14.CSS定位
1.元素的定位属性
元素的定位属性主要包括定位模式和边偏移两部分。
1)定位模式(定位的分类)
在CSS中,position属性用于定义元素的定位模式,其基本语法格式如下:
1 选择器{position:属性值;}
position属性的常用值:
-
static:自动定位(默认定位方式)
-
relative:相对定位,相对于其原文档流的位置进行定位
-
absolute:绝对定位,相对于其上一个已经定位的父元素进行定位
-
fixed:固定定位,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位
2)边偏移
-
top:顶端偏移量
-
bottom:底部偏移量
-
left:左侧偏移量
-
right:右侧偏移量
也就说,以后定位要和这边偏移搭配使用了, 比如 top: 100px; left: 30px; 等等
2.静态定位(static)
静态定位是所有元素的默认定位方式,当position属性的取值为static时,可以将元素定位于静态位置。 所谓静态位置就是各个元素在HTML文档流中默认的位置。
上面的话翻译成白话:就是网页中所有元素都默认的是静态定位哦! 其实就是标准流的特性。
在静态定位状态下,无法通过边偏移属性(top、bottom、left或right)来改变元素的位置。
静态定位唯一的用处: 就是取消定位。 position: static;
3.相对定位(relative)
相对定位是将元素相对于它在标准流中的位置进行定位,当position属性的取值为relative时,可以将元素定位于相对位置。
对元素设置相对定位后,可以通过边偏移属性改变元素的位置,但是它在文档流中的位置仍然保留。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .dv1 { 8 width: 100px; 9 height: 100px; 10 background-color: red; 11 position: relative; 12 left: 120px; 13 top: 100px; 14 } 15 .dv2 { 16 width: 100px; 17 height: 100px; 18 background-color: blue; 19 } 20 </style> 21 </head> 22 <body> 23 <div class="dv1"></div> 24 <div class="dv2"></div> 25 </body> 26 </html>
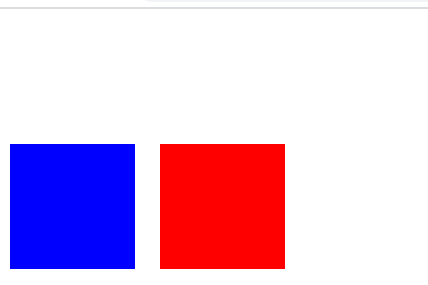
注意:
-
相对定位最重要的一点是,它可以通过边偏移移动位置,但是原来的所占的位置,继续占有。
-
其次,每次移动的位置,是以自己的左上角为基点移动(相对于自己来移动位置)
就是说,相对定位的盒子仍在标准流中,它后面的盒子仍以标准流方式对待它。(相对定位不脱标)
如果说浮动的主要目的是 让多个块级元素一行显示,那么定位的主要价值就是移动位置, 让盒子到我们想要的位置上去。
4.绝对定位(absolute)
如果文档可滚动,绝对定位元素会随着它滚动,因为元素最终会相对于正常流的某一部分定位。
当position属性的取值为absolute时,可以将元素的定位模式设置为绝对定位。
绝对定位最重要的一点是,它可以通过边偏移移动位置,但是它完全脱标,完全不占位置。
若所有父元素(祖先)都没有定位,以浏览器当前屏幕为准对齐(document文档),相对于body。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .dv1 { 8 width: 100px; 9 height: 100px; 10 background-color: blue; 11 position: absolute; 12 left: 130px; 13 top: 50px; 14 } 15 .dv2 { 16 width: 120px; 17 height: 120px; 18 background-color: red; 19 } 20 </style> 21 </head> 22 <body> 23 <div class="dv1"></div> 24 <div class="dv2"></div> 25 </body> 26 </html>
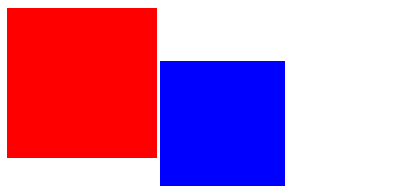
若所有父元素(祖先)有定位,依据最近的已经定位(绝对、固定或相对定位)的父元素(祖先)进行定位。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .dv1 { 8 width: 120px; 9 height: 120px; 10 background-color: blue; 11 position: absolute; 12 } 13 .dv2 { 14 width: 80px; 15 height: 80px; 16 background-color: red; 17 position: absolute; 18 top: 0; 19 } 20 </style> 21 </head> 22 <body> 23 <div class="dv1"> 24 <div class="dv2"></div> 25 </div> 26 </body> 27 </html>
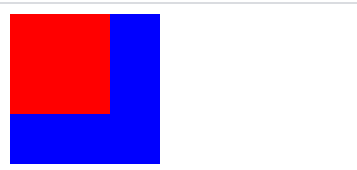
子绝父相
这句话的意思是子级是绝对定位的话,父级要用相对定位。
绝对定位是将元素依据最近的已经定位(绝对、固定或相对定位)的父元素(祖先)进行定位。就是说, 子级是绝对定位,父亲只要是定位即可(不管父亲是绝对定位还是相对定位,甚至是固定定位都可以)。但是为什么会有“子绝父相”这个词呢?
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .parent1 { 8 width: 100px; 9 height: 100px; 10 background-color: red; 11 } 12 .parent2 { 13 width: 100px; 14 height: 100px; 15 background-color: pink; 16 position: relative; 17 } 18 .parent3 { 19 width: 100px; 20 height: 100px; 21 background-color: blue; 22 } 23 .child { 24 width: 50px; 25 height: 50px; 26 background-color: green; 27 position: absolute; 28 top: 20px; 29 } 30 </style> 31 </head> 32 <body> 33 <div class="parent1"></div> 34 <div class="parent2"> 35 <div class="child"></div> 36 </div> 37 <div class="parent3"></div> 38 </body> 39 </html>
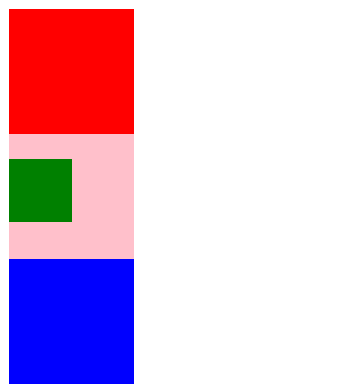
因为子级是绝对定位,不会占有位置, 可以放到父盒子里面的任何一个地方。
父盒子布局时,需要占有位置,因此父亲只能是相对定位。
这就是子绝父相的由来。
绝对定位的盒子水平/垂直居中
设置left,top值均为50%,同时margin-left设置为绝对定位元素(要居中的元素)width的一半取负,margin-top设为其height的一半取负。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .parent { 8 width: 300px; 9 height: 200px; 10 background-color: blue; 11 position: relative; 12 } 13 .child { 14 width: 100px; 15 height: 70px; 16 background-color: red; 17 position: absolute; 18 left: 50%; 19 top: 50%; 20 margin-left: -50px; 21 margin-top: -40px; 22 } 23 </style> 24 </head> 25 <body> 26 <div class="parent"> 27 <div class="child"></div> 28 </div> 29 </body> 30 </html>
5.固定定位(fixed)
固定定位是绝对定位的一种特殊形式,类似于 正方形是一个特殊的 矩形。它以浏览器窗口作为参照物来定义网页元素。当position属性的取值为fixed时,即可将元素的定位模式设置为固定定位。
当对元素设置固定定位后,它将脱离标准文档流的控制,始终依据浏览器窗口来定义自己的显示位置。不管浏览器滚动条如何滚动也不管浏览器窗口的大小如何变化,该元素都会始终显示在浏览器窗口的固定位置。
固定定位有两点:
-
固定定位的元素跟父亲没有任何关系,只认浏览器。
-
固定定位完全脱标,不占有位置,不随着滚动条滚动。
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <style> 7 .dv1 { 8 width: 50px; 9 height: 50px; 10 background-color: red; 11 position: fixed; 12 right: 50px; 13 bottom: 50px; 14 } 15 .dv2 { 16 width: 50px; 17 height: 2000px; 18 background-color: blue; 19 } 20 </style> 21 </head> 22 <body> 23 <div class="dv1"></div> 24 <div class="dv2"></div> 25 </body> 26 </html>

6.四种定位总结
| 定位模式 | 是否脱标占有位置 | 是否可以使用边偏移 | 移动位置基准 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 静态static | 不脱标,正常模式 | 不可以 | 正常模式 |
| 相对定位relative | 脱标,占有位置 | 可以 | 相对自身位置移动 |
| 绝对定位absolute | 完全脱标,不占有位置 | 可以 | 相对于定位父级移动位置 |
| 固定定位fixed | 完全脱标,不占有位置 | 可以 | 相对于浏览器移动位置 |




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号