OOP-实验三
实验任务一
源代码
button.hpp
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Button {
public:
Button(const std::string &label_);
const std::string& get_label() const;
void click();
private:
std::string label;
};
Button::Button(const std::string &label_): label{label_} {
}
inline const std::string& Button::get_label() const {
return label;
}
inline void Button::click() {
std::cout << "Button '" << label << "' clicked\n";
}
window.hpp
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include "button.hpp"
// 窗口类
class Window{
public:
Window(const std::string &title_);
void display() const;
void close();
void add_button(const std::string &label);
void click_button(const std::string &label);
private:
bool has_button(const std::string &label) const;
private:
std::string title;
std::vector<Button> buttons;
};
Window::Window(const std::string &title_): title{title_} {
buttons.push_back(Button("close"));
}
inline void Window::display() const {
std::string s(40, '*');
std::cout << s << std::endl;
std::cout << "window : " << title << std::endl;
int cnt = 0;
for(const auto &button: buttons)
std::cout << ++cnt << ". " << button.get_label() << std::endl;
std::cout << s << std::endl;
}
inline void Window::close() {
std::cout << "close window '" << title << "'" << std::endl;
click_button("close");
}
inline bool Window::has_button(const std::string &label) const {
for(const auto &button: buttons)
if(button.get_label() == label)
return true;
return false;
}
inline void Window::add_button(const std::string &label) {
if(has_button(label))
std::cout << "button " << label << " already exists!\n";
else
buttons.push_back(Button(label));
}
inline void Window::click_button(const std::string &label) {
for(auto &button:buttons)
if(button.get_label() == label) {
button.click();
return;
}
std::cout << "no button: " << label << std::endl;
}
task1.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "window.hpp"
#include <iostream>
void test(){
Window w("Demo");
w.add_button("add");
w.add_button("remove");
w.add_button("modify");
w.add_button("add");
w.display();
w.close();
}
int main() {
std::cout << "用组合类模拟简单GUI:\n";
test();
}
运行结果
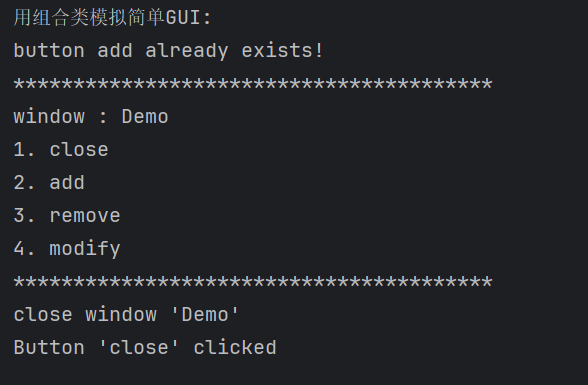
实验结论
1.window类和button是组合类,button是window的成员
2.1改为公有可以在类外部使用此函数,但可能会造成对外接口冗余,维护困难,当修改此函数后,维护起来相当麻烦;破坏了封装性。
2.2可以根据用户需要,用户需要的功能设为public;如果仅仅是内部实现细节,最好设为private,保持类的封装性;如果容易破坏对象状态,要设为priate。
3.接口1返回引用,不会拷贝,性能高,但由于是引用,如果原对象被删除,引用会悬空,安全性较差;接口2返回的是副本 ,性能较低,但与原对象解耦合,安全性较高
4.将push_back改为emplace_back可以运行;push_back是先构造一个临时对象,之后再调用移动构造或拷贝构造函数加入容器,适合小对象且要求可读性要强的场景;emplace_back是直接在容器内部构造,性能较好,适合对象较复杂的场景。
实验任务二
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
void test1();
void test2();
void output1(const std::vector<int> &v);
void output2(const std::vector<int> &v);
void output3(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& v);
int main() {
std::cout << "深复制验证1: 标准库vector<int>\n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n深复制验证2: 标准库vector<int>嵌套使用\n";
test2();
}
void test1() {
std::vector<int> v1(5, 42);
const std::vector<int> v2(v1);
std::cout << "**********拷贝构造后**********\n";
std::cout << "v1: "; output1(v1);
std::cout << "v2: "; output1(v2);
v1.at(0) = -1;
std::cout << "**********修改v1[0]后**********\n";
std::cout << "v1: "; output1(v1);
std::cout << "v2: "; output1(v2);
}
void test2() {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> v1{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6, 7}};
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> v2(v1);
std::cout << "**********拷贝构造后**********\n";
std::cout << "v1: "; output3(v1);
std::cout << "v2: "; output3(v2);
v1.at(0).push_back(-1);
std::cout << "**********修改v1[0]后**********\n";
std::cout << "v1: \n"; output3(v1);
std::cout << "v2: \n"; output3(v2);
}
// 使用xx.at()+循环输出vector<int>数据项
void output1(const std::vector<int> &v) {
if(v.size() == 0) {
std::cout << '\n';
return;
}
std::cout << v.at(0);
for(auto i = 1; i < v.size(); ++i)
std::cout << ", " << v.at(i);
std::cout << '\n';
}
// 使用迭代器+循环输出vector<int>数据项
void output2(const std::vector<int> &v) {
if(v.size() == 0) {
std::cout << '\n';
return;
}
auto it = v.begin();
std::cout << *it;
for(it = v.begin()+1; it != v.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ", " << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
}
// 使用auto for分行输出vector<vector<int>>数据项
void output3(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& v) {
if(v.size() == 0) {
std::cout << '\n';
return;
}
for(auto &i: v)
output2(i);
}
运行结果
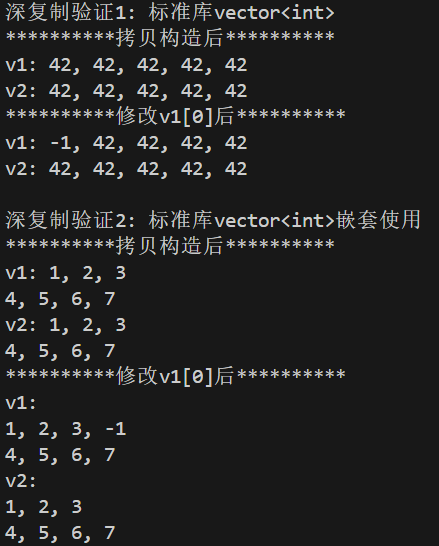
实验结论
1.这两行分别使用了vector的构造函数和拷贝构造函数;包含5个数据项;
2.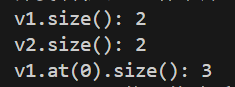
v1.size()为2;v2.size()为2、v1[0].size()为3;
3.把v1.at(0) = -1;写成v1[0] = -1;能实现同等效果;前者会进行安全性检查,更有安全性,后者则不会,但性能会更优;
4.1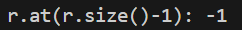
能输出-1,因为r是引用,引用的对象是v1.at(0),即r使用的也是v1.at(0)的存储空间,所以当其改变时,使用r输出的值也是改变后的值;
4.2使用const &类型不会引入拷贝,内存上节省空间;但不可修改。
5.1实现的是深复制
5.2 当v是vectorint &;当v是const vectorconst int &;at()必须提供带 const 修饰的重载版本
实验任务三
源代码
vectorInt.hpp
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
// 动态int数组对象类
class vectorInt{
public:
vectorInt();
vectorInt(int n_);
vectorInt(int n_, int value);
vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi);
~vectorInt();
int size() const;
int& at(int index);
const int& at(int index) const;
vectorInt& assign(const vectorInt &vi);
int* begin();
int* end();
const int* begin() const;
const int* end() const;
private:
int n; // 当前数据项个数
int *ptr; // 数据区
};
vectorInt::vectorInt():n{0}, ptr{nullptr} {
}
vectorInt::vectorInt(int n_): n{n_}, ptr{new int[n]} {
}
vectorInt::vectorInt(int n_, int value): n{n_}, ptr{new int[n_]} {
for(auto i = 0; i < n; ++i)
ptr[i] = value;
}
vectorInt::vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi): n{vi.n}, ptr{new int[n]} {
for(auto i = 0; i < n; ++i)
ptr[i] = vi.ptr[i];
}
vectorInt::~vectorInt() {
delete [] ptr;
}
int vectorInt::size() const {
return n;
}
const int& vectorInt::at(int index) const {
if(index < 0 || index >= n) {
std::cerr << "IndexError: index out of range\n";
std::exit(1);
}
return ptr[index];
}
int& vectorInt::at(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= n) {
std::cerr << "IndexError: index out of range\n";
std::exit(1);
}
return ptr[index];
}
vectorInt& vectorInt::assign(const vectorInt &vi) {
if(this == &vi)
return *this;
int *ptr_tmp;
ptr_tmp = new int[vi.n];
for(int i = 0; i < vi.n; ++i)
ptr_tmp[i] = vi.ptr[i];
delete[] ptr;
n = vi.n;
ptr = ptr_tmp;
return *this;
}
int* vectorInt::begin() {
return ptr;
}
int* vectorInt::end() {
return ptr+n;
}
const int* vectorInt::begin() const {
return ptr;
}
const int* vectorInt::end() const {
return ptr+n;
}
test3.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "vectorInt.hpp"
#include <iostream>
void test1();
void test2();
void output1(const vectorInt &vi);
void output2(const vectorInt &vi);
int main() {
std::cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
}
void test1() {
int n;
std::cout << "Enter n: ";
std::cin >> n;
vectorInt x1(n);
for(auto i = 0; i < n; ++i)
x1.at(i) = (i+1)*10;
std::cout << "x1: "; output1(x1);
vectorInt x2(n, 42);
vectorInt x3(x2);
x2.at(0) = -1;
std::cout << "x2: "; output1(x2);
std::cout << "x3: "; output1(x3);
}
void test2() {
const vectorInt x(5, 42);
vectorInt y;
y.assign(x);
std::cout << "x: "; output2(x);
std::cout << "y: "; output2(y);
}
// 使用xx.at()+循环输出vectorInt对象数据项
void output1(const vectorInt &vi) {
if(vi.size() == 0) {
std::cout << '\n';
return;
}
std::cout << vi.at(0);
for(auto i = 1; i < vi.size(); ++i)
std::cout << ", " << vi.at(i);
std::cout << '\n';
}
// 使用迭代器+循环输出vectorInt对象数据项
void output2(const vectorInt &vi) {
if(vi.size() == 0) {
std::cout << '\n';
return;
}
auto it = vi.begin();
std::cout << *it;
for(it = vi.begin()+1; it != vi.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ", " << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
}
运行结果

实验结论
1.版本2缺少自赋值检查;版本2先删除再复制,如果复制过程中出现问题会导致数据区指针ptr悬空;
2.1进行类型转换;转换前的 this 类型:vectorInt,转换后的类型:const vectorInt;调用 const 成员函数版本,非 const 版本复用 const 版本的实现逻辑,实现代码复用;
2.2目的是移除const限定符;转换前的返回类型:const int&,转换后的返回类型:int&;移除 const 限定符,实现代码复用
3.1分别调用非const和const版本;const版本适合进行数据的访问,不对数据进行修改,实现数据保护,而非const版本则适用于要对数据进行修改的场景
3.2迭代器其实就是指针的封装,迭代器的使用方式就是指针的使用方式
4.可以使用标准库代替for循环的复制和赋值操作;第一行为用n个value填充指针指向地址开始的空间;第二行和第三行为将后一个指针指向地址开始的n个值复制给前一个指针指向地址开始的n个值。
实验任务四
源代码
matrix.hpp
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
// 类Matrix声明
class Matrix {
public:
Matrix(int rows_, int cols_, double value = 0); // 构造rows_*cols_矩阵对象, 初值value
Matrix(int rows_, double value = 0); // 构造rows_*rows_方阵对象, 初值value
Matrix(const Matrix &x); // 深复制
~Matrix();
void set(const double *pvalue, int size); // 按行复制pvalue指向的数据,要求size=rows*cols,否则报错退出
void clear(); // 矩阵对象数据项置0
const double& at(int i, int j) const; // 返回矩阵对象索引(i,j)对应的数据项const引用(越界则报错后退出)
double& at(int i, int j); // 返回矩阵对象索引(i,j)对应的数据项引用(越界则报错后退出)
int rows() const; // 返回矩阵对象行数
int cols() const; // 返回矩阵对象列数
void print() const; // 按行打印数据
private:
int n_rows; // 矩阵对象内元素行数
int n_cols; // 矩阵对象内元素列数
double *ptr; // 数据区
};
Matrix :: Matrix(int rows_, int cols_, double value) {
if(rows_ <= 0 || cols_ <= 0) {
std::cout << "行数或列数必须为正整数\n";
exit(1);
}
n_rows = rows_;
n_cols = cols_;
ptr = new double[n_rows * n_cols];
std::fill_n(ptr, n_rows * n_cols, value);
}
Matrix :: Matrix(int rows_, double value) {
if(rows_ <= 0) {
std::cout << "方阵行列数必须为正整数\n";
exit(1);
}
n_rows = rows_;
n_cols = rows_;
ptr = new double[n_rows * n_cols];
std::fill_n(ptr, n_rows * n_cols, value);
}
Matrix :: Matrix(const Matrix &x) {
n_rows = x.n_rows;
n_cols = x.n_cols;
ptr = new double[n_rows * n_cols];
std::copy_n(x.ptr, n_rows * n_cols, ptr);
}
Matrix :: ~Matrix() {
delete [] ptr;
}
void Matrix :: set(const double *pvalue, int size) {
if(size != n_rows * n_cols) {
std::cout << "矩阵大小不匹配\n";
exit(1);
}
std::copy_n(pvalue, size, ptr);
}
void Matrix :: clear() {
std::fill_n(ptr, n_rows * n_cols, 0);
}
const double& Matrix :: at(int i, int j) const {
if(i < 0 || i >= n_rows || j < 0 || j >= n_cols) {
std::cout << "索引越界\n";
exit(1);
}
return ptr[i * n_cols + j];
}
double& Matrix :: at(int i, int j) {
return const_cast<double &>((static_cast<const Matrix*>(this))->at(i, j));
}
int Matrix :: rows() const {
return n_rows;
}
int Matrix :: cols() const {
return n_cols;
}
void Matrix :: print() const {
for(int i = 0; i < n_rows; ++i) {
std::cout << at(i, 0);
for(int j = 1; j < n_cols; ++j)
std::cout << ", " << at(i, j);
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
task4.cpp
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "matrix.hpp"
void test1();
void test2();
void output(const Matrix &m, int row_index);
int main() {
std::cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
}
void test1() {
double x[1000] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int n, m;
std::cout << "Enter n and m: ";
std::cin >> n >> m;
Matrix m1(n, m); // 创建矩阵对象m1, 大小n×m
m1.set(x, n*m); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m1赋值
Matrix m2(m, n); // 创建矩阵对象m2, 大小m×n
m2.set(x, m*n); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m1赋值
Matrix m3(n); // 创建一个n×n方阵对象
m3.set(x, n*n); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m3赋值
std::cout << "矩阵对象m1: \n"; m1.print();
std::cout << "矩阵对象m2: \n"; m2.print();
std::cout << "矩阵对象m3: \n"; m3.print();
}
void test2() {
Matrix m1(2, 3, -1);
const Matrix m2(m1);
std::cout << "矩阵对象m1: \n"; m1.print();
std::cout << "矩阵对象m2: \n"; m2.print();
m1.clear();
m1.at(0, 0) = 1;
std::cout << "m1更新后: \n";
std::cout << "矩阵对象m1第0行 "; output(m1, 0);
std::cout << "矩阵对象m2第0行: "; output(m2, 0);
}
// 输出矩阵对象row_index行所有元素
void output(const Matrix &m, int row_index) {
if(row_index < 0 || row_index >= m.rows()) {
std::cerr << "IndexError: row index out of range\n";
exit(1);
}
std::cout << m.at(row_index, 0);
for(int j = 1; j < m.cols(); ++j)
std::cout << ", " << m.at(row_index, j);
std::cout << '\n';
}
运行结果

实验结论
如果若把内部存储double *ptr;换成 std::vector
实验任务五
源代码
contact.hpp
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
// 联系人类
class Contact {
public:
Contact(const std::string &name_, const std::string &phone_);
const std::string &get_name() const;
const std::string &get_phone() const;
void display() const;
private:
std::string name; // 必填项
std::string phone; // 必填项
};
Contact::Contact(const std::string &name_, const std::string &phone_):name{name_}, phone{phone_} {
}
const std::string& Contact::get_name() const {
return name;
}
const std::string& Contact::get_phone() const {
return phone;
}
void Contact::display() const {
std::cout << name << ", " << phone;
}
contactBook.hpp
点击查看代码
# pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include "contact.hpp"
// 通讯录类
class ContactBook {
public:
void add(const std::string &name, const std::string &phone); // 添加联系人
void remove(const std::string &name); // 移除联系人
void find(const std::string &name) const; // 查找联系人
void display() const; // 显示所有联系人
size_t size() const;
private:
int index(const std::string &name) const; // 返回联系人在contacts内索引,如不存在,返回-1
void sort(); // 按姓名字典序升序排序通讯录
private:
std::vector<Contact> contacts;
};
void ContactBook::add(const std::string &name, const std::string &phone) {
if(index(name) == -1) {
contacts.push_back(Contact(name, phone));
std::cout << name << " add successfully.\n";
sort();
return;
}
std::cout << name << " already exists. fail to add!\n";
}
void ContactBook::remove(const std::string &name) {
int i = index(name);
if(i == -1) {
std::cout << name << " not found, fail to remove!\n";
return;
}
contacts.erase(contacts.begin()+i);
std::cout << name << " remove successfully.\n";
}
void ContactBook::find(const std::string &name) const {
int i = index(name);
if(i == -1) {
std::cout << name << " not found!\n";
return;
}
contacts[i].display();
std::cout << '\n';
}
void ContactBook::display() const {
for(auto &c: contacts) {
c.display();
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
size_t ContactBook::size() const {
return contacts.size();
}
// 待补足1:int index(const std::string &name) const;实现
// 返回联系人在contacts内索引; 如不存在,返回-1
int ContactBook::index(const std::string &name) const {
for(size_t i = 0; i < contacts.size(); ++i) {
if(contacts[i].get_name() == name) {
return static_cast<int>(i);
}
}
return -1;
}
// 待补足2:void ContactBook::sort();实现
// 按姓名字典序升序排序通讯录
void ContactBook::sort() {
std::sort(contacts.begin(), contacts.end(), [](const Contact &a, const Contact &b) -> bool {
return a.get_name() < b.get_name();
});
}
task5.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "contactBook.hpp"
void test() {
ContactBook contactbook;
std::cout << "1. add contacts\n";
contactbook.add("Bob", "18199357253");
contactbook.add("Alice", "17300886371");
contactbook.add("Linda", "18184538072");
contactbook.add("Alice", "17300886371");
std::cout << "\n2. display contacts\n";
std::cout << "There are " << contactbook.size() << " contacts.\n";
contactbook.display();
std::cout << "\n3. find contacts\n";
contactbook.find("Bob");
contactbook.find("David");
std::cout << "\n4. remove contact\n";
contactbook.remove("Bob");
contactbook.remove("David");
}
int main() {
test();
}
运行结果
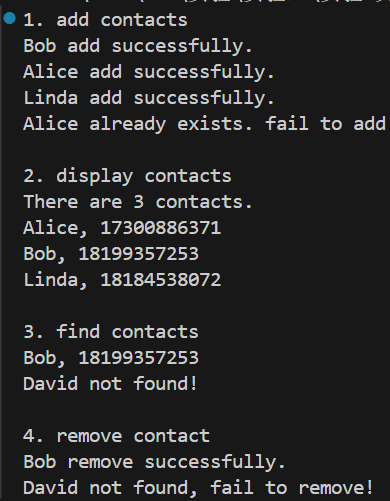
实验结论
扩展的时候要注意功能模块化,这样扩展功能的时候可以做到低耦合
实验总结
-
深刻体验到面向对象编程的过程以及类之间的组合关系,设计类的时候要注意public、private等成员的隐私范围;
-
了解了类型转换函数
static_cast<>()函数,和去const转换函数const_cast<>()。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号