第10章异常-Exception
第10章异常-Exception
10.1看个实际的问题和一段代码
运行下面的代码,看看有什么问题->引出异常和异常处理机制Exception01.java
public static void main(String[] args){
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
int res = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("程序继续运行....");
}
10.2解决方案-异常捕获
对异常进行捕获,保证程序可以继续运行.
package com.ming.exception;
/**
* @author 明
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Exception01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. num1 / num2 => 10 / 0
//2. 当执行到 num1 / num2 因为 num2 = 0, 程序就会出现(抛出)异常 ArithmeticException
//3. 当抛出异常后,程序就退出,崩溃了 , 下面的代码就不在执行
//4. 大家想想这样的程序好吗? 不好,不应该出现了一个不算致命的问题,就导致整个系统崩溃
//5. java 设计者,提供了一个叫 异常处理机制来解决该问题
// int res = num1 / num2;
//如果程序员,认为一段代码可能出现异常/问题,可以使用try-catch异常处理机制来解决
//从而保证程序的健壮性
//将该代码块->选中->快捷键 ctrl + alt + t -> 选中 try-catch
//6. 如果进行异常处理,那么即使出现了异常,程序可以继续执行
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
int res = 0;
try {
res = num1 / num2;
} catch (Exception e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("出现异常的原因=" + e.getMessage());//输出异常信息
}
System.out.println("程序继续运行....");
}
}
10.3 异常介绍
● 基本概念
Java语言中,将程序执行中发生的不正常情况称为“异常”。(开发过程中的语法错误和逻辑错误不是异常)
● 执行过程中所发生的异常事件可分为两大类
-
Error(错误): Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如: JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。比如: StackOverflowError[栈溢出]和OOM(out of memory), Error 是严重错误,程序会崩溃。
-
Exception: 其它因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,可以使用针对性的代码进行处理。例如空指针访问,试图读取不存在的文件,网络连接中断等等,Exception 分为两大类: 运行时异常[程序运行时,发生的异常]和编译时异常[编程时,编译器检查出的异常]。
10.4 异常体系图一览
10.4.1 异常体系图
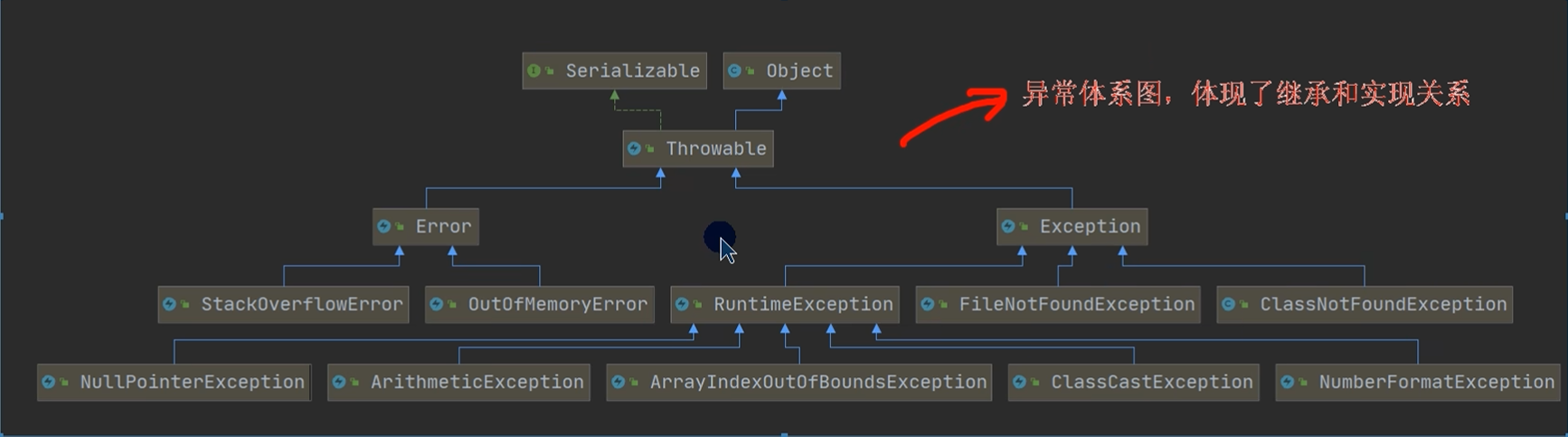
10.4.2 异常体系图的小结
- 异常分为两大类,运行时异常和编译时异常.
- 运行时异常,编译器检查不出来。一般是指编程时的逻辑错误,是程序员应该避免其出现的异常。java.lang.RuntimeException类及它的子类都是运行时异常
- 对于运行时异常,可以不作处理,因为这类异常很普遍,若全处理可能会对程序的可读性和运行效率产生影响
- 编译时异常,是编译器要求必须处置的异常。
10.5 常见的运行时异常
10.5.1 常见的运行时异常包括
- NullPointerException 空指针异常
- ArithmeticException 数学运算异常
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界异常
- ClassCastException 类型转换异常
- NumberFormatException 数字格式不正确异常[]
10.5.2 常见的运行时异常举例
- NullPointerException 空指针异常 NullPointerException_.java
当应用程序试图在需要对象的地方使用 null 时,抛出该异常,看案例演示。
public class NullPointerException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
}
}
- ArithmeticException数学运算异常ArithmeticException_.java
当出现异常的运算条件时,抛出此异常。例如,一个整数“除以零”时,抛出此类的一个实例,案例演示
public class ArithmeticException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
int num =a / b; //抛出ArithmeticException
System.out.println(num);
}
}
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException数组下标越界异常
用非法索引访问数组时抛出的异常。如果索引为负或大于等于数组大小,则该索引为非法索引
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,4};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
- ClassCastException类型转换异常
当试图将对象强制转换为不是实例的子类时,抛出该异常。例如,以下代码将生成一个ClassCastException
public class ClassCastException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A b = new B(); //向上转型
B b2 = (B)b;//向下转型,这里是OK
C c2 = (C)b;//这里抛出ClassCastException
}
}
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C extends A {}
- NumberFormatException数字格式不正确异常
public class NumberFormatException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "sky";
//将String 转成 int
int num = Integer.parseInt(name);//抛出NumberFormatException
System.out.println(num);//1234
}
}
10.6编译异常
10.6.1 介绍
编译异常是指在编译期间,就必须处理的异常,否则代码不能通过编译。
10.6.2 常见的编译异常
- SQLException //操作数据库时,查询表可能发生异常
- IOException //操作文件时,发生的异常
- FileNotFoundException //当操作一个不存在的文件时,发生异常
- ClassNotFoundException //加载类,而该类不存在时,异常
- EOFException // 操作文件,到文件末尾,发生异常
- IllegalArguementException //参数异常
10.6.3 案例说明
因为我们还没有学习SQL,文件编程等等,这里我们先举一个(FileNotFoundException)案例来说明,其它异常使用方式类似,演示:
代码
public class Exception02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis;
fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\aa.jpg");
int len;
while ((len = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(len);
}
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
10.7 异常课堂练习
看看下面代码是否正确,为什么? 课堂练习 4 个题 4min
String friends[]={"tom","jack","milan"};
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
System.out.println(friends[i]);
}
//出现ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Cat c=new Cat();
cat=null;
System.out.println(cat.name);
//出现NullPointerException
public class AAA{
int x;//默认 0
public static void main(String[] args) {
int y;
AAA a=new AAA();
y=3/a.x; //==> 3 / 0
System.out.println(“program ends ok!”);
}
}//ArithmeticException
class Person {
public static void main(String[] args)
Object obj = new Date();
Person person;
person = (Person)obj;
System.out.println(person);
}
} //出现ClassCastException
10.8 异常处理
10.8.1 基本介绍
异常处理就是当异常发生时,对异常处理的方式。
10.8.2 异常处理的方式
try-catch-finally
程序员在代码中捕获发生的异常,自行处理throws
将发生的异常抛出,交给调用者(方法)来处理,最顶级的处理者就是JVM
10.8.3 示意图
try-catch-finally 处理机制示意图
try {
// 代码/可能有异常
} catch(Exception e) {
// 捕获到异常
// 1.当异常发生时
// 2.系统将异常封装成Exception 对象 e,传递给catch
// 3.得到异常对象后,程序员,自己处理
// 4.注意,如果没有发生异常 catch代码块不执行
} finally{
// 1.不管try代码块是否有异常发生,始终要执行finally
// 2.所以,通常将释放资源的代码,放在finally
}
throws 处理机制图
try-catch-finally和throws二选一- 如果程序员,没有显示是处理异常,默认
throws
10.9 try-catch 异常处理
10.9.1 try-catch 方式处理异常说明 TryCatch01.java
- Java提供
try和catch块来处理异常。try块用于包含可能出错的代码,catch块用于处理try块中发生的异常。可以根据需要在程序中有多个try...catch块。 - 基本语法
try {
// 可疑代码
// 将异常生成对应的异常对象,传递给catch块
} catch(异常) {
// 对异常的处理
}
// 如果没有finally,语法是可以通过
10.9.2 try-catch 方式处理异常-快速入门
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1=10;
int num2=0;
try{
int res = num1 / num2;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
10.9.3 try-catch 方式处理异常-注意事项 TryCatchDetail.java
- 如果异常发生了,则异常发生后面的代码不会执行,直接进入到
catch块。 - 如果异常没有发生,则顺序执行
try的代码块,不会进入到catch。 - 如果希望不管是否发生异常,都执行某段代码(比如关闭连接,释放资源等)则使用如下代码-
finally {}
try{
//可疑代码
}catch(异常){
//...
}finally{
//释放资源等..
}
try {
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("数字:" + a);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("不管是否发生异常,始终执行的代码~");
}
代码
public class TryCatchDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ctrl + atl + t
//解读
//1. 如果异常发生了,则异常发生后面的代码不会执行,直接进入到catch块
//2. 如果异常没有发生,则顺序执行try的代码块,不会进入到catch
//3. 如果希望不管是否发生异常,都执行某段代码(比如关闭连接,释放资源等)则使用如下代码- finally
try {
String str = "ming";
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("数字:" + a);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("异常信息=" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally代码块被执行...");
}
System.out.println("程序继续...");
}
}
- 可以有多个
catch语句,捕获不同的异常(进行不同的业务处理),要求父类异常在后,子类异常在前,比如(Exception在后,NullPointerException在前),如果发生异常,只会匹配一个catch,案例演示
代码
public class TryCatchDetail02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//解读
//1.如果try代码块有可能有多个异常
//2.可以使用多个catch 分别捕获不同的异常,相应处理
//3.要求子类异常写在前面,父类异常写在后面
try {
Person person = new Person();
//person = null;
System.out.println(person.getName());//NullPointerException
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
int res = n1 / n2;//ArithmeticException
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常=" + e.getMessage());
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("算术异常=" + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
}
}
}
class Person {
private String name = "jack";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
- 可以进行
try-finally配合使用,这种用法相当于没有捕获异常,因此程序会直接崩掉/退出。应用场景,就是执行一段代码,不管是否发生异常,都必须执行某个业务逻辑
public class TryCatchDetail03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
可以进行 try-finally 配合使用, 这种用法相当于没有捕获异常,
因此程序会直接崩掉/退出。应用场景,就是执行一段代码,不管是否发生异常,
都必须执行某个业务逻辑
*/
try{
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
System.out.println(n1 / n2);
}finally {
System.out.println("执行了finally..");
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行..");
}
}
10.9.4 异常处理课堂练习
1) 题 1 TryCatchExercise01.java
public class Exception01 {
public static int method() {
try {
String[] names = new String[3];//String[]数组
if (names[1].equals("tom")) { //NullPointerException
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) { //捕获
return 3;
} finally { //必须执行
return 4; //返回4
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method()); //4
}
}
//输出什么?
题1解析与答案
- 代码分析:
在try块中,names[1].equals("tom")会触发NullPointerException(因为数组元素未初始化,为null)。
异常被catch (NullPointerException e)捕获,准备返回3,但finally块一定会执行,最终返回finally中的4。 - 答案:4
2) 题 2TryCatchExercise02.java
public class Exception02 {
public static int method() {
int i = 1;
try {
i++; //i = 2
String[] names = new String[3];
if (names[1].equals("tom")) { //空指针
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return ++i; //i = 3
} finally { //必须执行
return ++i; //i = 4
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method()); //输出4
}
}
//练习2 返回
题2解析与答案
- 代码分析:
try块中names[1].equals("tom")触发NullPointerException,进入对应catch块,i先自增为3(准备返回3)。
执行finally块,i再次自增为4,最终返回finally中的4。 - 答案:4
3) 题 3TryCatchExercise03.java
public class ExceptionExe01 {
public static int method() {
int i = 1;//i = 1
try {
i++;//i=2
String[] names = new String[3];
if (names[1].equals("tom")) {//空指针
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return ++i; //i = 3 => 保存临时变量 temp = 3;
} finally {
++i; //i = 4
System.out.println("i=" + i);//i = 4
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method());// 3
}
}
//练习3 i=4, 3
题3解析与答案
- 代码分析:
try块中触发NullPointerException,进入对应catch块,i自增为3(临时保存返回值3)。
执行finally块,i自增为4并打印i=4,但finally块没有返回语句,最终返回catch块中保存的临时值3。 - 答案:先打印
i=4,再输出3
10.9.5 try-catch-finally 执行顺序小结
- 如果没有出现异常,则执行
try块中所有语句,不执行catch块中语句,如果有finally,最后还需要执行finally里面的语句 - 如果出现异常,则
try块中异常发生后,try块剩下的语句不再执行。将执行catch块中的语句,如果有finally,最后还需要执行finally里面的语句!
10.9.6 课后练习题: TryCatchExercise04.java
如果用户输入的不是一个整数,就提示他反复输入,直到输入一个整数为止
public class TryCatchExercise04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果用户输入的不是一个整数,就提示他反复输入,直到输入一个整数为止
//思路
//1. 创建Scanner对象
//2. 使用无限循环,去接收一个输入
//3. 然后将该输入的值,转成一个int
//4. 如果在转换时,抛出异常,说明输入的内容不是一个可以转成int的内容
//5. 如果没有抛出异常,则break 该循环
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = 0;
String inputStr = "";
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:"); //
inputStr = scanner.next();
try {
num = Integer.parseInt(inputStr); //这里是可能抛出异常
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("你输入的不是一个整数:");
}
}
System.out.println("你输入的值是=" + num);
}
}
10.10 throws 异常处理
10.10.1 基本介绍
- 如果一个方法(中的语句执行时)可能生成某种异常,但是并不能确定如何处理这种异常,则此方法应显示地声明抛出异常,表明该方法将不对这些异常进行处理,而由该方法的调用者负责处理。
- 在方法声明中用
throws语句可以声明抛出异常的列表,throws后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类。
10.10.2 快速入门案例
演示,初步体会一把. Throws01.java
public static void readFile(String file) throws FileNotFoundException {
// ......
// 读文件的操作可能产生FileNotFoundException类型的异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/aa.txt");
// .........
}
10.10.3 注意事项和使用细节 ThrowsDetail.java
- 对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如 try-catch 或者 throws
- 对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是 throws 的方式处理[举例]
- 子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法,所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常的类型的子类型[举例]
- 在 throws 过程中,如果有方法 try-catch,就相当于处理异常,就可以不必 throws
public class ThrowsDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
f2();
}
public static void f2() /*throws ArithmeticException*/ {
//1.对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如 try-catch 或者 throws
//2.对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是throws的方式处理
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
double res = n1 / n2;
}
public static void f1() throws FileNotFoundException {
//这里大家思考问题 调用f3() 报错
//解读
//1. 因为f3() 方法抛出的是一个编译异常
//2. 即这时,就要f1() 必须处理这个编译异常
//3. 在f1() 中,要么 try-catch-finally ,或者继续throws 这个编译异常
f3(); // 抛出异常
}
public static void f3() throws FileNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://aa.txt");
}
public static void f4() {
//解读:
//1. 在f4()中调用方法f5() 是OK
//2. 原因是f5() 抛出的是运行异常
//3. 而java中,并不要求程序员显示处理,因为有默认处理机制
f5();
}
public static void f5() throws ArithmeticException {
}
}
10.11 自定义异常
10.11.1 基本概念
当程序中出现了某些“错误”,但该错误信息并没有在Throwable子类中描述处理,这个时候可以自己设计异常类,用于描述该错误信息。
10.11.2 自定义异常的步骤
- 定义类:自定义异常类名(程序员自己写),继承
Exception或RuntimeException - 如果继承
Exception,属于编译异常 - 如果继承
RuntimeException,属于运行异常(一般来说,继承RuntimeException)
10.11.3 自定义异常的应用实例 CustomException.java
当我们接收Person对象年龄时,要求范围在 18 - 120 之间,否则抛出一个自定义异常(要求 继承RuntimeException),并给出提示信息。
public class CustomException {
public static void main(String[] args) /*throws AgeException*/ {
int age = 180;
//要求范围在 18 – 120 之间,否则抛出一个自定义异常
if(!(age >= 18 && age <= 120)) {
//这里我们可以通过构造器,设置信息
throw new AgeException("年龄需要在 18~120之间");
}
System.out.println("你的年龄范围正确.");
}
}
//自定义一个异常
//解读
//1. 一般情况下,我们自定义异常是继承 RuntimeException
//2. 即把自定义异常做成 运行时异常,好处时,我们可以使用默认的处理机制
//3. 即比较方便
class AgeException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeException(String message) {//构造器
super(message);
}
}
10.12 throw 和 throws 的区别
10.12.1 一览表
| 意义 | 位置 | 后面跟的东西 | |
|---|---|---|---|
throws |
异常处理的一种方式 | 方法声明处 | 异常类型 |
throw |
手动生成异常对象的关键字 | 方法体中 | 异常对象 |
10.12.2 测试题-下面的测试输出什么 ThrowException.java2mi
public class ThrowException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ReturnExceptionDemo.methodA();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
ReturnExceptionDemo.methodB();
}
}
class ReturnExceptionDemo {
static void methodA() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法A");
throw new RuntimeException("制造异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("用A方法的finally");
}
}
static void methodB() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法B");
return;
} finally {
System.out.println("调用B方法的finally");
}
}
}
/*
输出结果
进入方法A
用A方法的finally
制造异常
进入方法B
调用B方法的finally
*/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号