环形链表---简单
题目:
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例:
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
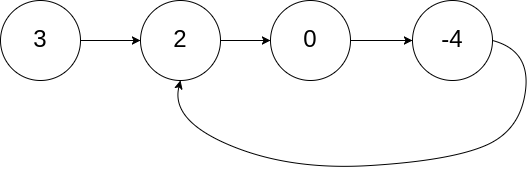
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
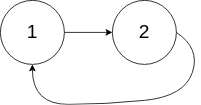
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:false 解释:链表中没有环。

思路:
用一个vector保留出现节点指针的次数就完事了。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr) return false; std::map<ListNode*,int> m; auto p=head; while(p) { if(m.find(p)==m.end()) { m[p]=1; p=p->next; } else { return true; } } return false; } };
进阶一点的:使用O(1)的内存实现,又快。这里我们先看一下大佬的:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { if(!head||!head->next) return false; ListNode* fast=head; ListNode* slow=head; while(fast&&fast->next) { fast=fast->next->next; slow=slow->next; if(fast==slow) return true; } return false; } };
解释一下:运用了双指针,这里一个快一个慢。有点典型


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号