实验7
demo1.c
代码
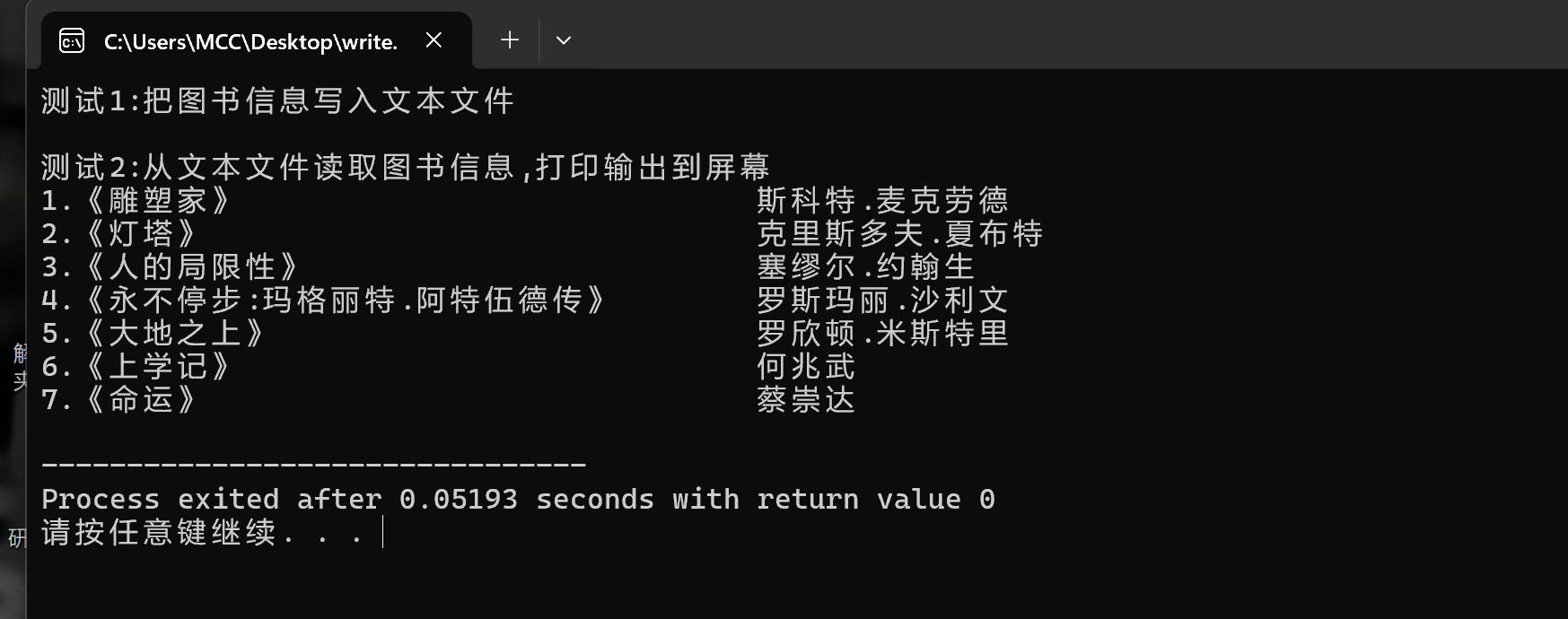
#include <stdio.h> #define N 80 #define M 100 typedef struct{ char name[N]; char author[N]; }Book; void write(); void read(); int main(){ printf("测试1:把图书信息写入文本文件\n"); write(); printf("\n测试2:从文本文件读取图书信息,打印输出到屏幕\n"); read(); return 0; } void write(){ int i,n; Book x[]={ {"《雕塑家》", "斯科特.麦克劳德"}, {"《灯塔》", "克里斯多夫.夏布特"}, {"《人的局限性》", "塞缪尔.约翰生"}, {"《永不停步:玛格丽特.阿特伍德传》", "罗斯玛丽.沙利文"}, {"《大地之上》", "罗欣顿·米斯特里"}, {"《上学记》", "何兆武"}, {"《命运》", "蔡崇达"} }; n=sizeof(x)/sizeof(x[0]); FILE *fp; fp=fopen("data2.dat","wb");//以写入2进制write的方式打开文件 if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file to write\n"); return; } //将结构体数组x中的图书信息以二进制形式写入dat2.dat fwrite(x,sizeof(Book),n,fp);//这是写在一行的嘛 //fwrite参数模型 fwrite(*ptr,size,number,FILE *stream) //ptr是写入数据的指针,size是每个数据项的大小,以字节为单位 //要写入数据项的数量,stream指向FILE结构体的指针,写入数据的 //文件流 fclose(fp); } void read(){ Book x[M]; int i,n; int number; FILE *fp; //以读的方式打开二进制文件data2.dat fp=fopen("data2.dat","rb"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open fail to read\n"); return; } i=0; while(!feof(fp)){ number=fread(&x[i],sizeof(Book),1,fp); if(number!=1) break; i++; } //在屏幕上打印输出 n=i; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ printf("%d.%-40s%-20s\n",i+1,x[i].name,x[i].author); } fclose(fp); }
结果1
demo2.c
代码
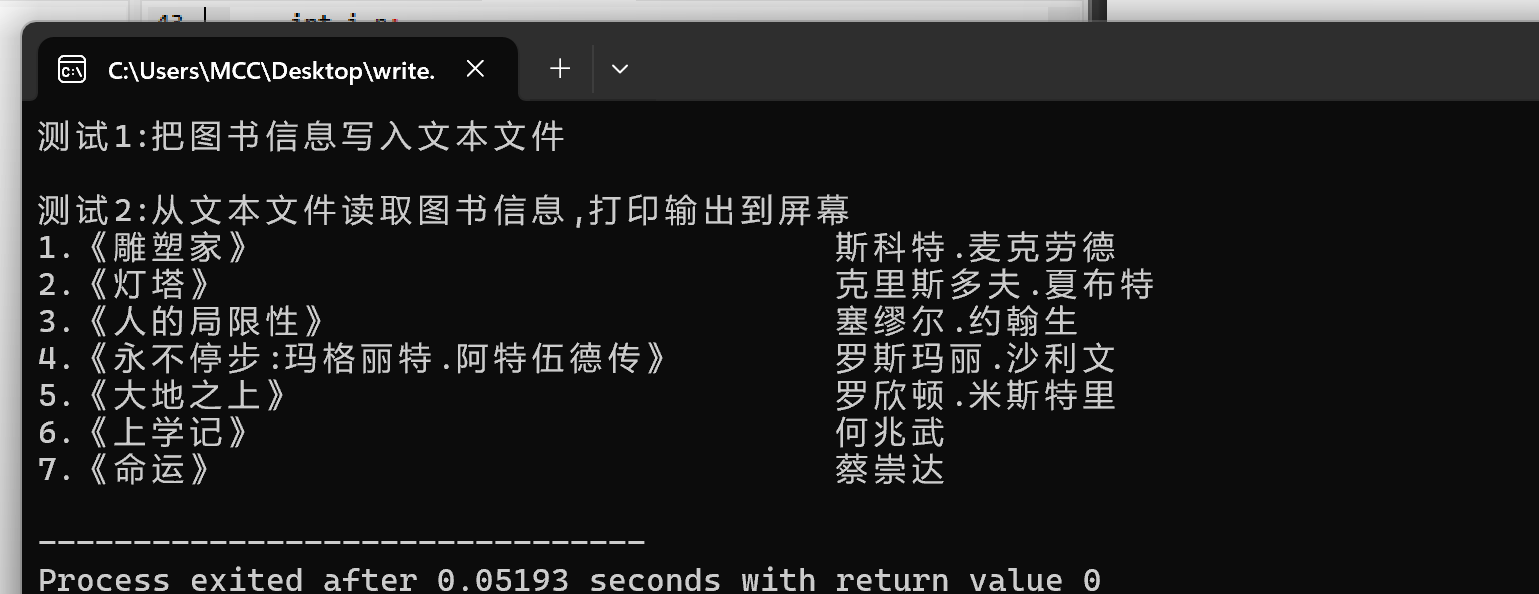
#include <stdio.h> #define N 80 #define M 100 typedef struct{ char name[N]; char author[N]; }Book; void write(); void read(); int main(){ printf("测试1:把图书信息写入文本文件\n"); write(); printf("\n测试2:从文本文件读取图书信息,打印输出到屏幕\n"); read(); return 0; } void write(){ int i,n; Book x[]={ {"《雕塑家》", "斯科特.麦克劳德"}, {"《灯塔》", "克里斯多夫.夏布特"}, {"《人的局限性》", "塞缪尔.约翰生"}, {"《永不停步:玛格丽特.阿特伍德传》", "罗斯玛丽.沙利文"}, {"《大地之上》", "罗欣顿·米斯特里"}, {"《上学记》", "何兆武"}, {"《命运》", "蔡崇达"} }; n=sizeof(x)/sizeof(x[0]); FILE *fp; fp=fopen("data2.dat","wb");//以写入2进制write的方式打开文件 if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file to write\n"); return; } //将结构体数组x中的图书信息以二进制形式写入dat2.dat fwrite(x,sizeof(Book),n,fp);//这是写在一行的嘛 //fwrite参数模型 fwrite(*ptr,size,number,FILE *stream) //ptr是写入数据的指针,size是每个数据项的大小,以字节为单位 //要写入数据项的数量,stream指向FILE结构体的指针,写入数据的 //文件流 fclose(fp); } void read(){ Book x[M]; int i,n; int number; FILE *fp; //以读的方式打开二进制文件data2.dat fp=fopen("data2.dat","rb"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open fail to read\n"); return; } i=0; while(!feof(fp)){ number=fread(&x[i],sizeof(Book),1,fp); //fread函数 fread(*ptr,size,number,*stream) //ptr指针是指文件存储的位置,size是每个数据项的大小 //number是要读取的数据项的数量,stream就是文件流 //填的不是指针 *fp都是地址比如fp //fread是指针fp一直以一个数据项为单位读文本一个个读下去 //将读到的数据存储到结构体x[i]中,且在fread函数中我们 //声明了x[i]结构体数据的大小就是Book也就是x[0]; if(number!=1) break; i++; } //在屏幕上打印输出 n=i; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ printf("%d.%-40s%-20s\n",i+1,x[i].name,x[i].author); } fclose(fp); }
结果
demo3.c
代码
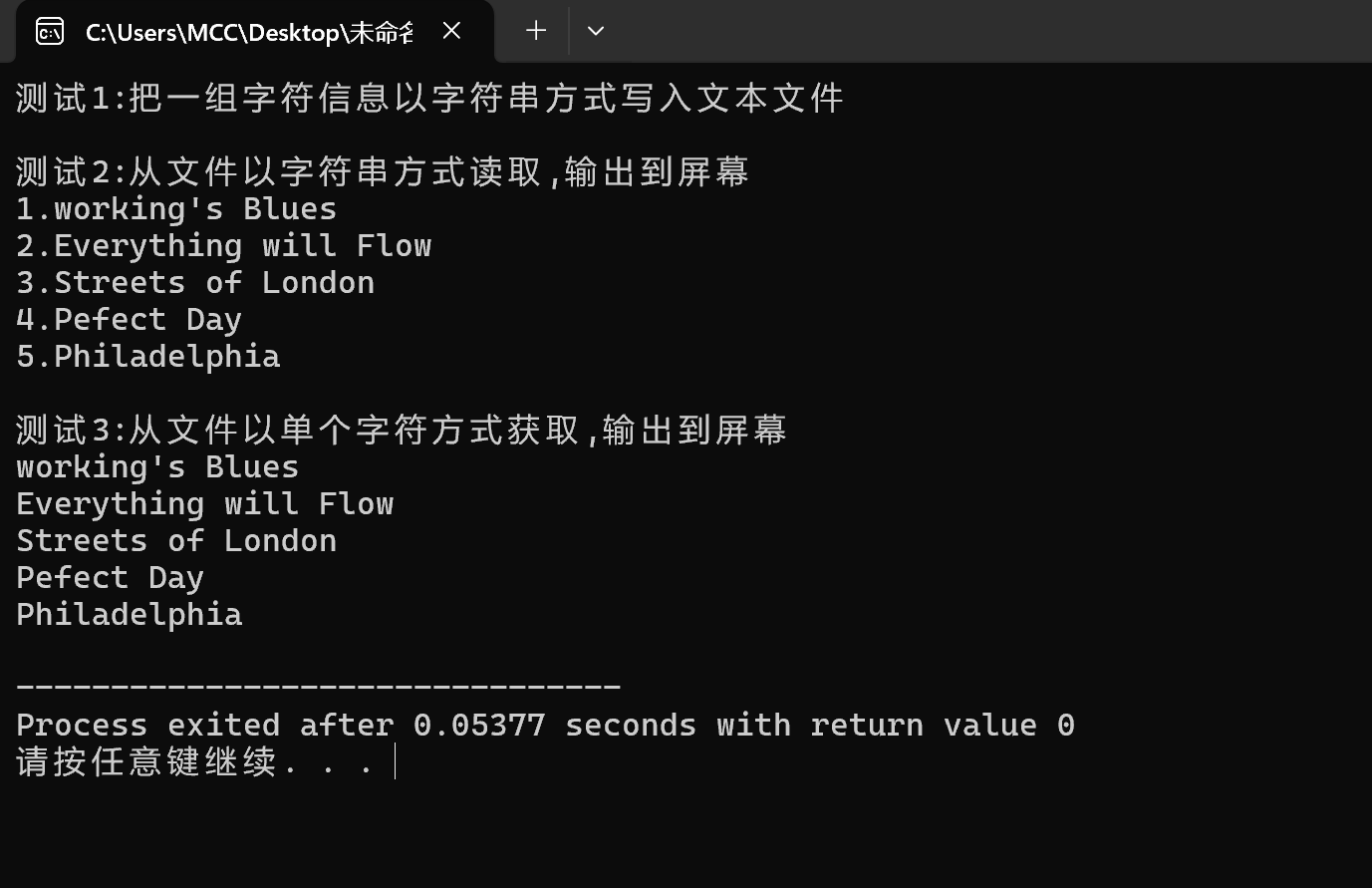
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 #define M 80 void write(); void read_str(); void read_char(); int main(){ printf("测试1:把一组字符信息以字符串方式写入文本文件\n"); write(); printf("\n测试2:从文件以字符串方式读取,输出到屏幕\n"); read_str(); printf("\n测试3:从文件以单个字符方式获取,输出到屏幕\n"); read_char(); return 0; } void write(){ char *ptr[N]={"working\'s Blues",//转义字符\'就是输出时 //是' "Everything will Flow", "Streets of London", "Pefect Day", "Philadelphia"}; int i; FILE *fp; fp=fopen("data3.txt","w"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file to write\n"); return; } for(i=0;i<N;i++){ fputs(ptr[i],fp);//fupts(char *str,FILE *stream) //str是写入的以null结尾的字符串指针 //stream是文件流 fputs("\n",fp); } fclose(fp); } void read_str(){ char songs[N][M]; int i; FILE *fp; fp=fopen("data3.txt","r"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file to read\n"); return; } for(i=0;i<N;i++) fgets(songs[i],80,fp); //char *fgets(char *str,int num, FILE *stream) //str:指向字符数组的指针,fgets会将读取的字符串存储在这里 //num表示要读取的最大字符数,包括空字符\0 //stream文件流指针 //fgets(songs[i],80,fp);表示存储到songs这个二维数组 //每一行之中 for(i=0;i<N;i++) printf("%d.%s",i+1,songs[i]); fclose(fp); } void read_char(){ char ch; FILE *fp; fp=fopen("data3.txt","r"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file to read\n"); return; } while(!feof(fp)){ ch=fgetc(fp); if(ch==EOF) break; putchar(ch); } fclose(fp); }
结果
demo4.c
代码
#include <stdio.h> #define N 80 #include <string.h> void read(); void remove_spaces(char *str_old,char *str_new); int main(){ printf("data4.txt统计结果:\n"); read(); return 0; } void read(){ FILE *fp; char x[N][N];char y[N][N]; fp=fopen("data4.txt","r"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file to read"); return; } int i=0;int l=0;int ans=0;int temp=0; while(!feof(fp)){ fgets(x[i],80,fp); remove_spaces(x[i],y[i]); i=i+1; } l=i; for(i=0;i<l;i++){ temp=strlen(y[i]); ans=ans+temp; } printf("行数: %d\n",l); printf("字符数(不计空白符): %d",ans); } void remove_spaces(char *str_old,char *str_new){ while(*str_old){ if(*str_old!=' '&&*str_old!='\n'&&str_old!='\t'){ *str_new++=*str_old; } str_old++; } *str_new='\0'; }
结果
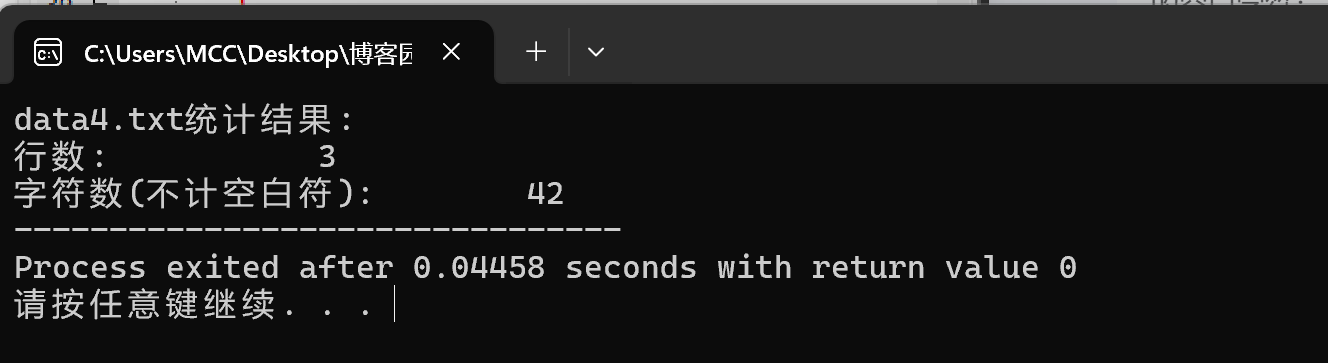
demo5.c
代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define N 10 typedef struct{ long id; //准考证号 char name[20]; //姓名 float objective; //客观题得分 float subjective; //主观题得分 float sum; //总分 char result[10]; //考试结果 }STU; void read(STU st[],int n); void write(STU st[],int n); void output(STU st[],int n); int process(STU st[],int n,STU st_pass[]); int main(){ STU stu[N],stu_pass[N]; int cnt; double pass_rate; printf("从文件读入%d个考生信息...\n",N); read(stu,N); printf("\n对考生成绩进行统计...\n"); cnt=process(stu,N,stu_pass); printf("\n考试通过的名单:\n"); output(stu,N); //输出所有考生完整信息到屏幕 write(stu,N); //输出考试通过的考生信息到文件 pass_rate=1.0*cnt/N; //通过率 printf("\n本次等级考试通过率:%.2f%%\n",pass_rate*100); return 0; } //把所有考生完整信息输出到屏幕上 //准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,结果 void output(STU st[], int n) { int i; printf("准考证号\t姓名\t客观题得分\t操作题得分\t总分\t\t结果\n"); for (i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%ld\t\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%s\n", st[i].id, st[i].name, st[i].objective, st[i].subjective, st[i].sum, st[i].result); } void read(STU st[],int n){ int i; FILE *fin; fin=fopen("examinee.txt","r"); if(fin==NULL){ printf("fail to open fail\n"); return; } while(!feof(fin))//!feof(fin) { for(i=0;i<n;i++) fscanf(fin,"%ld%s%f%f",&st[i].id,st[i].name, &st[i].objective,&st[i].subjective ); fclose(fin); } } //把通过考试的考生完整信息写入文件list_pass.txt //准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,结果 int process(STU st[],int n,STU st_pass[]){ int i;int t=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ st[i].sum=st[i].objective+st[i].subjective; if(st[i].sum>60){ strcpy(st[i].result,"通过"); st_pass[t]=st[i]; t=t+1; } else if(st[i].sum<60){ strcpy(st[i].result,"不通过"); } } write(st_pass,N); return t; } //如果有错误点击生产解决方案 void write(STU st[],int n){ FILE *fp; int num; fp=fopen("list_pass.txt","w"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open list file to write\n"); return; } num=sizeof(st)/sizeof(st[0]); fwrite(st,sizeof(STU),num,fp); fclose(fp); }
结果
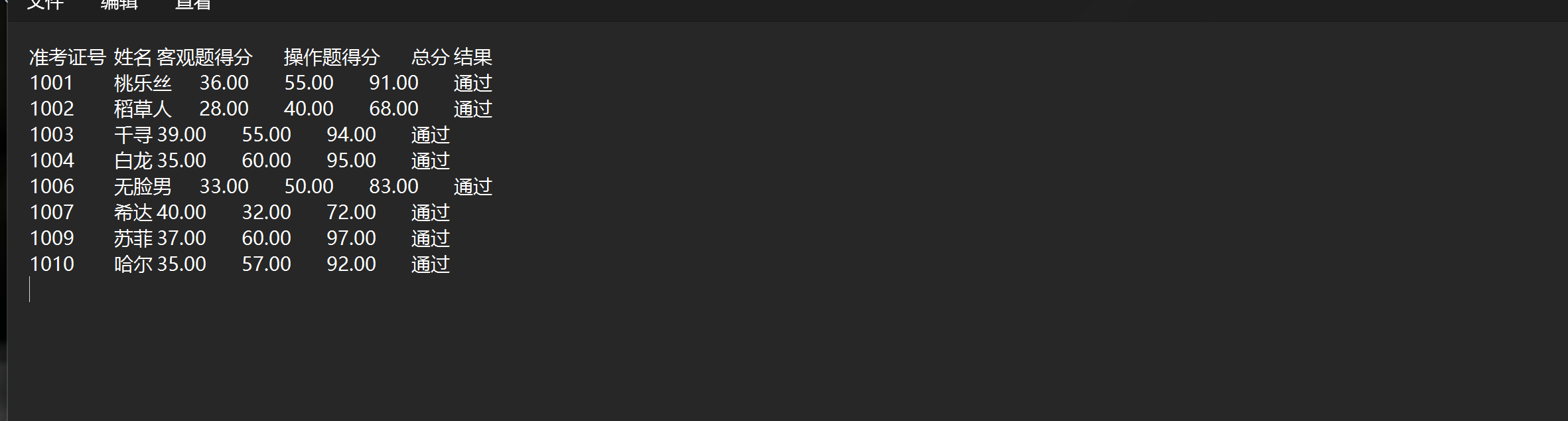
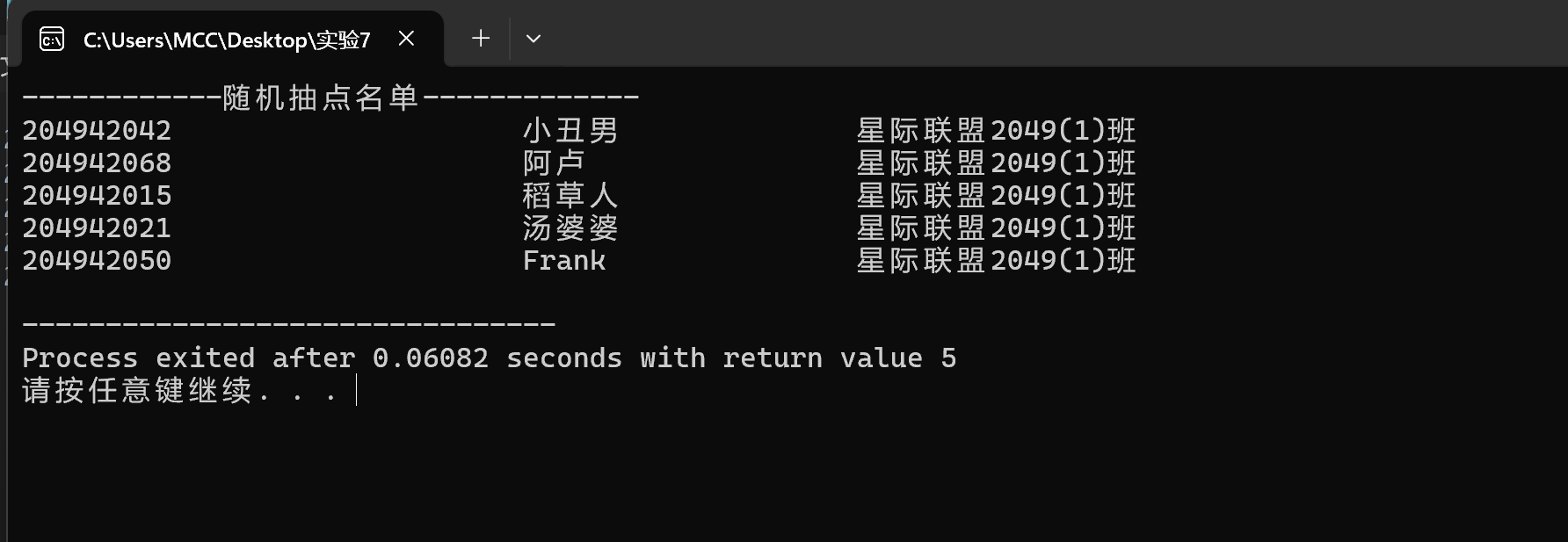
demo6.c
代码
#include <stdio.h> #define N 80 #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> typedef struct{ int id;//学号 char name[20];//名字 char classes[20];//班级 }Stu; void read(int n,Stu x[]); void write(int n,Stu x[]); int main(){ int i; int random_numbers[5]; Stu x[N]; read(N,x); for(i=0;i<5;i++){ random_numbers[i]=rand() %80;//生成5个0到79的随机数 //rand()函数生成随机数 x=rand()%70就是0到70的余数 } printf("------------随机抽点名单-------------\n"); for(i=0;i<5;i++){ printf("%-30d%-20s%-40s\n",x[random_numbers[i]].id, x[random_numbers[i]].name,x[random_numbers[i]].classes ); } Stu rdx[5]; for(i=0;i<5;i++){ rdx[i]=x[random_numbers[i]]; } write(5,rdx); } void read(int n,Stu x[]){ FILE *fp; int i; fp=fopen("list.txt","r"); for(i=0;i<n;i++){ fscanf(fp,"%d%s%s",&x[i].id,x[i].name,x[i].classes); } fclose(fp); } void write(int n,Stu x[]){ FILE *fp; fp=fopen("xie.txt","w"); if(fp==NULL){ printf("fail to open file to write\n"); return; } int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ fprintf(fp,"%-30d%-20s%-40s\n",x[i].id, x[i].name,x[i].classes ); } }
结果




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号