OOP-实验一
实验任务1
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c);
void test1();
void test2();
void test3();
int main() {
std::cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
std::cout << "\n测试3: \n";
test3();
}
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c) {
for(auto &i : c)
std::cout << i << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
}
void test1() {
using namespace std;
string s0{"0123456789"};
cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl;
string s1(s0);
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
string s2(s0.size(), ' ');
reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin());
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
}
void test2() {
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9};
cout << "v0: "; output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end());
cout << "v1: "; output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin());
cout << "v2: "; output(v2);
}
void test3() {
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
cout << "v0: "; output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end());
cout << "v1: "; output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end());
cout << "v2: "; output(v2);
vector<int> v3{v0};
rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end());
cout << "v3: "; output(v3);
vector<int> v4{v0};
rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end());
cout << "v4: "; output(v4);
vector<int> v5{v0};
rotate(v5.begin(), v5.end()-9, v5.end());
cout << "v5: "; output(v5);
}
运行测试
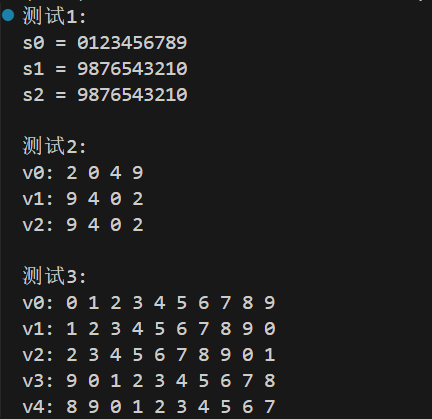
实验结论
1.reverse操作是将原容器反转,并用反转结果覆盖原容器;reverse_copy则是将原容器反转结果拷贝到目标容器(目标容器提供起始地址),并且原容器内容不变。
2.rotate采用循环移动的方式改变元素顺序;三个参数分别为序列开始迭代器、新的第一个元素的迭代器、序列结束迭代器。
实验任务2
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
// 模板函数声明
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c);
int generate_random_number();
void test1();
void test2();
int main() {
std::srand(std::time(0)); // 添加随机种子
std::cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
}
// 输出容器对象c中的元素
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c) {
for(auto &i: c)
std::cout << i << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
}
// 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数
// int generate_random_number() {
// return std::rand() % 101;
// }
// 测试1:对容器类对象指定迭代器区间赋值、排序
void test1() {
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), [](){return std::rand()%101;}); // 生成随机数填充v0
cout << "v0: "; output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对整个vector排序
cout << "v1: "; output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 只对中间部分排序,不包含首尾元素
cout << "v2: "; output(v2);
}
// 测试2:对容器类对象指定迭代器区间赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值
void test2() {
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0(10);
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), [](){return std::rand()%101;});
cout << "v0: "; output(v0);
// 求最大值和最小值
auto min_iter = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
auto max_iter = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *min_iter << endl;
cout << "最大值: " << *max_iter << endl;
// 同时求最大值和最小值
auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl;
cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl;
// 求平均值
double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0.0) / v0.size();
cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl;
sort(v0.begin(), v0.end());
double avg2 = accumulate(v0.begin()+1, v0.end()-1, 0.0) / (v0.size()-2);
cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl;
}
运行测试
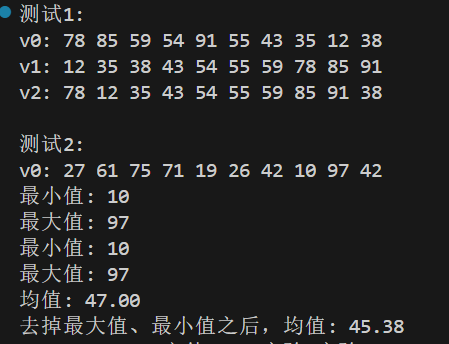
实验结论
1.generate算法作用是持续调用gen返回值赋值给指定范围容器的元素。
2.minmax_element相较于分别调用 min_element、max_element复杂度更低。
3.更改之后效果等同,采用的是lambda表达式,是一种在被调用的位置或作为参数传递给函数的位置定义匿名函数对象(闭包)的简便方法。
实验任务3
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
unsigned char func(unsigned char c);
void test1();
void test2();
int main() {
std::cout << "测试1: 字符串大小写转换\n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: 字符变换\n";
test2();
}
unsigned char func(unsigned char c) {
if(c == 'z')
return 'a';
if(c == 'Z')
return 'A';
if(std::isalpha(c))
return static_cast<unsigned char>(c+1);
return c;
}
void test1() {
std::string s1{"Hello World 2049!"};
std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n';
std::string s2;
for(auto c: s1)
s2 += std::tolower(c);
std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n';
std::string s3;
for(auto c: s1)
s3 += std::toupper(c);
std::cout << "s3 = " << s3 << '\n';
}
void test2() {
std::string s1{"I love cosmos!"};
std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n';
std::string s2(s1.size(), ' ');
std::transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(),
s2.begin(),
func);
std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n';
}
运行测试

实验结论
1.自定义函数func功能是将英文字母循环变为它的下一个字母,若不是字母表中的元素则不变
2.tolower将当前字母转换为小写;toupper 将当前字母转换为大写。
3.transform 4个参数分别表示原容器起始迭代器、原容器结束迭代器、目标容器起始迭代器、转换规则,如果把第3个参数s2.begin() 改成s1.begin() ,则会导致转换结果将原容器元素覆盖
实验任务4
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s);
bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s);
int main() {
using namespace std;
string s;
// 多组输入,直到按下Ctrl+Z结束测试
while(cin >> s) {
cout << boolalpha
<< "区分大小写: " << is_palindrome(s) << "\n"
<< "不区分大小写: " << is_palindrome_ignore_case(s) << "\n\n";
}
}
// 函数is_palindrome定义
bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s)
{
return std::equal(s.begin(), s.begin() + s.size()/2, s.rbegin());
}
// 函数is_palindrome_ignore_case定义
bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s)
{
return std::equal(s.begin(), s.begin() + s.size()/2, s.rbegin(),
[](char a, char b){
return std::tolower(a) == std::tolower(b);
});
}

实验结论
使用cin >> s输入时,输入的字符串中不能包含空格。如果希望测试字符串包含空格(如oop ),应改为std::getline(std::cin, s)//读取整行
实验任务5
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2);
int main() {
int x;
while(std::cin >> x) {
std::cout << "十进制: " << x << '\n'
<< "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << '\n'
<< "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << '\n'
<< "十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 12) << '\n'
<< "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << '\n'
<< "三十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 32) << "\n\n";
}
}
// 函数dec2n定义
std::string dec2n(int x, int n)
{
if (x == 0) {
return "0";
}
std::string result;
while (x > 0) {
int t = x % n;
result += (t>=10) ? ('A' + (t - 10)) : ('0' + t);
x /= n;
}
std::reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
测试运行
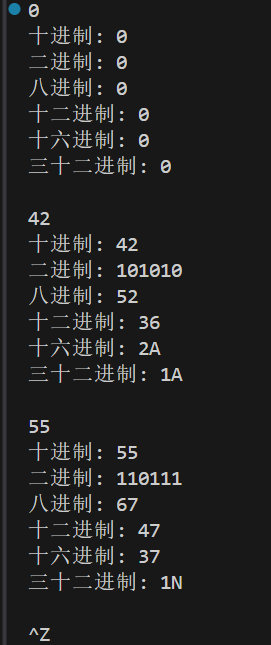
实验任务6
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string a;
for(int i = 0;i < 26;++i) {
a += ('a' + i);
}
for(int i = 0;i <= 26;++i) {
if(i == 0) cout<<setw(2)<<" ";
else cout<<setw(2)<<right<<i;
string t;
if(i > 0){
for(auto x : a)
t+=toupper(x);
}
else t = a;
rotate(t.begin(), t.begin()+i, t.end());
for(auto x : t)
cout<<setw(2)<<right<<x;
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行测试

实验任务7
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(time(0));
int n = 10,sum = 0;
while(n--)
{
int opration = rand() % 4;
switch(opration)
{
case 0:
{
int a = rand() % 10 + 1;
int b = rand() % 10 + 1;
cout << a << " + " << b << " = ";
int res = a+b,c;
cin>>c;
sum += (c == res) ? 1 : 0;
break;
}
case 1:
{
int a = rand() % 10 + 1;
int b = rand() % 10 + 1;
while(b > a) b = rand() % 10 + 1;
cout << a << " - " << b << " = ";
int res = a-b,c;
cin>>c;
sum += (c == res) ? 1 : 0;
break;
}
case 2:
{
int a = rand() % 10 + 1;
int b = rand() % 10 + 1;
cout << a << " * " << b << " = " ;
int res = a*b,c;
cin>>c;
sum += (c == res) ? 1 : 0;
break;
}
case 3:
{
int a = rand() % 10 + 1;
int b = rand() % 10 + 1;
while(a % b != 0) b = rand() % 10 + 1;
cout << a << " / " << b << " = " ;
int res = a/b,c;
cin>>c;
sum += (c == res) ? 1 : 0;
break;
}
}
}
double percent = sum/10.0 * 100;
cout << "准确率:" << fixed << setprecision(2) << percent << "%" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行测试
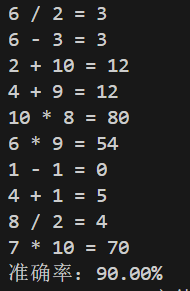
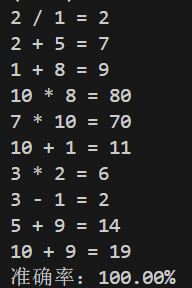
实验总结
学习了解了新的库函数reverse、rotate、generate、minmax_element、lambda表达式、tolower、toupper、transform、equal。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号