饼干妹妹的第二次博客作业
一、三次作业的知识点、题量、难度
考察的知识点
题目集4感觉是Java从编程到设计的分水岭,从基本的操作实现,到这一次作业的结构设计,才开始体验到了Java的设计困难之处,考察的知识点主要是类之间的继承和正则表达式的相关内容;
题目集5相对这三次是比较简单的,主要是给出类的结构设计然后去写出相应代码,还有一些对String的方法的使用;
题目集6主要是对正则表达式的使用以及对接口的简单应用。
作业的题量与难度
题目的难度整体不大,最难的感觉是题目集4的7-1,当时研究对检验日期的正则表达式废了好大劲,写出来的是这样的:
"(((([1-9])|([1-9][0-9])|([1-9][0-9]{2})|([1-9][0-9]{3})/((([13578]|1[02])/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2/([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8])))))|(((([1-9][0-9])(0[48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26]))|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))/2/29)) ((([02468])|(1[02468])|(2[02])):00)"
最后虽然正常测试日期都能过,但是在这一题中并没有做出来,是某一段的代码的方法使用不对,在下面会具体讲。
二、设计与分析
①题目集4(7-2)与题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较:
我这里先把源码贴上来:
题目集4(7-2):
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(); 6 int x = in.nextInt(); 7 int year = in.nextInt(); 8 int month = in.nextInt(); 9 int day = in.nextInt(); 10 switch(x) { 11 case 1: { 12 date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().setValue(year); 13 date.getDay().getMonth().setValue(month); 14 date.getDay().setValue(day); 15 if( !date.checkInputValidity() ) { 16 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 17 break; 18 } 19 System.out.print( date.getNextDays(in.nextInt()).showDate() ); 20 break; 21 } 22 case 2: { 23 date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().setValue(year); 24 date.getDay().getMonth().setValue(month); 25 date.getDay().setValue(day); 26 if( !date.checkInputValidity() ) { 27 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 28 break; 29 } 30 System.out.print( date.getPreviousNDays(in.nextInt()).showDate() ); 31 break; 32 } 33 case 3: { 34 date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().setValue(year); 35 date.getDay().getMonth().setValue(month); 36 date.getDay().setValue(day); 37 int y = in.nextInt(); 38 int m = in.nextInt(); 39 int d = in.nextInt(); 40 DateUtil lin = new DateUtil(d,m,y); 41 if( !( date.checkInputValidity() && lin.checkInputValidity() ) ) { 42 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 43 break; 44 } 45 System.out.print( date.getDaysofDates(lin) ); 46 break; 47 } 48 default: System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 53 class Year { 54 private int value = 1900; 55 Year() { 56 this.value = 1900; 57 } 58 Year(int value) { 59 this.value = value; 60 } 61 public int getValue() { 62 return value; 63 } 64 public void setValue(int value) { 65 this.value = value; 66 } 67 public boolean isLeapYear() { 68 if(this.value % 400 == 0 || (this.value % 4 == 0 && this.value % 100 != 0)) 69 return true; 70 else 71 return false; 72 } 73 public boolean validate() { 74 if(this.value < 1900 || this.value > 2050) 75 return false; 76 return true; 77 } 78 public void yearIncrement() { 79 this.value++; 80 } 81 public void yearReduction() { 82 this.value--; 83 } 84 } 85 86 class Month { 87 private int value = 1; 88 private Year year = new Year(); 89 Month() { 90 this.value = 1; 91 } 92 Month(int yearValue,int monthValue) { 93 this.value = monthValue; 94 this.year.setValue(yearValue); 95 } 96 public int getValue() { 97 return value; 98 } 99 public void setValue(int value) { 100 this.value = value; 101 } 102 public Year getYear() { 103 return year; 104 } 105 public void setYear(Year year) { 106 this.year = year; 107 } 108 public void resetMin() { 109 this.value = 1; 110 } 111 public void resetMax() { 112 this.value = 12; 113 } 114 public boolean validat() { 115 if(this.value < 1 || this.value > 12) 116 return false; 117 return true; 118 } 119 public void monthIncrement() { 120 this.value++; 121 } 122 public void monthReduction() { 123 this.value--; 124 } 125 } 126 127 class Day { 128 private int value = 1; 129 private Month month = new Month(); 130 private int[] mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 131 Day() { 132 this.value = 1; 133 } 134 Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue) { 135 this.value = dayValue; 136 this.month.setValue(monthValue); 137 this.month.getYear().setValue(yearValue); 138 } 139 public int getDayOfMonth(int year,int month) { 140 int days = this.mon_maxnum[month - 1]; 141 if(month == 2 && (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)) ) 142 days = 29; 143 return days; 144 } 145 public int getValue() { 146 return value; 147 } 148 public void setValue(int value) { 149 this.value = value; 150 } 151 public Month getMonth() { 152 return month; 153 } 154 public void setMonth(Month month) { 155 this.month = month; 156 } 157 public void resetMin() { 158 this.value = 1; 159 } 160 public void resetMax() { 161 if(this.month.getValue() == 1 || this.month.getValue() == 3 || this.month.getValue() == 5 || this.month.getValue() == 7 || this.month.getValue() == 8 || this.month.getValue() == 10 || this.month.getValue() == 12) 162 this.value = 31; 163 else if(this.month.getValue() == 4 || this.month.getValue() == 6 || this.month.getValue() == 9 || this.month.getValue() == 11) 164 this.value = 30; 165 else { 166 if( this.month.getYear().isLeapYear() ) 167 this.value = 29; 168 else 169 this.value = 28; 170 } 171 } 172 public boolean validate() { 173 if(this.value < 1 || this.value > 31) 174 return false; 175 return true; 176 } 177 public void dayIncrement() { 178 this.value++; 179 } 180 public void dayReduction() { 181 this.value--; 182 } 183 } 184 185 class DateUtil { 186 private Day day = new Day(); 187 DateUtil() { 188 this.day.setValue(1); 189 this.day.getMonth().setValue(1); 190 this.day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(1900); 191 } 192 DateUtil(int d,int m,int y) { 193 this.day.setValue(d); 194 this.day.getMonth().setValue(m); 195 this.day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); 196 } 197 public Day getDay() { 198 return day; 199 } 200 public void setDay(Day day) { 201 this.day = day; 202 } 203 public boolean checkInputValidity() { 204 if( !this.day.validate() || !this.day.getMonth().validat() || !this.day.getMonth().getYear().validate() ) 205 return false; 206 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() ) { 207 if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 2 && this.day.getValue() > 29) { 208 return false; 209 } 210 if( (this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 4 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 6 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 9 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 11) && this.day.getValue() > 30) { 211 return false; 212 } 213 }//判断闰年输入 214 215 if( !this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() ) { 216 if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 2 && this.day.getValue() > 28) { 217 return false; 218 } 219 220 if( (this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 4 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 6 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 9 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 11) && this.day.getValue() > 30) { 221 return false; 222 } 223 }//判断平年输入 224 return true; 225 } 226 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { 227 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() ) 228 return true; 229 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getValue() ) 230 return true; 231 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && this.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue() ) 232 return true; 233 return false; 234 } 235 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { 236 if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && this.day.getValue() == date.day.getValue() ) 237 return true; 238 return false; 239 } 240 public String showDate() { 241 String s = new String( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + this.day.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + this.day.getValue() ); 242 return s; 243 } 244 public DateUtil getNextDays(int n) {//求后n天 245 DateUtil lin = new DateUtil( this.day.getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() ); 246 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { 247 lin.day.dayIncrement(); 248 if(lin.day.getValue() > lin.day.getDayOfMonth( lin.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), lin.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ) { 249 lin.day.setValue(1); 250 lin.day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 251 if(lin.day.getMonth().getValue() > 12) { 252 lin.day.getMonth().setValue(1); 253 lin.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 254 } 255 } 256 } 257 return lin; 258 } 259 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {//求前n天 260 DateUtil lin = new DateUtil( this.day.getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() ); 261 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { 262 lin.day.dayReduction(); 263 if(lin.day.getValue() < 1) { 264 lin.day.getMonth().monthReduction(); 265 if(lin.day.getMonth().getValue() < 1) { 266 lin.day.getMonth().setValue(12); 267 lin.day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 268 } 269 lin.day.setValue(lin.day.getDayOfMonth(lin.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), lin.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ); 270 } 271 } 272 return lin; 273 } 274 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { 275 int i = 0; 276 if( compareDates(date) ) { 277 while( !equalTwoDates(date) ) { 278 i++; 279 date.day.dayIncrement(); 280 if(date.day.getValue() > date.day.getDayOfMonth( date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), date.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ) { 281 date.day.setValue(1); 282 date.day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 283 if(date.day.getMonth().getValue() > 12) { 284 date.day.getMonth().setValue(1); 285 date.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 286 } 287 } 288 } 289 } 290 else { 291 while( !equalTwoDates(date) ) { 292 i++; 293 date.day.dayReduction(); 294 if(date.day.getValue() < 1) { 295 date.day.getMonth().monthReduction(); 296 if(date.day.getMonth().getValue() < 1) { 297 date.day.getMonth().setValue(12); 298 date.day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 299 } 300 date.day.setValue(date.day.getDayOfMonth(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), date.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ); 301 } 302 } 303 } 304 return i; 305 } 306 }
相关分析:
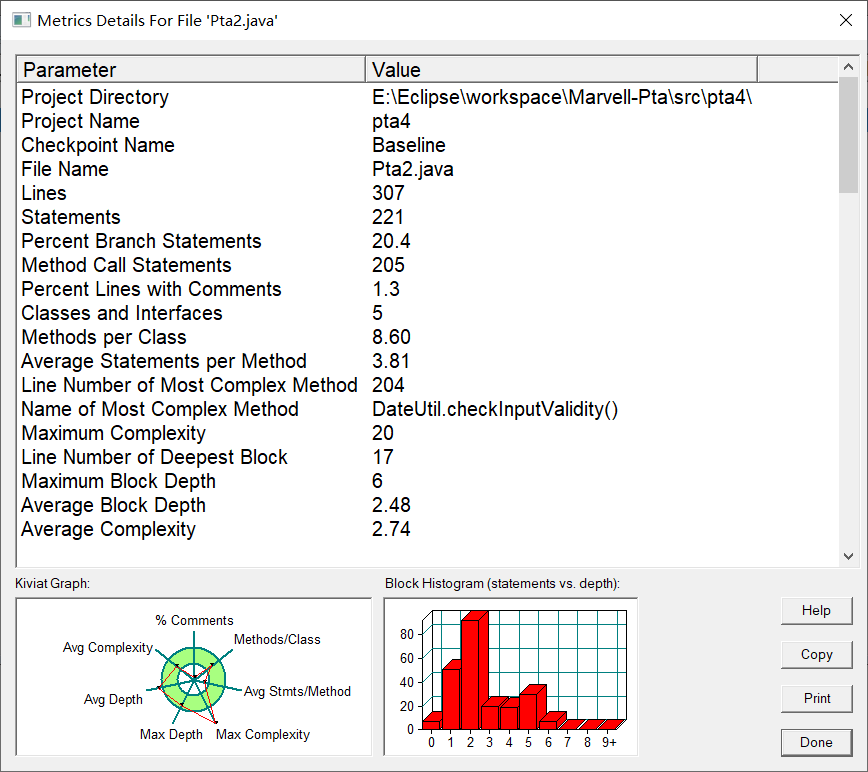
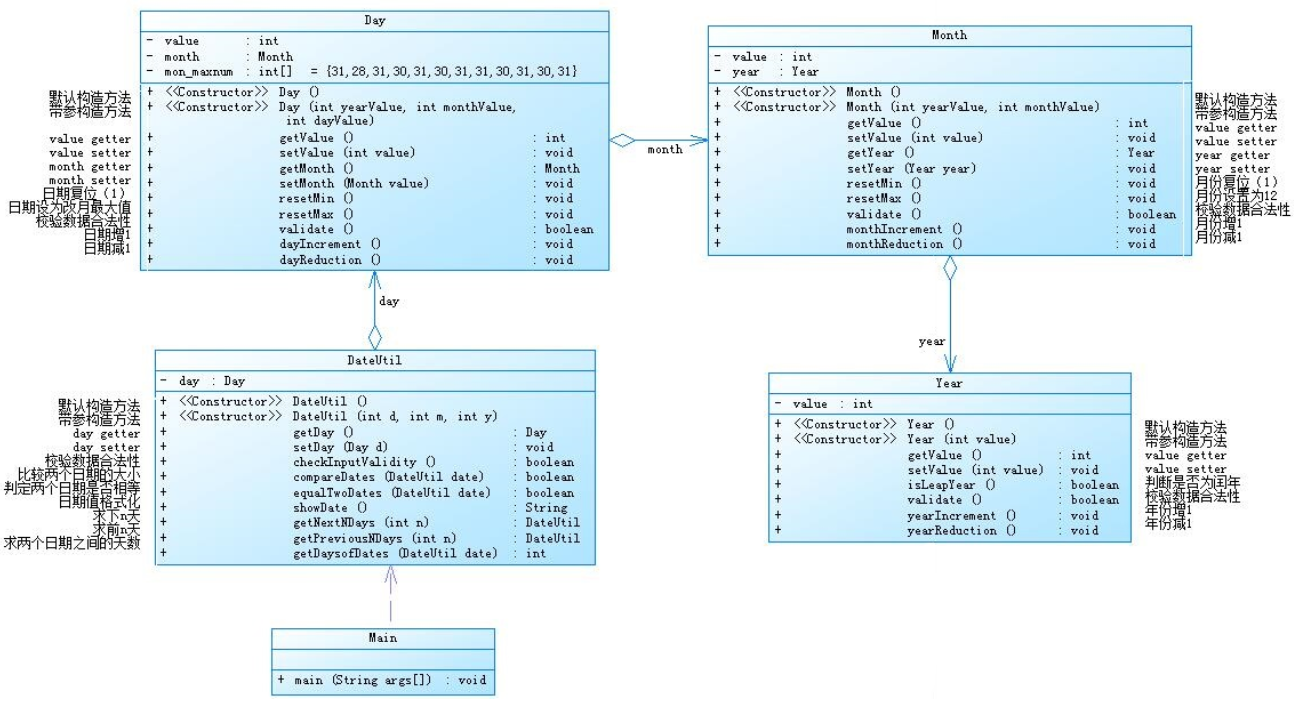
类图设计:
题目集5(7-5):
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(); 6 int x = in.nextInt(); 7 int year = in.nextInt(); 8 int month = in.nextInt(); 9 int day = in.nextInt(); 10 switch(x) { 11 case 1: { 12 date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().setValue(year); 13 date.getDay().getMonth().setValue(month); 14 date.getDay().setValue(day); 15 if( !date.checkInputValidity() ) { 16 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 17 break; 18 } 19 int n = in.nextInt(); 20 System.out.print( year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " next " + n + " days is:" + date.getNextDays(n).showDate() ); 21 break; 22 } 23 case 2: { 24 date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().setValue(year); 25 date.getDay().getMonth().setValue(month); 26 date.getDay().setValue(day); 27 if( !date.checkInputValidity() ) { 28 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 29 break; 30 } 31 int n = in.nextInt(); 32 System.out.print( year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " previous " + n + " days is:" + date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate() ); 33 break; 34 } 35 case 3: { 36 date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().setValue(year); 37 date.getDay().getMonth().setValue(month); 38 date.getDay().setValue(day); 39 int y = in.nextInt(); 40 int m = in.nextInt(); 41 int d = in.nextInt(); 42 DateUtil lin = new DateUtil(d,m,y); 43 if( !( date.checkInputValidity() && lin.checkInputValidity() ) ) { 44 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 45 break; 46 } 47 System.out.print( "The days between " + year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " and " + y + "-" + m + "-" + d + " are:" + date.getDaysofDates(lin) ); 48 break; 49 } 50 default: System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 class Year { 56 private int value = 1900; 57 Year() { 58 this.value = 1900; 59 } 60 Year(int value) { 61 this.value = value; 62 } 63 public int getValue() { 64 return value; 65 } 66 public void setValue(int value) { 67 this.value = value; 68 } 69 public boolean isLeapYear() { 70 if(this.value % 400 == 0 || (this.value % 4 == 0 && this.value % 100 != 0)) 71 return true; 72 else 73 return false; 74 } 75 public boolean validate() { 76 if(this.value < 1820 || this.value > 2020) 77 return false; 78 return true; 79 } 80 public void yearIncrement() { 81 this.value++; 82 } 83 public void yearReduction() { 84 this.value--; 85 } 86 } 87 88 class Month { 89 private int value = 1; 90 private Year year = new Year(); 91 Month() { 92 this.value = 1; 93 } 94 Month(int yearValue,int monthValue) { 95 this.value = monthValue; 96 this.year.setValue(yearValue); 97 } 98 public int getValue() { 99 return value; 100 } 101 public void setValue(int value) { 102 this.value = value; 103 } 104 public Year getYear() { 105 return year; 106 } 107 public void setYear(Year year) { 108 this.year = year; 109 } 110 public void resetMin() { 111 this.value = 1; 112 } 113 public void resetMax() { 114 this.value = 12; 115 } 116 public boolean validat() { 117 if(this.value < 1 || this.value > 12) 118 return false; 119 return true; 120 } 121 public void monthIncrement() { 122 this.value++; 123 } 124 public void monthReduction() { 125 this.value--; 126 } 127 } 128 129 class Day { 130 private int value = 1; 131 private Month month = new Month(); 132 private int[] mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 133 Day() { 134 this.value = 1; 135 } 136 Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue) { 137 this.value = dayValue; 138 this.month.setValue(monthValue); 139 this.month.getYear().setValue(yearValue); 140 } 141 public int getDayOfMonth(int year,int month) { 142 int days = this.mon_maxnum[month - 1]; 143 if(month == 2 && (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)) ) 144 days = 29; 145 return days; 146 } 147 public int getValue() { 148 return value; 149 } 150 public void setValue(int value) { 151 this.value = value; 152 } 153 public Month getMonth() { 154 return month; 155 } 156 public void setMonth(Month month) { 157 this.month = month; 158 } 159 public void resetMin() { 160 this.value = 1; 161 } 162 public void resetMax() { 163 if(this.month.getValue() == 1 || this.month.getValue() == 3 || this.month.getValue() == 5 || this.month.getValue() == 7 || this.month.getValue() == 8 || this.month.getValue() == 10 || this.month.getValue() == 12) 164 this.value = 31; 165 else if(this.month.getValue() == 4 || this.month.getValue() == 6 || this.month.getValue() == 9 || this.month.getValue() == 11) 166 this.value = 30; 167 else { 168 if( this.month.getYear().isLeapYear() ) 169 this.value = 29; 170 else 171 this.value = 28; 172 } 173 } 174 public boolean validate() { 175 if(this.value < 1 || this.value > 31) 176 return false; 177 return true; 178 } 179 public void dayIncrement() { 180 this.value++; 181 } 182 public void dayReduction() { 183 this.value--; 184 } 185 } 186 187 class DateUtil { 188 private Day day = new Day(); 189 DateUtil() { 190 this.day.setValue(1); 191 this.day.getMonth().setValue(1); 192 this.day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(1900); 193 } 194 DateUtil(int d,int m,int y) { 195 this.day.setValue(d); 196 this.day.getMonth().setValue(m); 197 this.day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); 198 } 199 public Day getDay() { 200 return day; 201 } 202 public void setDay(Day day) { 203 this.day = day; 204 } 205 public boolean checkInputValidity() { 206 if( !this.day.validate() || !this.day.getMonth().validat() || !this.day.getMonth().getYear().validate() ) 207 return false; 208 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() ) { 209 if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 2 && this.day.getValue() > 29) { 210 return false; 211 } 212 if( (this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 4 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 6 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 9 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 11) && this.day.getValue() > 30) { 213 return false; 214 } 215 }//判断闰年输入 216 217 if( !this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() ) { 218 if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 2 && this.day.getValue() > 28) { 219 return false; 220 } 221 222 if( (this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 4 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 6 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 9 || this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 11) && this.day.getValue() > 30) { 223 return false; 224 } 225 }//判断平年输入 226 return true; 227 } 228 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { 229 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() ) 230 return true; 231 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getValue() ) 232 return true; 233 if( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && this.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue() ) 234 return true; 235 return false; 236 } 237 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { 238 if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && this.day.getValue() == date.day.getValue() ) 239 return true; 240 return false; 241 } 242 public String showDate() { 243 String s = new String( this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + this.day.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + this.day.getValue() ); 244 return s; 245 } 246 public DateUtil getNextDays(int n) {//求后n天 247 DateUtil lin = new DateUtil( this.day.getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() ); 248 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { 249 lin.day.dayIncrement(); 250 if(lin.day.getValue() > lin.day.getDayOfMonth( lin.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), lin.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ) { 251 lin.day.setValue(1); 252 lin.day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 253 if(lin.day.getMonth().getValue() > 12) { 254 lin.day.getMonth().setValue(1); 255 lin.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 256 } 257 } 258 } 259 return lin; 260 } 261 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {//求前n天 262 DateUtil lin = new DateUtil( this.day.getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() ); 263 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { 264 lin.day.dayReduction(); 265 if(lin.day.getValue() < 1) { 266 lin.day.getMonth().monthReduction(); 267 if(lin.day.getMonth().getValue() < 1) { 268 lin.day.getMonth().setValue(12); 269 lin.day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 270 } 271 lin.day.setValue(lin.day.getDayOfMonth(lin.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), lin.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ); 272 } 273 } 274 return lin; 275 } 276 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { 277 int i = 0; 278 if( compareDates(date) ) { 279 while( !equalTwoDates(date) ) { 280 i++; 281 date.day.dayIncrement(); 282 if(date.day.getValue() > date.day.getDayOfMonth( date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), date.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ) { 283 date.day.setValue(1); 284 date.day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 285 if(date.day.getMonth().getValue() > 12) { 286 date.day.getMonth().setValue(1); 287 date.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 288 } 289 } 290 } 291 } 292 else { 293 while( !equalTwoDates(date) ) { 294 i++; 295 date.day.dayReduction(); 296 if(date.day.getValue() < 1) { 297 date.day.getMonth().monthReduction(); 298 if(date.day.getMonth().getValue() < 1) { 299 date.day.getMonth().setValue(12); 300 date.day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 301 } 302 date.day.setValue(date.day.getDayOfMonth(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), date.day.getMonth().getValue() ) ); 303 } 304 } 305 } 306 return i; 307 } 308 }
相关分析:
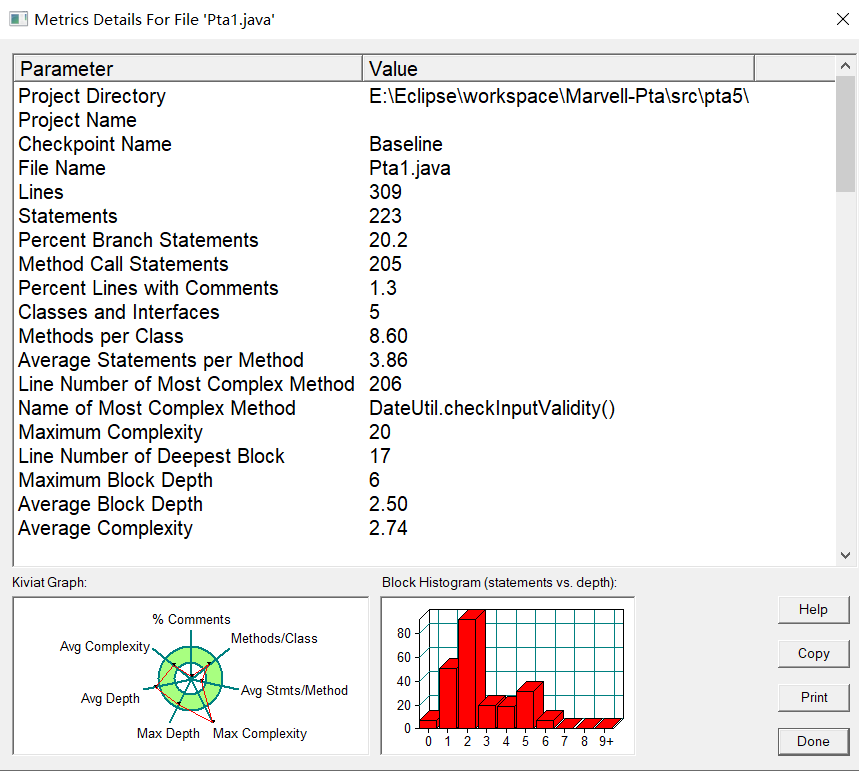
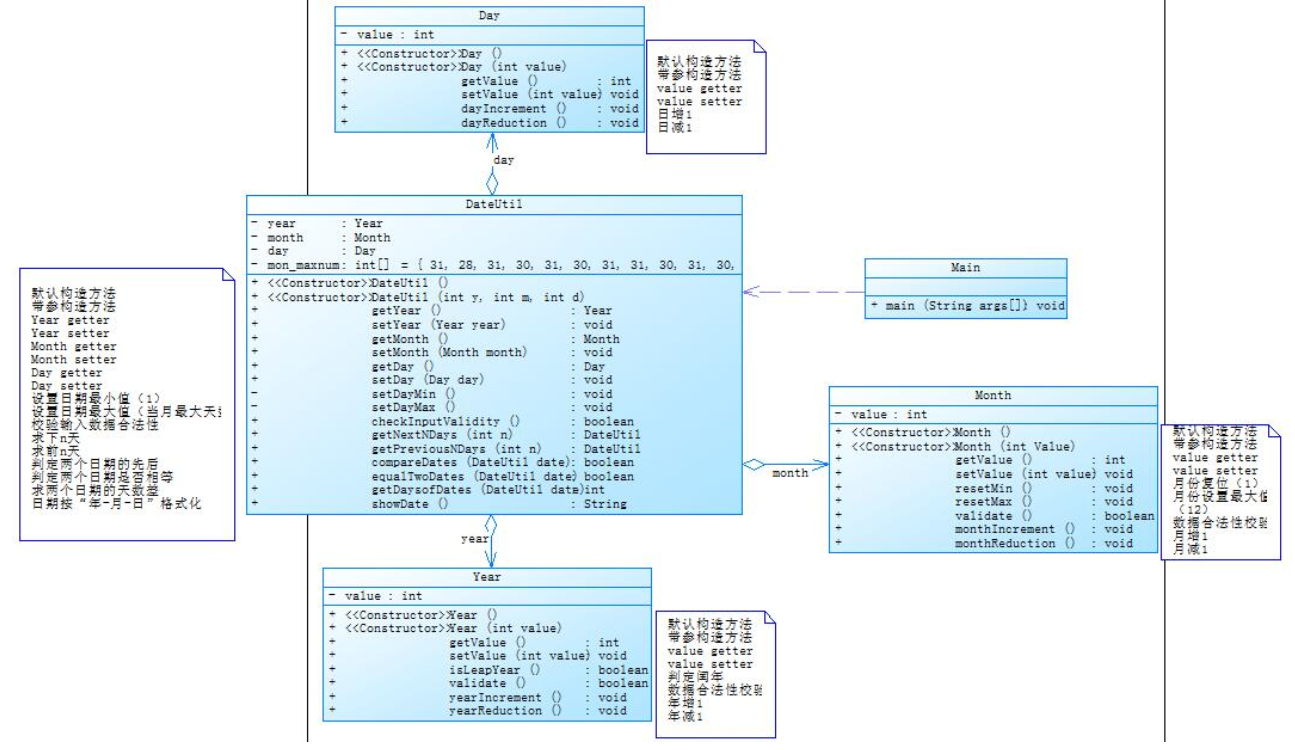
类图设计:
题目集4(7-2)的设计对于编码人员是比较不好的,其一是使用这种多重嵌套类的模式,写出来的代码可读性差,也难以进行测试和优化,比如“年”类的某个方法出现错误,在“月”,“日”等其它类中要进行大量的修改,甚至可能出现新的错误,极其难维护;相对于另一个的好处是各个类负责各个职责,不会出错;
题目集5(7-4)的问题出在各个类的方法重复性太高,如DateUtil类中有的方法,其他的类也有相似的。
②题目集4(7-3),题目集6(7-5,7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思想与技术运用(封装,继承,多态,接口等)
老规矩,先贴代码:
题目集4(7-3):
1 import java.util.*; 2 import java.lang.Math; 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 7 int x = in.nextInt(); 8 switch(x) { 9 case 1:{ 10 double radius = in.nextDouble(); 11 if(radius < 0) 12 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 13 else { 14 Circle lin = new Circle( radius ); 15 16 System.out.println( "Circle's area:" + String.format("%.2f", lin.getArea()) ); 17 } 18 break; 19 } 20 case 2:{ 21 double width = in.nextDouble(); 22 double length = in.nextDouble(); 23 if(width < 0 || length < 0) 24 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 25 else { 26 Rectangle lin = new Rectangle(width,length); 27 System.out.println( "Rectangle's area:" + String.format("%.2f", lin.getArea()) ); 28 } 29 break; 30 } 31 case 3:{ 32 double radius = in.nextDouble(); 33 if(radius < 0) 34 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 35 else { 36 Ball lin = new Ball(radius); 37 System.out.println( "Ball's surface area:" + String.format("%.2f", lin.getArea()) ); 38 System.out.println( "Ball's volume:" + String.format("%.2f", lin.getVolume()) ); 39 } 40 break; 41 } 42 case 4:{ 43 double width = in.nextDouble(); 44 double length = in.nextDouble(); 45 double height = in.nextDouble(); 46 if(width < 0 || length < 0 || height < 0) 47 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 48 else { 49 Box lin = new Box( width,length,height ); 50 System.out.println( "Box's surface area:" + String.format("%.2f", lin.getArea()) ); 51 System.out.println( "Box's volume:" + String.format("%.2f", lin.getVolume()) ); 52 } 53 break; 54 } 55 default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 class Shape { 60 Shape() { 61 System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); 62 } 63 public double getArea() { 64 return 0; 65 } 66 } 67 68 class Circle extends Shape { 69 private double radius; 70 Circle() { 71 System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); 72 } 73 Circle(double radius) { 74 this.radius = radius; 75 System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); 76 } 77 public double getRadius() { 78 return radius; 79 } 80 public void setRadius(double radius) { 81 this.radius = radius; 82 } 83 @Override 84 public double getArea() { 85 return Math.PI*this.radius*this.radius; 86 } 87 } 88 89 class Rectangle extends Shape{ 90 private double width; 91 private double length; 92 Rectangle() { 93 System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); 94 } 95 Rectangle(double width,double length) { 96 this.width = width; 97 this.length = length; 98 System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); 99 } 100 public double getWidth() { 101 return width; 102 } 103 public void setWidth(double width) { 104 this.width = width; 105 } 106 public double getLength() { 107 return length; 108 } 109 public void setLength(double length) { 110 this.length = length; 111 } 112 @Override 113 public double getArea() { 114 return this.length*this.width; 115 } 116 } 117 118 class Ball extends Circle { 119 Ball() { 120 System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); 121 } 122 Ball(double riadus) { 123 super.setRadius(riadus); 124 System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); 125 } 126 @Override 127 public double getArea() { 128 return 4*Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius(); 129 } 130 public double getVolume() { 131 return (4.0/3.0)*Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius(); 132 } 133 } 134 135 class Box extends Rectangle { 136 private double height; 137 Box() { 138 System.out.println("Constructing Box"); 139 } 140 Box(double width,double length,double height) { 141 super.setWidth(width); 142 super.setLength(length); 143 this.height = height; 144 System.out.println("Constructing Box"); 145 } 146 public double getHeight() { 147 return height; 148 } 149 public void setHeight(double height) { 150 this.height = height; 151 } 152 @Override 153 public double getArea() { 154 return 2*(super.getLength()*super.getWidth() + super.getLength()*this.height + super.getWidth()*this.height); 155 } 156 public double getVolume() { 157 return super.getLength()*super.getWidth()*this.height; 158 } 159 }
题目集6(7-5):
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 abstract class Shape { 4 public double getArea() { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 public boolean validate() { 8 return false; 9 } 10 @Override 11 public String toString() { 12 return "12"; 13 } 14 } 15 16 class Circle1 extends Shape { 17 private double radius; 18 Circle1() { 19 this.radius = 1; 20 } 21 Circle1(double radius) { 22 this.radius = radius; 23 } 24 public double getRadius() { 25 return radius; 26 } 27 public void setRadius(double radius) { 28 this.radius = radius; 29 } 30 @Override 31 public double getArea() { 32 return Math.PI*this.radius*this.radius; 33 } 34 @Override 35 public boolean validate() { 36 if(this.radius <= 0) 37 return false; 38 return true; 39 } 40 } 41 42 class Rectangle1 extends Shape { 43 private double width; 44 private double length; 45 Rectangle1() { 46 this.width = 1; 47 this.length = 1; 48 } 49 Rectangle1(double width,double length) { 50 this.width = width; 51 this.length = length; 52 } 53 public double getWidth() { 54 return width; 55 } 56 public void setWidth(double width) { 57 this.width = width; 58 } 59 public double getLength() { 60 return length; 61 } 62 public void setLength(double length) { 63 this.length = length; 64 } 65 @Override 66 public double getArea() { 67 return this.width*this.length; 68 } 69 @Override 70 public boolean validate() { 71 if(this.length <= 0 || this.width <= 0) 72 return false; 73 return true; 74 } 75 } 76 77 class Triangle extends Shape { 78 private double side1; 79 private double side2; 80 private double side3; 81 Triangle() { 82 this.side1 = 1; 83 this.side2 = 1; 84 this.side3 = 1; 85 } 86 Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){ 87 this.side1 = side1; 88 this.side2 = side2; 89 this.side3 = side3; 90 } 91 public double getSide1() { 92 return side1; 93 } 94 public void setSide1(double side1) { 95 this.side1 = side1; 96 } 97 public double getSide2() { 98 return side2; 99 } 100 public void setSide2(double side2) { 101 this.side2 = side2; 102 } 103 public double getSide3() { 104 return side3; 105 } 106 public void setSide3(double side3) { 107 this.side3 = side3; 108 } 109 @Override 110 public double getArea() { 111 return (1.0/4.0)*Math.sqrt((this.side1+this.side2+this.side3)*(this.side1+this.side2-this.side3)*(this.side1+this.side3-this.side2)*(this.side2+this.side3-this.side1)); 112 } 113 @Override 114 public boolean validate() { 115 if(this.side1 + this.side2 <= this.side3 || this.side1 + this.side3 <= this.side2 || this.side2 + this.side3 <= this.side1) 116 return false; 117 return true; 118 } 119 } 120 121 public class Main { 122 123 public static void main(String[] args) { 124 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 125 int a = in.nextInt(); 126 int b = in.nextInt(); 127 int c = in.nextInt(); 128 if(a < 0 || b < 0 || c < 0) { 129 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 130 return; 131 } 132 // if(a == 0 && b == 0 && c == 0) 133 // return; 134 Shape[] shape = new Shape[a+b+c]; 135 int m = 0; 136 for(int i = 0;i < a;i++) 137 shape[m++] = new Circle1(in.nextDouble()); 138 for(int i = 0;i < b;i++) 139 shape[m++] = new Rectangle1(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); 140 for(int i = 0;i < c;i++) 141 shape[m++] = new Triangle(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); 142 143 for(int i = 0;i < shape.length;i++) { 144 if( !shape[i].validate() ) { 145 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 146 return; 147 } 148 } 149 150 double[] arr = new double[shape.length]; 151 for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++) 152 arr[i] = shape[i].getArea(); 153 154 System.out.println("Original area:"); 155 for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++) { 156 // if(i == arr.length-1) 157 // System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",arr[i]) + " "); 158 // else 159 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",arr[i]) + " "); 160 } 161 162 double sum = 0; 163 for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++) 164 sum += arr[i]; 165 System.out.println("\nSum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sum)); 166 167 Arrays.sort(arr); 168 System.out.println("Sorted area:"); 169 for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++) { 170 // if(i == arr.length-1) 171 // System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",arr[i]) + " "); 172 // else 173 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",arr[i]) + " "); 174 } 175 176 System.out.print("\nSum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sum)); 177 } 178 }
题目集6(7-6):
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 interface GetArea { 4 public default double getArea() { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 } 8 9 class Circle implements GetArea { 10 private double radius; 11 Circle() { 12 this.radius = 1; 13 } 14 Circle(double radius) { 15 this.radius = radius; 16 } 17 public double getRadius() { 18 return radius; 19 } 20 public void setRadius(double radius) { 21 this.radius = radius; 22 } 23 @Override 24 public double getArea() { 25 return Math.PI*this.radius*this.radius; 26 } 27 } 28 29 class Rectangle implements GetArea { 30 private double width; 31 private double length; 32 Rectangle() { 33 this.width = 1; 34 this.length = 1; 35 } 36 Rectangle(double width,double length) { 37 this.width = width; 38 this.length = length; 39 } 40 public double getWidth() { 41 return width; 42 } 43 public void setWidth(double width) { 44 this.width = width; 45 } 46 public double getLength() { 47 return length; 48 } 49 public void setLength(double length) { 50 this.length = length; 51 } 52 @Override 53 public double getArea() { 54 return this.width*this.length; 55 } 56 } 57 58 public class Main { 59 60 public static void main(String[] args) { 61 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 62 double raidus = in.nextDouble(); 63 double width = in.nextDouble(); 64 double length = in.nextDouble(); 65 if(raidus <= 0 || width <= 0 || length <= 0) { 66 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 67 return; 68 } 69 GetArea[] area = {new Circle(raidus),new Rectangle(width,length)}; 70 for(int i = 0;i < area.length;i++) 71 System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", area[i].getArea())); 72 } 73 74 }
我个人认为,题目集4(7-3)是对继承的考察,而题目集6(7-5)是在题目集4(7-3)上的一些需求延伸;题目集6(7-6)主要考察的是对接口的理解。
题目集4(7-3)和题目集6(7-5)主要是让我们设计一个父类Shape,然后子类Circle和Rectangle继承来实现题目的需求,难度并不大;
题目集6(7-6)是通过创建一个接口,然后通过设计可以使用这个接口的类来完成需求。
③对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
这三次题目集中我认为最难的还是题目集4的第一题那个收集水文数据中对日期和时间的检验因为要考虑闰年平年和二月份的最大日期情况;最简单的反而是题目集6,只有一些基础的检验,我不能理解
题目集4中用到的正则表达式:
检验日期和时间:
1 "(((([1-9])|([1-9][0-9])|([1-9][0-9]{2})|([1-9][0-9]{3})/((([13578]|1[02])/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2/([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8])))))|(((([1-9][0-9])(0[48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26]))|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))/2/29)) ((([02468])|(1[02468])|(2[02])):00)"
检验水位和流量:
1 "([1-9][0-9]{0,2}(\\.[0-9]{1,3})?)"
检验流量:
1 "([1-9]\\.[0-9]{2})"
这一题我并没有做出来,一开始是因为检验时间和日期的正则表达式有问题,但后面修改好了,可以检验正常的时间日期数据,具体出问题的点在下面这些部分:
1 checkdate[i].setMeasureDateTime(str1[0].trim()); 2 checkdate[i].setObjectWaterLevel(Double.parseDouble(str1[1].trim()) ); 3 checkdate[i].setActualWaterLevel(Double.parseDouble(str1[2].trim()) ); 4 String str2[] = str[i].split("/"); 5 checkdate[i].setObjectGateOpening(Double.parseDouble(str2[0].trim()) ); 6 checkdate[i].setActralGateOpening( Double.parseDouble(str2[1].trim()) ); 7 checkdate[i].setWaterFlow( Double.parseDouble(str1[3].trim()) );
这些是用来消除一些空格的,但是由于在之前的类的设计中数据类型定义数据不是浮点型,使得数据需要进行字符串和浮点类型之间的转换,在存储时出现了报错,导致整个题目出现了问题;
题目集5我并没有用正则表达式为主来区分这些字符,我是先分离出每个关键字再统计Java关键字,这里就不多讲了;
题目集6的正则表达式也并没有多少好讲的,这里就不讲了。
④题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
源码如下:
import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String[] key = { "abstract", "assert", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char", "class", "const", "continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extends", "final", "finally", "float", "for", "false", "goto", "if", "implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", "native", "new", "null" , "package", "private", "protected", "public","true", "return", "strictfp", "short", "static", "super", "switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw", "throws","transient", "try", "void", "volatile", "while" }; Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>(); for(int i = 0;i < key.length;i++) { map.put(key[i], 0); } StringBuilder a = new StringBuilder(); String p = new String(in.nextLine()); while(!p.equals("exit")) { String str0[] = p.split("//"); a.append(str0[0]); p = in.nextLine(); } if(a.toString().isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } String str1[] = a.toString().split("(//*)|(/*/)"); StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder(); for(int i = 0;i < str1.length;i = i+2) { b.append(str1[i]); } String str2[] = b.toString().split("\""); StringBuilder c = new StringBuilder(); for(int i = 0;i < str2.length;i = i+2) { c.append(str2[i]); } String str[] = c.toString().split("[';']|['.']|[',']|\\[|\\]|['+']|['-']|['*']|['/']|['>']|['<']|[':']|['{']|['}']|['(']|[')'][' ']|[(,)( )]"); for(int i = 0;i < str.length;i++) str[i] = str[i].trim(); // for(int i = 0;i < str.length;i++) // System.out.println(str[i]); for(int i = 0;i < str.length;i++) { for(int j = 0;j < key.length;j++) { if(str[i].equals(key[j])) { int m = map.get(key[j]); map.put(key[j],m+1); } } } Set set = map.keySet(); Object[] arr = set.toArray(); Arrays.sort(arr); for(Object n:arr) { if(map.get(n) != 0) System.out.println(map.get(n) + "\t" + n); } } }
在统计关键词出现的次数方面我使用的是Map类,具体实现是先将每一个关键词单独分离出来,然后统计关键词出现的次数,我主要遇到的问题是在对Map的相关方法在刚开始的时候并不是很理解,在调用的时候出现了报错,然后返回的出现次数是错误的,其他的并没有什么问题。
三、踩坑心得
这三次作业还是不难的,唯一猜的坑就是那个统计水文数据的,希望下次能提前做好这方面的功课,留出充足的时间来准备比较难的题目
四、总结
这三次题目集我是真切的感受到了Java的魅力,通过对类结构一系列的设计能简化许多很麻烦的操作,收获还是很大的,但是到现在的学习还是不够,对Java的理解还是不够透彻,多操作多实践多提问才能更好学习和研究。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号