WEB-UI自动化测试-02-八大元素定位方式
使用优先级
ID → Name → CSS Selector → XPath → Class Name → Link Text → Partial Link Text → Tag Name
ID
唯一,同一页面内不会重复。有ID优先用ID
d.find_element(By.ID, "searchKey")
name
次优选择,可能不唯一。
d.find_element(By.NAME, "searchKey")
class
类名定位;不唯一,一般不用
el = d.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "s_input")
els = d.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "s_input")
print(len(els)) # 2
tag_name
通过HTML标签名,不唯一且重复性最高,一般不单独用
# 根据HTML的标签名查询
el = d.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, "input")
els = d.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME, "input") # 查询页面上所有的input标签
print(len(els)) # 5
link_text
只有A标签能用,根据a标签的文本内容精准匹配
partial_link_text
同Link_text,区别在于partial_link_text是模糊匹配,link_text是精准匹配
el = d.find_element(By.LINK_TEXT, "首页") # 查找页面上所有A标签中,文本内容等于"首页"字的元素
el = d.find_element(By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT, "首") # 查找页面上所有A标签中,文本内容包含"首"字的元素
xpath
通过XML路径语言定位,功能最强大,几乎可以定位任何元素,用的最多。缺点:性能较差,语法复杂
// 文档中的任意位置 //div - 文档中所有div
. 当前节点 .//input - 当前节点下的input
.. 父节点 ../div - 父节点的div
@ 属性 @id - id属性
* 通配符 //* - 所有元素
1. 路径定位
绝对路径
绝对路径从文档根节点开始,通过依次指定每个层级的节点来定位目标节点。
el = d.find_element(By.XPATH, "/html/body/div[2]/div/div[1]/form/ul/li[2]/input")
相对路径:
相对路径是相对于当前上下文节点来定位目标节点的路径表达式。
el = d.find_element(By.XPATH, "//a[@href='/book/bookclass.html']") # 找任意位置的a标签中属性href='/'的元素
2. 属性定位
语法
//*[@属性名='值']
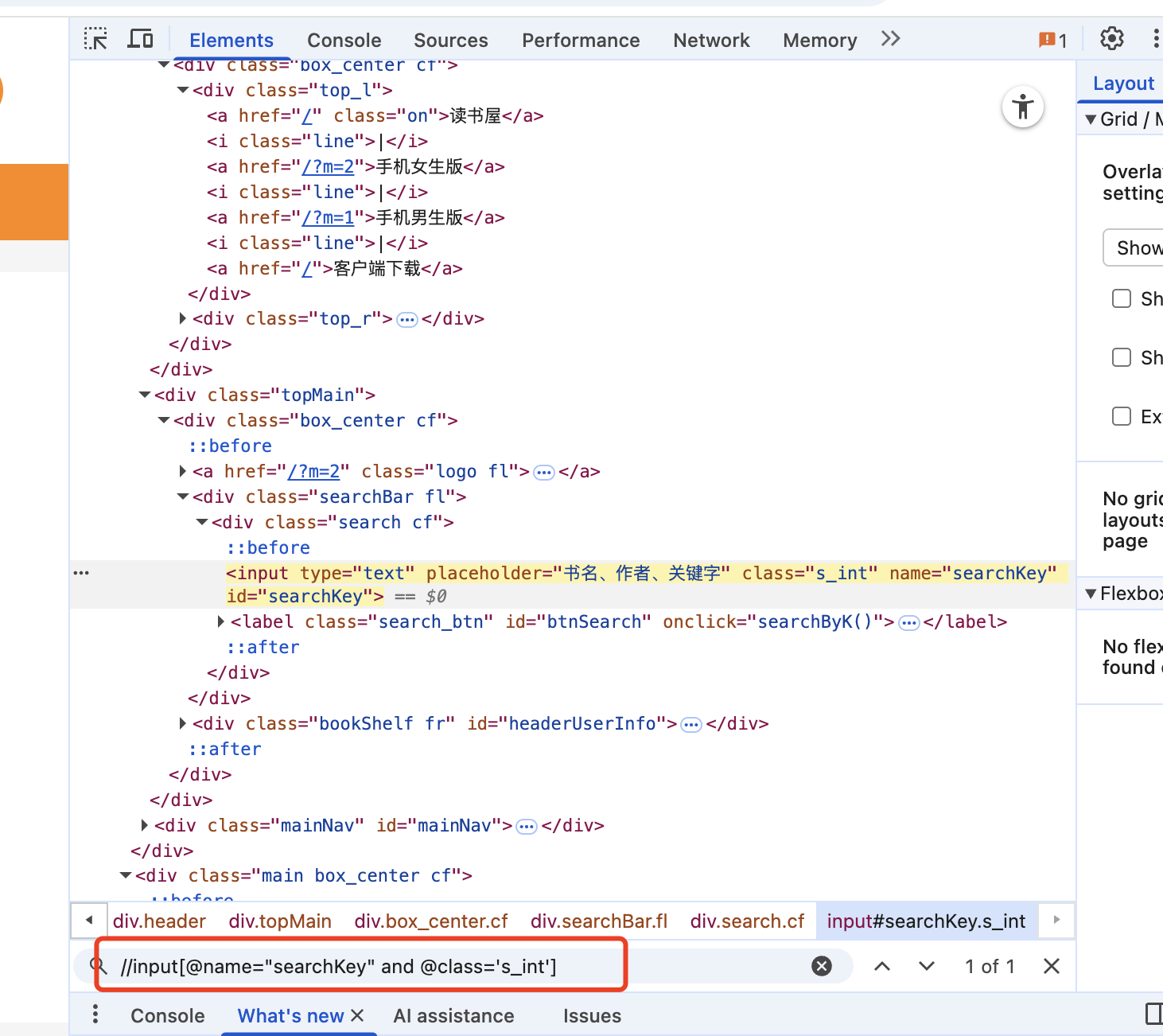
//input[@name='searchKey'] # 找任意位置的input标签,并且name属性为searchKey
//input[@name="searchKey" and @class="s_int"] # 从整个页面中查找name="searchKey" 并且 @class="s_int"]的元素
模糊匹配
语法
//标签名[contains(@属性, '值')] 找包含xx元素
//*[starts-with(@placeholder,'手机')] # 找placeholder属性以手机开头的元素
//标签名[starts-with(@属性, '值')] 以xx开头的元素
//*[contains(@class, 's_input icon_name')] # 找class属性包含s_input icon_name的元素
//input[contains(@class, 's_input icon_name')] # 找input标签中class属性包含s_input icon_name的元素
3.文本定位
文本跟属性不同,文本是text(),与属性的@有区别
//*[text()='我的书架'] # 找任意位置文本为 我的书架 的元素
模糊搜索同样适用
//*[contains(text(),'我的')]
//*[starts-with(text(),'我的')]
css
通过CSS选择器语法定位。性能好,语法简洁;缺点:某些复杂定位不如XPath
.代表class
.s_input # 找class=s_input的元素
input[class='s_input'] # input标签中class=s_input的元素
input. s_input # 同上
#代表id
#txtUName # 找ID=txtUName的元素
input#txtPassword
>直接子元素,只能找一层父子关系
div.search>input # 找class=search的div标签,并且子元素标签为input的元素
空格 后代元素 子孙后代,不限层级
div.search input # 找class=search的div标签,并且后代元素标签为input的元素
div.search i
+ 同级元素
div.search input+label # 选择所有 class 为 "search" 的 div 元素内部、紧跟在 input 元素后面的第一个同级 label 元素。
css-网格定位
#在name=txtPassword的上方找一个input元素
driver.find_element(locate_with(By.TAG_NAME,"input").above({By.XPATH:'//*[@name="txtPassword"]'}))
locate_with() # 用于创建相对定位策略。
.above # 在参考元素的上方查找,above里面是参考元素,locate_with是要找的元素
.below # 在参考元素的下方查找
d.find_element(locate_with(By.TAG_NAME, 'input').below({By.CSS_SELECTOR:'input.s_input'})) #




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号