Pandas 读写sqlite数据库
SQLite3工具实现了简单、轻量级的DBMS SQL,因此可以内置于用python语言实现的任何应用。若想使用数据库的所有功能而又不想安装真正的数据库,这个工具就是最佳选择。若想在使用真正的数据库之前练习数据库操作,或在单一程序中使用数据库存储数据而无需考虑接口,SQLite3都是不错的选择。
一、使用Pandas库提供的API
1. 写数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
frame = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5),
columns=['white', 'red', 'blue', 'black', 'green'])
engine= create_engine('sqlite:///foo.db')
print(frame)
frame.to_sql('colors', engine)
输出结果如下:
white red blue black green
0 0 1 2 3 4
1 5 6 7 8 9
2 10 11 12 13 14
3 15 16 17 18 19
2. 读数据
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine= create_engine('sqlite:///foo.db')
frame = pd.read_sql('colors', engine)
print(frame)
输出结果如下:
AttributeError: 'OptionEngine' object has no attribute 'execute'
二、用python自带的sqllite接口
1. 读数据
import pandas as pd
import sqlite3
# 连接Sqlite数据库
con = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
# 执行SQL查询,并返回结果作为DataFrame对象
df = pd.read_sql_query("SELECT * from students", con)
# 关闭数据库连接
con.close()
# 打印结果
print(df)
2. 写数据
import sqlite3
# 创建DataFrame对象
df = pd.DataFrame({
'id': [1, 2, 3],
'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'age': [20, 25, 30]
})
# 连接Sqlite数据库
con = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
# 将数据写入Sqlite数据库中
df.to_sql('students', con, if_exists='replace')
# 关闭数据库连接
con.close()
3. pandas文档
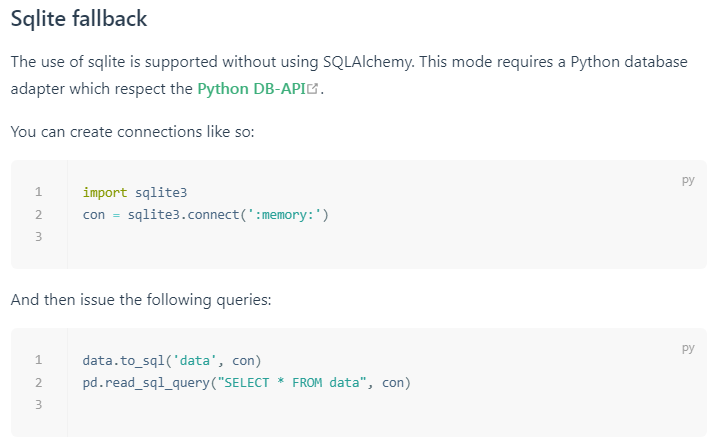
4. 封装函数
def write_sqlite(df, db_name, tb_name, w_type):
con = sqlite3.connect(db_name)
df.to_sql(tb_name, con, if_exists=w_type)
con.close()
print("write success.")
def read_sqlite(db_name, tb_name):
con = sqlite3.connect(db_name)
sql_q = "SELECT * FROM {}".format(tb_name)
df = pd.read_sql_query(sql_q, con)
con.close()
return df




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号