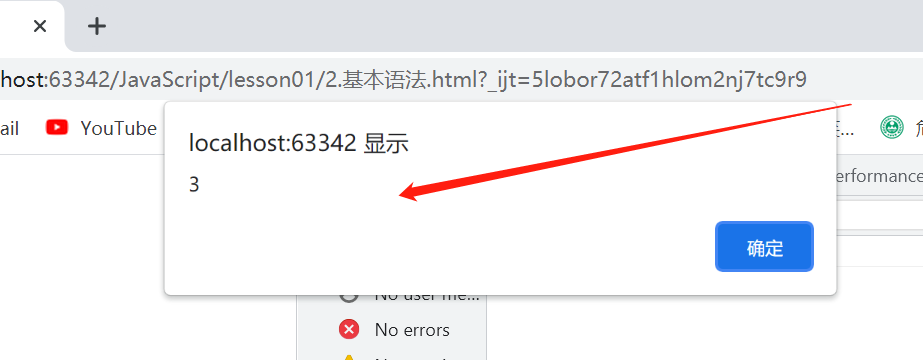
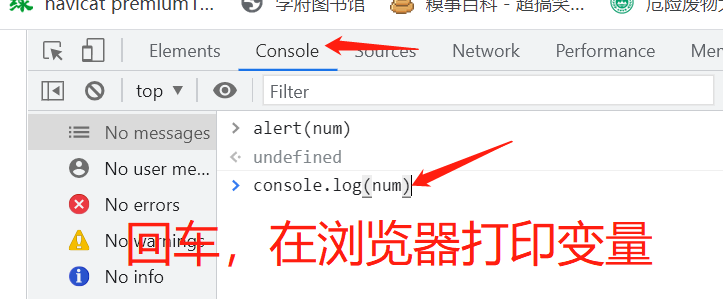
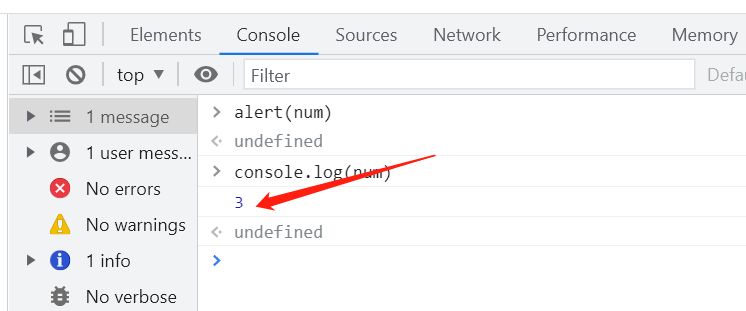
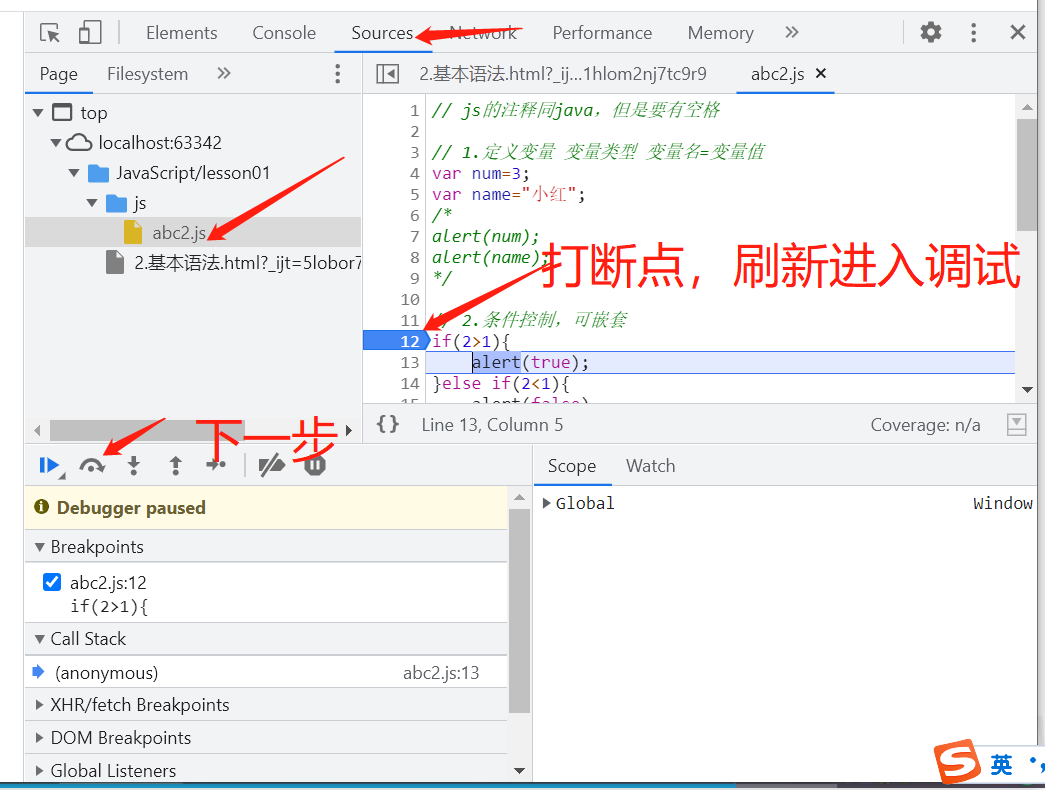
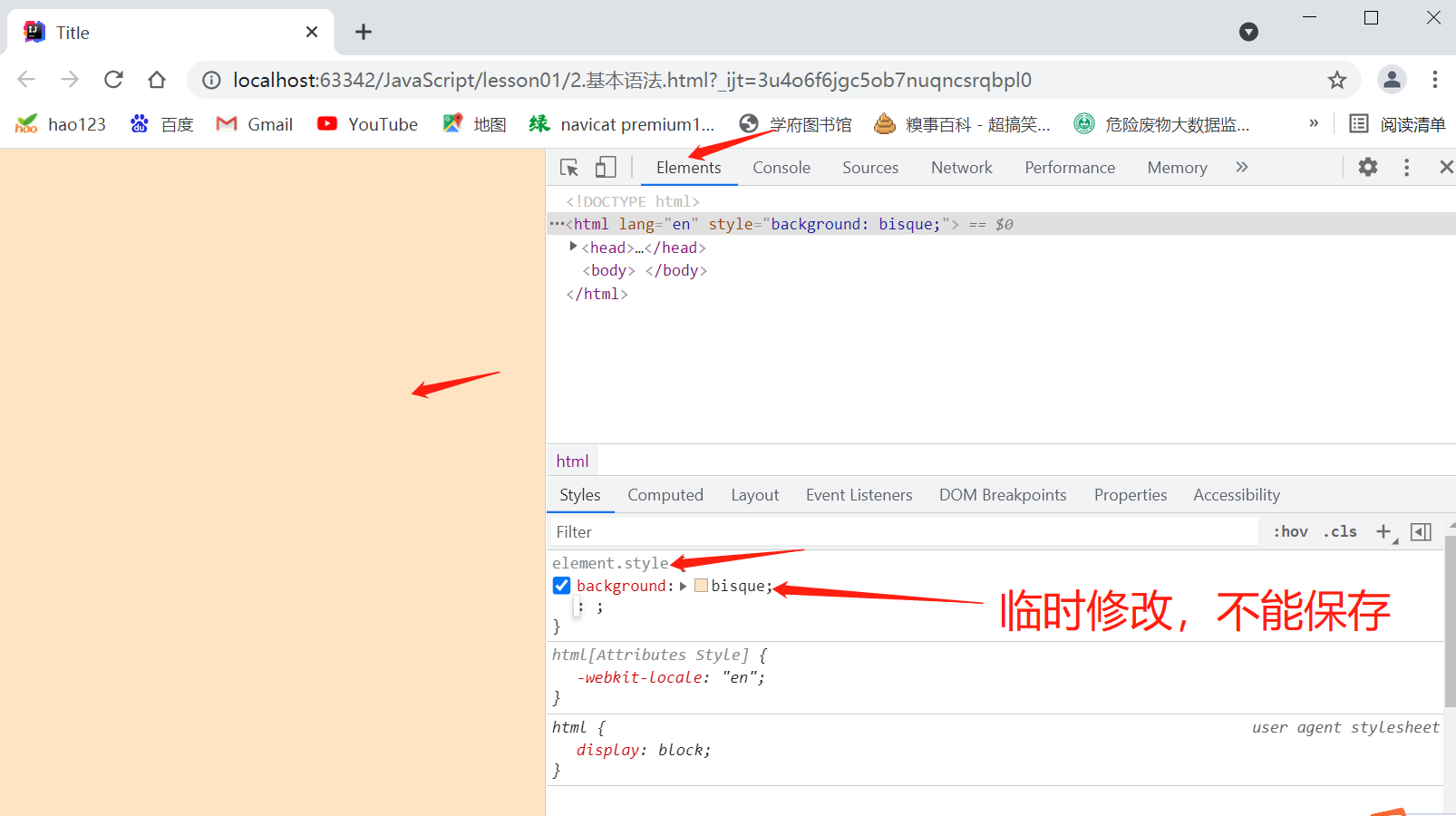
基本语法
// js的注释同java,但是要有空格
// 1.定义变量 变量类型 变量名=变量值
var num=3;
var name="小红";
/*
alert(num);
alert(name);
*/
// 2.条件控制,可嵌套
if(2>1){
alert(true);
}else if(2<1){
alert(false)
}else {
alert("出错了")
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
数据类型




// 浮点数问题
console.log((1/3)===(1-(2/3)));// false 尽量避免使用浮点数,会损失精度
console.log(Math.abs((1/3)-(1-(2/3)))<0.000000000000001);// true 利用这种方式判断是否相等



严格检查模式
'use strict' // 此为严格检查,最好所有js代码都加上这句话,此句必须写在第一行
let i=1; // es6中这样定义
var j = 2; // var 不建议使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc3.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
字符串类型
"use strict";
// 1.单行字符串
console.log('a');// a
console.log("a");// a
console.log("a'b'c");// a'b'c
console.log('a"b"c');// a"b"c
// 2.转义符号
console.log('a\'b\'c');// a'b'c \符号 转义
console.log("a\nb");// \n 换行
console.log("a\tb");// a b \t Tab空格
console.log("\u4e2d");// 中 unicode字符
console.log("\x41");// A ASCII字符
// 3.多行字符串 Tab键上面的符号
let a=`你好
hello world
123abc
`;
console.log(a);
/*
你好
hello world
123abc
*/
// 4.模板字符串
let name='mingmao';
let age=18;
let msg=`你好呀,${age}岁的${name}`;// Tab键上面的符号
console.log(msg);// 你好呀,18岁的mingmao
// 5.字符串长度
let stu="student";
console.log(stu.length);// 7
console.log(stu[3]);// d
// 6.字符串的可变性,不可变
// stu[1]='h';// 报错
// 7.大小写转换
console.log(stu.toUpperCase());// STUDENT
console.log(stu.toLowerCase());// student
// 8.获取字符串中某个字符的下标
console.log(stu.indexOf('u'));// 2
// 9.截取子字符串 [)
console.log(stu.substring(3,6));// den
console.log(stu.substring(2));// udent
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
数组
"use strict";
// 数组可以包含任意的数据类型
// 1.定义数组
let arr=[0,1,2,3,4];
console.log(arr);// (5) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
// 2.长度
console.log(arr.length);// 5
//3.数组可变,元素和长度均可变
arr[0]=8;
console.log(arr);// (5) [8, 1, 2, 3, 4]
arr.length=10;
console.log(arr);// (10) [8, 1, 2, 3, 4, empty × 5]
arr.length=3;
console.log(arr);// (3) [8, 1, 2]
// 4.数组的方法
arr=[10,9,5,3,6,3,2,8];
console.log(arr);// (8) [10, 9, 5, 3, 6, 3, 2, 8]
console.log(arr.indexOf(6));// 4 获得某元素的下标
console.log(arr.slice(2,6));// (4) [5, 3, 6, 3] 获取子数组
console.log(arr.slice(5));// (3) [3, 2, 8]
arr.push('a','b');// 在数组末尾加入一个或多个元素
console.log(arr);// (10) [10, 9, 5, 3, 6, 3, 2, 8, 'a', 'b']
arr.pop();// 弹出数组最末尾的一个元素
console.log(arr);// (9) [10, 9, 5, 3, 6, 3, 2, 8, 'a']
arr.unshift('a','b');// 在数组头部加入一个或多个元素
console.log(arr);// (11) ['a', 'b', 10, 9, 5, 3, 6, 3, 2, 8, 'a']
arr.shift();// 弹出数组最开头的一个元素
console.log(arr);// (10) ['b', 10, 9, 5, 3, 6, 3, 2, 8, 'a']
arr.sort();// 数组排序
console.log(arr);// (10) [10, 2, 3, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 'a', 'b'] 有字符串时当做字符串数组排序
arr.reverse();// 数组元素反转
console.log(arr);// (10) ['b', 'a', 9, 8, 6, 5, 3, 3, 2, 10]
let arr2=arr.concat([2,3]);// 在数组末尾拼接一个数组,生成新数组,不改变原数组
console.log(arr2);// (12) ['b', 'a', 9, 8, 6, 5, 3, 3, 2, 10, 2, 3]
let str=arr.join('-');// 使用'-'连接数组,变为字符串,不改变原数组
console.log(str);//b-a-9-8-6-5-3-3-2-10
arr.fill(5);// 用特定值填充数组
console.log(arr);// (10) [5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5]
// 5.多维数组
let marr=[[1,2,3],[9,6],['a','b','c','d']];//定义
console.log(marr);// (3) [Array(3), Array(2), Array(4)]
console.log(marr[1][1]);// 6 取值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
对象
"use strict";
// 若干个键值对,所有键都是字符串,值是任意对象
/*
1.定义
let 对象={
属性名:属性值,
属性名:属性值,
属性名:属性值
};
*/
let person={
name:"mingmao",
age: 18,
email: "2792178110@qq.com",
score: 80
};
console.log(person.name);// mingmao 获取对象属性值
person.age=20;// 给属性赋值
console.log(person.age);// 20
console.log(person['age']);// 20
// 2.使用不存定的属性不会报错,会出现undefined
console.log(person.haha);// undefined
// 3.对象的操作
delete person.email;// 动态的删减属性
console.log(person);// {name: 'mingmao', age: 20, score: 80}
person.sex="女";// 动态的增加属性
console.log(person);// {name: 'mingmao', age: 20, score: 80, sex: '女'}
// 4.对象的方法
console.log('age' in person);// true 判断属性是否在对象中
console.log('toString' in person);// true 判断方法是否在对象中,继承父类的
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('age'));// true 判断是否是对象自己的属性
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('toString'));//false 判断是否是对象自己的方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc3.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
流程控制
"use strict";
// 1.if判断
let age=3;
if(age>3){
alert("haha");
}else if(age<3) {
alert("nihao");
}else {
alert("kuwa~");
}
// 2.while循环
while(age<10){
age++;
console.log(age);
}
// 3.do while 循环
do{
age++;
console.log(age);
}while (age<20);
// 4.for循环
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
console.log(i+1);
}
// 5.数组循环
let arr=[1,2,3,4,5];
// 方式一:
arr.forEach(function (value) {
console.log(value);
});
// 方式二:尽量不要用for in
for (let a in arr){
console.log(arr[a]);
}
// 方式三:
for (let a1 of arr){
console.log(a1);
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc4.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Map和Set集合
"use strict";
// 1.Map 键值对
let map=new Map([["小红",90],["小明",100],["小丽",80]]);
console.log(map.get("小明"));// 100 通过键获取值
map.set("小丽",60);// 通过键修改值
console.log(map.get("小丽"));// 60
map.set("小李",85);// 增加键值对
console.log(map);// Map(4) {'小红' => 90, '小明' => 100, '小丽' => 80, '小李' => 85}
map.delete("小红");// 删除键值对
console.log(map);// Map(3) {'小明' => 100, '小丽' => 60, '小李' => 85}
// 2.Set 无序不重复集合
let set=new Set([1,2,3,9,7,3,1,1]);
console.log(set);// Set(5) {1, 2, 3, 9, 7} 自动去掉重复元素
set.add(10);// 增加元素
console.log(set);// Set(6) {1, 2, 3, 9, 7, …}
set.delete(9);// 删除元素
console.log(set);// Set(5) {1, 2, 3, 7, 10}
console.log(set.has(10));// true 判断set是否包含某个元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc5.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Iterable迭代
"use strict";
let map=new Map([["小红",90],["小明",80],["小丽",95]]);
// 1.遍历map,set亦同
// 方式一:
for (let m of map){
console.log(m);
}
// 方式二:
map.forEach(function (value, key, map) {
console.log(value);// 90 80 95
console.log(key);// 小红 小明 小丽
});
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc6.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
函数
定义函数
"use strict";
// 1.绝对值函数定义方式一:
function abs(x) {
if(x>=0){
return x;
}else {
return -x;
}
}
console.log(abs(-10));// 10 调用
// 2.绝对值函数定义方式二:
let abs1=function (x) {
if(x>=0){
return x;
}else {
return -x;
}
};
console.log(abs1(-9));// 9 调用
// 3.注意,js可以传任意个参数,也可以不传递参数,都不会报错。解决方式如下:
// arguments可以获取传递参数数组
function abs2(x) {
if((typeof x !=="number") || (arguments.length>1)){
throw "not a number";
}
if(x>=0){
return x;
}else {
return -x;
}
}
// console.log(abs2());// 报错 abc1.js:25 Uncaught not a number
// console.log(abs2(2,3));// 报错 abc1.js:25 Uncaught not a number
// 4.获取除了定义的参数之外的其他参数rest
function add(a,b,...rest) {
console.log(rest);
return a+b;
}
console.log(add(3,4));// [] 7
console.log(add(2,5,6,7,8,));// (3) [6, 7, 8] 7
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
变量作用域及常量
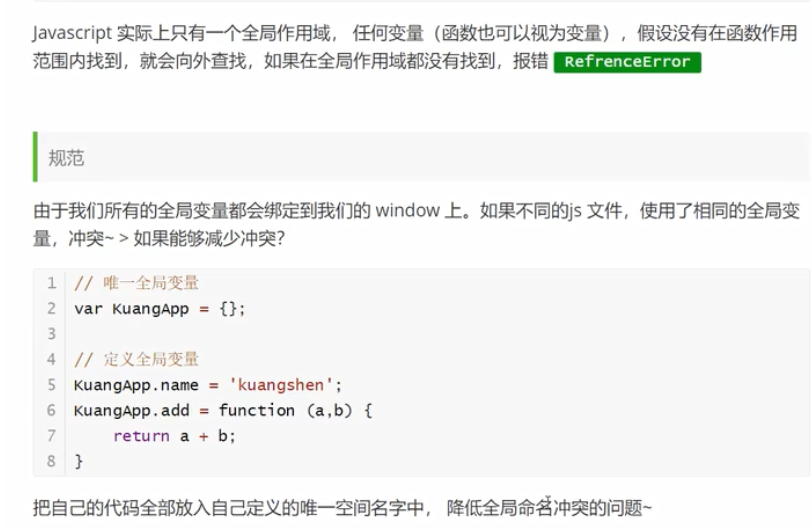
"use strict";
// 1.解决全局作用域冲突
let mingMao={};//全局绑定变量,所有变量和方法都绑定它,避免全局作用域冲突
mingMao.num=10;
console.log(mingMao.num);// 10
mingMao.add=function (a,b) {
return a+b;
}
console.log(mingMao.add(2,3));// 5
// 2.解决局部作用域冲突,不要用var,要是用let定义变量
// 3.常量
const PI=3.14;
console.log(PI);// 3.14
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
方法
"use strict";
// 方式一:合起来写
let mingmao={
name:"mm",
birth:1998,
age:function f() {
let now=new Date().getFullYear();
let number = now-this.birth;
return number;
}
};
console.log(mingmao.age());// 23
// 方式二:拆开来写
function getAge() {
let now1=new Date().getFullYear();
let number1 = now1-this.birth1;
return number1;
}
let mingmao1={
name1:'mm',
birth1:1998,
age1:getAge
};
console.log(mingmao1.age1());// 23
// 控制this的指向
let xiaoming={
name1:"xiaoming",
age1:getAge,
birth1:2000
}
console.log(getAge.apply(xiaoming,[]));// 21
console.log(getAge.apply(mingmao1,[]));// 23
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc3.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
内部对象

Date
"use strict";
// 基本使用
let date = new Date();
console.log(date);// Sun Sep 26 2021 14:40:10 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
console.log(date.getFullYear());// 2021 年
console.log(date.getMonth()+1);// 9 月
console.log(date.getDate());// 26 日
console.log(date.getDay());// 0 星期
console.log(date.getHours());// 14 时
console.log(date.getMinutes());// 44 分
console.log(date.getSeconds());// 4 秒
console.log(date.getTime());// 时间戳 1632638805779 1970.1.1 00:00:00 至今 全世界统一 毫秒数
console.log(new Date(1632638805779));//时间戳转化为时间 Sun Sep 26 2021 14:46:45 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
// 转换
console.log(date);// Sun Sep 26 2021 14:59:05 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
console.log(date.toLocaleString());// 2021/9/26 下午2:59:05
console.log(date.toUTCString());// Sun, 26 Sep 2021 06:59:05 GMT
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
json

"use strict";
// json和js对象的转换
let user={
name:"mingmao",
age:8,
sex:"女"
};
console.log(user);// {name: 'mingmao', age: 8, sex: '女'} 可展开,有键值对
// js对象转化为json字符串
let jsonUser = JSON.stringify(user);
console.log(jsonUser);// {"name":"mingmao","age":8,"sex":"女"} 不可展开
// json字符串转化为js对象
let parse = JSON.parse(jsonUser);
console.log(parse);// {name: 'mingmao', age: 8, sex: '女'} 可展开,有键值对
let parse1 = JSON.parse('{"name":"mingmao","age":8,"sex":"女"}');
console.log(parse1);// {name: 'mingmao', age: 8, sex: '女'} 可展开,有键值对
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
面向对象
"use strict";
let user={
name:"user",
age:18,
run:function () {
console.log(this.name+"run...");
}
};
let xiaoming={
name:"xiaoming"
};
// xiaoming的原型是user
xiaoming.__proto__=user;
console.log(user.run());// userrun...
console.log(xiaoming);// {name: 'xiaoming'}
console.log(xiaoming.run());// xiaomingrun...
console.log(xiaoming.age);// 18
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
面向对象class继承
"use strict";
// 1.定义一个类
// 原先的做法
function Student(name) {
this.name=name;
}
//增加一个方法
Student.prototype.hello=function () {
alert('hello');
};
new Student('xiaoming').hello();
// ES6之后
class Student1 {
constructor(name) {
this.name=name;
}
hello1(){
alert('hello world');
}
}
new Student1('小红').hello1();
// 2.继承
class Xiaoxuesheng extends Student{
constructor(name,grade) {
super(name);
this.grade=grade;
}
myGrade(){
alert("我是一名小学生");
}
}
new Xiaoxuesheng('xiaoli',3).myGrade();
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
操作BOM对象


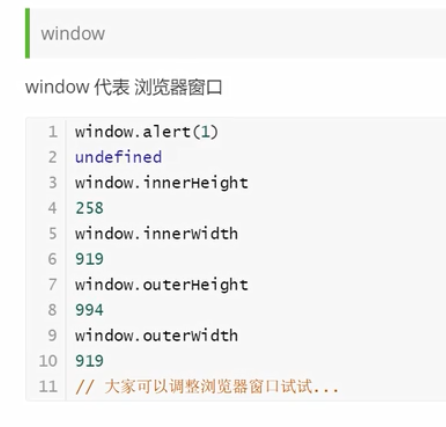


"use strict";
// 1.window
window.alert(1);// 1
// 获取浏览器窗口内部的宽和高
console.log(window.innerWidth);// 503
console.log(window.innerHeight);// 515
// 获取浏览器窗口外部的宽和高
console.log(window.outerWidth);// 1194
console.log(window.outerHeight);// 634
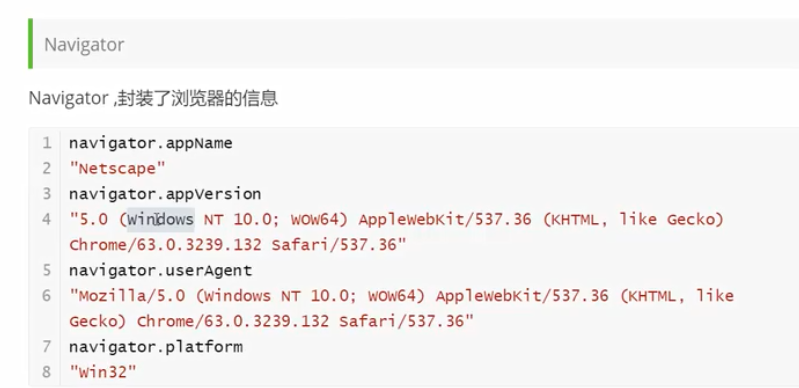
// 2.Navigator 不建议使用
console.log(navigator.appName);// Netscape
console.log(navigator.appVersion);// 5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/93.0.4577.82 Safari/537.36
console.log(navigator.userAgent);// Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/93.0.4577.82 Safari/537.36
console.log(navigator.platform);// Win32
// 3.screen 获取屏幕尺寸
console.log(screen.width);// 1280
console.log(screen.height);// 720
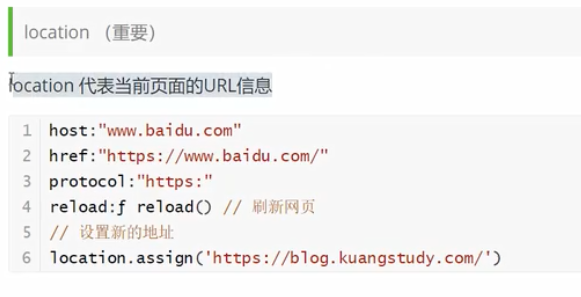
// 4.location 代表当前页面的URL信息 重要
// 打开百度页面,以百度为例
/*
console.log(location.host);// 'www.baidu.com'
console.log(location.href);// 'https://www.baidu.com/?tn=02003390_19_hao_pg'
console.log(location.protocol);// 'https:'
location.reload()// 刷新页面
location.assign('https://www.cnblogs.com/mingmao/');// 转到新页面
*/
// 5.document 代表当前页面
// 打开百度界面,以百度为例
// 修改标题
document.title;// '百度一下,你就知道'
document.title='mingmao';// 'mingmao'
// 获取网页的cookie
document.cookie;// 'BIDUPSID=892DC260548D7B24BEB310276F57A508; PSTM=1628927605; BAIDUID=D382FC9FAD
// 6.history 代表浏览器的历史记录 不建议使用
history.forward();// 前进
history.back();// 后退
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--document测试用例-->
<dl id="app">
<dt>java</dt>
<dd>javase</dd>
<dd>javaee</dd>
</dl>
<script>
// 获取具体的文档树节点
console.log(document.getElementById('app'));// 显示出完整的dl 但是此语句只有写在body内部才有效
</script>
</body>
</html>
操作DOM对象
获取DOM节点

"use strict";
// 1.获取特定节点
console.log(document.getElementsByTagName('h1'));// 获得h1
// console.log(document.getElementById('p1'));// null 此方法获取不到p1 只能在body中写此语句才行
console.log(document.getElementsByClassName('p2'));// 获得p2
// let father=console.log(document.getElementById('father'));// null 此方法获取不到div 只能在body中写此语句才行
// 2.获取父节点下的所有子节点
/*
需放在body中
let father=document.getElementById('father');// 获取div
console.log(father);
let childrens = father.children;// 获取父节点下的所有子节点
console.log(childrens);
console.log(father.firstChild);// 获取父节点下的第一个子节点
console.log(father.lastChild);// 获取父节点下的最后一个子节点
*/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/abc1.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<h1>标题一</h1>
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p class="p2">p2</p>
</div>
<script>
console.log(document.getElementById('p1'));// 获取p1
let father=document.getElementById('father');// 获取div
console.log(father);
let childrens = father.children;// 获取父节点下的所有子节点
console.log(childrens);
console.log(father.firstChild);// 获取父节点下的第一个子节点
console.log(father.lastChild);// 获取父节点下的最后一个子节点
</script>
</body>
</html>
更新DOM节点
"use strict";
let id1=document.getElementById('id1');//
console.log(id1);
// 修改文本的值
id1.innerText='abc';// abc
// 解析HTML文本标签
id1.innerHTML='<strong>123</strong>';// 123
// 操作文本和js:改变文本颜色,字体大小,边距
id1.style.color='red';
id1.style.fontSize='80px';
id1.style.padding='2em';
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="id1"></div>
<!--要把此引入放在body内的最下面,可解决获取dom节点问题-->
<script src="js/abc2.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
删除dom节点
"use strict";
// 先获取父节点,再通过父节点删除自己
let p1=document.getElementById('p1');
let father=p1.parentElement;
father.removeChild(p1);
// 删除父节点下的第二个节点
father.removeChild(father.children[1]);
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<h1>标题一</h1>
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p class="p2">p2</p>
</div>
<script src="js/abc3.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
创建和插入dom节点
"use strict";
// 1.覆盖操作
let p1=document.getElementById('p1');
p1.innerText="abc";
// 2.追加操作
let p=document.getElementById('p');
let father=document.getElementById('father');
father.appendChild(p);// 将原先的p移动到father的末尾元素,原先的p消失
// 3.创建新节点
let newP=document.createElement('p');// 创建一个p标签
newP.id='newP';
newP.innerText='p4';
father.appendChild(newP);
// 4.创建新节点2
let myScript=document.createElement('script');
myScript.setAttribute('type','text/javascript');
father.appendChild(myScript);
// 5.创建新节点3
let myStyle=document.createElement('style');
myStyle.setAttribute('type','text/css');
myStyle.innerHTML='body{background-color:green;}';
let head=document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
head.appendChild(myStyle);
// 6.把节点插入到指定位置
father.insertBefore(newP,p1);// 把newP插在p1前面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="p">java</p>
<div id="father">
<h1>标题一</h1>
<p id="p1">p1</p>
<p class="p2">p2</p>
</div>
<script src="js/abc4.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
操作表单

"use strict";
// 获取和修改表单的值
// 文本框
let input_text=document.getElementById('username');
input_text.value='abc';
console.log(input_text.value);
// 多选框
let boy_radio=document.getElementById('boy');
let girl_radio=document.getElementById('girl');
console.log(boy_radio.value);// man
console.log(girl_radio.value);// woman
girl_radio.checked=true;// 设置女被选中
console.log(boy_radio.checked);// false 或 true 表示是否被选中
console.log(girl_radio.checked);
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="#" method="post">
<span>用户名:</span><input type="text" id="username"/>
</form>
<p>
<span>性别:</span>
<input type="radio" name="sex" value="man" id="boy"/>男
<input type="radio" name="sex" value="woman" id="girl"/>女
</p>
<script src="js/js1.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
提交表单及MD5加密
"use strict";
// 提交按钮绑定事件
function a() {
alert("提交成功");
let uname=document.getElementById('username');
let pwd=document.getElementById('input-password');
let md5pwd=document.getElementById('md5-password');
console.log(uname.value);
// MD5算法 对密码加密
md5pwd.value=md5(pwd.value);
console.log(pwd.value);
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- MD5链接-->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/blueimp-md5/2.10.0/js/md5.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<form action="#" method="post">
<span>用户名:</span><input type="text" id="username" name="username"/><br/>
<span>密码:</span><input type="password" id="input-password"/>
<input type="hidden" id="md5-password" name="password"/><br/>
<!-- 绑定事件 onclick:被点击-->
<button type="submit" onclick="a()">提交</button>
</form>
<script src="js/js2.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
jQuery
jQuery官网
jQuery文档
CDNjQuery加速1
CDNjQuery加速2
初识jQuery
"use strict";
// jQuery:$(选择器).action() css选择器
$('#test-jQuery').click(function () {
alert('hello,jQuery');
});
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<a href="" id="test-jQuery">点我</a>
<script src="js/js1.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
jQuery选择器
"use strict";
// 标签
$('p').click();
// id
$('#id1').click();
// 类
$('.class1').click();
jQuery事件
"use strict";
// 鼠标事件
// 当网页元素加载完毕之后响应事件
$(function () {
$('#divMove').mousemove(function (e) {
$('#mouseMove').text('x:'+e.pageX+'y:'+e.pageY);
});
});
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
mouse: <span id="mouseMove"></span>
<div id="divMove">
点这里移动鼠标试试
</div>
<script src="js/js3.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
jQuery操作dom元素
"use strict";
// 1.节点文本操作
//获得值
console.log($('#test-ul li[name=python]').text());// python
// 设置值,覆盖
$('#test-ul li[name=python]').text('abc');
//获得值
console.log($('#test-ul li[name=python]').html());// abc
// 设置值,覆盖
$('#test-ul li[name=python]').html('<strong>123</strong>');
// 2.css操作
$('#test-ul li[name=python]').css('color','red');
// 3.元素的显示和隐藏
$('#test-ul li[name=python]').hide();
$('#test-ul li[name=python]').show();
// 4.娱乐测试
console.log($(window).width());
console.log($(window).height());
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="test-ul">
<li class="js">JavaScript</li>
<li name="python">python</li>
</ul>
<script src="js/js4.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
前端小结




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号