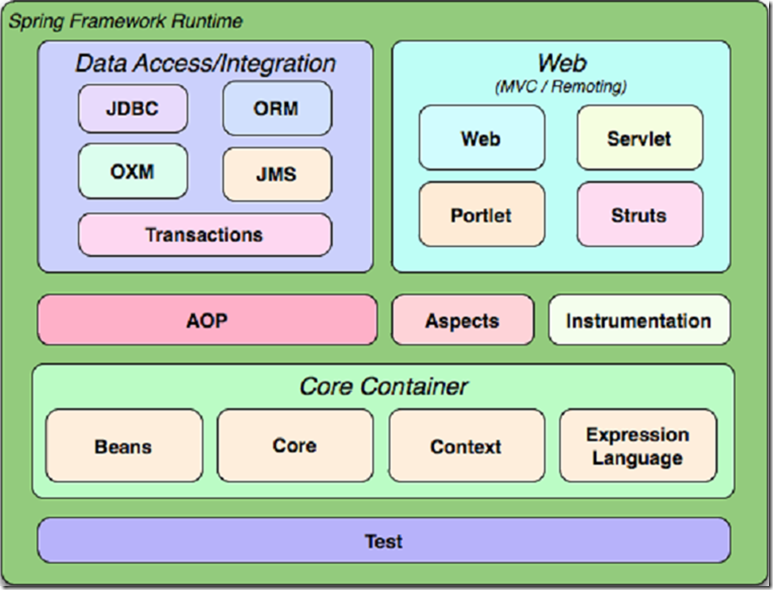
Spring框架
面向bean比纳城
IOC:控制反转
AOP实现
数据访问支持:简化JDBC\Hibenate编码 + 声明式事务
Web集成
Beans\core\context关系:
Bean:元素
Core:功能
context:容器
Spring要解决的问题;Ioc将组件对象的控制从代码转移给外部容器
【1】解决依赖注入的问题,使用者的代码完成解耦工作【DI】
——依赖注入:是指一个类对象需要正常执行时,首先需要把另一个对象注入进来
——核心:依赖注入,Spring替我们完成了依赖注入。——IOC,控制反转实现!
——IOC:如果存在大量的接口,需要实现类来完成注入工作。那么一旦需要修改实现类的时候,所有这些被注入的实现类都需要通过修改源码的方式来进行修改。如果修改遗漏,或者检查起来会非常麻烦!!
——实现: JDOM:解析XML文件;反射机制;工厂模式 (单例模式)
——XML配置:beans\aop\contexts ----[ejb]
——配置XML文件:scope:属性支持单例、多例
-XmlBeanFactory:默认懒加载——获取bean时才构造生成。
-获取bean方式:getBean(class\name)
-ClassPathXmlApplicationContext :默认是单例且立即加载; ——配置为多例后,为懒加载
-factory-method="newInstance" lazy-init="false" 实现静态工厂模式——实现单例与懒加载
dao 依赖于 service:
<bean name="beanDao1" class="com.m.dao.impl.BeanDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean name="beanDao2" class="com.m.dao.impl.BeanDaoImpl2"></bean><bean name="beanService" class="com.m.service.impl.BeanServiceImpl">
<property name="dao" ref="beanDao1"></property>
<property name="dao2" ref="beanDao2"></property>
</bean>
配置属性:
<bean name="beanDao1" class="com.m.dao.impl.BeanDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean name="beanDao2" class="com.m.dao.impl.BeanDaoImpl2"></bean><bean name="beanService" class="com.m.service.impl.BeanServiceImpl">
<property name="dao" ref="beanDao1"></property>
<property name="dao2" ref="beanDao2"></property>
<property name="str" value="hello"></property>
<property name="num" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
构造配置依赖注入:
<bean name="beanDao1" class="com.m.dao.impl.BeanDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean name="beanDao2" class="com.m.dao.impl.BeanDaoImpl2"></bean>
<bean name="beanService" class="com.m.service.impl.BeanServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="dao" index="0" ref="beanDao1"/>
<constructor-arg name="dao2" index="1" ref="beanDao2"/>
<constructor-arg name="str" index="2" value="hello" type="java.lang.String"/>
<constructor-arg name="num" index="3" value="12345" type="java.lang.Integer"/>
</bean>
数组、list\set 、 Map 、Properity
<bean name="beanService" class="com.m.service.impl.BeanServiceImpl2">
<property name="strArr">
<array>
<value>h</value>
<value>e</value>
<value>l</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="intList">
<array>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="strSet">
<array>
<value>d</value>
<value>e</value>
<value>f</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="k1" value="v1" ></entry>
<entry key="k2" value="v2" ></entry>
<entry key="k3" value="v3" ></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="p1">vp1</prop>
<prop key="p2">vp2</prop>
<prop key="p3">vp3</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
-Spring以Bean的方式管理所有的组件,Java EE的全部组件都被视为Bean管理
-Bean在Spring的容器中运行,Spring负责创建Bean的实例,并管理其生命周期
AOP:面向切面编程
切入点表达式,符合该表达式的方法可以被织入增强处理:
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public * com.m.service.impl.*.*(..))"
id="servicePointcut"/>
<aop:aspect ref="serviceAdvice"> //增强类name
<aop:before method="beforeService"
pointcut-ref="servicePointcut"/>
<aop:after method="afterService"
pointcut-ref="servicePointcut"/>
<aop:after-returning method="returnService" returning="name"
pointcut-ref="servicePointcut"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="exceptionService" throwing="ex"
pointcut-ref="servicePointcut"/>
<aop:around method="aroundService"
pointcut-ref="servicePointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config><bean name="serviceAdvice" class="com.m.advice.BaseServiceAdvice"></bean>
============================跟配置注解等效==================================
配置文件指明:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.m"/> //扫描对应包下所有的类
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> //增强类注解@Component
@Aspect========增强类
//切入点
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.m.service.impl.*.*(..))") //对应增强方法的切入
public void myPointcut(){}=======对应增强方法
//前置
@Before("myPointcut()")
//后置
@After("myPointcut()")
//环绕
@Around("myPointcut()")//返回值
@AfterReturning(pointcut="myPointcut()",returning="name")
//异常
@AfterThrowing(pointcut="myPointcut()",throwing="ex")
@Controller
@Autowired ===等价于
@Resource
@Qualifier("beanServiceImpl4") //必须对应类名,首字母小写==============
@Service
// @Autowired
@Resource
@Qualifier("beanDaoImpl3")================
@Repository
Autowired注解是按照类型(byType)装配依赖对象 || 按照名称(byName)来装配,可以结合@Qualifier注解一起使用
① Autowired:Spring的注解
1) byName:Qualifier注解指定ByName的Name
② Resource:J2EE的注解
1) 装配顺序
a. Name和Type都指定,那么就必须都匹配
b. 如果Name和Type都不指定,那么先Name,再Type
AOP与OOP区别:
OOP:针对业务处理过程的实体及其属性和行为进行抽象封装,以获得更加清晰高效的逻辑单元划分
AOP:针对业务处理过程中的切面进行提取,它所面对的是处理过程中的某个步骤或者阶段,以获得逻辑过程中各部分之间低耦合的隔离效果。这两种设计思想在目标上有着本质的差异


![MT5C{0K6L%YJ~N))IO[{L7E_thumb[2] MT5C{0K6L%YJ~N))IO[{L7E_thumb[2]](https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/1955435/202008/1955435-20200813160537377-1440580916.png)

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号