2-5
类中的构造器也称为构造方法,是在进行创建对象的时候必须要调用的。并且构造器有以下两个特点:
1、要与类名相同
作用
1、new 本质在调用构造方法
2、初始化对象的值
注意点 、
1、定义有参构造之后,如果想使用无参构造,显示的定义一个无参的构造
public class Person {
String name;
//显示的定义构造器
//实列化初始值
//1.使用new关键字,本质是在调用构造器
public Person()
{
this.name="kkk";
}
//有参构造:一旦定义了有参构造,无参就必须显示定义
public Person(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
}
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实列化文件
Person person = new Person("kkkkkk");
System.out.println(person.name);
}
}
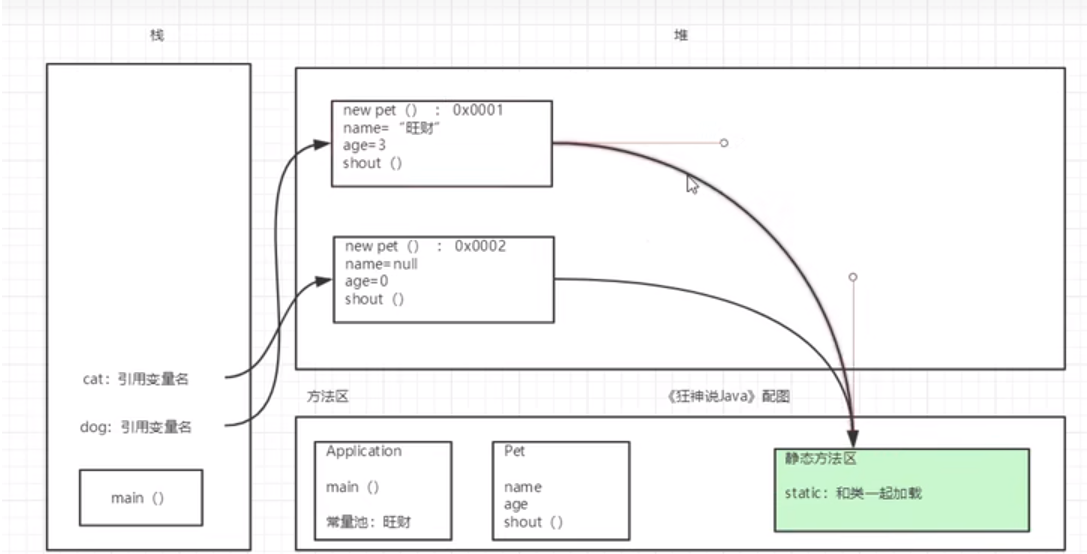
创建对象内存分析
封装
特点1、该露的露,该藏的藏 “高内聚,低耦合”
高内聚,低耦合:高内聚就是类的内部数据操作细节自己完成,不允许外部干涉;低耦合:仅暴露少量的方法给 外部使用 属性私有,get/set;
2、封装(数据的隐藏)通常,禁止直接访问一个对象中数据的实际表示
作用:
1、提高程序的安全性,保护数据
2、隐藏代码实现细节
3、统一接口
4、 系统可维护性增加
继承
继承的本质是对某一批类的抽象,从而实现对现实世界更好的建模
extands=》“扩展”,子类是父类的扩展
java中的类只有单继承,没有多继承 一个子类只有一个父类,而一个父类可以有多个子类
子类能够继承父类的所有方法
public class Person {
public int money=100;
public void say(){
System.out.println("说了一句话");
}
}
public class Student extends Person {}
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.say();//student 可以继承使用Person的Say方法
}
}
super this之间的区别
public class Person {
protected String name="yyg";
public Person()
{
System.out.println("Person无参执行了");
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
private String name="zmm";
public Student()
{
super();
System.out.println("student执行了无参构造");
}
public void test(String name)
{
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
}
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.test("kkk");
}
}
/*
输出
Person无参执行了
student执行了无参构造
kkk
zmm
yyg
注意:this 是指代的当前的对象
super是指代的当前对象的父类
(属性或者方法都可以)
子类的无参构造中有super() 自动调用父类的无参构造
*/
super注意点事项
1、super调用父类的构造方法, 必须在构造方法第一个
2、super必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中
3、super和this不能同时调用构造方法
4、super只能在继承条件下才可以使用
5、super()调用父类的构造
重写
静态方法和非静态方法区别很大!
静态方法:方法的调用只和左边,即定义的数据类型有关
非静态方法:重写
public class A extends B{
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("A=>test()");
}
}
// 重写都是方法的重写,和属性无关
public class B {
public void test()
{
System.out.println("B=>test()");
}
}
package February_5;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法的调用只和左边,
A a=new A();
a.test();//调用A
//父类的引用指向了子类
B b=new A();
b.test();//调用B
}
}
//A=>test()
//A=>test()
//重写:需要有继承关系 子类重写父类的方法
1.方法名必须相同
2、参数列表必须相同
3、修饰符:范围可以扩大但不能被缩小: public -》protected》Default》private
4、抛出的异常:范围可以被缩小,但不能扩大: ClassNotFoundExcetion ---》Exception(大)
重写,子类的方法和父类必须要一致:方法体 不同!
为什么需要重写?
1、父类的功能,子类不一定需要,或者不一定满足!
多态
动态编译:类型:可扩展性
即同一个方法可以根据对象的不同而采取多种不同的行为方式
package February_5;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//一个对象的实际类型是确定的
// new Student();
//new Person();
//可以指向的引用类型就不确定了 :父类的引用指向子类
Student s1 = new Student();
Person s2=new Student();
Object s3=new Student();
//对象能执行哪些方法,主要看对象左边的类型和右边关系不大!
s2.run();//子类重写父类的方法,执行子类的方法
s1.run();
s1.eat();
((Student)s2).eat();
}
}
package February_5;
public class Person {
public void run()
{
System.out.println("run");
}
}
package February_5;
public class Student extends Person {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Student run");
}
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("Student eat!");
}
}
//多态注意事项
1、多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态
2、父类和子类,有联系 类型转换异常 ClassCastException!
3、存在条件:继承关系,方法需要重写,父类引用指向子类对象! Father f1=new Son()
1、static 方法,属子类 ,它不属于实列
2、final 常量
3、private方法;
instanceof(类型转换) 引用类型,判断一个对象是什么
//System.out.println(x instanceof y);//编译通过 只需要判断x 与y之间是否存在父子关系
//Object > Person >Student
//Object > Person >Teacher
//Object > String
Object object =new Student();
System.out.println(object instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher);//false
System.out.println(object instanceof Object);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof String);//false
Person person= new Student();
System.out.println(person instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher);//false
System.out.println(person instanceof Object);//true
//System.out.println(person instanceof String);//编译报错
static
package February_5;
public class Demo03 {
//2、赋初始值
{
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
static//1、只执行一次
{
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
public Demo03()//3
{
System.out.println("构造代码块");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo03 demo03 = new Demo03();
System.out.println("=====");
Demo03 demo031 = new Demo03();
}
}
//静态代码块
匿名代码块
构造代码块
=====
匿名代码块
构造代码块
//static 代码块只能执行一次
抽象类
abstract 关键字
package February_5;
//abstract 抽象类 类 extends:单继承 (接口可以多继承)
public abstract class Demo04 {
//abstract, 抽象方法,只有方法名字,没有方法的实现
public abstract void doSomething();
//1、不能new 这个抽象类,只能靠子类来实现它:进行约束!
//2、抽象类中可以写普通方法
//3、抽象方法必须在抽象类中
}
package February_5;
//抽象类的所有方法,继承了它的子类,都必须实现它的方法
public class Demo05 extends Demo04 {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
}
}
接口
接口只有规范,自己无法写方法 抽象的抽象
接口的本质就是契约
package February_6;
//类可以实现接口 implements 接口
//实现接口的类,就需要重写接口中的方法
//多继承 利用接口来实现多继承
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService,TimeService {
@Override
public void add(String name) {
}
@Override
public void delete(String name) {
}
@Override
public void update(String name) {
}
@Override
public void query(String name) {
}
@Override
public void timer() {
}
}
/*
1、约束
2、定义一些方法,让不同的人实现
3、public abstract
4、public static final
5、接口不能被实列化,接口中没有构造方法
6、implements可以实现多个接口
7、必须要重写接口中的方法
* */
package February_6;
public interface UserService {
//接口中的所有定义都是抽象的public
void add(String name);
void delete(String name);
void update(String name);
void query(String name);
}
package February_6;
public interface TimeService {
void timer();
}
内部类
package February_6;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//没有名字初始化类,不用将实列保存在变量中 匿名类
new Apple().eat();
AdminService adminService = new AdminService() {
@Override
public void hello() {
}
};
}
}
class Apple{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("1");
}
}
interface AdminService{
void hello();
}
package February_6;
public class Outer {
private int id=0;
public void out()
{
System.out.println("外部类方法");
}
//局部内部类
public void method()
{
class Inner{
public void in()
{
}
}
}
public class inner
{
public void in()
{
System.out.println("内部类方法");
}
//获得外部类的私有属性
public void getID()
{
System.out.println(id);
}
}
}
异常
检查性异常
运行时异常
错误Error
异常体系结构
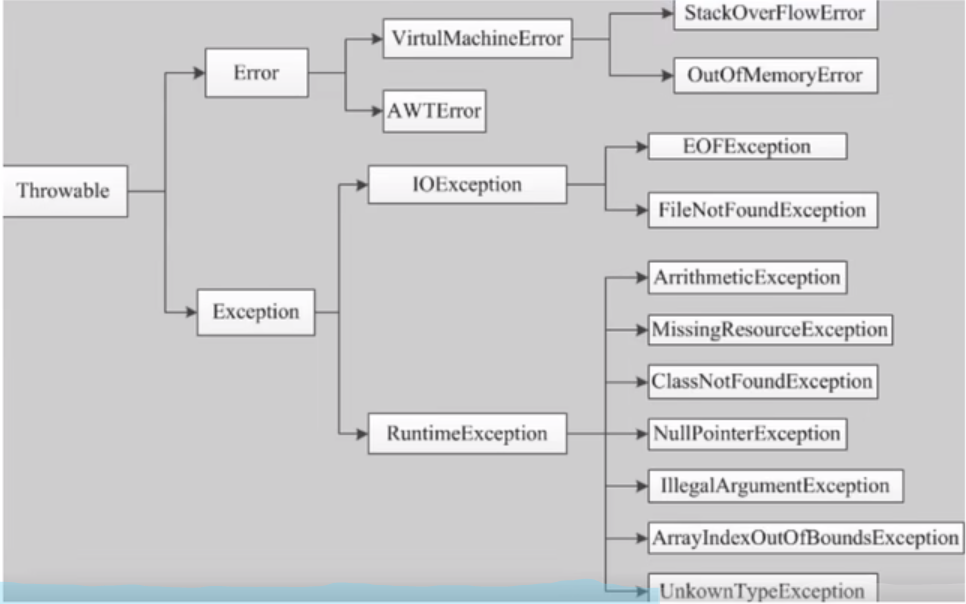
java异常处理机制
抛出异常
捕获异常
package February_6;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=1;
int b=0;
try{
//监控异常
System.out.println(a/b);
}
catch (Exception e)//捕获异常
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
finally
{//处理善后工作
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}//ctrl +alt +t 快捷键加try catch 异常


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号