第三次cplus实验
一。验证性实验结论:
在面向对象程序设计中,程序模块是由类构成的。类是对问题的抽象描述,在类这种抽象机制中的一个特定实体即为对象。而利用特定的值去构造对象,将对象初始化为特定状态即为构造函数,使用已经存在的对象去初始化同类的新对象即为复制构造函数,析构函数则是用来完成生存期即将结束的对象在被删除前的一些清理工作。
二。编程实验部分
1.源代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class rec 4 { 5 public: 6 rec(); 7 rec(float length,float width); 8 rec(rec &p0); 9 ~rec(); 10 float get() { return a*b; } 11 private: 12 float a,b; 13 }; 14 rec::rec() 15 { 16 a=0; 17 b=0; 18 } 19 rec::rec(float length,float width) 20 { 21 a=length; 22 b=width; 23 } 24 rec::rec(rec &p0) 25 { 26 a=p0.a; 27 b=p0.b; 28 a*b; 29 } 30 rec::~rec() 31 { 32 } 33 int main() 34 { 35 float length,width,area; 36 cout<<"Please input the length and width:"; 37 cin>>length; 38 cin>>width; 39 rec p1; 40 rec p2(length,width); 41 rec p3(p2); 42 area=p3.get(); 43 cout<<"The area is:"; 44 cout<<area<<endl; 45 return 0; 46 }
运行结果:
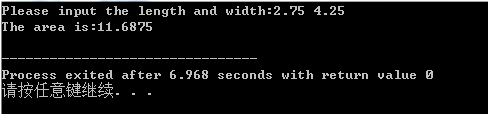
2.源代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Complex 4 { 5 private: 6 double real; 7 double imaginary; 8 public: 9 Complex(double r0,double i0); 10 Complex(double r0); 11 void add(Complex &c0); 12 void show(); 13 }; 14 Complex::Complex(double r0,double i0) 15 { 16 real=r0; 17 imaginary=i0; 18 } 19 void Complex::add(Complex &c0) 20 { 21 real+=c0.real; 22 imaginary+=c0.imaginary; 23 } 24 void Complex::show() 25 { 26 cout<<real<<(imaginary>0?"+":"-")<<imaginary<<"i"<<endl; 27 } 28 Complex::Complex(double r0) 29 { 30 real=r0; 31 imaginary=0; 32 } 33 int main() 34 { 35 Complex c1(3,5); 36 Complex c2=4.5; 37 c1.add(c2); 38 c1.show(); 39 return 0; 40 }
运行结果: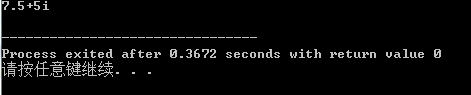
三。实验分析与讨论
这次实验接触到了上学期我们没有学的新知识:类与对象,构造函数,复制构造函数以及析构函数。在这次实验中,首先我发现了一个问题:编程第二题中UML图的Comlex行(public第三行)我没有用到,最后依然编译成功,结果无误。其次,我了解并初步掌握了各类构造函数的操作。仅仅依靠实验中了练习是远远不够的,只有多加操作,多加练习,才能真正掌握这些新知识。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号