字符串例题讲集
前言
有关字符串的算法是一个极其神奇 \((Amazing)\) 并且令人着迷 \((Addicting)\) 的部分,这篇博客将涉及 KMP , Trie树 , AC-AM 和 Manacher ,以及关于 01Trie 的应用。
(PS: 以习题为主,主要应用于讲课,故 未有全面解析 ,将逐渐补全)
KMP
KMP为一种高效的解决字符串匹配的算法,时间复杂度为 \(O(n+m)\)
Code
inline void KMP()
{
int k=0; nxt[1]=0;
for(int i=2;i<=lt;i+=1)
{
while(k&&t[i]!=t[k+1]) k=nxt[k];
if(t[i]==t[k+1]) k+=1;
nxt[i]=k;
}
}
板子我就先放这里了(
例题
题目大意
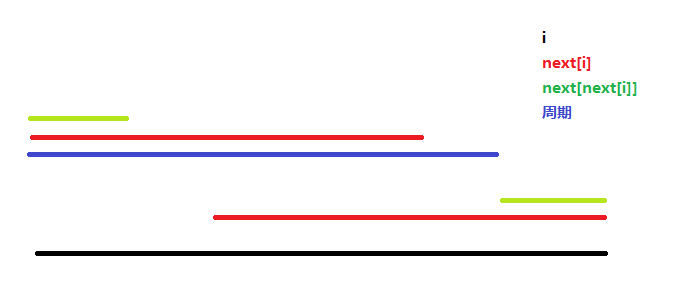
对于一个仅含小写字母的字符串 a,p 为 a 的前缀且 p≠a,那么我们称 p 为 a 的 proper 前缀。
规定字符串 Q(可以是空串)表示 aaa 的周期,当且仅当 Q 是 a 的 proper 前缀且 aaa 是 Q+Q 的前缀。
例如 ab 是 abab 的一个周期,因为 ab 是 abab 的 proper 前缀,且 abab 是 ab+ab 的前缀。
求给定字符串所有前缀的最大周期长度之和。
有一张来自 Orion545 图比较好,我薅一下
Cpde
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int n,nxt[1000010],x;
char s[1000010];
long long ans;
inline void KMP()
{
int k=0; nxt[1]=0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i+=1)
{
while(k&&s[i]!=s[k+1]) k=nxt[k];
if(s[i]==s[k+1]) k+=1;
nxt[i]=k;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",s+1);
KMP();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i+=1)
{
x=nxt[i];
while(nxt[x]>0) x=nxt[x];
if(x) nxt[i]=x,ans+=i-x;
}
printf("%lld",ans);
return 0;
}
Trie
\(Trie\) ,名为字典树,树如其名,就像一本字典一样,可以查单词¿¿¿
Code
提供两款风味的 $Trie $ \(Tree\) 模板
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1e5+10;
struct node
{
int path,end;
char ch;
node *next[26];
node(char ch=' ')
{
this->path=0;
this->end=0;
this->ch=ch;
for(int i=0;i<26;i+=1)
this->next[i]=nullptr;
}
};
class Trie
{
private:
node *root;
public:
Trie(){root=new node();}
~Trie(){destroy(root);}
void destroy(node *t)
{
for(int i=0;i<26;i+=1)
if(t->next[i]) t=t->next[i];
delete(t);
}
void add(char *s)
{
node *t=root;
while(*s)
{
if(t->next[*s-'a']==nullptr)
t->next[*s-'a']=new node(*s);
t=t->next[*s-'a']; t->path+=1;
++s;
}
t->end+=1;
}
void remove(char *s)
{
if(!query(s)) return ;
node *t=root;
while(*s)
{
t=t->next[*s-'a']; t->path-=1;
++s;
}
t->end-=1;
}
int query(char *s)
{
node *t=root;
while(*s)
{
if(t->next[*s-'a']==nullptr) return 0;
t=t->next[*s-'a'];
++s;
}
return t->end;
}
}cyr;
class Tree
{
private:
int tr[MAXN][26],tot;
int path[MAXN<<5],end[MAXN<<5];
public:
Tree(){tot=0;}
void add(char *s)
{
int p=0;
while(*s)
{
if(tr[p][*s-'a']==0)
tr[p][*s-'a']=++tot;
p=tr[p][*s-'a'];
path[p]+=1;
++s;
}
end[p]+=1;
}
void remove(char *s)
{
if(!query(s)) return ;
int p=0;
while(*s)
{
p=tr[p][*s-'a'];
path[p]-=1;
++s;
}
end[p]-=1;
}
int query(char *s)
{
int p=0;
while(*s)
{
if(tr[p][*s-'a']==0) return 0;
p=tr[p][*s-'a'];
++s;
}
return end[p];
}
}dqr;
char s[MAXN];
int main()
{
scanf("%s",s);
cyr.add(s);
cout<<cyr.query(s);
cyr.remove(s);
cout<<cyr.query(s);
scanf("%s",s);
dqr.add(s);
cout<<dqr.query(s);
dqr.remove(s);
cout<<dqr.query(s);
}
例题
先来一道 SP4033 热热身
题目大意:
\(n\) 个数字串,问是否存在两个数字串,使得一个是另一个的前缀(啊,就这)
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int path,end;
node *next[10];
node(){
this->end=0; this->path=0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i+=1)
this->next[i]=nullptr;
}
};
int T,n;
char s[15];
class Trie
{
private:
node *root;
bool flag;
public:
Trie(){root=new node();}
~Trie(){destroy(root);}
void destroy(node *t)
{
for(int i=0;i<10;i+=1)
if(t->next[i])
destroy(t->next[i]);
delete(t);
}
void add(char *s)
{
node *t=root;
while(*s)
{
if(t->next[*s-'0']==nullptr)
t->next[*s-'0']=new node();
t=t->next[*s-'0'];
t->path+=1;
++s;
}
t->end=1;
}
void dfs(node *t)
{
if(flag) return;
if(t->end&&t->path>=2)
{
flag=true;
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i+=1)
if(t->next[i])
dfs(t->next[i]);
}
void check()
{
flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<10;i+=1)
if(root->next[i])
dfs(root->next[i]);
if(!flag) printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
};
inline void work()
{
Trie cyr;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i+=1)
{
scanf("%s",s);
cyr.add(s);
}
cyr.check();
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--) work();
return 0;
}
再来一道 P2922 练练手
题目大意:
\(m\) 个截获信息,\(n\) 个破译信息,问对于每个破译信息最多可能匹配多少个截获信息
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1e4+10;
struct node
{
int path,end;
node *next[2];
node()
{
this->path=0; this->end=0;
for(int i=0;i<2;i+=1)
this->next[i]=nullptr;
}
};
class Trie
{
private:
node *root;
public:
Trie(){root=new node();}
~Trie(){destroy(root);}
void destroy(node *t)
{
for(int i=0;i<2;i+=1)
if(t->next[i]) t=t->next[i];
delete(t);
}
void add(int *a,int l)
{
node *t=root;
for(int i=1;i<=l;i+=1)
{
if(t->next[a[i]]==nullptr)
t->next[a[i]]=new node();
t=t->next[a[i]]; t->path+=1;
}
t->end+=1;
}
int query(int *a,int l)
{
int cnt=0;
node *t=root;
for(int i=1;i<=l;i+=1)
{
if(t->next[a[i]]==nullptr) return cnt;
t=t->next[a[i]];
if(t->end) cnt+=t->end;
}
return cnt+t->path-t->end;
}
}cyr;
int n,m,len,a[MAXN];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i+=1)
{
scanf("%d",&len);
for(int j=1;j<=len;j+=1)
scanf("%d",&a[j]);
cyr.add(a,len);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i+=1)
{
scanf("%d",&len);
for(int j=1;j<=len;j+=1)
scanf("%d",&a[j]);
printf("%d\n",cyr.query(a,len));
}
return 0;
}
AC-AM
又名 \(AC自动机\) ,可简单的理解为在 \(Trie\) 树上跑 \(KMP\), 虽然不是那么恰当, 但其核心也在于失配指针(又叫 \(fail\) 指针), \(fail\) 边的实质是连接的两个字符串具有相同的后缀
三道经典班子题......
例题
相信大家都可以秒了它们的
那么...就再来一道沝题P3966
题目大意
给定 \(n\) 个字符串,问每个字符串在所有字符串中的出现总次数
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int val;
node *fail;
node *next[26];
node()
{
this->val=0;
this->fail=nullptr;
for(int i=0;i<26;i+=1)
this->next[i]=nullptr;
}
};
class Trie
{
private:
node *root;
queue<node*> q;
stack<node*> c;
public:
Trie(){root=new node();}
~Trie(){destroy(root);}
void destroy(node *t)
{
for(int i=0;i<26;i+=1)
if(t->next[i]) destroy(t->next[i]);
delete(t);
}
void add(char *s)
{
node *t=root;
while(*s)
{
if(t->next[*s-'a']==nullptr)
t->next[*s-'a']=new node();
t=t->next[*s-'a'];
t->val+=1; ++s;
}
}
void build_fail()
{
node *t=root;
node *p;
for(int i=0;i<26;i+=1)
{
if(t->next[i])
{
t->next[i]->fail=root;
q.push(t->next[i]);
c.push(t->next[i]);;
}
}
while(!q.empty())
{
t=q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<26;i+=1)
{
if(t->next[i])
{
p=t->fail;
while(p)
{
if(p->next[i])
{
t->next[i]->fail=p->next[i];
break;
}
p=p->fail;
}
if(p==nullptr) t->next[i]->fail=root;
q.push(t->next[i]);c.push(t->next[i]);
}
}
}
}
void get_val()
{
node *t;
while(!c.empty())
{
t=c.top(); c.pop();
t->fail->val+=t->val;
}
}
int query(char *s)
{
node *t=root;
while(*s) t=t->next[*(s++)-'a'];
return t->val;
}
}cyr;
int n;
char s[201][1000000];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i+=1)
{
scanf("%s",s[i]);
cyr.add(s[i]);
}
cyr.build_fail(); cyr.get_val();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i+=1)
printf("%d\n",cyr.query(s[i]));
return 0;
}
\(\Large \; To \; Be \; Continue...\)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号