saltstack使用
saltstack中salt-key的用法
介绍:
saltstack中master和minion是依靠证书来进行加密通信的。
在saltstack中salt-key命令是用来管理证书的
用法:
salt-key [options]
参数:


常用参数:
- -L, --list-all #显示已经或未认证的被控端id
- -a ACCEPT, --accept=ACCEPT #接受单个id证书请求
- -A, --accept-all #接受所有id证书请求
- -r REJECT, --reject=REJECT #拒绝指定的公钥
- -R, --reject-all #拒绝所有正在请求的公钥
- -d DELETE, --delete=DELETE #删除指定的公钥
- -D, --delete-all #删除所有的公钥
证书状态
salt-key -L
Accepted Keys: #已经接受的key
Denied Keys: #拒绝的key
Unaccepted Keys:#未加入的key
Rejected Keys:#吊销的key
实例:
1.检查所有证书
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
web1
web2
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
2.删除指定证书
-d
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -d web1
The following keys are going to be deleted:
Accepted Keys:
web1
Proceed? [N/y] y
Key for minion web1 deleted.
删除所有证书
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -D
The following keys are going to be deleted:
Accepted Keys:
web1
web2
Proceed? [N/y] y
Key for minion web1 deleted.
Key for minion web2 deleted.
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
3.接受单个证书
-a
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
web1
web2
Rejected Keys:
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -a web1
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
web1
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion web1 accepted.
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
web1
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
web2
Rejected Keys:
[root@salt-master ~]# salt '*' test.ping
web1:
True
接收所有证书
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -A
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
web2
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion web2 accepted.
4.拒绝单个证书认证
-r
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
web1
web2
Rejected Keys:
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -r web1
The following keys are going to be rejected:
Unaccepted Keys:
web1
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion web1 rejected.
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
web2
Rejected Keys:
web1
拒绝所有
[root@salt-master ~]# salt-key -R
The following keys are going to be rejected:
Unaccepted Keys:
web2
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion web2 rejected.
如果不想交互,加个-y就可以了
证书的所有文件都在salt-master中
注意保存
[root@salt-master master]# pwd
/etc/salt/pki/master
[root@salt-master master]# tree
.
├── master.pem
├── master.pub
├── minions
├── minions_autosign
├── minions_denied
├── minions_pre
└── minions_rejected
├── web1
└── web2
[root@mcw01 ~]# ls /srv/ [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/ cloud cloud.conf.d cloud.deploy.d cloud.maps.d cloud.profiles.d cloud.providers.d master masterbak master.d minion minion.d minion_id pki proxy proxy.d roster [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/pki/ master minion [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/pki/master/ master.pem master.pub minions minions_autosign minions_denied minions_pre minions_rejected [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/pki/master/minions mcw01 [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/pki/master/minions_autosign/ [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/pki/master/minions_denied/ [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/pki/master/minions_pre/ [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/pki/master/minions_rejected/ [root@mcw01 ~]# salt * test.ping No minions matched the target. No command was sent, no jid was assigned. ERROR: No return received [root@mcw01 ~]# salt '*' test.ping mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
salt-key用法2
salt-key:这里应该怎么讲呢,授权可能更合适一些,授权节点percona-node3:
[root@mysql_haproxy ~]#salt-key -a percona-node3
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
percona-node3
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion percona-node3 accepted.
[root@mysql_haproxy ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
percona-node3
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
同理添加其他节点:
[root@mysql_haproxy ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
percona-node1
percona-node2
percona-node3
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
操作
-l ARG, –list=ARG
显示某种类型公钥。参数”pre”,”un”和”unaccecpted”将显示不接受的/无符号的keys.”acc”或”accepted”将显示同意/有符号的keys.”rej”或者”rejected”将显示拒绝列表,最后”all”将显示所有keys。
# salt-key -l 'pre'
Unaccepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_93
# salt-key -l 'un'
Unaccepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_93
# salt-key -l 'unaccecpted'
Unaccepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_93
# salt-key -l 'acc'
Accepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_67
YQD_2014_12_06_57_68
YQD_2014_12_06_57_69
# salt-key -l 'accepted'
Accepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_67
YQD_2014_12_06_57_68
YQD_2014_12_06_57_69
# salt-key -l 'rej'
Rejected Keys:
# salt-key -l 'rejected'
Rejected Keys:
-L, –list-all
在master上显示所有公钥: accepted, pending, and rejected.
# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_67
YQD_2014_12_06_57_68
YQD_2014_12_06_57_69
Unaccepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_93
Rejected Keys:
-a ACCEPT, –accept=ACCEPT
命令行执行接受minion名称的key
-A, –accept-all
接受所有等待的Key
# salt-key -A
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_93
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion YQD_2014_12_06_57_93 accepted.
-r REJECT, –reject=REJECT
拒绝某个key,这个只能绝unaccepted keys里面的key,并不能拒绝accepted keys里面的key,如果匹配accepted keys里面的key,需要加上–include-all参数,同理想同意Rejected Keys里面的key也要下加这个参数,如下所示:
[root@localhost ~]# salt-key --include-all -r YQD_WS_NO_2_11
The following keys are going to be rejected:
Accepted Keys:
YQD_WS_NO_2_11
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion YQD_WS_NO_2_11 rejected.
[root@localhost ~]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
YQD_WS_NO_2_11
[root@localhost ~]# salt-key --include-all -a YQD_WS_NO_2_11
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Rejected Keys:
YQD_WS_NO_2_11
Proceed? [n/Y] y
Key for minion YQD_WS_NO_2_11 accepted.
[root@localhost ~]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
YQD_WS_NO_2_11
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
-R, –reject-all
拒绝所有等待的公钥
-p PRINT, –print=PRINT
打印指定的公钥
-P, –print-all
打印所有公钥
-d DELETE, –delete=DELETE
删除某个key
-D, –delete-all
删除所有key
# salt-key -D
The following keys are going to be deleted:
Accepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_67
YQD_2014_12_06_57_68
YQD_2014_12_06_57_69
YQD_2014_12_06_57_93
Proceed? [N/y] n
-f FINGER, –finger=FINGER
打印指定key的指纹
# salt-key -f YQD_2014_12_06_57_68
Accepted Keys:
YQD_2014_12_06_57_68: 20:a5:f9:85:0b:3d:d7:ba:8f:98:7b:1d:53:fa:a2:2e
–out=OUTPUT, –output=OUTPUT
[root@localhost ~]# salt-key --out=yaml
minions:
- YQD_WS_NO_2_11
minions_pre: []
minions_rejected: []
[root@localhost ~]# salt-key --out=jeson
minions:
- YQD_WS_NO_2_11
minions_pre:
minions_rejected:
-F, –finger-all 打印所有key指纹:
C#
[root@localhost ~]# salt-key -F
Local Keys:
master.pem: 93:90:ce:9d:ed:5d:d0:8b:d5:48:e5:43:99:92:93:f9
master.pub: 9c:ad:e5:8c:cc:ba:49:62:d8:55:83:ad:b9:68:08:ff
Accepted Keys:
YQD_WS_NO_2_11: 6c:ce:46:30:a5:59:c2:7e:71:ce:64:80:24:46:4a:87
自己一些操作
主机名用的是hosts文件里面的
[root@mcw02 ~]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 10.0.0.11 vm1.cluster.com kibana
先拒绝
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: mcw01 Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: vm2.cluster.com Rejected Keys: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -r vm2.cluster.com The following keys are going to be rejected: Unaccepted Keys: vm2.cluster.com Proceed? [n/Y] y Key for minion vm2.cluster.com rejected. [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: mcw01 Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: Rejected Keys: vm2.cluster.com [root@mcw01 ~]#
拒绝之后,无法加入
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -a vm2.cluster.com The key glob 'vm2.cluster.com' does not match any unaccepted keys. [root@mcw01 ~]#
显示所有状态的key
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key --include-all Accepted Keys: mcw01 Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: Rejected Keys: vm2.cluster.com [root@mcw01 ~]#
打印指定公钥,公钥是不一样的,这两个
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -p mcw01 Accepted Keys: mcw01: -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAyTxKCqHByVVOI86yhM3T UdW04ekQOwUzt3c+xjESkXkK52CcW+63bj0dFUWo/ou/hVFFQeVpVua6DYIwiXR6 l36nihYd8S5CCJXXW04B1+3bzjNA8wqYZjDWQ2C+kVF5A7r3XVucrdKPhCli4pRi CpPWPkPH8FWHIMdrQPP+MdorRUP4mF7ftdjq7pDkOgxp/PSrRVGi7Tri/DMJlstb HGxC/KM06eKSDhwpNXpIVNVjLteu2u+lNXN/CbKBCtqtZv/492v7RL075zQnkHsu ZSCwZfpGAU9EeB+6FcuO9mDI/MmPaAir4X3TTukPxpAo8imOSWvvpHwvV01imowv OQIDAQAB -----END PUBLIC KEY----- [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -p vm2.cluster.com Rejected Keys: vm2.cluster.com: -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA2fAKMxjHl05+lc0/WoQe yGW+1UJlutaBhjUELxnr9MuhgWf+0wL0rBVe+ZJ69K1LPDH+rIKo/JofrvlRpYGv eLtOj21w6o/JI19u42rG8+O8eTQs56H4cnU+Ue2BcK+uBJZ5ypbqYpnaRz9BxpGQ WxHcTBckcBqetcML7ndA4QN3KhiM7FeX/8Ju7TUyWOyGBzZ1oRHZo8SWOz0sHqwC eJWYHh15LNcc2X44n2Dik5dWUwn7elwxGJw3CmgxZmCc/jDyPNWU2wRZLhRPeqT7 V7qUGMC7lm6ux35vTSU95VD6AOkGWXgprSjgoLOrckYpaZ8uJfAxxW0UMijm0l0p 0QIDAQAB -----END PUBLIC KEY----- [root@mcw01 ~]#
跟上面的打印对比下,命令打印的和对应机器的文件是一样的
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/pki/master/minions_rejected/vm2.cluster.com -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA2fAKMxjHl05+lc0/WoQe yGW+1UJlutaBhjUELxnr9MuhgWf+0wL0rBVe+ZJ69K1LPDH+rIKo/JofrvlRpYGv eLtOj21w6o/JI19u42rG8+O8eTQs56H4cnU+Ue2BcK+uBJZ5ypbqYpnaRz9BxpGQ WxHcTBckcBqetcML7ndA4QN3KhiM7FeX/8Ju7TUyWOyGBzZ1oRHZo8SWOz0sHqwC eJWYHh15LNcc2X44n2Dik5dWUwn7elwxGJw3CmgxZmCc/jDyPNWU2wRZLhRPeqT7 V7qUGMC7lm6ux35vTSU95VD6AOkGWXgprSjgoLOrckYpaZ8uJfAxxW0UMijm0l0p 0QIDAQAB -----END PUBLIC KEY----- [root@mcw01 ~]#
再对比查看下服务端的公钥和私钥。
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/pki/master/m master.pem master.pub minions/ minions_autosign/ minions_denied/ minions_pre/ minions_rejected/ [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/pki/master/master.pub -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA6qlp+YqgQW31niIhpeoE s1maVhy0zEKXJC2sx9ToxS8zXKPn/ibMFlQwsHqFvIVtE+E4t5sibPQZDFseEl/A rSfkyLE+Mj9Iy4rwhSZRR0BegeudaUldKZimPqMx4+HO7xvu5EZtCuKDKEzxbVRz zTD768tDti5DxaDHIU9Y9RPbpP/gjrsDk9O/KE7Y2W8JFkiCUSjRhLBkfCvudZec csHbP26o/D8JP8+74DmHgR2P/rFmUh7MrrdSXHXVphM1HVcRgXSz4mDj05fly9IX KJ/nUIIrSJT5i0Hn68bTcWabH7mStPbJnpjunP8shVEc60X6p55xvZKu+ERg4lAl MwIDAQAB -----END PUBLIC KEY----- [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/pki/master/master.pem -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- MIIEpAIBAAKCAQEA6qlp+YqgQW31niIhpeoEs1maVhy0zEKXJC2sx9ToxS8zXKPn /ibMFlQwsHqFvIVtE+E4t5sibPQZDFseEl/ArSfkyLE+Mj9Iy4rwhSZRR0Begeud aUldKZimPqMx4+HO7xvu5EZtCuKDKEzxbVRzzTD768tDti5DxaDHIU9Y9RPbpP/g jrsDk9O/KE7Y2W8JFkiCUSjRhLBkfCvudZeccsHbP26o/D8JP8+74DmHgR2P/rFm Uh7MrrdSXHXVphM1HVcRgXSz4mDj05fly9IXKJ/nUIIrSJT5i0Hn68bTcWabH7mS tPbJnpjunP8shVEc60X6p55xvZKu+ERg4lAlMwIDAQABAoIBAQDpFS22OAPF+bqm P7C8ZB4XJ0Etl4Xd/aaywMuGEezDL4cM1aFxyIefBjD2mjyMbNtTi7oSZX1kS3E1 3KuaBJIVbDLLRYJJ1qIvyuns14qUA1PcKHRKSBzJXF6EiQTdHUW2K0C2bV2SGju8 o/CKcAA2KBmStGulYX7fpjsk0vPBOPlfjRQTmNKRHI6Sl02oQslkeNSUnV+OaArn NvVMfMNpwd6WY6xT8n3hPHSGBymTMr5DguAzCac5aPD/+lzAU15Yice++ZYsvqzl DCNIzZ6Iccb7Z8zjyDRVs2BzzdSSSHLPTeh1RavW/TmU1DGLQlmpWiad/AvHEgJR TzcsT3RBAoGBAPbHfop4ZZ+vKXHRAVsao93Efxb5SkOQqtxwc/r+4yGwHhjXYZQw e/VeoEcQVDcyYB/JRzJDtX3x0THXHFjgq74vqjRfbsw9+S4YhyypKfU7Ku72kHvW nbVl1Q/W++g8pHROM3bGP/c/DhGprnHUxN44CkTxSitZioFLHeUrvwnvAoGBAPNu A0HCuMiPwT0UNEoumua0mQceKWpzOI5vcX3ZG4wBwvezZFAB6VPLT4YrPqI5LAzc aBSymaeShR9iejA/MKoRqpj0FZ1+ofAryW5FClNcW0TAEm9wX28RSobyKRy5wbj9 AB3e3XOoFnxbPZNlj3dQ1shGGLZBLn4kIXKTVez9AoGBAI16KW2xQHGfth7uN9zH FRLayBGfsZeypIHkZlmLLyPtGBQdxm9yrF4rda/ICL/sPXd7qTmD39TogYoVTMcX Zt6N7QJBg//Lt8NZhIVyJf/Vf/Onn4WfsKKCUvfVxG2L9qxG+PIrDhjtKV+u67eO x56uehS0UFUx7FnberQbtFY5AoGAUjMJ4oDQSNlSFT/nUE1gfRrquZ6TuaBirqYv GqHfTW2i2mW3L9UVZvg2SEX+BmVr3IPomWSdwhoV3b0xKW2ND0Cb7L4vNll2cVU3 1YZ2sCN1pkd9cift8eFS2zKWc16+barxCSUiflV6Ek/1APrAcTfY7xPMcG6eNnYY 3UmnMDkCgYAumDVfgic4jU+nNh7z21C+E9dixMUa/o2AEU8Eo7GA42zePLYfo3uE PHbYAgLkbqaUR72jFNk6kFVy4+MUpUmKOtLHj+R0GNOSzkkbbPjpHsY0k602FM0j HoQPraCY6MyHK6UQR/r32+6Itafi76awqzYFk1eTkhzeqTKgIoHSyg== -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY----- [root@mcw01 ~]#
打印所有的公钥
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -P Accepted Keys: mcw01: -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAyTxKCqHByVVOI86yhM3T UdW04ekQOwUzt3c+xjESkXkK52CcW+63bj0dFUWo/ou/hVFFQeVpVua6DYIwiXR6 l36nihYd8S5CCJXXW04B1+3bzjNA8wqYZjDWQ2C+kVF5A7r3XVucrdKPhCli4pRi CpPWPkPH8FWHIMdrQPP+MdorRUP4mF7ftdjq7pDkOgxp/PSrRVGi7Tri/DMJlstb HGxC/KM06eKSDhwpNXpIVNVjLteu2u+lNXN/CbKBCtqtZv/492v7RL075zQnkHsu ZSCwZfpGAU9EeB+6FcuO9mDI/MmPaAir4X3TTukPxpAo8imOSWvvpHwvV01imowv OQIDAQAB -----END PUBLIC KEY----- Rejected Keys: vm2.cluster.com: -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA2fAKMxjHl05+lc0/WoQe yGW+1UJlutaBhjUELxnr9MuhgWf+0wL0rBVe+ZJ69K1LPDH+rIKo/JofrvlRpYGv eLtOj21w6o/JI19u42rG8+O8eTQs56H4cnU+Ue2BcK+uBJZ5ypbqYpnaRz9BxpGQ WxHcTBckcBqetcML7ndA4QN3KhiM7FeX/8Ju7TUyWOyGBzZ1oRHZo8SWOz0sHqwC eJWYHh15LNcc2X44n2Dik5dWUwn7elwxGJw3CmgxZmCc/jDyPNWU2wRZLhRPeqT7 V7qUGMC7lm6ux35vTSU95VD6AOkGWXgprSjgoLOrckYpaZ8uJfAxxW0UMijm0l0p 0QIDAQAB -----END PUBLIC KEY----- [root@mcw01 ~]#
显示指定,显示所有指纹信息
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: mcw01 Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: Rejected Keys: vm2.cluster.com [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -f mcw01 Accepted Keys: mcw01: 25:b0:92:27:f5:06:d5:e9:70:36:a6:cf:56:0f:2c:18:f5:7b:11:3f:a6:fb:01:02:d6:49:ef:9d:4b:57:52:ba [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -F Local Keys: master.pem: 47:a5:8d:09:62:5e:32:63:bb:f6:9a:b2:2a:d2:fa:a9:38:27:8a:fe:7d:f1:cd:cd:9f:a1:29:b4:6a:9f:8a:35 master.pub: 3b:a4:4d:55:f7:05:a8:49:6b:95:45:56:17:eb:ba:b4:ad:25:fa:90:d5:09:11:cd:3e:72:14:d2:eb:60:32:eb Accepted Keys: mcw01: 25:b0:92:27:f5:06:d5:e9:70:36:a6:cf:56:0f:2c:18:f5:7b:11:3f:a6:fb:01:02:d6:49:ef:9d:4b:57:52:ba Rejected Keys: vm2.cluster.com: a0:b4:e7:ba:e4:2c:90:3a:98:17:35:06:d0:57:ca:0a:38:db:ef:bf:79:ba:06:36:0f:79:08:b5:66:5a:d4:d4 [root@mcw01 ~]#
[root@mcw01 ~]# md5sum /etc/salt/pki/master/master.pem 64cface97a6c2f3670c0e8679a1adb83 /etc/salt/pki/master/master.pem [root@mcw01 ~]#
免交互加入key,加个-y参数
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: mcw01 mcw03 vm2.cluster.com Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: mcw04 Rejected Keys: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -a mcw04 -y The following keys are going to be accepted: Unaccepted Keys: mcw04 Key for minion mcw04 accepted. [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: mcw01 mcw03 mcw04 vm2.cluster.com Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: Rejected Keys: [root@mcw01 ~]#
日常命令参数
master端




minion端


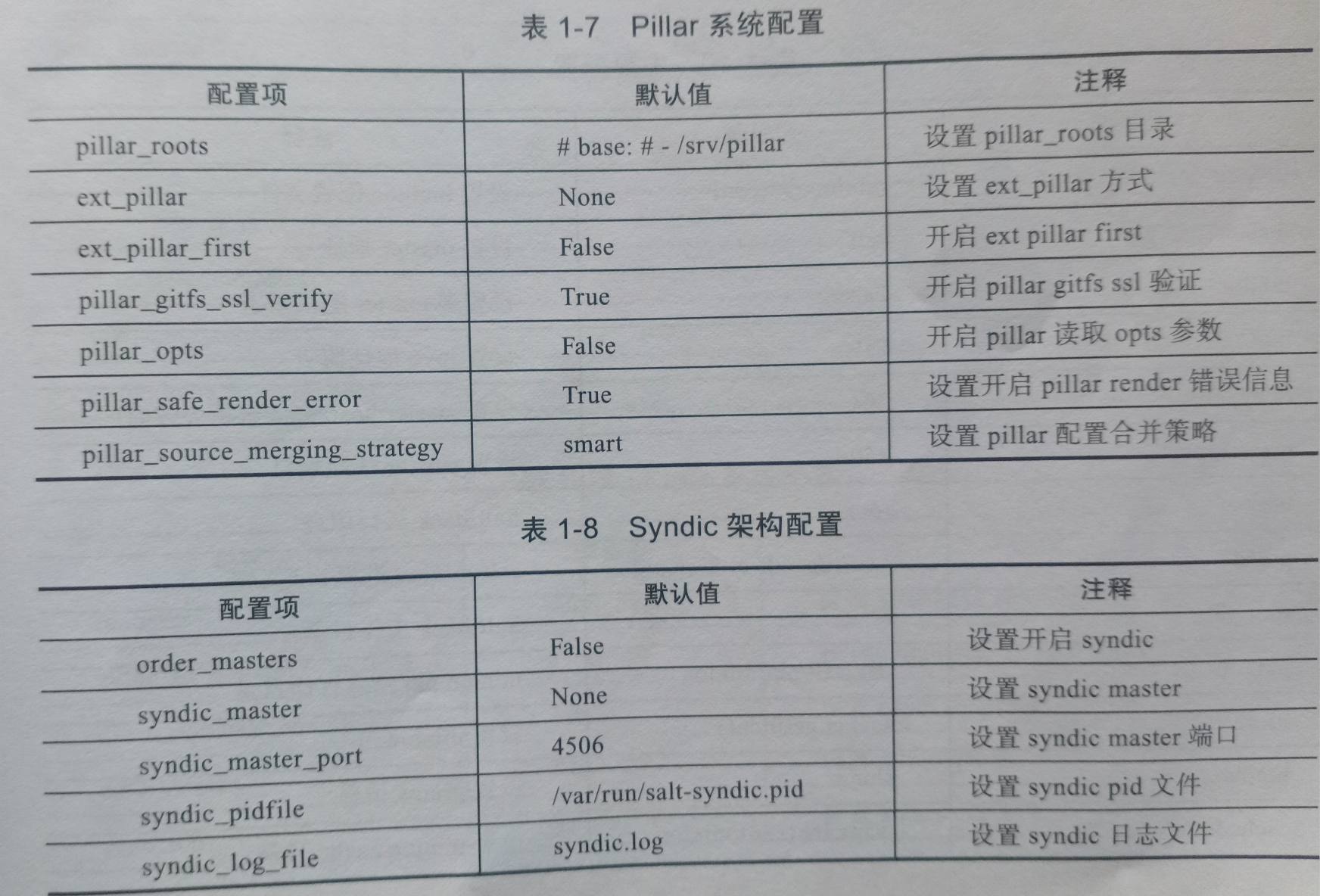
saltstack配置文件
master配置文件


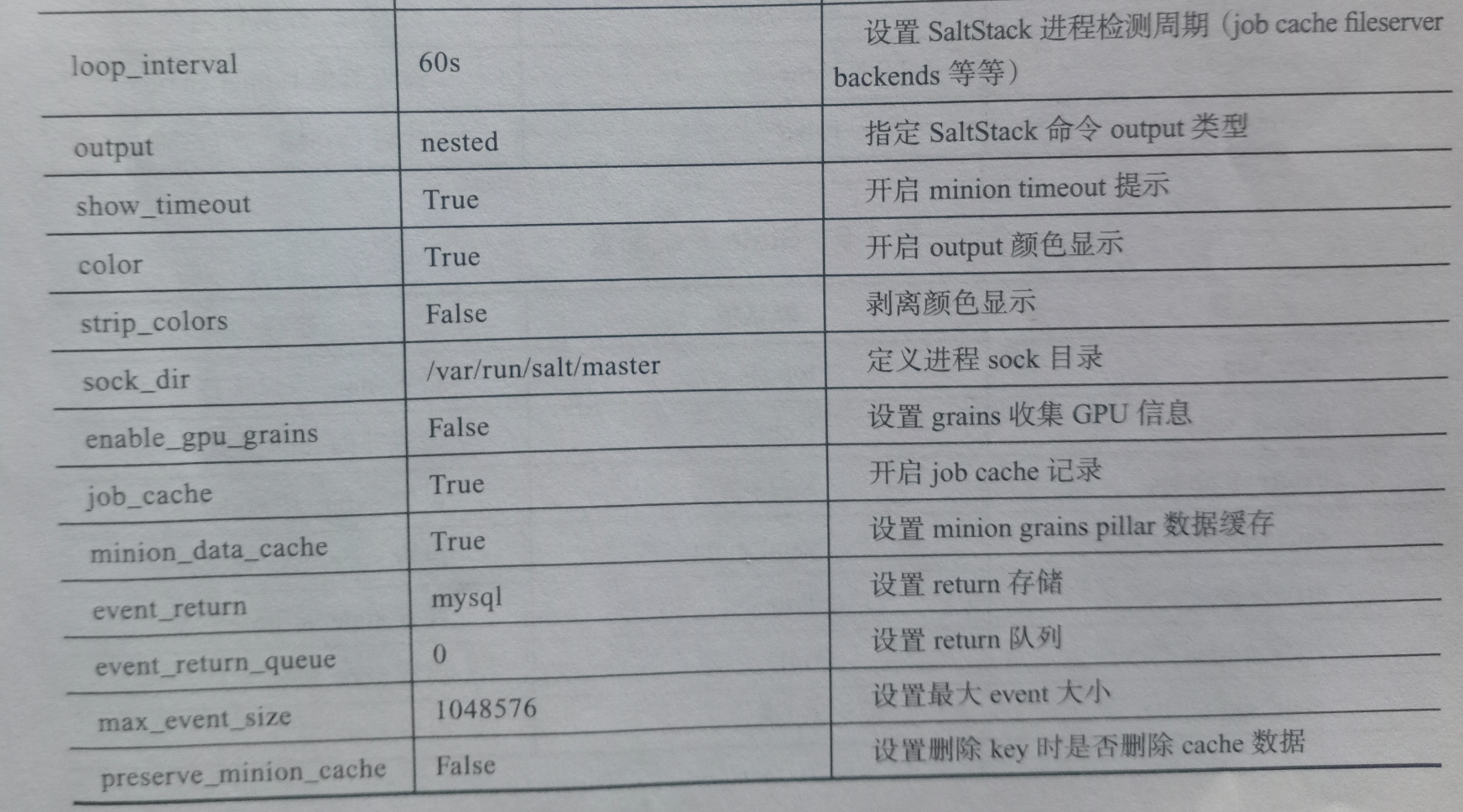
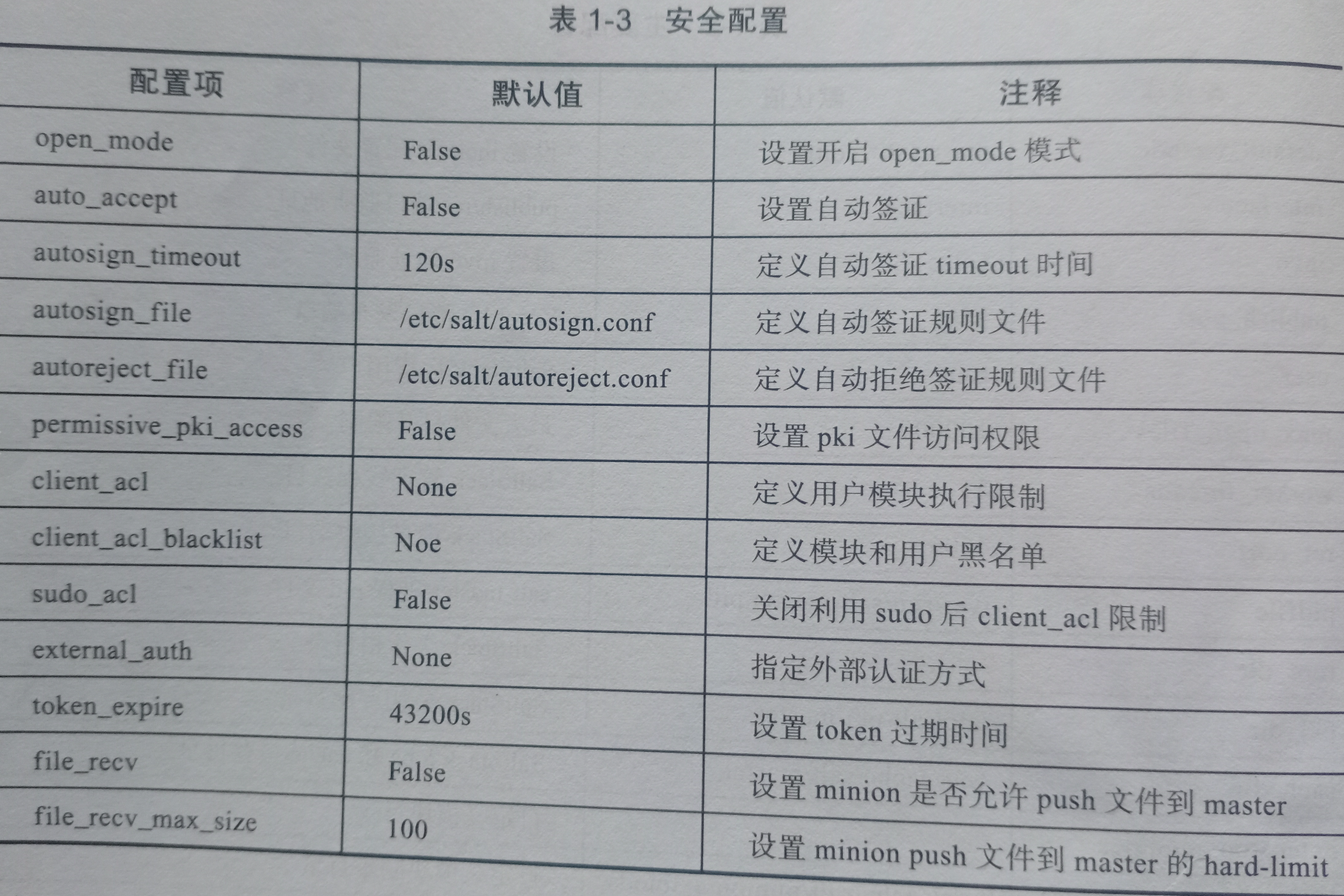
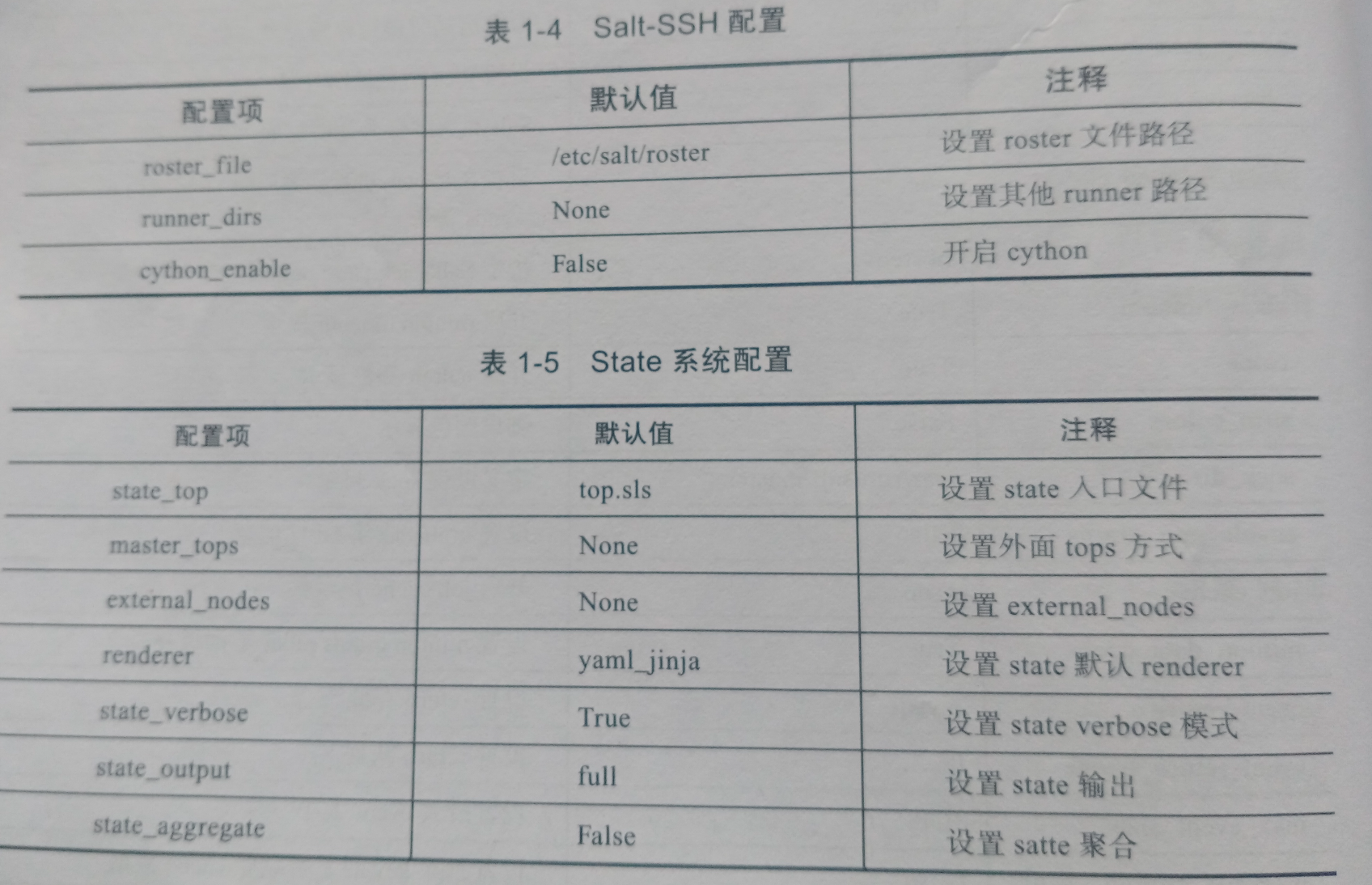
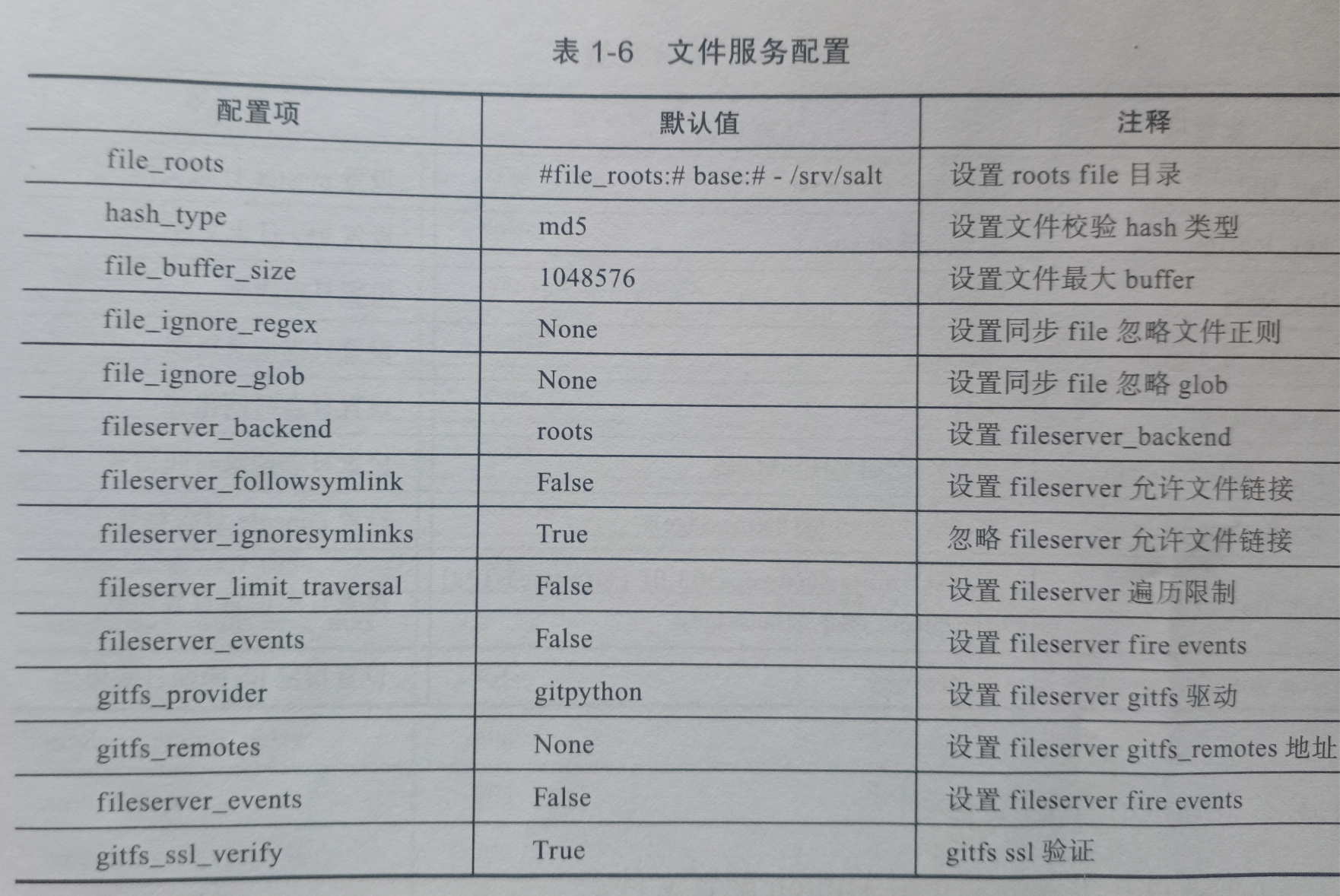

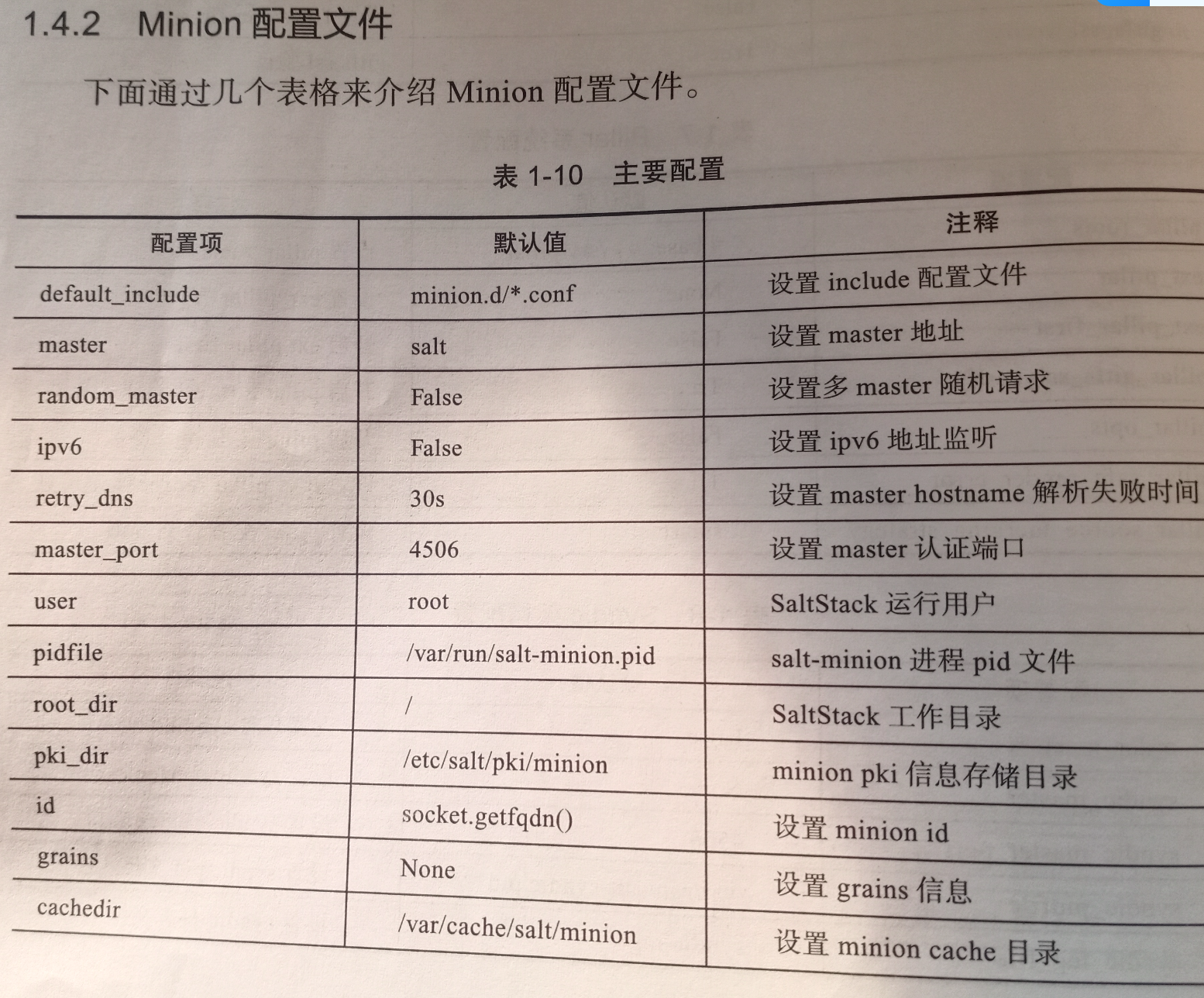
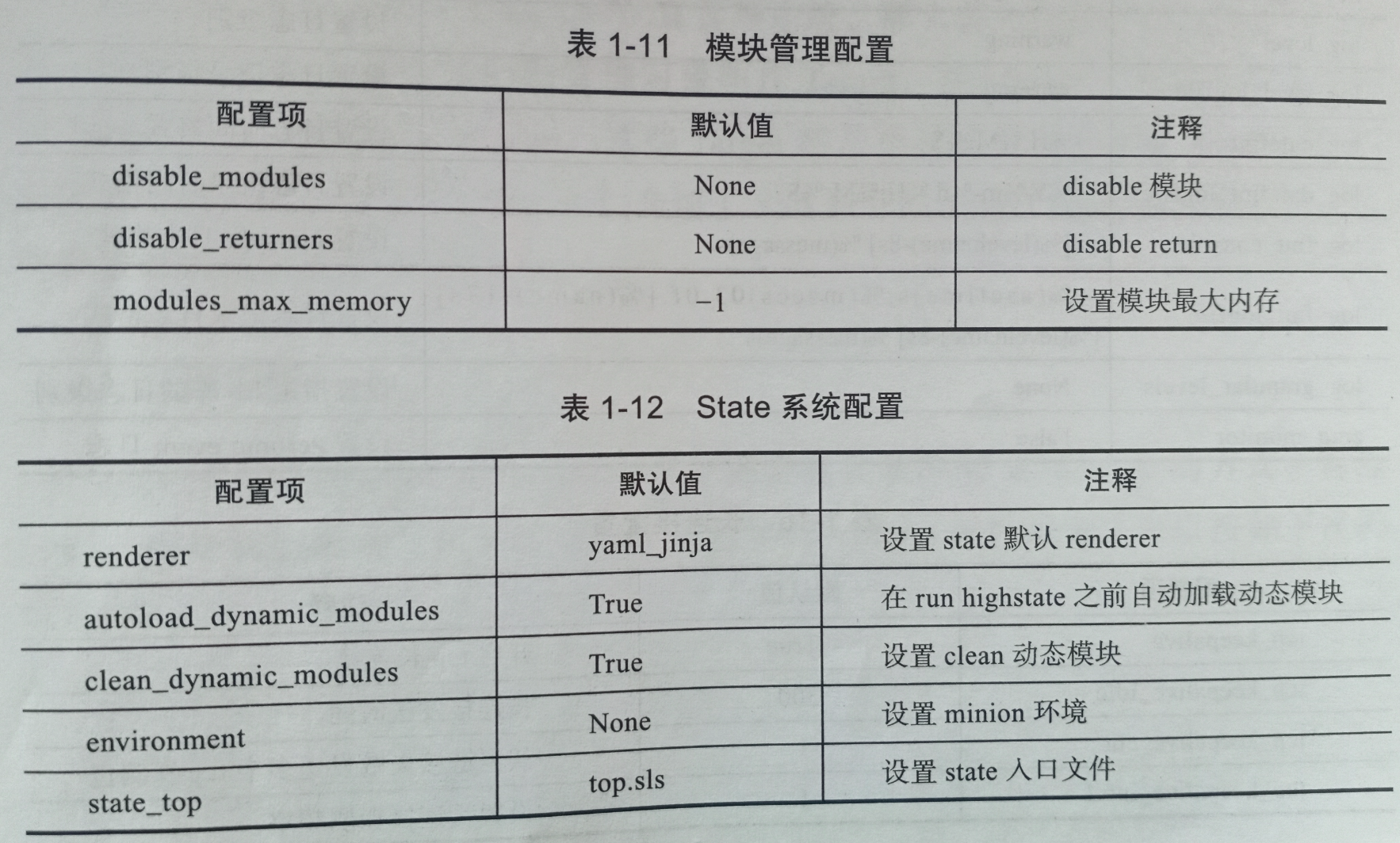
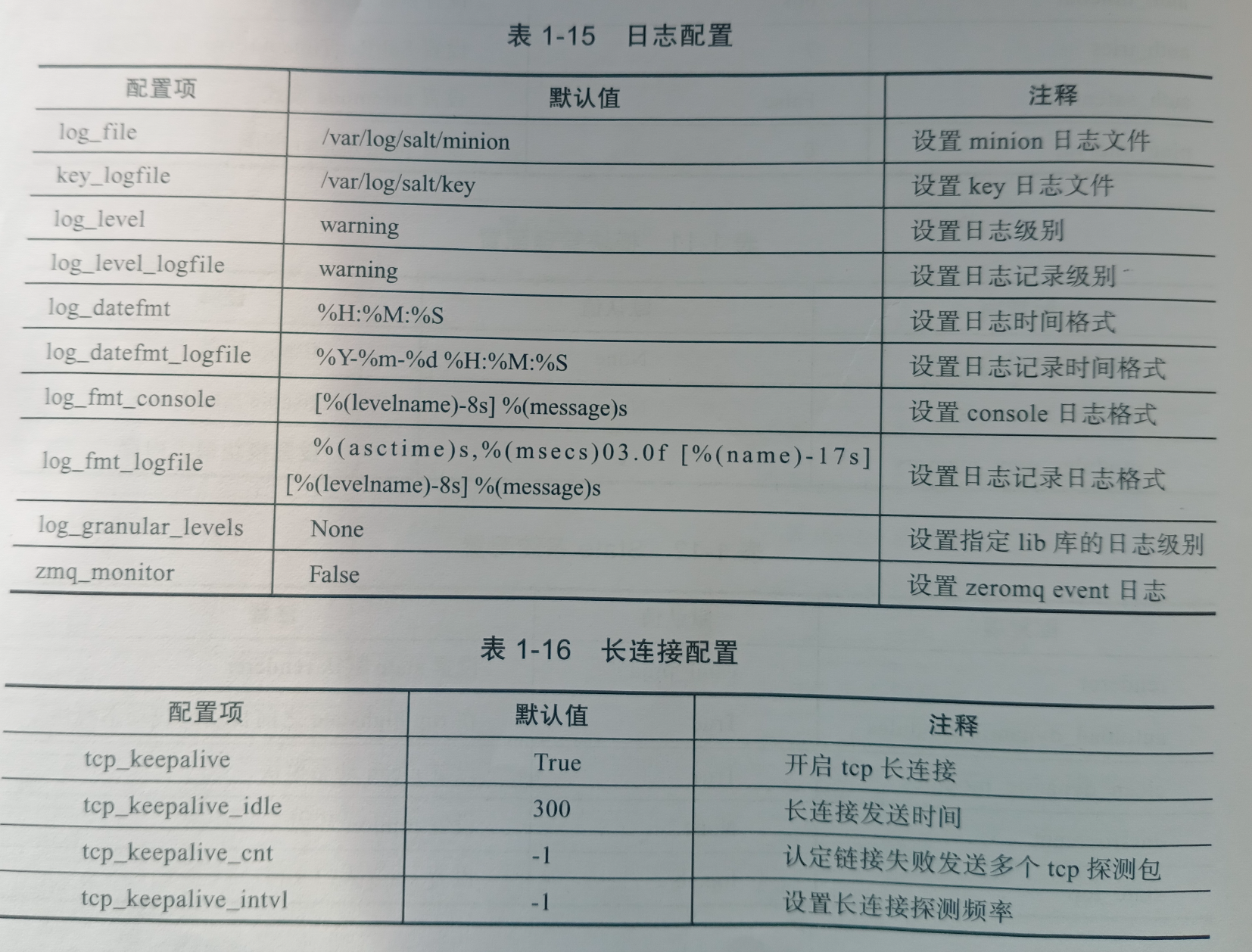
minion配置文件


saltstack组件之-从管理对象说起
1、正则匹配
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt "mcw*" test.ping mcw03: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -E "mcw*" test.ping mcw01: True mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
对比加 -E参数和不加的区别
不加,支持*通配符,不支持.*的正则匹配。也就是你想支持正则匹配,加上,更好,
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt "m*0*" test.ping mcw01: True mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt "m.*0*" test.ping No minions matched the target. No command was sent, no jid was assigned. ERROR: No return received [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -E "m.*0*" test.ping mcw01: True mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt "m[a-z]+0*" test.ping No minions matched the target. No command was sent, no jid was assigned. ERROR: No return received [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -E "m[a-z]+0*" test.ping mcw01: True mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
2、列表匹配
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt -L mcw01,mcw03 test.ping mcw01: True mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -L 'mcw01,mcw03' test.ping mcw01: True mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt 'mcw01,mcw03' test.ping No minions matched the target. No command was sent, no jid was assigned. ERROR: No return received [root@mcw01 ~]#
3、grians匹配
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt -L 'mcw01,vm2.cluster.com' grains.setvals "{'myname':'mcw'}" mcw01: ---------- myname: mcw vm2.cluster.com: ---------- myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: mcw01 mcw03 vm2.cluster.com Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: Rejected Keys: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -G 'myname:mcw' test.ping vm2.cluster.com: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
4、组匹配
修改配置,添加组
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
##### Node Groups ###### ########################################## # Node groups allow for logical groupings of minion nodes. A group consists of # a group name and a compound target. Nodgroups can reference other nodegroups # with 'N@' classifier. Ensure that you do not have circular references. # #nodegroups: # group1: 'L@foo.domain.com,bar.domain.com,baz.domain.com or bl*.domain.com' # group2: 'G@os:Debian and foo.domain.com' # group3: 'G@os:Debian and N@group1' # group4: # - 'G@foo:bar' # - 'or' # - 'G@foo:baz'
添加配置后重启
L@后面可以接多个机器,作用同 参数 -L;G@后面可以接grains的键值对;并且可以用or and来拼接多个条件。多个条件的时候,也可以用多个-来拼接。
如下:mcwgroup2这个组,条件就是在mcw01和mcw03中,满足grains配置myname是mcw的机器。满足条件的只有mcw01,因为mcw03的值是xiaoma。所以下面使用这个组的时候,只有mcw01满足条件。
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master nodegroups: mcwgroup1: 'L@mcw01,mcw03 or vm2.cluster.com' mcwgroup2: 'G@myname:mcw and L@mcw01,mcw03' mcwgroup3: 'G@myname:mcw and N@mcwgroup1' mcwgroup4: - 'G@myname:mcw' - 'or' - 'G@myname:xiaoma' [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
测试执行。
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt '*' grains.item myname mcw01: ---------- myname: mcw vm2.cluster.com: ---------- myname: mcw mcw03: ---------- myname: mcw04: ---------- myname: xiaoma [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -N mcwgroup1 test.ping mcw03: True vm2.cluster.com: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -N mcwgroup2 test.ping mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -N mcwgroup3 test.ping vm2.cluster.com: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -N mcwgroup4 test.ping mcw04: True vm2.cluster.com: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
5、复合匹配
跟上面的组的条件一样,但是这里是命令行的判断筛选执行。也就是命名组的时候的条件判断,也可以在命令行使用。
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt '*' grains.item myname mcw03: ---------- myname: mcw04: ---------- myname: xiaoma vm2.cluster.com: ---------- myname: mcw mcw01: ---------- myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -C 'G@myname:mcw and L@mcw01,mcw03' test.ping mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
6、pillar值匹配
salt -I 'key:value' test.ping
参考下面pillar复杂配置,第四个
目前机器信息如下:
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: mcw01 mcw03 mcw04 vm2.cluster.com Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: Rejected Keys: [root@mcw01 ~]#
效果是mcw的主机有下面的所有的配置
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 pillar.item zabbix mcw01: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix port: 10050 user: admin version: 2.2.4 xinzeng1: val1 xinzeng2: val2 [root@mcw01 ~]#
非mcw的机器只有下面的配置
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt vm2.cluster.com pillar.item zabbix vm2.cluster.com: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 xinzeng1: val1 [root@mcw01 ~]#
因此我要根据xingzeng1 和xingzeng2来匹配机器。xinzeng2的都是包含mcw的机器,xinzeng1是不包含mcw的机器+包含mcw的机器,也就是不包含mcw的机器是没有xinzeng2的配置的。如下结果,验证了前面这句话。
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt -I 'zabbix:xinzeng2' test.ping mcw03: True mcw04: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -I 'zabbix:xinzeng1' test.ping mcw03: True mcw04: True vm2.cluster.com: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
因为zabbix:xingzeng2 可以,xinzeng2:val2也是可以。但是zabbix:xingzeng2:val1就不对了,因为关系正常的可以是zabbix:xinzeng1:val1。也就是根据层级关系,可以多层冒号去对应匹配上,有一层没有对应上就匹配不上。
k:k:v
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt -I 'zabbix:xinzeng2' test.ping mcw03: True mcw04: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -I 'zabbix:xinzeng2:val2' test.ping mcw03: True mcw04: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -I 'zabbix:xinzeng2:val1' test.ping No minions matched the target. No command was sent, no jid was assigned. ERROR: No return received [root@mcw01 ~]#
我们可以看到,匹配是符合预期的
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt -I 'zabbix:xinzeng1:val1' test.ping mcw03: True mcw04: True mcw01: True vm2.cluster.com: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
7、CIDR匹配
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt "*" cmd.run 'hostname -I' mcw03: 10.0.0.13 vm2.cluster.com: 10.0.0.12 mcw04: 10.0.0.14 192.168.80.4 172.168.4.4 192.168.1.1 mcw01: 10.0.0.11 172.17.0.1 172.18.0.1 [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -S "10.0.0.0/24" test.ping vm2.cluster.com: True mcw04: True mcw03: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
target 参数
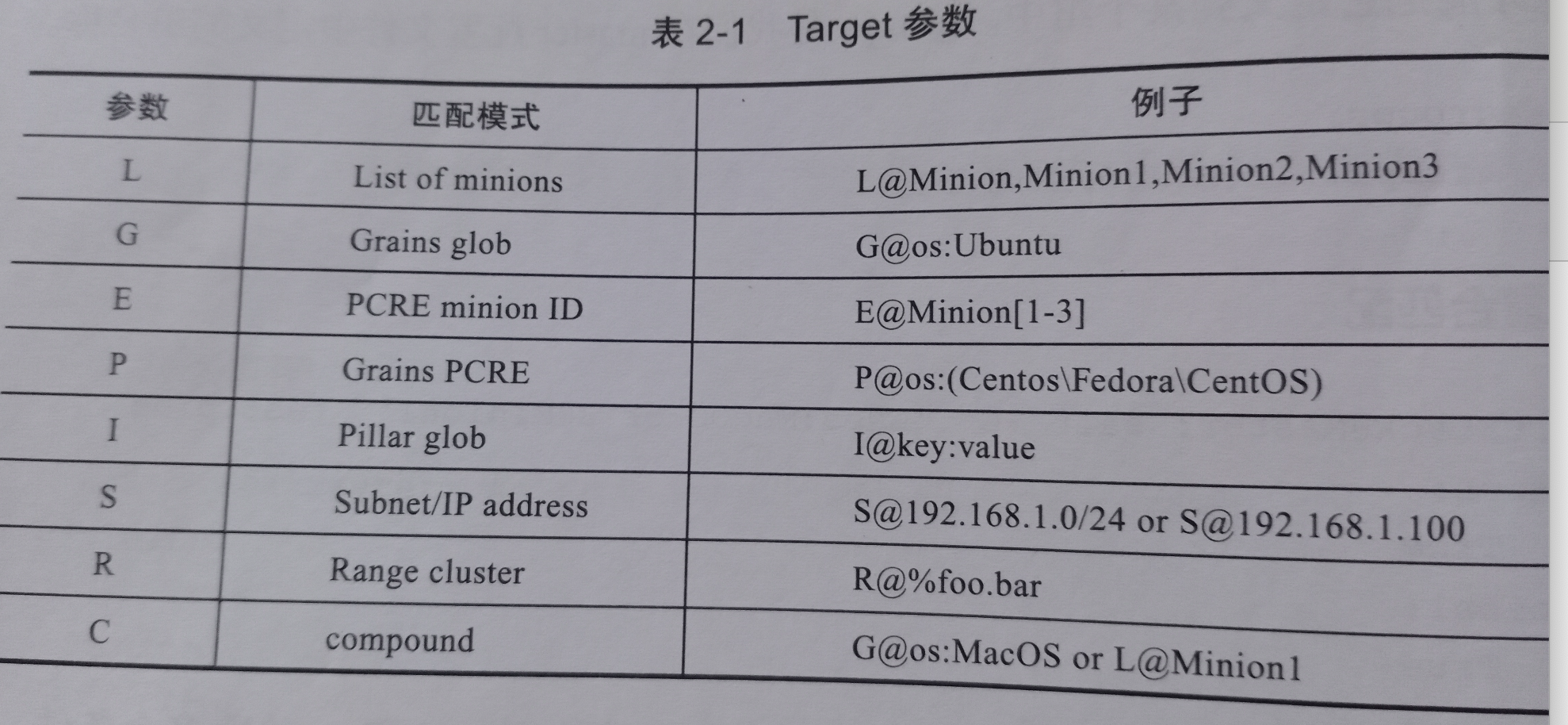
管理对象属性之 -grains使用
前面写了salt的grains在minion端和master端的自定义配置。
查看grains相关的命令
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt 'mcw01' sys.list_functions grains mcw01: - grains.append - grains.delkey - grains.delval - grains.equals - grains.fetch - grains.filter_by - grains.get - grains.get_or_set_hash - grains.has_value - grains.item - grains.items - grains.ls - grains.remove - grains.set - grains.setval - grains.setvals [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看命令详情,详情中也有命令使用案例
只看某一个命令 grains.append
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt 'mcw01' sys.doc grains.append grains.append: New in version 0.17.0 Append a value to a list in the grains config file. If the grain doesn't exist, the grain key is added and the value is appended to the new grain as a list item. key The grain key to be appended to val The value to append to the grain key convert If convert is True, convert non-list contents into a list. If convert is False and the grain contains non-list contents, an error is given. Defaults to False. delimiter The key can be a nested dict key. Use this parameter to specify the delimiter you use, instead of the default ``:``. You can now append values to a list in nested dictionary grains. If the list doesn't exist at this level, it will be created. New in version 2014.7.6 CLI Example: salt '*' grains.append key val [root@mcw01 ~]#
看所有的文档信息
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt 'mcw01' sys.doc grains

[root@mcw01 ~]# salt 'mcw01' sys.doc grains grains.append: New in version 0.17.0 Append a value to a list in the grains config file. If the grain doesn't exist, the grain key is added and the value is appended to the new grain as a list item. key The grain key to be appended to val The value to append to the grain key convert If convert is True, convert non-list contents into a list. If convert is False and the grain contains non-list contents, an error is given. Defaults to False. delimiter The key can be a nested dict key. Use this parameter to specify the delimiter you use, instead of the default ``:``. You can now append values to a list in nested dictionary grains. If the list doesn't exist at this level, it will be created. New in version 2014.7.6 CLI Example: salt '*' grains.append key val grains.delkey: New in version 2017.7.0 Remove a grain completely from the grain system, this will remove the grain key and value key The grain key from which to delete the value. force Force remove the grain even when it is a mapped value. Defaults to False CLI Example: salt '*' grains.delkey key grains.delval: New in version 0.17.0 Delete a grain value from the grains config file. This will just set the grain value to ``None``. To completely remove the grain, run ``grains.delkey`` or pass ``destructive=True`` to ``grains.delval``. key The grain key from which to delete the value. destructive Delete the key, too. Defaults to False. force Force remove the grain even when it is a mapped value. Defaults to False CLI Example: salt '*' grains.delval key grains.equals: Used to make sure the minion's grain key/value matches. Returns ``True`` if matches otherwise ``False``. New in version 2017.7.0 CLI Example: salt '*' grains.equals fqdn <expected_fqdn> salt '*' grains.equals systemd:version 219 grains.fetch: Attempt to retrieve the named value from grains, if the named value is not available return the passed default. The default return is an empty string. The value can also represent a value in a nested dict using a ":" delimiter for the dict. This means that if a dict in grains looks like this:: {'pkg': {'apache': 'httpd'}} To retrieve the value associated with the apache key in the pkg dict this key can be passed:: pkg:apache :param delimiter: Specify an alternate delimiter to use when traversing a nested dict. This is useful for when the desired key contains a colon. See CLI example below for usage. New in version 2014.7.0 :param ordered: Outputs an ordered dict if applicable (default: True) New in version 2016.11.0 CLI Example: salt '*' grains.get pkg:apache salt '*' grains.get abc::def|ghi delimiter='|' grains.filter_by: New in version 0.17.0 Look up the given grain in a given dictionary for the current OS and return the result Although this may occasionally be useful at the CLI, the primary intent of this function is for use in Jinja to make short work of creating lookup tables for OS-specific data. For example: {% set apache = salt['grains.filter_by']({ 'Debian': {'pkg': 'apache2', 'srv': 'apache2'}, 'RedHat': {'pkg': 'httpd', 'srv': 'httpd'}, }, default='Debian') %} myapache: pkg.installed: - name: {{ apache.pkg }} service.running: - name: {{ apache.srv }} Values in the lookup table may be overridden by values in Pillar. An example Pillar to override values in the example above could be as follows: apache: lookup: pkg: apache_13 srv: apache The call to ``filter_by()`` would be modified as follows to reference those Pillar values: {% set apache = salt['grains.filter_by']({ ... }, merge=salt['pillar.get']('apache:lookup')) %} :param lookup_dict: A dictionary, keyed by a grain, containing a value or values relevant to systems matching that grain. For example, a key could be the grain for an OS and the value could the name of a package on that particular OS. Changed in version 2016.11.0 The dictionary key could be a globbing pattern. The function will return the corresponding ``lookup_dict`` value where grain value matches the pattern. For example: # this will render 'got some salt' if Minion ID begins from 'salt' salt '*' grains.filter_by '{salt*: got some salt, default: salt is not here}' id :param grain: The name of a grain to match with the current system's grains. For example, the value of the "os_family" grain for the current system could be used to pull values from the ``lookup_dict`` dictionary. Changed in version 2016.11.0 The grain value could be a list. The function will return the ``lookup_dict`` value for a first found item in the list matching one of the ``lookup_dict`` keys. :param merge: A dictionary to merge with the results of the grain selection from ``lookup_dict``. This allows Pillar to override the values in the ``lookup_dict``. This could be useful, for example, to override the values for non-standard package names such as when using a different Python version from the default Python version provided by the OS (e.g., ``python26-mysql`` instead of ``python-mysql``). :param default: default lookup_dict's key used if the grain does not exists or if the grain value has no match on lookup_dict. If unspecified the value is "default". New in version 2014.1.0 :param base: A lookup_dict key to use for a base dictionary. The grain-selected ``lookup_dict`` is merged over this and then finally the ``merge`` dictionary is merged. This allows common values for each case to be collected in the base and overridden by the grain selection dictionary and the merge dictionary. Default is unset. New in version 2015.5.0 CLI Example: salt '*' grains.filter_by '{Debian: Debheads rule, RedHat: I love my hat}' # this one will render {D: {E: I, G: H}, J: K} salt '*' grains.filter_by '{A: B, C: {D: {E: F, G: H}}}' 'xxx' '{D: {E: I}, J: K}' 'C' # next one renders {A: {B: G}, D: J} salt '*' grains.filter_by '{default: {A: {B: C}, D: E}, F: {A: {B: G}}, H: {D: I}}' 'xxx' '{D: J}' 'F' 'default' # next same as above when default='H' instead of 'F' renders {A: {B: C}, D: J} grains.get: Attempt to retrieve the named value from grains, if the named value is not available return the passed default. The default return is an empty string. The value can also represent a value in a nested dict using a ":" delimiter for the dict. This means that if a dict in grains looks like this:: {'pkg': {'apache': 'httpd'}} To retrieve the value associated with the apache key in the pkg dict this key can be passed:: pkg:apache :param delimiter: Specify an alternate delimiter to use when traversing a nested dict. This is useful for when the desired key contains a colon. See CLI example below for usage. New in version 2014.7.0 :param ordered: Outputs an ordered dict if applicable (default: True) New in version 2016.11.0 CLI Example: salt '*' grains.get pkg:apache salt '*' grains.get abc::def|ghi delimiter='|' grains.get_or_set_hash: Perform a one-time generation of a hash and write it to the local grains. If that grain has already been set return the value instead. This is useful for generating passwords or keys that are specific to a single minion that don't need to be stored somewhere centrally. State Example: some_mysql_user: mysql_user: - present - host: localhost - password: {{ salt['grains.get_or_set_hash']('mysql:some_mysql_user') }} CLI Example: salt '*' grains.get_or_set_hash 'django:SECRET_KEY' 50 Warning: This function could return strings which may contain characters which are reserved as directives by the YAML parser, such as strings beginning with ``%``. To avoid issues when using the output of this function in an SLS file containing YAML+Jinja, surround the call with single quotes. grains.has_value: Determine whether a key exists in the grains dictionary. Given a grains dictionary that contains the following structure:: {'pkg': {'apache': 'httpd'}} One would determine if the apache key in the pkg dict exists by:: pkg:apache CLI Example: salt '*' grains.has_value pkg:apache grains.item: Return one or more grains CLI Example: salt '*' grains.item os salt '*' grains.item os osrelease oscodename Sanitized CLI Example: salt '*' grains.item host sanitize=True grains.items: Return all of the minion's grains CLI Example: salt '*' grains.items Sanitized CLI Example: salt '*' grains.items sanitize=True grains.ls: Return a list of all available grains CLI Example: salt '*' grains.ls grains.remove: New in version 0.17.0 Remove a value from a list in the grains config file key The grain key to remove. val The value to remove. delimiter The key can be a nested dict key. Use this parameter to specify the delimiter you use, instead of the default ``:``. You can now append values to a list in nested dictionary grains. If the list doesn't exist at this level, it will be created. New in version 2015.8.2 CLI Example: salt '*' grains.remove key val grains.set: Set a key to an arbitrary value. It is used like setval but works with nested keys. This function is conservative. It will only overwrite an entry if its value and the given one are not a list or a dict. The ``force`` parameter is used to allow overwriting in all cases. New in version 2015.8.0 :param force: Force writing over existing entry if given or existing values are list or dict. Defaults to False. :param destructive: If an operation results in a key being removed, delete the key, too. Defaults to False. :param delimiter: Specify an alternate delimiter to use when traversing a nested dict, the default being ``:`` CLI Example: salt '*' grains.set 'apps:myApp:port' 2209 salt '*' grains.set 'apps:myApp' '{port: 2209}' grains.setval: Set a grains value in the grains config file key The grain key to be set. val The value to set the grain key to. destructive If an operation results in a key being removed, delete the key, too. Defaults to False. refresh_pillar Whether pillar will be refreshed. Defaults to True. CLI Example: salt '*' grains.setval key val salt '*' grains.setval key "{'sub-key': 'val', 'sub-key2': 'val2'}" grains.setvals: Set new grains values in the grains config file destructive If an operation results in a key being removed, delete the key, too. Defaults to False. refresh_pillar Whether pillar will be refreshed. Defaults to True. CLI Example: salt '*' grains.setvals "{'key1': 'val1', 'key2': 'val2'}" [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看一些命令下么有哪些,比如pillar下面还有哪些可用
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.list_functions pillar mcw01: - pillar.data - pillar.ext - pillar.fetch - pillar.file_exists - pillar.filter_by - pillar.get - pillar.item - pillar.items - pillar.keys - pillar.ls - pillar.obfuscate - pillar.raw [root@mcw01 ~]#
通过Grains模块定义Grains
通过 salt '*' sys.doc grains 来查看相关的命令和使用方法
salt 'cong-55' sys.doc grains.append
通过salt 'minion_id' sys.doc MODULE.FUNCION 来查看对应模板的函数的使用方法
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.list_functions pillar mcw01: - pillar.data - pillar.ext - pillar.fetch - pillar.file_exists - pillar.filter_by - pillar.get - pillar.item - pillar.items - pillar.keys - pillar.ls - pillar.obfuscate - pillar.raw
添加grains信息
grains.append 将grains的key和value添加到grains配置文件中以列表形式保存,类型 list
salt ‘minion_id' grains.append KEY VALUE
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.append OSType Linux ##key OSType,value Linux
cong-55:
----------
OSType:
- Linux
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.append OSType Linu2
cong-55:
----------
OSType:
- Linux
- Linu2
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.get OSType
cong-55:
- Linux
- Linu2
[root@cong-33 _grains]#
grains经过上面的命令已经把grains信息添加到了minion端,还写进来minion端的一个配置文件了
[root@cong-55 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains ##已经把grains的信息写入这个文件 OSType: - Linux
- Linux2 [root@cong-55 ~]#
grains.setvals 批量添加grains信息
salt '*' grains.setvals "{'key1': 'val1', 'key2': 'val2'}"
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.setvals "{'IDC':'abc','CITY':'GZ'}"
cong-55:
----------
CITY:
GZ
IDC:
abc
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.get IDC
cong-55:
abc
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.get CITY
cong-55:
GZ
[root@cong-33 _grains]#
也可以grains.item key
查看minion端的配置文件
[root@cong-55 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains CITY: GZ IDC: abc OSType: - Linux
- Linux2 [root@cong-55 ~]#
grains.append 是将value添加到key的列表中,如果key不存在将创建
grains.setvals 添加多个grains的key和value到grains配置文件中,类型是key-value
append 值是多个元素的列表,setvals值是key的单个元素值
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item myname mcw01: ---------- myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.get myname mcw01: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.append myname mcw2 mcw01: The key myname is not a valid list [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item myhobby mcw01: ---------- myhobby: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.get myhobby mcw01: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.append myhobby lanqiu mcw01: ---------- myhobby: - lanqiu [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.append myhobby zuqiu mcw01: ---------- myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.append myhobby yumaoqiu kanshu mcw01: ---------- myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu [root@mcw01 ~]#
下面就是上面命令添加进去的
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]#
添加或者修改键的值为一个列表
[root@salt002.zz.x.com axs]# salt vm-sso002* grains.setvals "{'fqdn_ip4':['10.x.x.88']}" vm-sso002.zz.x.com: ---------- fqdn_ip4: - 10.x.x.88 [root@salt002.zz.x.com axs]# salt vm-sso002* grains.item fqdn_ip4 vm-sso002.zz.x.com: ---------- fqdn_ip4: - 10.x.x.88 [root@salt002.zz.x.com axs]#
@删除grains信息
grains.delkey 删除grains的key和value
salt '*' grains.delkey key
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.delkey IDC
cong-55:
None
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.get IDC
cong-55:
[root@cong-33 _grains]#
查看minion端信息
[root@cong-55 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains CITY: GZ OSType: - Linux [root@cong-55 ~]#
grains.delval 删除grains的value
salt '*' grains.delval key
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.delval CITY
cong-55:
None
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.get CITY
cong-55:
None
[root@cong-33 _grains]#
查看minion端的配置
[root@cong-55 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains CITY: null OSType: - Linux [root@cong-55 ~]#
grains.delkey 会把key和value一起删掉,
grains.delval只是把value删掉,key还在,key的值变为null
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains mygongzuo: - beijing myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu myhome: - baoding myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.delkey myhome mcw01: ---------- changes: ---------- comment: The key 'myhome' exists but is a dict or a list. Use 'force=True' to overwrite. result: False ERROR: Minions returned with non-zero exit code [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item myhome mcw01: ---------- myhome: - baoding [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.delkey myhome force=True mcw01: ---------- changes: ---------- myhome: None comment: result: True [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains mygongzuo: - beijing myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.delval mygongzuo mcw01: ---------- changes: ---------- comment: The key 'mygongzuo' exists but is a dict or a list. Use 'force=True' to overwrite. result: False ERROR: Minions returned with non-zero exit code [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.delval mygongzuo force=True mcw01: ---------- changes: ---------- mygongzuo: None comment: result: True [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains mygongzuo: null myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.delkey myname mcw01: ---------- changes: ---------- myname: None comment: result: True [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains mygongzuo: null myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]#
grains.remove 从grains配置文件中的列表中删除一个值
删除grains的key列表中的一个value值,如果grains的key和value不是列表不能删除
salt '*' grains.remove key val
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.get OSType
cong-55:
- Linux
- Linu2
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.remove OSType Linux
cong-55:
----------
OSType:
- Linu2
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' grains.item OSType
cong-55:
----------
OSType:
- Linu2
[root@cong-33 _grains]#
通过minion配置文件定义grains
加到这里没有生效
/etc/salt/minion.d/grains
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion.d/grains [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/minion.d/grains grains: roles: - webserver - memcache myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item roles mcw01: ---------- roles: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item myname mcw01: ---------- myname: [root@mcw01 ~]#
加到下面生效了,并且列表的元素,可以不用空两个字符在写-
/etc/salt/grains
[root@mcw01 ~]# rm -rf /etc/salt/minion.d/grains [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains mygongzuo: null myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu roles: - webserver - memcache myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion.service [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item roles mcw01: ---------- roles: - webserver - memcache [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item myname mcw01: ---------- myname: mcw [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /etc/salt/grains mygongzuo: null myhobby: - lanqiu - zuqiu - yumaoqiu roles: - webserver - memcache myname: mcw myclass: - 1 - 2 [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 grains.item myclass mcw01: ---------- myclass: - 1 - 2 [root@mcw01 ~]#
grains的相关函数:
[root@cong-33 _grains]# salt 'cong-55' sys.list_functions grains
cong-55:
- grains.append
- grains.delkey
- grains.delval
- grains.equals
- grains.fetch
- grains.filter_by
- grains.get
- grains.get_or_set_hash
- grains.has_value
- grains.item
- grains.items
- grains.ls
- grains.remove
- grains.set
- grains.setval
- grains.setvals
数据管理中心-pillar
查看pillar的模块用法
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt 'mcw01' sys.list_functions pillar mcw01: - pillar.data - pillar.ext - pillar.fetch - pillar.file_exists - pillar.filter_by - pillar.get - pillar.item - pillar.items - pillar.keys - pillar.ls - pillar.obfuscate - pillar.raw [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看pillar详细用法

[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.doc pillar pillar.data: This function is an alias of ``items``. Calls the master for a fresh pillar and generates the pillar data on the fly Contrast with :py:func:`raw` which returns the pillar data that is currently loaded into the minion. pillar If specified, allows for a dictionary of pillar data to be made available to pillar and ext_pillar rendering. these pillar variables will also override any variables of the same name in pillar or ext_pillar. New in version 2015.5.0 pillar_enc If specified, the data passed in the ``pillar`` argument will be passed through this renderer to decrypt it. Note: This will decrypt on the minion side, so the specified renderer must be set up on the minion for this to work. Alternatively, pillar data can be decrypted master-side. For more information, see the :ref:`Pillar Encryption <pillar-encryption>` documentation. Pillar data that is decrypted master-side, is not decrypted until the end of pillar compilation though, so minion-side decryption will be necessary if the encrypted pillar data must be made available in an decrypted state pillar/ext_pillar rendering. New in version 2017.7.0 pillarenv Pass a specific pillar environment from which to compile pillar data. If not specified, then the minion's :conf_minion:`pillarenv` option is not used, and if that also is not specified then all configured pillar environments will be merged into a single pillar dictionary and returned. New in version 2016.11.2 saltenv Included only for compatibility with :conf_minion:`pillarenv_from_saltenv`, and is otherwise ignored. CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.items pillar.ext: Changed in version 2016.3.6,2016.11.3,2017.7.0 The supported ext_pillar types are now tunable using the :conf_master:`on_demand_ext_pillar` config option. Earlier releases used a hard-coded default. Generate the pillar and apply an explicit external pillar external A single ext_pillar to add to the ext_pillar configuration. This must be passed as a single section from the ext_pillar configuration (see CLI examples below). For more complicated ``ext_pillar`` configurations, it can be helpful to use the Python shell to load YAML configuration into a dictionary, and figure out >>> import salt.utils.yaml >>> ext_pillar = salt.utils.yaml.safe_load(""" ... ext_pillar: ... - git: ... - issue38440 https://github.com/terminalmage/git_pillar: ... - env: base ... """) >>> ext_pillar {'ext_pillar': [{'git': [{'mybranch https://github.com/myuser/myrepo': [{'env': 'base'}]}]}]} >>> ext_pillar['ext_pillar'][0] {'git': [{'mybranch https://github.com/myuser/myrepo': [{'env': 'base'}]}]} In the above example, the value to pass would be ``{'git': [{'mybranch https://github.com/myuser/myrepo': [{'env': 'base'}]}]}``. Note that this would need to be quoted when passing on the CLI (as in the CLI examples below). pillar : None If specified, allows for a dictionary of pillar data to be made available to pillar and ext_pillar rendering. These pillar variables will also override any variables of the same name in pillar or ext_pillar. New in version 2015.5.0 CLI Examples: salt '*' pillar.ext '{libvirt: _}' salt '*' pillar.ext "{'git': ['master https://github.com/myuser/myrepo']}" salt '*' pillar.ext "{'git': [{'mybranch https://github.com/myuser/myrepo': [{'env': 'base'}]}]}" pillar.fetch: New in version 0.14 Attempt to retrieve the named value from :ref:`in-memory pillar data <pillar-in-memory>`. If the pillar key is not present in the in-memory pillar, then the value specified in the ``default`` option (described below) will be returned. If the merge parameter is set to ``True``, the default will be recursively merged into the returned pillar data. The value can also represent a value in a nested dict using a ":" delimiter for the dict. This means that if a dict in pillar looks like this:: {'pkg': {'apache': 'httpd'}} To retrieve the value associated with the ``apache`` key in the ``pkg`` dict this key can be passed as:: pkg:apache key The pillar key to get value from default The value specified by this option will be returned if the desired pillar key does not exist. If a default value is not specified, then it will be an empty string, unless :conf_minion:`pillar_raise_on_missing` is set to ``True``, in which case an error will be raised. merge : ``False`` If ``True``, the retrieved values will be merged into the passed default. When the default and the retrieved value are both dictionaries, the dictionaries will be recursively merged. New in version 2014.7.0 Changed in version 2016.3.7,2016.11.4,2017.7.0 If the default and the retrieved value are not of the same type, then merging will be skipped and the retrieved value will be returned. Earlier releases raised an error in these cases. merge_nested_lists If set to ``False``, lists nested within the retrieved pillar dictionary will *overwrite* lists in ``default``. If set to ``True``, nested lists will be *merged* into lists in ``default``. If unspecified (the default), this option is inherited from the :conf_minion:`pillar_merge_lists` minion config option. Note: This option is ignored when ``merge`` is set to ``False``. New in version 2016.11.6 delimiter Specify an alternate delimiter to use when traversing a nested dict. This is useful for when the desired key contains a colon. See CLI example below for usage. New in version 2014.7.0 pillarenv If specified, this function will query the master to generate fresh pillar data on the fly, specifically from the requested pillar environment. Note that this can produce different pillar data than executing this function without an environment, as its normal behavior is just to return a value from minion's pillar data in memory (which can be sourced from more than one pillar environment). Using this argument will not affect the pillar data in memory. It will however be slightly slower and use more resources on the master due to the need for the master to generate and send the minion fresh pillar data. This tradeoff in performance however allows for the use case where pillar data is desired only from a single environment. New in version 2017.7.0 saltenv Included only for compatibility with :conf_minion:`pillarenv_from_saltenv`, and is otherwise ignored. New in version 2017.7.0 CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.get pkg:apache salt '*' pillar.get abc::def|ghi delimiter='|' pillar.file_exists: New in version 2016.3.0 This is a master-only function. Calling from the minion is not supported. Use the given path and search relative to the pillar environments to see if a file exists at that path. If the ``saltenv`` argument is given, restrict search to that environment only. Will only work with ``pillar_roots``, not external pillars. Returns True if the file is found, and False otherwise. path The path to the file in question. Will be treated as a relative path saltenv Optional argument to restrict the search to a specific saltenv CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.file_exists foo/bar.sls pillar.filter_by: New in version 2017.7.0 Look up the given pillar in a given dictionary and return the result :param lookup_dict: A dictionary, keyed by a pillar, containing a value or values relevant to systems matching that pillar. For example, a key could be a pillar for a role and the value could the name of a package on that particular OS. The dictionary key can be a globbing pattern. The function will return the corresponding ``lookup_dict`` value where the pillar value matches the pattern. For example: # this will render 'got some salt' if ``role`` begins with 'salt' salt '*' pillar.filter_by '{salt*: got some salt, default: salt is not here}' role :param pillar: The name of a pillar to match with the system's pillar. For example, the value of the "role" pillar could be used to pull values from the ``lookup_dict`` dictionary. The pillar value can be a list. The function will return the ``lookup_dict`` value for a first found item in the list matching one of the ``lookup_dict`` keys. :param merge: A dictionary to merge with the results of the pillar selection from ``lookup_dict``. This allows another dictionary to override the values in the ``lookup_dict``. :param default: default lookup_dict's key used if the pillar does not exist or if the pillar value has no match on lookup_dict. If unspecified the value is "default". :param base: A lookup_dict key to use for a base dictionary. The pillar-selected ``lookup_dict`` is merged over this and then finally the ``merge`` dictionary is merged. This allows common values for each case to be collected in the base and overridden by the pillar selection dictionary and the merge dictionary. Default is unset. CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.filter_by '{web: Serve it up, db: I query, default: x_x}' role pillar.get: New in version 0.14 Attempt to retrieve the named value from :ref:`in-memory pillar data <pillar-in-memory>`. If the pillar key is not present in the in-memory pillar, then the value specified in the ``default`` option (described below) will be returned. If the merge parameter is set to ``True``, the default will be recursively merged into the returned pillar data. The value can also represent a value in a nested dict using a ":" delimiter for the dict. This means that if a dict in pillar looks like this:: {'pkg': {'apache': 'httpd'}} To retrieve the value associated with the ``apache`` key in the ``pkg`` dict this key can be passed as:: pkg:apache key The pillar key to get value from default The value specified by this option will be returned if the desired pillar key does not exist. If a default value is not specified, then it will be an empty string, unless :conf_minion:`pillar_raise_on_missing` is set to ``True``, in which case an error will be raised. merge : ``False`` If ``True``, the retrieved values will be merged into the passed default. When the default and the retrieved value are both dictionaries, the dictionaries will be recursively merged. New in version 2014.7.0 Changed in version 2016.3.7,2016.11.4,2017.7.0 If the default and the retrieved value are not of the same type, then merging will be skipped and the retrieved value will be returned. Earlier releases raised an error in these cases. merge_nested_lists If set to ``False``, lists nested within the retrieved pillar dictionary will *overwrite* lists in ``default``. If set to ``True``, nested lists will be *merged* into lists in ``default``. If unspecified (the default), this option is inherited from the :conf_minion:`pillar_merge_lists` minion config option. Note: This option is ignored when ``merge`` is set to ``False``. New in version 2016.11.6 delimiter Specify an alternate delimiter to use when traversing a nested dict. This is useful for when the desired key contains a colon. See CLI example below for usage. New in version 2014.7.0 pillarenv If specified, this function will query the master to generate fresh pillar data on the fly, specifically from the requested pillar environment. Note that this can produce different pillar data than executing this function without an environment, as its normal behavior is just to return a value from minion's pillar data in memory (which can be sourced from more than one pillar environment). Using this argument will not affect the pillar data in memory. It will however be slightly slower and use more resources on the master due to the need for the master to generate and send the minion fresh pillar data. This tradeoff in performance however allows for the use case where pillar data is desired only from a single environment. New in version 2017.7.0 saltenv Included only for compatibility with :conf_minion:`pillarenv_from_saltenv`, and is otherwise ignored. New in version 2017.7.0 CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.get pkg:apache salt '*' pillar.get abc::def|ghi delimiter='|' pillar.item: New in version 0.16.2 Return one or more pillar entries from the :ref:`in-memory pillar data <pillar-in-memory>`. delimiter Delimiter used to traverse nested dictionaries. Note: This is different from :py:func:`pillar.get <salt.modules.pillar.get>` in that no default value can be specified. :py:func:`pillar.get <salt.modules.pillar.get>` should probably still be used in most cases to retrieve nested pillar values, as it is a bit more flexible. One reason to use this function instead of :py:func:`pillar.get <salt.modules.pillar.get>` however is when it is desirable to retrieve the values of more than one key, since :py:func:`pillar.get <salt.modules.pillar.get>` can only retrieve one key at a time. New in version 2015.8.0 pillarenv If specified, this function will query the master to generate fresh pillar data on the fly, specifically from the requested pillar environment. Note that this can produce different pillar data than executing this function without an environment, as its normal behavior is just to return a value from minion's pillar data in memory (which can be sourced from more than one pillar environment). Using this argument will not affect the pillar data in memory. It will however be slightly slower and use more resources on the master due to the need for the master to generate and send the minion fresh pillar data. This tradeoff in performance however allows for the use case where pillar data is desired only from a single environment. New in version 2017.7.6,2018.3.1 saltenv Included only for compatibility with :conf_minion:`pillarenv_from_saltenv`, and is otherwise ignored. New in version 2017.7.6,2018.3.1 CLI Examples: salt '*' pillar.item foo salt '*' pillar.item foo:bar salt '*' pillar.item foo bar baz pillar.items: Calls the master for a fresh pillar and generates the pillar data on the fly Contrast with :py:func:`raw` which returns the pillar data that is currently loaded into the minion. pillar If specified, allows for a dictionary of pillar data to be made available to pillar and ext_pillar rendering. these pillar variables will also override any variables of the same name in pillar or ext_pillar. New in version 2015.5.0 pillar_enc If specified, the data passed in the ``pillar`` argument will be passed through this renderer to decrypt it. Note: This will decrypt on the minion side, so the specified renderer must be set up on the minion for this to work. Alternatively, pillar data can be decrypted master-side. For more information, see the :ref:`Pillar Encryption <pillar-encryption>` documentation. Pillar data that is decrypted master-side, is not decrypted until the end of pillar compilation though, so minion-side decryption will be necessary if the encrypted pillar data must be made available in an decrypted state pillar/ext_pillar rendering. New in version 2017.7.0 pillarenv Pass a specific pillar environment from which to compile pillar data. If not specified, then the minion's :conf_minion:`pillarenv` option is not used, and if that also is not specified then all configured pillar environments will be merged into a single pillar dictionary and returned. New in version 2016.11.2 saltenv Included only for compatibility with :conf_minion:`pillarenv_from_saltenv`, and is otherwise ignored. CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.items pillar.keys: New in version 2015.8.0 Attempt to retrieve a list of keys from the named value from the pillar. The value can also represent a value in a nested dict using a ":" delimiter for the dict, similar to how pillar.get works. delimiter Specify an alternate delimiter to use when traversing a nested dict CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.keys web:sites pillar.ls: New in version 2015.8.0 Calls the master for a fresh pillar, generates the pillar data on the fly (same as :py:func:`items`), but only shows the available main keys. CLI Examples: salt '*' pillar.ls pillar.obfuscate: New in version 2015.8.0 Same as :py:func:`items`, but replace pillar values with a simple type indication. This is useful to avoid displaying sensitive information on console or flooding the console with long output, such as certificates. For many debug or control purposes, the stakes lie more in dispatching than in actual values. In case the value is itself a collection type, obfuscation occurs within the value. For mapping types, keys are not obfuscated. Here are some examples: * ``'secret password'`` becomes ``'<str>'`` * ``['secret', 1]`` becomes ``['<str>', '<int>']`` * ``{'login': 'somelogin', 'pwd': 'secret'}`` becomes ``{'login': '<str>', 'pwd': '<str>'}`` CLI Examples: salt '*' pillar.obfuscate pillar.raw: Return the raw pillar data that is currently loaded into the minion. Contrast with :py:func:`items` which calls the master to fetch the most up-to-date Pillar. CLI Example: salt '*' pillar.raw With the optional key argument, you can select a subtree of the pillar raw data.:: salt '*' pillar.raw key='roles' [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看pillar配置文件默认路径
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master ##### Pillar settings ##### ########################################## # Salt Pillars allow for the building of global data that can be made selectively # available to different minions based on minion grain filtering. The Salt # Pillar is laid out in the same fashion as the file server, with environments, # a top file and sls files. However, pillar data does not need to be in the # highstate format, and is generally just key/value pairs. #pillar_roots: # base: # - /srv/pillar # #ext_pillar: # - hiera: /etc/hiera.yaml # - cmd_yaml: cat /etc/salt/yaml
添加pillar数据
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /srv/ [root@mcw01 ~]# mkdir /srv/pillar [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/packages.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/services.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# tree /srv/ /srv/ └── pillar ├── packages.sls ├── services.sls └── top.sls 1 directory, 3 files [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/top.sls base: #指定环境 '*': #Target ,注意,这里需要空两格 - packages #引用packages.sls或者packages/init.sls - services #引用services.sls或者services/init.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/packages.sls zabbix: package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/services.sls zabbix: port: 10050 user: admin [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看pillar数据
1、当重启salt-minion之后,才看到生效的,好像不重启,也可以看到,只是生效时间比较慢。可以看到,上面zabbix下定义的键值对,这里都能看到,包括两个sls定义在同名zabbix下的所有键值对
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 pillar.item zabbix mcw01: ---------- zabbix: [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 pillar.item zabbix mcw01: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix port: 10050 user: admin version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]#
当没有重启的salt-minion的时候,没有查到,远程重启,没有起来。手动从mcw03重启了下salt-minion。然后在mcw01上,就可以看到mcw03有的zabbix的相关键值对了。
因为上面target 指定的是所有机器,所以所有机器都有下面的zabbix的数据。
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 pillar.item zabbix mcw03: ---------- zabbix: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 cmd.run 'systemctl restart salt-minion' mcw03: Minion did not return. [No response] The minions may not have all finished running and any remaining minions will return upon completion. To look up the return data for this job later, run the following command: salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20231231133951780789 ERROR: Minions returned with non-zero exit code [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 pillar.item zabbix mcw03: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix port: 10050 user: admin version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]#
2、如果是下面加法,是不行的,用逗号隔开多个机器不行.可以用一些匹配
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/top.sls base: '*': - packages #- services 'mcw01,mcw03': - services [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 pillar.item zabbix mcw01: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]#
也可以用*来匹配多个target。匹配上的主机mcw的,都是有四个键值对。没有匹配上的,没有services下的键值对。
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/top.sls base: '*': - packages #- services 'mcw[0-9]*': - services [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 pillar.item zabbix mcw01: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix port: 10050 user: admin version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 pillar.item zabbix mcw03: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix port: 10050 user: admin version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt vm2.cluster.com pillar.item zabbix vm2.cluster.com: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]#
3、可以用的复杂目录结构
如下。top下mcw的主机包含role下的base ,base下包含zabbix下的init,init下包含zabbix下的services。packages和services下就是这两个文件下各自定义了zabbix的两个键值对。
结果是:mcw的机器是四个键值对,非mcw的机器是两个键值对,
定义pillar文件的总结:
- 最终只是用了下面标红的两个配置文件的内容,通过top.sls,加上以pillar为根目录出发,点分文件。
- 文件里面用include来包含其它文件的配置,来关联上多个文件之间的关系。而目录下的init文件,不用写,因为没有指定目录下某个文件,就会默认就会找init这个文件。
- 文件里面,就是起个名字,冒号,另起一行空两格写其它的键值对,这个名字就作为pillar的某个使用的键了。
- 这个名字可以在不同的文件中定义,定义的同名的,当pillar查的时候,各个文件里这个名字下的都是属于这个名字的键值对。
[root@mcw01 ~]# tree /srv/ /srv/ └── pillar ├── packages.sls ├── role │ └── base.sls ├── top.sls └── zabbix ├── init.sls └── services.sls 3 directories, 5 files [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/top.sls base: '*': - packages #- services 'mcw[0-9]*': - role.base [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/role/base.sls include: - zabbix - packages [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/zabbix/init.sls include: - zabbix.services [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/zabbix/services.sls zabbix: port: 10050 user: admin [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/packages.sls zabbix: package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]#
重启一下服务,看下效果,可以看到,效果符合预期。
[root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# salt vm2.cluster.com pillar.item zabbix vm2.cluster.com: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 pillar.item zabbix mcw01: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix port: 10050 user: admin version: 2.2.4 [root@mcw01 ~]#
4、上面复杂配置新增键值对,并且不用重启minion服务,而是命令刷新,进行检验
至于所有配置详情,查看上面的标题3 。
[root@mcw01 ~]# tree /srv/ /srv/ └── pillar ├── packages.sls ├── role │ └── base.sls ├── top.sls └── zabbix ├── init.sls └── services.sls 3 directories, 5 files [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/packages.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/packages.sls zabbix: package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 xinzeng1: val1 [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/zabbix/services.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/zabbix/services.sls zabbix: port: 10050 user: admin xinzeng2: val2 [root@mcw01 ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar mcw03: True mcw04: True vm2.cluster.com: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt vm2.cluster.com pillar.item zabbix vm2.cluster.com: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix version: 2.2.4 xinzeng1: val1 [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 pillar.item zabbix mcw01: ---------- zabbix: ---------- package-name: zabbix port: 10050 user: admin version: 2.2.4 xinzeng1: val1 xinzeng2: val2 [root@mcw01 ~]#
针对管理对象的操作-module
1、查看mcw01支持的所有module列表
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.list_modules mcw01: - acl - aliases - alternatives - archive - artifactory - baredoc - beacons - bigip - btrfs - buildout - chroot - cloud - cmd - composer - config - consul - container_resource - cp - cron - cryptdev - data - defaults - devinfo - devmap - dig - disk - django - dnsmasq - dnsutil - drbd - environ - ethtool - event - extfs - file - firewalld - freezer - gem - genesis - git - glassfish - glusterfs - google_chat - grafana4 - grains - group - hashutil - helm - highstate_doc - hosts - http - hue - incron - ini - inspector - introspect - iosconfig - ip - ipset - iptables - jboss7 - jboss7_cli - jinja - k8s - kernelpkg - key - keyboard - kmod - kubeadm - locale - locate - log - logrotate - lowpkg - lvm - mandrill - match - mattermost - mine - minion - modjk - mount - msteams - nagios_rpc - namecheap_domains - namecheap_domains_dns - namecheap_domains_ns - namecheap_ssl - namecheap_users - network - nexus - nginx - nova - npm - nspawn - nxos - nxos_api - nxos_upgrade - openscap - openstack_config - opsgenie - out - pagerduty - pagerduty_util - pam - parallels - partition - peeringdb - pillar - pip - pkg - pkg_resource - postfix - ps - publish - pushover - pyenv - random - random_org - rbenv - rest_sample_utils - restartcheck - ret - rsync - rvm - s3 - s6 - salt_proxy - salt_version - saltcheck - saltutil - schedule - scsi - sdb - seed - selinux - serverdensity_device - service - shadow - slack - slsutil - smbios - smtp - solrcloud - sqlite3 - ssh - state - status - statuspage - supervisord - svn - sys - sysctl - sysfs - syslog_ng - system - telegram - telemetry - temp - test - timezone - tuned - udev - uptime - user - vault - vbox_guest - virtualenv - vsphere - webutil - x509 - xfs - xml - zabbix - zenoss [root@mcw01 ~]#
2、查看指定module的所有function
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.list_functions cmd mcw01: - cmd.exec_code - cmd.exec_code_all - cmd.has_exec - cmd.powershell - cmd.powershell_all - cmd.retcode - cmd.run - cmd.run_all - cmd.run_bg - cmd.run_chroot - cmd.run_stderr - cmd.run_stdout - cmd.script - cmd.script_retcode - cmd.shell - cmd.shell_info - cmd.shells - cmd.tty - cmd.which - cmd.which_bin [root@mcw01 ~]#
3、查看指定module的用法
指定模块指定函数用法
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.doc cmd.run cmd.run: Execute the passed command and return the output as a string :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, on linux while using run, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.run 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If ``False``, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to ``True`` to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param bool bg: If ``True``, run command in background and do not await or deliver its results New in version 2016.3.0 :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.run 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str prepend_path: $PATH segment to prepend (trailing ':' not necessary) to $PATH New in version 2018.3.0 :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param bool encoded_cmd: Specify if the supplied command is encoded. Only applies to shell 'powershell' and 'pwsh'. New in version 2018.3.0 Older versions of powershell seem to return raw xml data in the return. To avoid raw xml data in the return, prepend your command with the following before encoding: `$ProgressPreference='SilentlyContinue'; <your command>` The following powershell code block will encode the `Write-Output` command so that it will not have the raw xml data in the return: # target string $Command = '$ProgressPreference="SilentlyContinue"; Write-Output "hello"' # Convert to Base64 encoded string $Encoded = [convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($command)) Write-Output $Encoded :param bool raise_err: If ``True`` and the command has a nonzero exit code, a CommandExecutionError exception will be raised. Warning: This function does not process commands through a shell unless the python_shell flag is set to True. This means that any shell-specific functionality such as 'echo' or the use of pipes, redirection or &&, should either be migrated to cmd.shell or have the python_shell=True flag set here. The use of python_shell=True means that the shell will accept _any_ input including potentially malicious commands such as 'good_command;rm -rf /'. Be absolutely certain that you have sanitized your input prior to using python_shell=True :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 :param int windows_codepage: 65001 Only applies to Windows: the minion uses `C:\Windows\System32\chcp.com` to verify or set the code page before the command `cmd` is executed. Code page 65001 corresponds with UTF-8 and allows international localization of Windows. New in version 3002 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run "ls -l | awk '/foo/{print \\$2}'" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.run template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \\$2}'" Specify an alternate shell with the shell parameter: salt '*' cmd.run "Get-ChildItem C:\\ " shell='powershell' A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.run "grep f" stdin='one\\ntwo\\nthree\\nfour\\nfive\\n' If an equal sign (``=``) appears in an argument to a Salt command it is interpreted as a keyword argument in the format ``key=val``. That processing can be bypassed in order to pass an equal sign through to the remote shell command by manually specifying the kwarg: salt '*' cmd.run cmd='sed -e s/=/:/g' [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看指定模块所有函数用法

[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.doc cmd cmd.exec_code: Pass in two strings, the first naming the executable language, aka - python2, python3, ruby, perl, lua, etc. the second string containing the code you wish to execute. The stdout will be returned. All parameters from :mod:`cmd.run_all <salt.modules.cmdmod.run_all>` except python_shell can be used. CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.exec_code ruby 'puts "cheese"' salt '*' cmd.exec_code ruby 'puts "cheese"' args='["arg1", "arg2"]' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' cmd.exec_code_all: Pass in two strings, the first naming the executable language, aka - python2, python3, ruby, perl, lua, etc. the second string containing the code you wish to execute. All cmd artifacts (stdout, stderr, retcode, pid) will be returned. All parameters from :mod:`cmd.run_all <salt.modules.cmdmod.run_all>` except python_shell can be used. CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.exec_code_all ruby 'puts "cheese"' salt '*' cmd.exec_code_all ruby 'puts "cheese"' args='["arg1", "arg2"]' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' cmd.has_exec: Returns true if the executable is available on the minion, false otherwise CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.has_exec cat cmd.powershell: Execute the passed PowerShell command and return the output as a dictionary. Other ``cmd.*`` functions (besides ``cmd.powershell_all``) return the raw text output of the command. This function appends ``| ConvertTo-JSON`` to the command and then parses the JSON into a Python dictionary. If you want the raw textual result of your PowerShell command you should use ``cmd.run`` with the ``shell=powershell`` option. For example: salt '*' cmd.run '$PSVersionTable.CLRVersion' shell=powershell salt '*' cmd.run 'Get-NetTCPConnection' shell=powershell New in version 2016.3.0 Warning: This passes the cmd argument directly to PowerShell without any further processing! Be absolutely sure that you have properly sanitized the command passed to this function and do not use untrusted inputs. In addition to the normal ``cmd.run`` parameters, this command offers the ``depth`` parameter to change the Windows default depth for the ``ConvertTo-JSON`` powershell command. The Windows default is 2. If you need more depth, set that here. Note: For some commands, setting the depth to a value greater than 4 greatly increases the time it takes for the command to return and in many cases returns useless data. :param str cmd: The powershell command to run. :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to "powershell". Can also use "pwsh" for powershell core if present on the system :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.powershell 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param bool reset_system_locale: Resets the system locale :param str saltenv: The salt environment to use. Default is 'base' :param int depth: The number of levels of contained objects to be included. Default is 2. Values greater than 4 seem to greatly increase the time it takes for the command to complete for some commands. eg: ``dir`` New in version 2016.3.4 :param bool encode_cmd: Encode the command before executing. Use in cases where characters may be dropped or incorrectly converted when executed. Default is False. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 :returns: :dict: A dictionary of data returned by the powershell command. CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.powershell "$PSVersionTable.CLRVersion" cmd.powershell_all: Execute the passed PowerShell command and return a dictionary with a result field representing the output of the command, as well as other fields showing us what the PowerShell invocation wrote to ``stderr``, the process id, and the exit code of the invocation. This function appends ``| ConvertTo-JSON`` to the command before actually invoking powershell. An unquoted empty string is not valid JSON, but it's very normal for the Powershell output to be exactly that. Therefore, we do not attempt to parse empty Powershell output (which would result in an exception). Instead we treat this as a special case and one of two things will happen: - If the value of the ``force_list`` parameter is ``True``, then the ``result`` field of the return dictionary will be an empty list. - If the value of the ``force_list`` parameter is ``False``, then the return dictionary **will not have a result key added to it**. We aren't setting ``result`` to ``None`` in this case, because ``None`` is the Python representation of "null" in JSON. (We likewise can't use ``False`` for the equivalent reason.) If Powershell's output is not an empty string and Python cannot parse its content, then a ``CommandExecutionError`` exception will be raised. If Powershell's output is not an empty string, Python is able to parse its content, and the type of the resulting Python object is other than ``list`` then one of two things will happen: - If the value of the ``force_list`` parameter is ``True``, then the ``result`` field will be a singleton list with the Python object as its sole member. - If the value of the ``force_list`` parameter is ``False``, then the value of ``result`` will be the unmodified Python object. If Powershell's output is not an empty string, Python is able to parse its content, and the type of the resulting Python object is ``list``, then the value of ``result`` will be the unmodified Python object. The ``force_list`` parameter has no effect in this case. Note: An example of why the ``force_list`` parameter is useful is as follows: The Powershell command ``dir x | Convert-ToJson`` results in - no output when x is an empty directory. - a dictionary object when x contains just one item. - a list of dictionary objects when x contains multiple items. By setting ``force_list`` to ``True`` we will always end up with a list of dictionary items, representing files, no matter how many files x contains. Conversely, if ``force_list`` is ``False``, we will end up with no ``result`` key in our return dictionary when x is an empty directory, and a dictionary object when x contains just one file. If you want a similar function but with a raw textual result instead of a Python dictionary, you should use ``cmd.run_all`` in combination with ``shell=powershell``. The remaining fields in the return dictionary are described in more detail in the ``Returns`` section. Example: salt '*' cmd.run_all '$PSVersionTable.CLRVersion' shell=powershell salt '*' cmd.run_all 'Get-NetTCPConnection' shell=powershell New in version 2018.3.0 Warning: This passes the cmd argument directly to PowerShell without any further processing! Be absolutely sure that you have properly sanitized the command passed to this function and do not use untrusted inputs. In addition to the normal ``cmd.run`` parameters, this command offers the ``depth`` parameter to change the Windows default depth for the ``ConvertTo-JSON`` powershell command. The Windows default is 2. If you need more depth, set that here. Note: For some commands, setting the depth to a value greater than 4 greatly increases the time it takes for the command to return and in many cases returns useless data. :param str cmd: The powershell command to run. :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to "powershell". Can also use "pwsh" for powershell core if present on the system :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.powershell_all 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param bool reset_system_locale: Resets the system locale :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param str saltenv: The salt environment to use. Default is 'base' :param int depth: The number of levels of contained objects to be included. Default is 2. Values greater than 4 seem to greatly increase the time it takes for the command to complete for some commands. eg: ``dir`` :param bool encode_cmd: Encode the command before executing. Use in cases where characters may be dropped or incorrectly converted when executed. Default is False. :param bool force_list: The purpose of this parameter is described in the preamble of this function's documentation. Default value is False. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 :return: A dictionary with the following entries: result For a complete description of this field, please refer to this function's preamble. **This key will not be added to the dictionary when force_list is False and Powershell's output is the empty string.** stderr What the PowerShell invocation wrote to ``stderr``. pid The process id of the PowerShell invocation retcode This is the exit code of the invocation of PowerShell. If the final execution status (in PowerShell) of our command (with ``| ConvertTo-JSON`` appended) is ``False`` this should be non-0. Likewise if PowerShell exited with ``$LASTEXITCODE`` set to some non-0 value, then ``retcode`` will end up with this value. :rtype: dict CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.powershell_all "$PSVersionTable.CLRVersion" CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.powershell_all "dir mydirectory" force_list=True cmd.retcode: Execute a shell command and return the command's return code. :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.retcode 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.retcode 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :rtype: int :rtype: None :returns: Return Code as an int or None if there was an exception. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.retcode "file /bin/bash" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.retcode template=jinja "file {{grains.pythonpath[0]}}/python" A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.retcode "grep f" stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' cmd.run: Execute the passed command and return the output as a string :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, on linux while using run, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.run 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If ``False``, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to ``True`` to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param bool bg: If ``True``, run command in background and do not await or deliver its results New in version 2016.3.0 :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.run 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str prepend_path: $PATH segment to prepend (trailing ':' not necessary) to $PATH New in version 2018.3.0 :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param bool encoded_cmd: Specify if the supplied command is encoded. Only applies to shell 'powershell' and 'pwsh'. New in version 2018.3.0 Older versions of powershell seem to return raw xml data in the return. To avoid raw xml data in the return, prepend your command with the following before encoding: `$ProgressPreference='SilentlyContinue'; <your command>` The following powershell code block will encode the `Write-Output` command so that it will not have the raw xml data in the return: # target string $Command = '$ProgressPreference="SilentlyContinue"; Write-Output "hello"' # Convert to Base64 encoded string $Encoded = [convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($command)) Write-Output $Encoded :param bool raise_err: If ``True`` and the command has a nonzero exit code, a CommandExecutionError exception will be raised. Warning: This function does not process commands through a shell unless the python_shell flag is set to True. This means that any shell-specific functionality such as 'echo' or the use of pipes, redirection or &&, should either be migrated to cmd.shell or have the python_shell=True flag set here. The use of python_shell=True means that the shell will accept _any_ input including potentially malicious commands such as 'good_command;rm -rf /'. Be absolutely certain that you have sanitized your input prior to using python_shell=True :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 :param int windows_codepage: 65001 Only applies to Windows: the minion uses `C:\Windows\System32\chcp.com` to verify or set the code page before the command `cmd` is executed. Code page 65001 corresponds with UTF-8 and allows international localization of Windows. New in version 3002 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run "ls -l | awk '/foo/{print \\$2}'" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.run template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \\$2}'" Specify an alternate shell with the shell parameter: salt '*' cmd.run "Get-ChildItem C:\\ " shell='powershell' A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.run "grep f" stdin='one\\ntwo\\nthree\\nfour\\nfive\\n' If an equal sign (``=``) appears in an argument to a Salt command it is interpreted as a keyword argument in the format ``key=val``. That processing can be bypassed in order to pass an equal sign through to the remote shell command by manually specifying the kwarg: salt '*' cmd.run cmd='sed -e s/=/:/g' cmd.run_all: Execute the passed command and return a dict of return data :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.run_all 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.run_all 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str prepend_path: $PATH segment to prepend (trailing ':' not necessary) to $PATH New in version 2018.3.0 :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param bool encoded_cmd: Specify if the supplied command is encoded. Only applies to shell 'powershell' and 'pwsh'. New in version 2018.3.0 Older versions of powershell seem to return raw xml data in the return. To avoid raw xml data in the return, prepend your command with the following before encoding: `$ProgressPreference='SilentlyContinue'; <your command>` The following powershell code block will encode the `Write-Output` command so that it will not have the raw xml data in the return: # target string $Command = '$ProgressPreference="SilentlyContinue"; Write-Output "hello"' # Convert to Base64 encoded string $Encoded = [convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($command)) Write-Output $Encoded :param bool redirect_stderr: If set to ``True``, then stderr will be redirected to stdout. This is helpful for cases where obtaining both the retcode and output is desired, but it is not desired to have the output separated into both stdout and stderr. New in version 2015.8.2 :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param bool bg: If ``True``, run command in background and do not await or deliver its results New in version 2016.3.6 :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run_all "ls -l | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.run_all template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.run_all "grep f" stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' cmd.run_bg: New in version 2016.3.0 Execute the passed command in the background and return its PID Note: If the init system is systemd and the backgrounded task should run even if the salt-minion process is restarted, prepend ``systemd-run --scope`` to the command. This will reparent the process in its own scope separate from salt-minion, and will not be affected by restarting the minion service. :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str shell: Shell to execute under. Defaults to the system default shell. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.run_bg 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.run_bg 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str prepend_path: $PATH segment to prepend (trailing ':' not necessary) to $PATH New in version 2018.3.0 :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. Warning: This function does not process commands through a shell unless the ``python_shell`` argument is set to ``True``. This means that any shell-specific functionality such as 'echo' or the use of pipes, redirection or &&, should either be migrated to cmd.shell or have the python_shell=True flag set here. The use of ``python_shell=True`` means that the shell will accept _any_ input including potentially malicious commands such as 'good_command;rm -rf /'. Be absolutely certain that you have sanitized your input prior to using ``python_shell=True``. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run_bg "fstrim-all" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.run_bg template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \\$2}'" Specify an alternate shell with the shell parameter: salt '*' cmd.run_bg "Get-ChildItem C:\\ " shell='powershell' If an equal sign (``=``) appears in an argument to a Salt command it is interpreted as a keyword argument in the format ``key=val``. That processing can be bypassed in order to pass an equal sign through to the remote shell command by manually specifying the kwarg: salt '*' cmd.run_bg cmd='ls -lR / | sed -e s/=/:/g > /tmp/dontwait' cmd.run_chroot: New in version 2014.7.0 This function runs :mod:`cmd.run_all <salt.modules.cmdmod.run_all>` wrapped within a chroot, with dev and proc mounted in the chroot :param str root: Path to the root of the jail to use. :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input.: :param str runas: User to run script as. :param str group: Group to run script as. :param str shell: Shell to execute under. Defaults to the system default shell. :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :parar str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param list binds: List of directories that will be exported inside the chroot with the bind option. New in version 3000 :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.run_chroot 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param dict clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run_chroot /var/lib/lxc/container_name/rootfs 'sh /tmp/bootstrap.sh' cmd.run_stderr: Execute a command and only return the standard error :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.run_stderr 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.run_stderr 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str prepend_path: $PATH segment to prepend (trailing ':' not necessary) to $PATH New in version 2018.3.0 :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run_stderr "ls -l | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.run_stderr template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.run_stderr "grep f" stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' cmd.run_stdout: Execute a command, and only return the standard out :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.run_stdout 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.run_stdout 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str prepend_path: $PATH segment to prepend (trailing ':' not necessary) to $PATH New in version 2018.3.0 :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.run_stdout "ls -l | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.run_stdout template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.run_stdout "grep f" stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' cmd.script: Download a script from a remote location and execute the script locally. The script can be located on the salt master file server or on an HTTP/FTP server. The script will be executed directly, so it can be written in any available programming language. :param str source: The location of the script to download. If the file is located on the master in the directory named spam, and is called eggs, the source string is salt://spam/eggs :param str args: String of command line args to pass to the script. Only used if no args are specified as part of the `name` argument. To pass a string containing spaces in YAML, you will need to doubly-quote it: salt myminion cmd.script salt://foo.sh "arg1 'arg two' arg3" :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. Note: For Window's users, specifically Server users, it may be necessary to specify your runas user using the User Logon Name instead of the legacy logon name. Traditionally, logons would be in the following format. ``Domain/user`` In the event this causes issues when executing scripts, use the UPN format which looks like the following. ``user@domain.local`` More information <https://github.com/saltstack/salt/issues/55080> :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str group: Group to run script as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param bool bg: If True, run script in background and do not await or deliver its results :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.script 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: If the command has not terminated after timeout seconds, send the subprocess sigterm, and if sigterm is ignored, follow up with sigkill :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.script salt://scripts/runme.sh salt '*' cmd.script salt://scripts/runme.sh 'arg1 arg2 "arg 3"' salt '*' cmd.script salt://scripts/windows_task.ps1 args=' -Input c:\tmp\infile.txt' shell='powershell' salt '*' cmd.script salt://scripts/runme.sh stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' cmd.script_retcode: Download a script from a remote location and execute the script locally. The script can be located on the salt master file server or on an HTTP/FTP server. The script will be executed directly, so it can be written in any available programming language. The script can also be formatted as a template, the default is jinja. Only evaluate the script return code and do not block for terminal output :param str source: The location of the script to download. If the file is located on the master in the directory named spam, and is called eggs, the source string is salt://spam/eggs :param str args: String of command line args to pass to the script. Only used if no args are specified as part of the `name` argument. To pass a string containing spaces in YAML, you will need to doubly-quote it: "arg1 'arg two' arg3" :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param str group: Group to run script as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str shell: Specify an alternate shell. Defaults to the system's default shell. :param bool python_shell: If False, let python handle the positional arguments. Set to True to use shell features, such as pipes or redirection. :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.script_retcode 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param int timeout: If the command has not terminated after timeout seconds, send the subprocess sigterm, and if sigterm is ignored, follow up with sigkill :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.script_retcode salt://scripts/runme.sh salt '*' cmd.script_retcode salt://scripts/runme.sh 'arg1 arg2 "arg 3"' salt '*' cmd.script_retcode salt://scripts/windows_task.ps1 args=' -Input c:\tmp\infile.txt' shell='powershell' A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.script_retcode salt://scripts/runme.sh stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' cmd.shell: Execute the passed command and return the output as a string. New in version 2015.5.0 :param str cmd: The command to run. ex: ``ls -lart /home`` :param str cwd: The directory from which to execute the command. Defaults to the home directory of the user specified by ``runas`` (or the user under which Salt is running if ``runas`` is not specified). :param str stdin: A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. :param str runas: Specify an alternate user to run the command. The default behavior is to run as the user under which Salt is running. If running on a Windows minion you must also use the ``password`` argument, and the target user account must be in the Administrators group. Warning: For versions 2018.3.3 and above on macosx while using runas, to pass special characters to the command you need to escape the characters on the shell. Example: cmd.shell 'echo '\''h=\"baz\"'\''' runas=macuser :param str group: Group to run command as. Not currently supported on Windows. :param str password: Windows only. Required when specifying ``runas``. This parameter will be ignored on non-Windows platforms. New in version 2016.3.0 :param int shell: Shell to execute under. Defaults to the system default shell. :param bool bg: If True, run command in background and do not await or deliver its results :param dict env: Environment variables to be set prior to execution. Note: When passing environment variables on the CLI, they should be passed as the string representation of a dictionary. salt myminion cmd.shell 'some command' env='{"FOO": "bar"}' Note: When using environment variables on Window's, case-sensitivity matters, i.e. Window's uses `Path` as opposed to `PATH` for other systems. :param bool clean_env: Attempt to clean out all other shell environment variables and set only those provided in the 'env' argument to this function. :param str prepend_path: $PATH segment to prepend (trailing ':' not necessary) to $PATH New in version 2018.3.0 :param str template: If this setting is applied then the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. Currently jinja, mako, and wempy are supported. :param bool rstrip: Strip all whitespace off the end of output before it is returned. :param str umask: The umask (in octal) to use when running the command. :param str output_encoding: Control the encoding used to decode the command's output. Note: This should not need to be used in most cases. By default, Salt will try to use the encoding detected from the system locale, and will fall back to UTF-8 if this fails. This should only need to be used in cases where the output of the command is encoded in something other than the system locale or UTF-8. To see the encoding Salt has detected from the system locale, check the `locale` line in the output of :py:func:`test.versions_report <salt.modules.test.versions_report>`. New in version 2018.3.0 :param str output_loglevel: Control the loglevel at which the output from the command is logged to the minion log. Note: The command being run will still be logged at the ``debug`` loglevel regardless, unless ``quiet`` is used for this value. :param bool ignore_retcode: If the exit code of the command is nonzero, this is treated as an error condition, and the output from the command will be logged to the minion log. However, there are some cases where programs use the return code for signaling and a nonzero exit code doesn't necessarily mean failure. Pass this argument as ``True`` to skip logging the output if the command has a nonzero exit code. :param bool hide_output: If ``True``, suppress stdout and stderr in the return data. Note: This is separate from ``output_loglevel``, which only handles how Salt logs to the minion log. New in version 2018.3.0 :param int timeout: A timeout in seconds for the executed process to return. :param bool use_vt: Use VT utils (saltstack) to stream the command output more interactively to the console and the logs. This is experimental. Warning: This passes the cmd argument directly to the shell without any further processing! Be absolutely sure that you have properly sanitized the command passed to this function and do not use untrusted inputs. :param list success_retcodes: This parameter will allow a list of non-zero return codes that should be considered a success. If the return code returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 2019.2.0 :param list success_stdout: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard out should be considered a success. If stdout returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param list success_stderr: This parameter will allow a list of strings that when found in standard error should be considered a success. If stderr returned from the run matches any in the provided list, the return code will be overridden with zero. New in version 3004 :param bool stdin_raw_newlines: False If ``True``, Salt will not automatically convert the characters ``\n`` present in the ``stdin`` value to newlines. New in version 2019.2.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.shell "ls -l | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" The template arg can be set to 'jinja' or another supported template engine to render the command arguments before execution. For example: salt '*' cmd.shell template=jinja "ls -l /tmp/{{grains.id}} | awk '/foo/{print \$2}'" Specify an alternate shell with the shell parameter: salt '*' cmd.shell "Get-ChildItem C:\ " shell='powershell' A string of standard input can be specified for the command to be run using the ``stdin`` parameter. This can be useful in cases where sensitive information must be read from standard input. salt '*' cmd.shell "grep f" stdin='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\n' If an equal sign (``=``) appears in an argument to a Salt command it is interpreted as a keyword argument in the format ``key=val``. That processing can be bypassed in order to pass an equal sign through to the remote shell command by manually specifying the kwarg: salt '*' cmd.shell cmd='sed -e s/=/:/g' cmd.shell_info: New in version 2016.11.0 Provides information about a shell or script languages which often use ``#!``. The values returned are dependent on the shell or scripting languages all return the ``installed``, ``path``, ``version``, ``version_raw`` Args: shell (str): Name of the shell. Support shells/script languages include bash, cmd, perl, php, powershell, python, ruby and zsh list_modules (bool): True to list modules available to the shell. Currently only lists powershell modules. Returns: dict: A dictionary of information about the shell {'version': '<2 or 3 numeric components dot-separated>', 'version_raw': '<full version string>', 'path': '<full path to binary>', 'installed': <True, False or None>, '<attribute>': '<attribute value>'} Note: - ``installed`` is always returned, if ``None`` or ``False`` also returns error and may also return ``stdout`` for diagnostics. - ``version`` is for use in determine if a shell/script language has a particular feature set, not for package management. - The shell must be within the executable search path. CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.shell_info bash salt '*' cmd.shell_info powershell :codeauthor: Damon Atkins <https://github.com/damon-atkins> cmd.shells: Lists the valid shells on this system via the /etc/shells file New in version 2015.5.0 CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.shells cmd.tty: Echo a string to a specific tty CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.tty tty0 'This is a test' salt '*' cmd.tty pts3 'This is a test' cmd.which: Returns the path of an executable available on the minion, None otherwise CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.which cat cmd.which_bin: Returns the first command found in a list of commands CLI Example: salt '*' cmd.which_bin '[pip2, pip, pip-python]' [root@mcw01 ~]#
4、一次执行多个模块函数的用法
模块和传参都用逗号隔开
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 test.echo,service.status,cmd.run 'wo shi mcw',sshd,'ls /' mcw01: ---------- cmd.run: bin boot data dev etc home lib lib64 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var service.status: True test.echo: wo shi mcw [root@mcw01 ~]#
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt -L mcw01,mcw03 test.echo,service.status,cmd.run 'wo shi mcw',sshd,hostname mcw01: ---------- cmd.run: mcw01 service.status: True test.echo: wo shi mcw mcw03: ---------- cmd.run: mcw03 service.status: True test.echo: wo shi mcw [root@mcw01 ~]#
也可以指定传参
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt -L mcw01,mcw03 --args-separator=@ test.echo,service.status,cmd.run 'wo shi mcw'@sshd@hostname mcw03: ---------- cmd.run: mcw03 service.status: True test.echo: wo shi mcw mcw01: ---------- cmd.run: mcw01 service.status: True test.echo: wo shi mcw [root@mcw01 ~]#
配置管理从这里开始-states
1、查看所有states列表
跟上面列出所有模块,有点相似
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.list_state_modules mcw01: - acl - alias - alternatives - ansible - archive - artifactory - beacon - bigip - blockdev - btrfs - buildout - ceph - chronos_job - cloud - cmd - composer - cron - cryptdev - disk - elasticsearch - elasticsearch_index - elasticsearch_index_template - environ - esxdatacenter - etcd - ethtool - event - file - firewall - firewalld - gem - git - glassfish - glusterfs - gnomedesktop - gpg - grafana4_dashboard - grafana4_datasource - grafana4_org - grafana4_user - grains - group - helm - highstate_doc - host - http - incron - infoblox_a - infoblox_cname - infoblox_host_record - infoblox_range - ini - ipset - iptables - jboss7 - jenkins - junos - kernelpkg - keyboard - kmod - ldap - locale - logrotate - loop - lvm - lxc - marathon_app - modjk - modjk_worker - module - mount - msteams - network - nexus - npm - nxos - nxos_upgrade - openstack_config - opsgenie - pagerduty - pagerduty_escalation_policy - pagerduty_schedule - pagerduty_service - pagerduty_user - pip - pkg - pkgbuild - pkgng - pkgrepo - powerpath - process - pushover - pyenv - rbenv - rsync - rvm - salt - salt_proxy - saltutil - schedule - selinux - serverdensity_device - service - slack - smtp - solrcloud - sqlite3 - ssh_auth - ssh_known_hosts - stateconf - status - statuspage - supervisord - svn - sysctl - syslog_ng - telemetry_alert - test - timezone - tuned - uptime - user - vault - vbox_guest - virtualenv - webutil - winrepo - x509 - xml - zabbix_action - zabbix_host - zabbix_hostgroup - zabbix_mediatype - zabbix_template - zabbix_user - zabbix_usergroup - zabbix_usermacro - zabbix_valuemap - zenoss [root@mcw01 ~]#
2、查看指定states的所有function
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.list_state_functions file mcw01: - file.absent - file.accumulated - file.append - file.blockreplace - file.cached - file.comment - file.copy - file.decode - file.directory - file.exists - file.hardlink - file.keyvalue - file.line - file.managed - file.missing - file.mknod - file.mod_beacon - file.mod_run_check_cmd - file.not_cached - file.patch - file.prepend - file.recurse - file.rename - file.replace - file.retention_schedule - file.serialize - file.shortcut - file.symlink - file.tidied - file.touch - file.uncomment [root@mcw01 ~]#
3、查看指定states用法
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.state_doc file.managed mcw01: ---------- file: Operations on regular files, special files, directories, and symlinks ===================================================================== Salt States can aggressively manipulate files on a system. There are a number of ways in which files can be managed. Regular files can be enforced with the :mod:`file.managed <salt.states.file.managed>` state. This state downloads files from the salt master and places them on the target system. Managed files can be rendered as a jinja, mako, or wempy template, adding a dynamic component to file management. An example of :mod:`file.managed <salt.states.file.managed>` which makes use of the jinja templating system would look like this: /etc/http/conf/http.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://apache/http.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - attrs: ai - template: jinja - defaults: custom_var: "default value" other_var: 123 {% if grains['os'] == 'Ubuntu' %} - context: custom_var: "override" {% endif %} It is also possible to use the :mod:`py renderer <salt.renderers.py>` as a templating option. The template would be a Python script which would need to contain a function called ``run()``, which returns a string. All arguments to the state will be made available to the Python script as globals. The returned string will be the contents of the managed file. For example: def run(): lines = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'] lines.extend([source, name, user, context]) # Arguments as globals return '\n\n'.join(lines) Note: The ``defaults`` and ``context`` arguments require extra indentation (four spaces instead of the normal two) in order to create a nested dictionary. :ref:`More information <nested-dict-indentation>`. If using a template, any user-defined template variables in the file defined in ``source`` must be passed in using the ``defaults`` and/or ``context`` arguments. The general best practice is to place default values in ``defaults``, with conditional overrides going into ``context``, as seen above. The template will receive a variable ``custom_var``, which would be accessed in the template using ``{{ custom_var }}``. If the operating system is Ubuntu, the value of the variable ``custom_var`` would be *override*, otherwise it is the default *default value* The ``source`` parameter can be specified as a list. If this is done, then the first file to be matched will be the one that is used. This allows you to have a default file on which to fall back if the desired file does not exist on the salt fileserver. Here's an example: /etc/foo.conf: file.managed: - source: - salt://foo.conf.{{ grains['fqdn'] }} - salt://foo.conf.fallback - user: foo - group: users - mode: 644 - attrs: i - backup: minion Note: Salt supports backing up managed files via the backup option. For more details on this functionality please review the :ref:`backup_mode documentation <file-state-backups>`. The ``source`` parameter can also specify a file in another Salt environment. In this example ``foo.conf`` in the ``dev`` environment will be used instead. /etc/foo.conf: file.managed: - source: - 'salt://foo.conf?saltenv=dev' - user: foo - group: users - mode: '0644' - attrs: i Warning: When using a mode that includes a leading zero you must wrap the value in single quotes. If the value is not wrapped in quotes it will be read by YAML as an integer and evaluated as an octal. The ``names`` parameter, which is part of the state compiler, can be used to expand the contents of a single state declaration into multiple, single state declarations. Each item in the ``names`` list receives its own individual state ``name`` and is converted into its own low-data structure. This is a convenient way to manage several files with similar attributes. salt_master_conf: file.managed: - user: root - group: root - mode: '0644' - names: - /etc/salt/master.d/master.conf: - source: salt://saltmaster/master.conf - /etc/salt/minion.d/minion-99.conf: - source: salt://saltmaster/minion.conf Note: There is more documentation about this feature in the :ref:`Names declaration <names-declaration>` section of the :ref:`Highstate docs <states-highstate>`. Special files can be managed via the ``mknod`` function. This function will create and enforce the permissions on a special file. The function supports the creation of character devices, block devices, and FIFO pipes. The function will create the directory structure up to the special file if it is needed on the minion. The function will not overwrite or operate on (change major/minor numbers) existing special files with the exception of user, group, and permissions. In most cases the creation of some special files require root permissions on the minion. This would require that the minion to be run as the root user. Here is an example of a character device: /var/named/chroot/dev/random: file.mknod: - ntype: c - major: 1 - minor: 8 - user: named - group: named - mode: 660 Here is an example of a block device: /var/named/chroot/dev/loop0: file.mknod: - ntype: b - major: 7 - minor: 0 - user: named - group: named - mode: 660 Here is an example of a fifo pipe: /var/named/chroot/var/log/logfifo: file.mknod: - ntype: p - user: named - group: named - mode: 660 Directories can be managed via the ``directory`` function. This function can create and enforce the permissions on a directory. A directory statement will look like this: /srv/stuff/substuf: file.directory: - user: fred - group: users - mode: 755 - makedirs: True If you need to enforce user and/or group ownership or permissions recursively on the directory's contents, you can do so by adding a ``recurse`` directive: /srv/stuff/substuf: file.directory: - user: fred - group: users - mode: 755 - makedirs: True - recurse: - user - group - mode As a default, ``mode`` will resolve to ``dir_mode`` and ``file_mode``, to specify both directory and file permissions, use this form: /srv/stuff/substuf: file.directory: - user: fred - group: users - file_mode: 744 - dir_mode: 755 - makedirs: True - recurse: - user - group - mode Symlinks can be easily created; the symlink function is very simple and only takes a few arguments: /etc/grub.conf: file.symlink: - target: /boot/grub/grub.conf Recursive directory management can also be set via the ``recurse`` function. Recursive directory management allows for a directory on the salt master to be recursively copied down to the minion. This is a great tool for deploying large code and configuration systems. A state using ``recurse`` would look something like this: /opt/code/flask: file.recurse: - source: salt://code/flask - include_empty: True A more complex ``recurse`` example: {% set site_user = 'testuser' %} {% set site_name = 'test_site' %} {% set project_name = 'test_proj' %} {% set sites_dir = 'test_dir' %} django-project: file.recurse: - name: {{ sites_dir }}/{{ site_name }}/{{ project_name }} - user: {{ site_user }} - dir_mode: 2775 - file_mode: '0644' - template: jinja - source: salt://project/templates_dir - include_empty: True Retention scheduling can be applied to manage contents of backup directories. For example: /var/backups/example_directory: file.retention_schedule: - strptime_format: example_name_%Y%m%dT%H%M%S.tar.bz2 - retain: most_recent: 5 first_of_hour: 4 first_of_day: 14 first_of_week: 6 first_of_month: 6 first_of_year: all file.managed: Manage a given file, this function allows for a file to be downloaded from the salt master and potentially run through a templating system. name The location of the file to manage, as an absolute path. source The source file to download to the minion, this source file can be hosted on either the salt master server (``salt://``), the salt minion local file system (``/``), or on an HTTP or FTP server (``http(s)://``, ``ftp://``). Both HTTPS and HTTP are supported as well as downloading directly from Amazon S3 compatible URLs with both pre-configured and automatic IAM credentials. (see s3.get state documentation) File retrieval from Openstack Swift object storage is supported via swift://container/object_path URLs, see swift.get documentation. For files hosted on the salt file server, if the file is located on the master in the directory named spam, and is called eggs, the source string is salt://spam/eggs. If source is left blank or None (use ~ in YAML), the file will be created as an empty file and the content will not be managed. This is also the case when a file already exists and the source is undefined; the contents of the file will not be changed or managed. If source is left blank or None, please also set replaced to False to make your intention explicit. If the file is hosted on a HTTP or FTP server then the source_hash argument is also required. A list of sources can also be passed in to provide a default source and a set of fallbacks. The first source in the list that is found to exist will be used and subsequent entries in the list will be ignored. Source list functionality only supports local files and remote files hosted on the salt master server or retrievable via HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP. file_override_example: file.managed: - source: - salt://file_that_does_not_exist - salt://file_that_exists source_hash This can be one of the following: 1. a source hash string 2. the URI of a file that contains source hash strings The function accepts the first encountered long unbroken alphanumeric string of correct length as a valid hash, in order from most secure to least secure: Type Length ====== ====== sha512 128 sha384 96 sha256 64 sha224 56 sha1 40 md5 32 **Using a Source Hash File** The file can contain several checksums for several files. Each line must contain both the file name and the hash. If no file name is matched, the first hash encountered will be used, otherwise the most secure hash with the correct source file name will be used. When using a source hash file the source_hash argument needs to be a url, the standard download urls are supported, ftp, http, salt etc: Example: tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz: file.managed: - name: /tmp/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source: https://launchpad.net/tomdroid/beta/0.7.3/+download/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source_hash: https://launchpad.net/tomdroid/beta/0.7.3/+download/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.hash The following lines are all supported formats: /etc/rc.conf ef6e82e4006dee563d98ada2a2a80a27 sha254c8525aee419eb649f0233be91c151178b30f0dff8ebbdcc8de71b1d5c8bcc06a /etc/resolv.conf ead48423703509d37c4a90e6a0d53e143b6fc268 Debian file type ``*.dsc`` files are also supported. **Inserting the Source Hash in the SLS Data** The source_hash can be specified as a simple checksum, like so: tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz: file.managed: - name: /tmp/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source: https://launchpad.net/tomdroid/beta/0.7.3/+download/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source_hash: 79eef25f9b0b2c642c62b7f737d4f53f Note: Releases prior to 2016.11.0 must also include the hash type, like in the below example: tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz: file.managed: - name: /tmp/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source: https://launchpad.net/tomdroid/beta/0.7.3/+download/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source_hash: md5=79eef25f9b0b2c642c62b7f737d4f53f Known issues: If the remote server URL has the hash file as an apparent sub-directory of the source file, the module will discover that it has already cached a directory where a file should be cached. For example: tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz: file.managed: - name: /tmp/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source: https://launchpad.net/tomdroid/beta/0.7.3/+download/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz - source_hash: https://launchpad.net/tomdroid/beta/0.7.3/+download/tomdroid-src-0.7.3.tar.gz/+md5 source_hash_name When ``source_hash`` refers to a hash file, Salt will try to find the correct hash by matching the filename/URI associated with that hash. By default, Salt will look for the filename being managed. When managing a file at path ``/tmp/foo.txt``, then the following line in a hash file would match: acbd18db4cc2f85cedef654fccc4a4d8 foo.txt However, sometimes a hash file will include multiple similar paths: 37b51d194a7513e45b56f6524f2d51f2 ./dir1/foo.txt acbd18db4cc2f85cedef654fccc4a4d8 ./dir2/foo.txt 73feffa4b7f6bb68e44cf984c85f6e88 ./dir3/foo.txt In cases like this, Salt may match the incorrect hash. This argument can be used to tell Salt which filename to match, to ensure that the correct hash is identified. For example: /tmp/foo.txt: file.managed: - source: https://mydomain.tld/dir2/foo.txt - source_hash: https://mydomain.tld/hashes - source_hash_name: ./dir2/foo.txt Note: This argument must contain the full filename entry from the checksum file, as this argument is meant to disambiguate matches for multiple files that have the same basename. So, in the example above, simply using ``foo.txt`` would not match. New in version 2016.3.5 keep_source Set to ``False`` to discard the cached copy of the source file once the state completes. This can be useful for larger files to keep them from taking up space in minion cache. However, keep in mind that discarding the source file will result in the state needing to re-download the source file if the state is run again. New in version 2017.7.3 user The user to own the file, this defaults to the user salt is running as on the minion group The group ownership set for the file, this defaults to the group salt is running as on the minion. On Windows, this is ignored mode The permissions to set on this file, e.g. ``644``, ``0775``, or ``4664``. The default mode for new files and directories corresponds to the umask of the salt process. The mode of existing files and directories will only be changed if ``mode`` is specified. Note: This option is **not** supported on Windows. Changed in version 2016.11.0 This option can be set to ``keep``, and Salt will keep the mode from the Salt fileserver. This is only supported when the ``source`` URL begins with ``salt://``, or for files local to the minion. Because the ``source`` option cannot be used with any of the ``contents`` options, setting the ``mode`` to ``keep`` is also incompatible with the ``contents`` options. Note: keep does not work with salt-ssh. As a consequence of how the files are transferred to the minion, and the inability to connect back to the master with salt-ssh, salt is unable to stat the file as it exists on the fileserver and thus cannot mirror the mode on the salt-ssh minion attrs The attributes to have on this file, e.g. ``a``, ``i``. The attributes can be any or a combination of the following characters: ``aAcCdDeijPsStTu``. Note: This option is **not** supported on Windows. New in version 2018.3.0 template If this setting is applied, the named templating engine will be used to render the downloaded file. The following templates are supported: - :mod:`cheetah<salt.renderers.cheetah>` - :mod:`genshi<salt.renderers.genshi>` - :mod:`jinja<salt.renderers.jinja>` - :mod:`mako<salt.renderers.mako>` - :mod:`py<salt.renderers.py>` - :mod:`wempy<salt.renderers.wempy>` makedirs If set to ``True``, then the parent directories will be created to facilitate the creation of the named file. If ``False``, and the parent directory of the destination file doesn't exist, the state will fail. dir_mode If directories are to be created, passing this option specifies the permissions for those directories. If this is not set, directories will be assigned permissions by adding the execute bit to the mode of the files. The default mode for new files and directories corresponds umask of salt process. For existing files and directories it's not enforced. replace If set to ``False`` and the file already exists, the file will not be modified even if changes would otherwise be made. Permissions and ownership will still be enforced, however. context Overrides default context variables passed to the template. defaults Default context passed to the template. backup Overrides the default backup mode for this specific file. See :ref:`backup_mode documentation <file-state-backups>` for more details. show_changes Output a unified diff of the old file and the new file. If ``False`` return a boolean if any changes were made. create If set to ``False``, then the file will only be managed if the file already exists on the system. contents Specify the contents of the file. Cannot be used in combination with ``source``. Ignores hashes and does not use a templating engine. This value can be either a single string, a multiline YAML string or a list of strings. If a list of strings, then the strings will be joined together with newlines in the resulting file. For example, the below two example states would result in identical file contents: /path/to/file1: file.managed: - contents: - This is line 1 - This is line 2 /path/to/file2: file.managed: - contents: | This is line 1 This is line 2 contents_pillar New in version 0.17.0 Changed in version 2016.11.0 contents_pillar can also be a list, and the pillars will be concatenated together to form one file. Operates like ``contents``, but draws from a value stored in pillar, using the pillar path syntax used in :mod:`pillar.get <salt.modules.pillar.get>`. This is useful when the pillar value contains newlines, as referencing a pillar variable using a jinja/mako template can result in YAML formatting issues due to the newlines causing indentation mismatches. For example, the following could be used to deploy an SSH private key: /home/deployer/.ssh/id_rsa: file.managed: - user: deployer - group: deployer - mode: 600 - attrs: a - contents_pillar: userdata:deployer:id_rsa This would populate ``/home/deployer/.ssh/id_rsa`` with the contents of ``pillar['userdata']['deployer']['id_rsa']``. An example of this pillar setup would be like so: userdata: deployer: id_rsa: | -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- MIIEowIBAAKCAQEAoQiwO3JhBquPAalQF9qP1lLZNXVjYMIswrMe2HcWUVBgh+vY U7sCwx/dH6+VvNwmCoqmNnP+8gTPKGl1vgAObJAnMT623dMXjVKwnEagZPRJIxDy B/HaAre9euNiY3LvIzBTWRSeMfT+rWvIKVBpvwlgGrfgz70m0pqxu+UyFbAGLin+ GpxzZAMaFpZw4sSbIlRuissXZj/sHpQb8p9M5IeO4Z3rjkCP1cxI -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY----- Note: The private key above is shortened to keep the example brief, but shows how to do multiline string in YAML. The key is followed by a pipe character, and the multiline string is indented two more spaces. To avoid the hassle of creating an indented multiline YAML string, the :mod:`file_tree external pillar <salt.pillar.file_tree>` can be used instead. However, this will not work for binary files in Salt releases before 2015.8.4. contents_grains New in version 2014.7.0 Operates like ``contents``, but draws from a value stored in grains, using the grains path syntax used in :mod:`grains.get <salt.modules.grains.get>`. This functionality works similarly to ``contents_pillar``, but with grains. For example, the following could be used to deploy a "message of the day" file: write_motd: file.managed: - name: /etc/motd - contents_grains: motd This would populate ``/etc/motd`` file with the contents of the ``motd`` grain. The ``motd`` grain is not a default grain, and would need to be set prior to running the state: salt '*' grains.set motd 'Welcome! This system is managed by Salt.' contents_newline New in version 2014.7.0 Changed in version 2015.8.4 This option is now ignored if the contents being deployed contain binary data. If ``True``, files managed using ``contents``, ``contents_pillar``, or ``contents_grains`` will have a newline added to the end of the file if one is not present. Setting this option to ``False`` will ensure the final line, or entry, does not contain a new line. If the last line, or entry in the file does contain a new line already, this option will not remove it. contents_delimiter New in version 2015.8.4 Can be used to specify an alternate delimiter for ``contents_pillar`` or ``contents_grains``. This delimiter will be passed through to :py:func:`pillar.get <salt.modules.pillar.get>` or :py:func:`grains.get <salt.modules.grains.get>` when retrieving the contents. encoding If specified, then the specified encoding will be used. Otherwise, the file will be encoded using the system locale (usually UTF-8). See https://docs.python.org/3/library/codecs.html#standard-encodings for the list of available encodings. New in version 2017.7.0 encoding_errors Error encoding scheme. Default is ```'strict'```. See https://docs.python.org/2/library/codecs.html#codec-base-classes for the list of available schemes. New in version 2017.7.0 allow_empty New in version 2015.8.4 If set to ``False``, then the state will fail if the contents specified by ``contents_pillar`` or ``contents_grains`` are empty. follow_symlinks New in version 2014.7.0 If the desired path is a symlink follow it and make changes to the file to which the symlink points. check_cmd New in version 2014.7.0 The specified command will be run with an appended argument of a *temporary* file containing the new managed contents. If the command exits with a zero status the new managed contents will be written to the managed destination. If the command exits with a nonzero exit code, the state will fail and no changes will be made to the file. For example, the following could be used to verify sudoers before making changes: /etc/sudoers: file.managed: - user: root - group: root - mode: 0440 - attrs: i - source: salt://sudoers/files/sudoers.jinja - template: jinja - check_cmd: /usr/sbin/visudo -c -f **NOTE**: This ``check_cmd`` functions differently than the requisite ``check_cmd``. tmp_dir Directory for temp file created by ``check_cmd``. Useful for checkers dependent on config file location (e.g. daemons restricted to their own config directories by an apparmor profile). /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf: file.managed: - user: root - group: root - mode: 0755 - tmp_dir: '/etc/dhcp' - contents: "# Managed by Salt" - check_cmd: dhcpd -t -cf tmp_ext Suffix for temp file created by ``check_cmd``. Useful for checkers dependent on config file extension (e.g. the init-checkconf upstart config checker). /etc/init/test.conf: file.managed: - user: root - group: root - mode: 0440 - tmp_ext: '.conf' - contents: - 'description "Salt Minion"' - 'start on started mountall' - 'stop on shutdown' - 'respawn' - 'exec salt-minion' - check_cmd: init-checkconf -f skip_verify If ``True``, hash verification of remote file sources (``http://``, ``https://``, ``ftp://``) will be skipped, and the ``source_hash`` argument will be ignored. New in version 2016.3.0 selinux Allows setting the selinux user, role, type, and range of a managed file /tmp/selinux.test file.managed: - user: root - selinux: seuser: system_u serole: object_r setype: system_conf_t seranage: s0 New in version 3000 win_owner The owner of the directory. If this is not passed, user will be used. If user is not passed, the account under which Salt is running will be used. New in version 2017.7.0 win_perms A dictionary containing permissions to grant and their propagation. For example: ``{'Administrators': {'perms': 'full_control'}}`` Can be a single basic perm or a list of advanced perms. ``perms`` must be specified. ``applies_to`` does not apply to file objects. New in version 2017.7.0 win_deny_perms A dictionary containing permissions to deny and their propagation. For example: ``{'Administrators': {'perms': 'full_control'}}`` Can be a single basic perm or a list of advanced perms. ``perms`` must be specified. ``applies_to`` does not apply to file objects. New in version 2017.7.0 win_inheritance True to inherit permissions from the parent directory, False not to inherit permission. New in version 2017.7.0 win_perms_reset If ``True`` the existing DACL will be cleared and replaced with the settings defined in this function. If ``False``, new entries will be appended to the existing DACL. Default is ``False``. New in version 2018.3.0 Here's an example using the above ``win_*`` parameters: create_config_file: file.managed: - name: C:\config\settings.cfg - source: salt://settings.cfg - win_owner: Administrators - win_perms: # Basic Permissions dev_ops: perms: full_control # List of advanced permissions appuser: perms: - read_attributes - read_ea - create_folders - read_permissions joe_snuffy: perms: read - win_deny_perms: fred_snuffy: perms: full_control - win_inheritance: False verify_ssl If ``False``, remote https file sources (``https://``) and source_hash will not attempt to validate the servers certificate. Default is True. New in version 3002 [root@mcw01 ~]#
5、从一个简单的实例去了解states- file.managed简单文件管理。执行单个文件的

查看默认存放目录
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master ##### File Server settings ##### ########################################## # Salt runs a lightweight file server written in zeromq to deliver files to # minions. This file server is built into the master daemon and does not # require a dedicated port. # The file server works on environments passed to the master, each environment # can have multiple root directories, the subdirectories in the multiple file # roots cannot match, otherwise the downloaded files will not be able to be # reliably ensured. A base environment is required to house the top file. # Example: # file_roots: # base: # - /srv/salt/ # dev: # - /srv/salt/dev/services # - /srv/salt/dev/states # prod: # - /srv/salt/prod/services # - /srv/salt/prod/states # #file_roots: # base: # - /srv/salt # # The master_roots setting configures a master-only copy of the file_roots dictionary, # used by the state compiler. #master_roots: # base: # - /srv/salt-master
创建目录,创建文件。foo.conf是配置文件,one.sls是要部署的状态文件。复制为/tmp/foo.conf文件,salt://源文件是以/srv/salt默认目录作为根目录,然后找foo.conf文件,这个就是源文件。
[root@mcw01 ~]# ls /srv/ pillar [root@mcw01 ~]# mkdir /srv/salt [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/salt/one.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/one.sls /tmp/foo.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://foo.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - backup: minion [root@mcw01 ~]# echo "mcw test" > /srv/salt/foo.conf [root@mcw01 ~]# tree /srv/salt/ /srv/salt/ ├── foo.conf └── one.sls 0 directories, 2 files [root@mcw01 ~]#
执行部署。可以看到,通过/srv/salt/one.sls,在mcw01上执行了一下,就根据one定义的,将master上的/srv/salt/foo.conf,复制到了 mcw01 的/tmp/foo.conf 下。tmp/foo.conf这也是salt执行的id。我们可看到返回的结果,说这是个新的文件。
[root@mcw01 ~]# ls /tmp/ pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 state.sls one mcw01: ---------- ID: /tmp/foo.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/foo.conf updated Started: 22:35:16.057242 Duration: 84.946 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 Summary for mcw01 ------------ Succeeded: 1 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 84.946 ms [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /tmp/ foo.conf systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW [root@mcw01 ~]# ls -lh /tmp/foo.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 9 Jan 1 22:35 /tmp/foo.conf [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /tmp/foo.conf mcw test [root@mcw01 ~]#
我们在mcw03上创建一个同名的文件:
[root@mcw03 ~]# ls /tmp/ systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-chronyd.service-DM55tO systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vgauthd.service-blx3B1 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-mariadb.service-JlQLud systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vmtoolsd.service-mrh4Xg [root@mcw03 ~]# vim /tmp/foo.conf [root@mcw03 ~]# ls /tmp/ -lh total 4.0K -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 18 Jan 1 22:42 foo.conf drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-chronyd.service-DM55tO drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-mariadb.service-JlQLud drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vgauthd.service-blx3B1 drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vmtoolsd.service-mrh4Xg [root@mcw03 ~]# cat /tmp/foo.conf wo shi machangwei [root@mcw03 ~]#
salt命令在mcw03上执行一下,此时提示的是改变了什么,而不是新增文件了
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 state.sls one mcw03: ---------- ID: /tmp/foo.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/foo.conf updated Started: 22:44:45.250363 Duration: 92.206 ms Changes: ---------- diff: --- +++ @@ -1 +1 @@ -wo shi machangwei +mcw test Summary for mcw03 ------------ Succeeded: 1 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 92.206 ms [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]#
在mcw03上查看,这个文件也已经被master上的文件覆盖掉了
[root@mcw03 ~]# ls -lh /tmp/ total 4.0K -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 9 Jan 1 22:44 foo.conf drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-chronyd.service-DM55tO drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-mariadb.service-JlQLud drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vgauthd.service-blx3B1 drwx------ 3 root root 17 Nov 17 23:09 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vmtoolsd.service-mrh4Xg [root@mcw03 ~]# cat /tmp/foo.conf mcw test [root@mcw03 ~]#
6、states同时对多台机器进行配置管理

查看salt的文件情况。写的时候,可以参考下面的写法,下面是可以正常用的
[root@mcw01 salt]# tree . . ├── config │ ├── foo2.conf │ └── foo3.conf ├── foo1.conf ├── one.sls ├── three │ └── three.sls ├── top.sls └── two └── init.sls 3 directories, 7 files [root@mcw01 salt]# [root@mcw01 salt]# cat top.sls base: '*': - one 'mcw01': - two 'mcw03': - three.three [root@mcw01 salt]# cat one.sls /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://foo1.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - backup: minion [root@mcw01 salt]# cat two/init.sls /tmp/foo2.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://config/foo2.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - backup: minion [root@mcw01 salt]# cat three/three.sls /tmp/mcwconfig/foo3.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://config/foo3.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - backup: minion [root@mcw01 salt]# [root@mcw01 salt]# cat foo1.conf mcw test01 [root@mcw01 salt]# cat config/foo2.conf mcw test02 [root@mcw01 salt]# cat config/foo3.conf mcw test03 [root@mcw01 salt]#
执行,看执行返回信息,可以看到,这里是复制文件,如果目录不存在,不会创建目录
[root@mcw01 salt]# ls /tmp pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 [root@mcw01 salt]# salt "*" state.highstate mcw03: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: False Comment: Parent directory not present Started: 23:14:43.182954 Duration: 171.187 ms Changes: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo3.conf Function: file.managed Result: False Comment: Parent directory not present Started: 23:14:43.354698 Duration: 66.038 ms Changes: Summary for mcw03 ------------ Succeeded: 0 Failed: 2 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 237.225 ms mcw04: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: False Comment: Parent directory not present Started: 23:14:43.233171 Duration: 230.156 ms Changes: Summary for mcw04 ------------ Succeeded: 0 Failed: 1 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 230.156 ms mcw01: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: False Comment: Parent directory not present Started: 23:14:43.243809 Duration: 191.333 ms Changes: ---------- ID: /tmp/foo2.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/foo2.conf updated Started: 23:14:43.435534 Duration: 219.306 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 Summary for mcw01 ------------ Succeeded: 1 (changed=1) Failed: 1 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 410.639 ms vm2.cluster.com: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: False Comment: Parent directory not present Started: 23:14:43.266850 Duration: 523.227 ms Changes: Summary for vm2.cluster.com ------------ Succeeded: 0 Failed: 1 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 523.227 ms ERROR: Minions returned with non-zero exit code [root@mcw01 salt]#
我们给所有节点创建这个目录,然后重新执行一遍
[root@mcw01 salt]# salt "*" cmd.run "mkdir /tmp/mcwconfig" mcw04: mcw03: vm2.cluster.com: mcw01: [root@mcw01 salt]#
重新执行后,都成功了
[root@mcw01 salt]# salt "*" state.highstate mcw04: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf updated Started: 23:17:20.425355 Duration: 280.282 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 Summary for mcw04 ------------ Succeeded: 1 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 280.282 ms mcw03: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf updated Started: 23:17:20.612325 Duration: 213.006 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo3.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/mcwconfig/foo3.conf updated Started: 23:17:20.825853 Duration: 62.726 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 Summary for mcw03 ------------ Succeeded: 2 (changed=2) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 275.732 ms vm2.cluster.com: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf updated Started: 23:17:20.718736 Duration: 245.116 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 Summary for vm2.cluster.com ------------ Succeeded: 1 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 245.116 ms mcw01: ---------- ID: /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf updated Started: 23:17:21.239634 Duration: 284.955 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 ---------- ID: /tmp/foo2.conf Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/foo2.conf is in the correct state Started: 23:17:21.525230 Duration: 38.921 ms Changes: Summary for mcw01 ------------ Succeeded: 2 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 323.876 ms [root@mcw01 salt]#
然后我们检查一下结果:
在mcw02上也有one的结果,所有节点都有1,说明符合预期
[root@mcw02 ~]# ls /tmp systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-chronyd.service-HfikaF systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-php-fpm.service-x5FreD systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-elasticsearch.service-EZPlh4 systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-vgauthd.service-ifVvi8 systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-nginx.service-LXtssE systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-vmtoolsd.service-53dk2n [root@mcw02 ~]# [root@mcw02 ~]# ls /tmp/ mcwconfig systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-php-fpm.service-x5FreD systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-chronyd.service-HfikaF systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-vgauthd.service-ifVvi8 systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-elasticsearch.service-EZPlh4 systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-vmtoolsd.service-53dk2n systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-nginx.service-LXtssE [root@mcw02 ~]# ls /tmp/mcwconfig/ foo1.conf [root@mcw02 ~]# cat /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf mcw test01 [root@mcw02 ~]#
在MCW01上有one和two执行的结果,符合预期
[root@mcw01 salt]# ls /tmp/ foo2.conf pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW mcwconfig systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 [root@mcw01 salt]# cat /tmp/foo2.conf mcw test02 [root@mcw01 salt]# cat /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf mcw test01 [root@mcw01 salt]#
mcw03上除了one的还有three执行的结果的。符合预期
[root@mcw03 ~]# ls /tmp/ mcwconfig systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vgauthd.service-blx3B1 systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-chronyd.service-DM55tO systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-vmtoolsd.service-mrh4Xg systemd-private-d84146a49a7348e5a24d375f7bb722d1-mariadb.service-JlQLud [root@mcw03 ~]# ls /tmp/mcwconfig/ foo1.conf foo3.conf [root@mcw03 ~]# [root@mcw03 ~]# cat /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf mcw test01 [root@mcw03 ~]# cat /tmp/mcwconfig/foo3.conf mcw test03 [root@mcw03 ~]#
执行结果处理-return
1、查看所有return列表
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 sys.list_returners mcw01: - carbon - couchdb - etcd - highstate - local - local_cache - mattermost - multi_returner - pushover - rawfile_json - slack - slack_webhook - smtp - splunk - sqlite3 - syslog - telegram [root@mcw01 ~]#
2、使用redis作为return存储方式
查看客户端,已经安装Python 的redis 客户端
[root@mcw01 ~]# python -c 'import redis;print redis.VERSION' (3, 5, 3) [root@mcw01 ~]
默认就是db 0,进入redis之后
[root@mcw01 ~]# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> select 0 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "name" 127.0.0.1:6379> get name "mcw" 127.0.0.1:6379> exit [root@mcw01 ~]#
配置minion
[root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/ cloud cloud.conf.d cloud.deploy.d cloud.maps.d cloud.profiles.d cloud.providers.d grains master masterbak master.d minion minion.d minion_id pki proxy proxy.d roster [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /etc/salt/minion /etc/salt/minion [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion [root@mcw01 ~]# tail -3 /etc/salt/minion redis.db: '0' redis.host: '127.0.0.1' #ip域名都可以 redis.port: 6379 [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]#
执行完之后,redis啥也没有显示
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 cmd.run hostname --return redis mcw01: mcw01 [root@mcw01 ~]#
[root@mcw01 ~]# redis-cli monitor
OK
查看报错
[root@mcw01 ~]# tail -3 /var/log/salt/minion 2024-01-05 00:33:03,658 [salt.utils.parsers:1111][WARNING ][11840] Minion received a SIGTERM. Exiting. 2024-01-05 00:34:44,422 [salt.minion :2060][ERROR ][17969] Returner redis.returner could not be loaded: 'redis.returner' is not available. 2024-01-05 00:37:26,607 [salt.minion :2060][ERROR ][18253] Returner redis.returner could not be loaded: 'redis.returner' is not available. [root@mcw01 ~]#
看下默认注释掉的
###### Returner settings ###### ############################################ # Default Minion returners. Can be a comma delimited string or a list: # #return: mysql # #return: mysql,slack,redis # #return: # - mysql # - hipchat # - slack
再加个配置
###### Returner settings ######
############################################
# Default Minion returners. Can be a comma delimited string or a list:
#
#return: mysql
#
#return: mysql,slack,redis
#
#return:
# - mysql
# - hipchat
# - slack
return: redis
redis.db: '0'
redis.host: '127.0.0.1'
redis.port: 6379
开启
[root@mcw01 ~]# redis-cli monitor
OK
执行命令
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 cmd.run hostname --return redis mcw01: mcw01 [root@mcw01 ~]#
可以看到redis的输出
[root@mcw01 ~]# redis-cli monitor
OK
1704391078.371650 [0 127.0.0.1:50833] "SELECT" "0"
1704391078.372292 [0 127.0.0.1:50833] "HSET" "ret:20240104175758181713" "mcw01" "{\"success\": true, \"return\": \"mcw01\", \"retcode\": 0, \"jid\": \"20240104175758181713\", \"fun\": \"cmd.run\", \"fun_args\": [\"hostname\"], \"id\": \"mcw01\"}"
1704391078.372339 [0 127.0.0.1:50833] "EXPIRE" "ret:20240104175758181713" "86400"
1704391078.372351 [0 127.0.0.1:50833] "SET" "mcw01:cmd.run" "20240104175758181713"
1704391078.372361 [0 127.0.0.1:50833] "SADD" "minions" "mcw01"
如下,看redis中的数据,一一对应
当前只有一个成员,一个结果,一个任务id。
[root@mcw01 ~]# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "ret:20240104175758181713" 2) "minions" 3) "mcw01:cmd.run" 127.0.0.1:6379> type ret:20240104175758181713 hash 127.0.0.1:6379> hkeys ret:20240104175758181713 1) "mcw01" 127.0.0.1:6379> hget ret:20240104175758181713 mcw01 "{\"success\": true, \"return\": \"mcw01\", \"retcode\": 0, \"jid\": \"20240104175758181713\", \"fun\": \"cmd.run\", \"fun_args\": [\"hostname\"], \"id\": \"mcw01\"}" 127.0.0.1:6379> 127.0.0.1:6379> type minions set 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers minions 1) "mcw01" 127.0.0.1:6379> 127.0.0.1:6379> type mcw01:cmd.run string 127.0.0.1:6379> get mcw01:cmd.run "20240104175758181713" 127.0.0.1:6379>
再次执行
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 cmd.run "uptime" mcw01: 02:15:14 up 1 day, 1:51, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.06 [root@mcw01 ~]#
1704392114.943790 [0 127.0.0.1:50847] "SELECT" "0" 1704392114.944094 [0 127.0.0.1:50847] "HSET" "ret:20240104181514743282" "mcw01" "{\"success\": true, \"return\": \" 02:15:14 up 1 day, 1:51, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.06\", \"retcode\": 0, \"jid\": \"20240104181514743282\", \"fun\": \"cmd.run\", \"fun_args\": [\"uptime\"], \"id\": \"mcw01\"}" 1704392114.944139 [0 127.0.0.1:50847] "EXPIRE" "ret:20240104181514743282" "86400" 1704392114.944145 [0 127.0.0.1:50847] "SET" "mcw01:cmd.run" "20240104181514743282" 1704392114.944151 [0 127.0.0.1:50847] "SADD" "minions" "mcw01"
多个结果拼接了任务id
127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "ret:20240104175758181713" 2) "mcw01:cmd.run" 3) "ret:20240104181514743282" 4) "minions" 127.0.0.1:6379>
其它两个键还是复用的
127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "ret:20240104175758181713" 2) "mcw01:cmd.run" 3) "ret:20240104181514743282" 4) "minions" 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers minions 1) "mcw01" 127.0.0.1:6379> get mcw01:cmd.run "20240104181514743282" 127.0.0.1:6379>
mcw03,没有配置minion redis,所以灭有写进去。一个模块函数,就一个键
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 cmd.run "uptime" mcw01: 02:15:14 up 1 day, 1:51, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.06 [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -L mcw01,mcw03 cmd.run "uptime" mcw03: 02:19:53 up 1 day, 1:56, 1 user, load average: 0.01, 0.03, 0.05 mcw01: 02:19:53 up 1 day, 1:56, 3 users, load average: 0.06, 0.03, 0.05 [root@mcw01 ~]# salt -L mcw01,mcw03 test.ping mcw03: True mcw01: True [root@mcw01 ~]#
test.ping就是另外一个键
127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "ret:20240104175758181713" 2) "ret:20240104181953272801" 3) "mcw01:cmd.run" 4) "ret:20240104181514743282" 5) "minions" 127.0.0.1:6379> 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "ret:20240104175758181713" 2) "ret:20240104181953272801" 3) "mcw01:cmd.run" 4) "ret:20240104181514743282" 5) "mcw01:test.ping" 6) "ret:20240104182030031354" 7) "minions" 127.0.0.1:6379>
Job管理
1、通过salt-run来管理job
该命令对job管理的一些用法
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run -d|grep jobs jobs.active: Return a report on all actively running jobs from a job id centric salt-run jobs.active jobs.exit_success: salt-run jobs.exit_success 20160520145827701627 jobs.last_run: List all detectable jobs and associated functions salt-run jobs.last_run salt-run jobs.last_run target=nodename salt-run jobs.last_run function='cmd.run' salt-run jobs.last_run metadata="{'foo': 'bar'}" jobs.list_job: salt-run jobs.list_job 20130916125524463507 salt-run jobs.list_job 20130916125524463507 --out=pprint jobs.list_jobs: List all detectable jobs and associated functions If more than one of the below options are used, only jobs which match salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_metadata='{"foo": "bar", "baz": "qux"}' Can be passed as a string or a list. Returns jobs which match the salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_function='test.*' salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_function='["test.*", "pkg.install"]' salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_function='test.*,pkg.install' Can be passed as a string or a list. Returns jobs which match the salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_target='*.mydomain.tld' salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_target='["db*", "myminion"]' salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_target='db*,myminion' module is not installed, this argument will be ignored). Returns jobs module is not installed, this argument will be ignored). Returns jobs salt-run jobs.list_jobs salt-run jobs.list_jobs search_function='test.*' search_target='localhost' search_metadata='{"bar": "foo"}' salt-run jobs.list_jobs start_time='2015, Mar 16 19:00' end_time='2015, Mar 18 22:00' jobs.list_jobs_filter: List all detectable jobs and associated functions salt-run jobs.list_jobs_filter 50 salt-run jobs.list_jobs_filter 100 filter_find_job=False jobs.lookup_jid: salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20130916125524463507 salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20130916125524463507 --out=highstate jobs.master: salt-run jobs.master jobs.print_job: salt-run jobs.print_job 20130916125524463507 It can also be used to schedule jobs directly on the master, for example: [root@mcw01 ~]#

取消时有jid
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 cmd.run "sleep 600;whoami" ^C Exiting gracefully on Ctrl-c This job's jid is: 20240105155246308124 The minions may not have all finished running and any remaining minions will return upon completion. To look up the return data for this job later, run the following command: salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20240105155246308124 Exception ignored in: <generator object _read at 0x7fe602619200> Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/salt/transport/ipc.py", line 702, in _read TypeError: catching classes that do not inherit from BaseException is not allowed [root@mcw01 ~]#
理应有个结果的,没有看到预期的job运行结果
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20240105155246308124 [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看这个job详细记录
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run jobs.list_job 20240105155246308124 Arguments: - sleep 600;whoami Function: cmd.run Minions: - mcw03 Result: ---------- StartTime: 2024, Jan 05 15:52:46.308124 Target: mcw03 Target-type: glob User: root jid: 20240105155246308124 [root@mcw01 ~]#
我上面的命令睡的太久了,这次短一点就能看到效果了
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 cmd.run "sleep 6;whoami" ^C Exiting gracefully on Ctrl-c This job's jid is: 20240105155801236238 The minions may not have all finished running and any remaining minions will return upon completion. To look up the return data for this job later, run the following command: salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20240105155801236238 Exception ignored in: <generator object _read at 0x7fc733950d58> Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/salt/transport/ipc.py", line 702, in _read TypeError: catching classes that do not inherit from BaseException is not allowed [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20240105155801236238 mcw03: root [root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run jobs.list_job 20240105155801236238 Arguments: - sleep 6;whoami Function: cmd.run Minions: - mcw03 Result: ---------- mcw03: ---------- retcode: 0 return: root success: True StartTime: 2024, Jan 05 15:58:01.236238 Target: mcw03 Target-type: glob User: root jid: 20240105155801236238 [root@mcw01 ~]#
上面那个睡300秒的salt命令,虽然ctrl c 取消了,但是还是一直在后台继续运行这个命令,当过了睡眠时间之后,结果就出来了。过了10分钟以上,依然能查到这个job的结果信息
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run jobs.list_job 20240105155246308124 Arguments: - sleep 600;whoami Function: cmd.run Minions: - mcw03 Result: ---------- mcw03: ---------- retcode: 0 return: root success: True StartTime: 2024, Jan 05 15:52:46.308124 Target: mcw03 Target-type: glob User: root jid: 20240105155246308124 [root@mcw01 ~]#
2、通过saltstack module来管理job


查看相关module用法。上面的不支持杀job,这个可以
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt \* sys.doc saltutil |grep job saltutil.clear_job_cache: Forcibly removes job cache folders and files on a minion. salt '*' saltutil.clear_job_cache hours=12 saltutil.find_cached_job: Return the data for a specific cached job id. Note this only works if cache_jobs has previously been set to True on the minion. salt '*' saltutil.find_cached_job <job id> saltutil.find_job: Return the data for a specific job id that is currently running. The job id to search for and return data. salt '*' saltutil.find_job <job id> Note that the find_job function only returns job information when the job is still running. If the job is currently running, the output looks something like this: # salt my-minion saltutil.find_job 20160503150049487736 If the job has already completed, the job cannot be found and therefore the function returns # salt my-minion saltutil.find_job 20160503150049487736 saltutil.kill_all_jobs: Sends a kill signal (SIGKILL 9) to all currently running jobs salt '*' saltutil.kill_all_jobs saltutil.kill_job: Sends a kill signal (SIGKILL 9) to the named salt job's process salt '*' saltutil.kill_job <job id> salt master_minion saltutil.runner jobs.list_jobs saltutil.signal_job: Sends a signal to the named salt job's process salt '*' saltutil.signal_job <job id> 15 saltutil.term_all_jobs: Sends a termination signal (SIGTERM 15) to all currently running jobs salt '*' saltutil.term_all_jobs saltutil.term_job: Sends a termination signal (SIGTERM 15) to the named salt job's process salt '*' saltutil.term_job <job id> [root@mcw01 ~]#
执行后,取消命令
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 cmd.run 'sleep 200;whoami' ^C Exiting gracefully on Ctrl-c This job's jid is: 20240105160651751643 The minions may not have all finished running and any remaining minions will return upon completion. To look up the return data for this job later, run the following command: salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20240105160651751643 Exception ignored in: <generator object _read at 0x7f560fa4bbf8> Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/salt/transport/ipc.py", line 702, in _read TypeError: catching classes that do not inherit from BaseException is not allowed [root@mcw01 ~]#
查找这个job信息,然后kill job
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 saltutil.find_job 20240105160651751643 mcw03: ---------- arg: - sleep 200;whoami fun: cmd.run jid: 20240105160651751643 pid: 113644 ret: tgt: mcw03 tgt_type: glob user: root [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 saltutil.kill_job 20240105160651751643 mcw03: Signal 9 sent to job 20240105160651751643 at pid 113644 [root@mcw01 ~]#
salt命令ctrl c 取消后,依然在执行
Event和Reactor系统
1、查看event事件
首先执行命令,会夯住,然后在其它窗口执行命令,就会打印正在执行的命令的相关信息
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run state.event pretty=True
执行命令
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt \* test.ping
mcw04:
True
vm2.cluster.com:
True
mcw03:
True
mcw01:
True
[root@mcw01 ~]#
当执行上面的命令之后,查看事件的命令输出。可以看到每个事件的详细信息
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run state.event pretty=True 20240105161622436852 { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:16:22.437163", "minions": [ "mcw01", "mcw03", "mcw04", "vm2.cluster.com" ] } salt/job/20240105161622436852/new { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:16:22.438053", "arg": [], "fun": "test.ping", "jid": "20240105161622436852", "minions": [ "mcw01", "mcw03", "mcw04", "vm2.cluster.com" ], "missing": [], "tgt": "*", "tgt_type": "glob", "user": "root" } salt/job/20240105161622436852/ret/mcw04 { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:16:22.592677", "cmd": "_return", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "id": "mcw04", "jid": "20240105161622436852", "retcode": 0, "return": true, "success": true } salt/job/20240105161622436852/ret/vm2.cluster.com { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:16:22.597128", "cmd": "_return", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "id": "vm2.cluster.com", "jid": "20240105161622436852", "retcode": 0, "return": true, "success": true } salt/job/20240105161622436852/ret/mcw03 { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:16:22.608933", "cmd": "_return", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "id": "mcw03", "jid": "20240105161622436852", "retcode": 0, "return": true, "success": true } salt/job/20240105161622436852/ret/mcw01 { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:16:22.659923", "cmd": "_return", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "id": "mcw01", "jid": "20240105161622436852", "retcode": 0, "return": true, "success": true }
如果不加后面的那个参数,是一行输出的
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run state.event 20240105162044113396 {"minions": ["mcw01", "mcw03", "mcw04", "vm2.cluster.com"], "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:20:44.113843"} salt/job/20240105162044113396/new {"jid": "20240105162044113396", "tgt_type": "glob", "tgt": "*", "user": "root", "fun": "test.ping", "arg": [], "minions": ["mcw01", "mcw03", "mcw04", "vm2.cluster.com"], "missing": [], "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:20:44.115138"} salt/job/20240105162044113396/ret/vm2.cluster.com {"cmd": "_return", "id": "vm2.cluster.com", "success": true, "return": true, "retcode": 0, "jid": "20240105162044113396", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:20:44.323141"} salt/job/20240105162044113396/ret/mcw04 {"cmd": "_return", "id": "mcw04", "success": true, "return": true, "retcode": 0, "jid": "20240105162044113396", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:20:44.322121"} salt/job/20240105162044113396/ret/mcw03 {"cmd": "_return", "id": "mcw03", "success": true, "return": true, "retcode": 0, "jid": "20240105162044113396", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:20:44.325422"} salt/job/20240105162044113396/ret/mcw01 {"cmd": "_return", "id": "mcw01", "success": true, "return": true, "retcode": 0, "jid": "20240105162044113396", "fun": "test.ping", "fun_args": [], "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:20:44.395680"}
只有一个目标主机的时候,结果如下
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 cmd.run "hostname" mcw03: mcw03 [root@mcw01 ~]#
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run state.event pretty=True 20240105162223643698 { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:22:23.644129", "minions": [ "mcw03" ] } salt/job/20240105162223643698/new { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:22:23.644767", "arg": [ "hostname" ], "fun": "cmd.run", "jid": "20240105162223643698", "minions": [ "mcw03" ], "missing": [], "tgt": "mcw03", "tgt_type": "glob", "user": "root" } salt/job/20240105162223643698/ret/mcw03 { "_stamp": "2024-01-05T16:22:23.779438", "cmd": "_return", "fun": "cmd.run", "fun_args": [ "hostname" ], "id": "mcw03", "jid": "20240105162223643698", "retcode": 0, "return": "mcw03", "success": true }
2、在master上配置reactor
查看默认配置
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master ###### Reactor Settings ##### ########################################### # Define a salt reactor. See https://docs.saltproject.io/en/latest/topics/reactor/ #reactor: [] #Set the TTL for the cache of the reactor configuration. #reactor_refresh_interval: 60 #Configure the number of workers for the runner/wheel in the reactor. #reactor_worker_threads: 10 #Define the queue size for workers in the reactor. #reactor_worker_hwm: 10000
在默认配置下面添加如下配置
[root@mcw01 ~]# ls /srv/ pillar salt [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master reactor: - 'salt/auth' - /srv/reactor/Minion.sls - 'salt/minion/Minion/start': - /srv/reactor/auto.sls
添加上面涉及到的文件
[root@mcw01 ~]# ls /srv/ pillar salt [root@mcw01 ~]# mkdir /srv/reactor [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/reactor/Minion.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/reactor/auto.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /srv/salt/machangwei.sls [root@mcw01 ~]# echo mcwtest >> /srv/salt/example [root@mcw01 ~]# tree /srv/ /srv/ ├── pillar │ ├── packages.sls │ ├── role │ │ └── base.sls │ ├── top.sls │ └── zabbix │ ├── init.sls │ └── services.sls ├── reactor │ ├── auto.sls │ └── Minion.sls └── salt ├── config │ ├── foo2.conf │ └── foo3.conf ├── example ├── foo1.conf ├── machangwei.sls ├── one.sls ├── three │ └── three.sls ├── top.sls └── two └── init.sls 8 directories, 16 files [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/reactor/Minion.sls {% if 'act' in data and data['act'] == 'pend' and data['id'].startswith('mcw') %} key_accept: wheel.key.accept: - match: {{ data['id'] }} {% endif %} [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/reactor/auto.sls run_state: local.state.sls: - tgt: {{ data['id'] }} - arg: - machangwei run_init: local.cmd.run: - tgt: {{ data['id'] }} - arg: - echo initsok >>/tmp/cpis [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/machangwei.sls /tmp/example: file.managed: - source: salt://example [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/example mcwtest [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /tmp/ foo2.conf systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-chronyd.service-7J44xg systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT mcwconfig systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-elasticsearch.service-etizSP systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW pymp-3dcmrmkf systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vgauthd.service-UxixUS systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vmtoolsd.service-twrwNM yum_save_tx.2024-01-04.20-55.PzeUaB.yumtx [root@mcw01 ~]#
然后重启master
报错了
2024-01-06 11:22:01,454 [salt.config :1924][ERROR ][18691] Error parsing configuration file: /etc/salt/master - while parsing a block collection
in "/etc/salt/master", line 1065, column 3
did not find expected '-' indicator
in "/etc/salt/master", line 1066, column 5
这里缺少一个冒号
reactor: - 'salt/auth': - /srv/reactor/Minion.sls - 'salt/minion/Minion/start': - /srv/reactor/auto.sls
重启一下
[root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt \* cmd.run "ls /tmp" mcw04: mcwconfig systemd-private-ada6073b3c20458891dfe1a21ab245c1-chronyd.service-JEAJ6b systemd-private-ada6073b3c20458891dfe1a21ab245c1-vgauthd.service-ZPv7H0 systemd-private-ada6073b3c20458891dfe1a21ab245c1-vmtoolsd.service-aVrNC5 mcw03: mcwconfig systemd-private-4dbcfa68818d44768e798e4765af0c82-chronyd.service-OToQlB systemd-private-4dbcfa68818d44768e798e4765af0c82-mariadb.service-GPJFOb systemd-private-4dbcfa68818d44768e798e4765af0c82-vgauthd.service-qUxO3G systemd-private-4dbcfa68818d44768e798e4765af0c82-vmtoolsd.service-1nYdc3 mcw01: foo2.conf mcwconfig pymp-951xj82h pymp-wmpe5yl7 systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-chronyd.service-7J44xg systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-elasticsearch.service-etizSP systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vgauthd.service-UxixUS systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vmtoolsd.service-twrwNM systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 yum_save_tx.2024-01-04.20-55.PzeUaB.yumtx vm2.cluster.com: mcwconfig systemd-private-0aa91ae896084fb7ad13341d948d8ed5-chronyd.service-cEY397 systemd-private-0aa91ae896084fb7ad13341d948d8ed5-elasticsearch.service-FGXEjL systemd-private-0aa91ae896084fb7ad13341d948d8ed5-nginx.service-6ACRap systemd-private-0aa91ae896084fb7ad13341d948d8ed5-php-fpm.service-J2LXyb systemd-private-0aa91ae896084fb7ad13341d948d8ed5-vgauthd.service-BK42db systemd-private-0aa91ae896084fb7ad13341d948d8ed5-vmtoolsd.service-fQfw3v systemd-private-225a8b2272d3432f9b2e770d29806173-chronyd.service-xlUgJ5 systemd-private-225a8b2272d3432f9b2e770d29806173-elasticsearch.service-k8h3el systemd-private-225a8b2272d3432f9b2e770d29806173-nginx.service-bL2MYj systemd-private-225a8b2272d3432f9b2e770d29806173-php-fpm.service-vCbqbZ systemd-private-225a8b2272d3432f9b2e770d29806173-vgauthd.service-sdwjgO systemd-private-225a8b2272d3432f9b2e770d29806173-vmtoolsd.service-zWzMPp systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-chronyd.service-HfikaF systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-elasticsearch.service-EZPlh4 systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-nginx.service-LXtssE systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-php-fpm.service-x5FreD systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-vgauthd.service-ifVvi8 systemd-private-b04546fa3acb4f2faffec85254e771e1-vmtoolsd.service-53dk2n [root@mcw01 ~]#
查看mcw01的,并重启mcw01的minion
[root@mcw01 ~]# tree /srv/ /srv/ ├── pillar │ ├── packages.sls │ ├── role │ │ └── base.sls │ ├── top.sls │ └── zabbix │ ├── init.sls │ └── services.sls ├── reactor │ ├── auto.sls │ └── Minion.sls └── salt ├── config │ ├── foo2.conf │ └── foo3.conf ├── example ├── foo1.conf ├── machangwei.sls ├── one.sls ├── three │ └── three.sls ├── top.sls └── two └── init.sls 8 directories, 16 files [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /tmp/ foo2.conf systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-chronyd.service-7J44xg systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT mcwconfig systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-elasticsearch.service-etizSP systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vgauthd.service-UxixUS systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 pymp-wmpe5yl7 systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vmtoolsd.service-twrwNM yum_save_tx.2024-01-04.20-55.PzeUaB.yumtx [root@mcw01 ~]#
[root@mcw01 ~]# tree /srv/ /srv/ ├── pillar │ ├── packages.sls │ ├── role │ │ └── base.sls │ ├── top.sls │ └── zabbix │ ├── init.sls │ └── services.sls ├── reactor │ ├── auto.sls │ └── Minion.sls └── salt ├── config │ ├── foo2.conf │ └── foo3.conf ├── example ├── foo1.conf ├── machangwei.sls ├── one.sls ├── three │ └── three.sls ├── top.sls └── two └── init.sls 8 directories, 16 files [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /tmp/ foo2.conf systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-chronyd.service-7J44xg systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-chronyd.service-iPHBmT mcwconfig systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-elasticsearch.service-etizSP systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vgauthd.service-B90KjW pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vgauthd.service-UxixUS systemd-private-204b4e6d6f0e4b6aa338f9e695e667f3-vmtoolsd.service-KI4gu7 pymp-wmpe5yl7 systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-vmtoolsd.service-twrwNM yum_save_tx.2024-01-04.20-55.PzeUaB.yumtx [root@mcw01 ~]#
另外一个窗口中,可以看到已经执行了服务。以mcw开头的机器,就会执行key接受的这个任务,已经开始执行了,也就是执行了salt/auth,但是另外一个,还没有执行
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt-run state.event pretty=True salt/auth { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T04:17:53.227959", "act": "accept", "id": "mcw01", "pub": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAyTxKCqHByVVOI86yhM3T\nUdW04ekQOwUzt3c+xjESkXkK52CcW+63bj0dFUWo/ou/hVFFQeVpVua6DYIwiXR6\nl36nihYd8S5CCJXXW04B1+3bzjNA8wqYZjDWQ2C+kVF5A7r3XVucrdKPhCli4pRi\nCpPWPkPH8FWHIMdrQPP+MdorRUP4mF7ftdjq7pDkOgxp/PSrRVGi7Tri/DMJlstb\nHGxC/KM06eKSDhwpNXpIVNVjLteu2u+lNXN/CbKBCtqtZv/492v7RL075zQnkHsu\nZSCwZfpGAU9EeB+6FcuO9mDI/MmPaAir4X3TTukPxpAo8imOSWvvpHwvV01imowv\nOQIDAQAB\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n", "result": true } minion/refresh/mcw01 { "Minion data cache refresh": "mcw01", "_stamp": "2024-01-06T04:17:53.400935" } minion_start { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T04:17:54.125746", "cmd": "_minion_event", "data": "Minion mcw01 started at Sat Jan 6 12:17:54 2024", "id": "mcw01", "pretag": null, "tag": "minion_start" } salt/minion/mcw01/start { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T04:17:54.137136", "cmd": "_minion_event", "data": "Minion mcw01 started at Sat Jan 6 12:17:54 2024", "id": "mcw01", "pretag": null, "tag": "salt/minion/mcw01/start" } salt/job/20240106041755232327/ret/mcw01 { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T04:17:55.233395", "arg": [], "cmd": "_return", "fun": "mine.update", "fun_args": [], "id": "mcw01", "jid": "20240106041755232327", "pid": 22159, "retcode": 0, "return": null, "schedule": "__mine_interval", "success": true, "tgt": "mcw01", "tgt_type": "glob" }
上面虽然用到了salt/auth,但是并没有创建这个文件
[root@mcw01 ~]# ls /srv/ pillar reactor salt [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /srv/salt/ config example foo1.conf machangwei.sls one.sls three top.sls two [root@mcw01 ~]#
好像其它的机器,也是执行了一次salt/auth
salt/auth { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T05:39:27.056399", "act": "accept", "id": "mcw01", "pub": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAyTxKCqHByVVOI86yhM3T\nUdW04ekQOwUzt3c+xjESkXkK52CcW+63bj0dFUWo/ou/hVFFQeVpVua6DYIwiXR6\nl36nihYd8S5CCJXXW04B1+3bzjNA8wqYZjDWQ2C+kVF5A7r3XVucrdKPhCli4pRi\nCpPWPkPH8FWHIMdrQPP+MdorRUP4mF7ftdjq7pDkOgxp/PSrRVGi7Tri/DMJlstb\nHGxC/KM06eKSDhwpNXpIVNVjLteu2u+lNXN/CbKBCtqtZv/492v7RL075zQnkHsu\nZSCwZfpGAU9EeB+6FcuO9mDI/MmPaAir4X3TTukPxpAo8imOSWvvpHwvV01imowv\nOQIDAQAB\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n", "result": true } minion/refresh/mcw01 { "Minion data cache refresh": "mcw01", "_stamp": "2024-01-06T05:39:27.621480" } minion_start { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T05:39:28.419093", "cmd": "_minion_event", "data": "Minion mcw01 started at Sat Jan 6 13:39:28 2024", "id": "mcw01", "pretag": null, "tag": "minion_start" } salt/minion/mcw01/start { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T05:39:28.429517", "cmd": "_minion_event", "data": "Minion mcw01 started at Sat Jan 6 13:39:28 2024", "id": "mcw01", "pretag": null, "tag": "salt/minion/mcw01/start" } salt/job/20240106053929565215/ret/mcw01 { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T05:39:29.568721", "arg": [], "cmd": "_return", "fun": "mine.update", "fun_args": [], "id": "mcw01", "jid": "20240106053929565215", "pid": 32508, "retcode": 0, "return": null, "schedule": "__mine_interval", "success": true, "tgt": "mcw01", "tgt_type": "glob" } 20240106060548872715 { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T06:05:48.876066", "minions": [ "mcw01", "mcw03", "mcw04", "vm2.cluster.com" ] } salt/job/20240106060548872715/new { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T06:05:48.878543", "arg": [], "fun": "sys.list_functions", "jid": "20240106060548872715", "minions": [ "mcw01", "mcw03", "mcw04", "vm2.cluster.com" ], "missing": [], "tgt": "*", "tgt_type": "glob", "user": "root" } salt/auth { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T06:05:49.025359", "act": "accept", "id": "vm2.cluster.com", "pub": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA2fAKMxjHl05+lc0/WoQe\nyGW+1UJlutaBhjUELxnr9MuhgWf+0wL0rBVe+ZJ69K1LPDH+rIKo/JofrvlRpYGv\neLtOj21w6o/JI19u42rG8+O8eTQs56H4cnU+Ue2BcK+uBJZ5ypbqYpnaRz9BxpGQ\nWxHcTBckcBqetcML7ndA4QN3KhiM7FeX/8Ju7TUyWOyGBzZ1oRHZo8SWOz0sHqwC\neJWYHh15LNcc2X44n2Dik5dWUwn7elwxGJw3CmgxZmCc/jDyPNWU2wRZLhRPeqT7\nV7qUGMC7lm6ux35vTSU95VD6AOkGWXgprSjgoLOrckYpaZ8uJfAxxW0UMijm0l0p\n0QIDAQAB\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n", "result": true } salt/auth { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T06:05:49.021970", "act": "accept", "id": "mcw03", "pub": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAyku3ih15beDwGYIqXtnT\nJxIJ0Io0r9EkbD0bt6k3SMS1CO5CIAiywnTFTmKiLJcw/7OQi+hlBkpybSzwvAqy\nxnDFCTb+WrE0/2kZZTl1rMyIyE66yGWE70RYBVr6piyZuRRmn722PG2tvRSM7waR\nzYHxAcWCXPInAcWe/s2dh1IAJMxTifpFppOeMeNeF/EonKQIZHThW2ZxpflMe7vG\nm0l/9n2G8gN8M9w7udhc0p76YcnILbDqVU3QVULSeZLXxPpcpw428l7VIKhFE/HA\nnMsn42T+yp+iE8HAbKrZvtI569NsQMio68DN3z7ufVBFI8NKFe3bX9o7C8Q3qZFe\n9QIDAQAB\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n", "result": true } salt/auth { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T06:05:49.040672", "act": "accept", "id": "mcw04", "pub": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAnxPzUaGFkPQEL0lyNykl\nG0nuFTRJcloOW1b9wHOJiroGPe8ScDiVHVnGp/MPhOSfosQVUPdPH91k5+tmq1YS\nNCr6Vk8lWNdQfcXvSeSPWuVTBDgU6XSj3ToqjG22tVX8x5MQlIZZDdbrJvrMy92G\nWB43hwNKjs9GO07kTRbEYffyZSm2q2+zE8xBqAhYqtDXS9tlhR5qK/87bCd4iEwH\nvDzu4Lp7ayqukxpE2VbrY+pA8HeOsXKnN+gdD0dabHvUknCKe1Syz1ujLYlnGpmv\nhp2rXP7PiiQVxwG0gToVoDNJHi/0Q5zczd3IBLenEZd5VPJqXuto3Ino2nlB1+qt\nJQIDAQAB\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n", "result": true } salt/job/20240106060548872715/ret/mcw03 { "_stamp": "2024-01-06T06:05:51.679033", "cmd": "_return", "fun": "sys.list_functions", "fun_args": [], "id": "mcw03", "jid": "20240106060548872715", "retcode": 0, "return": [ "acl.delfacl", "acl.getfacl",
这种写法放到别处。报错了
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/xiaoma.sls run_init: local.cmd.run: - tgt: {{ data['id'] }} - arg: - echo xiaoma >>/tmp/xiaoma.conf [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 state.sls xiaoma mcw01: Data failed to compile: ---------- Rendering SLS 'base:xiaoma' failed: Jinja variable 'data' is undefined ERROR: Minions returned with non-zero exit code [root@mcw01 ~]#
把之前的这个tgt,改成mcw01
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/reactor/auto.sls run_state: local.state.sls: - tgt: mcw01 - arg: - machangwei run_init: local.cmd.run: - tgt: mcw01 - arg: - echo initsok >>/tmp/cpis [root@mcw01 ~]#
再次修改,还是不行
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/xiaoma.sls run_init: cmd.run: - tgt: mcw01 - arg: - echo xiaoma >>/tmp/xiaoma.conf [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 state.sls xiaoma mcw01: ---------- ID: run_init Function: cmd.run Result: False Comment: Command "run_init" run Started: 14:54:13.035365 Duration: 13.965 ms Changes: ---------- pid: 50689 retcode: 127 stderr: /bin/sh: run_init: command not found stdout: Summary for mcw01 ------------ Succeeded: 0 (changed=1) Failed: 1 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 13.965 ms ERROR: Minions returned with non-zero exit code [root@mcw01 ~]#
Renderer组件
Python定义state文件。通过观察可以发现,第一行就是告诉用salt,这是Python定义的state文件。然后定义一个run函数,函数里创建一个yaml转换为字典后的数据内容,然后返回这个数据。因为这个数据,也可以转换为yaml格式数据,所以跟定义yaml格式的state文件,效果一样。不过这里函数需要返回这个定义的数据。函数名称是否可以改变,以后测试一下。
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/test.sls #!py def run(): example={} example['/tmp/test'] = { 'file.managed': [ {'source':'salt://test'}, {'mode':'644'}, {'template':'jinja'}, {'group':'root'}, {'context':{ 'a': __grains__['os'], 'b': __pillar__['a'], }, }, ] } return example [root@mcw01 ~]#
对比yaml的state.sls文件
[root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/one.sls /tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://foo1.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - backup: minion [root@mcw01 ~]#
我们将yaml格式的yaml,用Python读取打印出来,可以看到和用Python定义的state文件,格式上是一样。我们以后,也可以用如下这种方式,去使用yaml文件。也就是Python里面,怎么定义的字典,yaml怎么去写,怎么相互转换的,可以去思考一下。并且键值对,键也可以是路径,也可以是函数名称。
Python里面取grains和pillar,用__grains_['os'],__pillar_['a']取值。而yaml里面,用grains['key'],pillar['key']取值
[root@mcw01 ~]# python3 Python 3.6.8 (default, Nov 14 2023, 16:29:52) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import yaml,json >>> with open('/srv/salt/one.sls','r') as f: ... print(yaml.safe_load(f)) ... {'/tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf': {'file.managed': [{'source': 'salt://foo1.conf'}, {'user': 'root'}, {'group': 'root'}, {'mode': 644}, {'backup': 'minion'}]}} >>> >>> with open('/srv/salt/one.sls','r') as f: ... print(json.dumps(yaml.safe_load(f),indent=4)) ... { "/tmp/mcwconfig/foo1.conf": { "file.managed": [ { "source": "salt://foo1.conf" }, { "user": "root" }, { "group": "root" }, { "mode": 644 }, { "backup": "minion" } ] } } >>> exit() [root@mcw01 ~]#
执行Python定义的state文件,创建需要的相关文件,并且查看结果,符合预期。这里需要pillar数据,
[root@mcw01 ~]# echo mcwtest >>/srv/salt/test [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/salt/test mcwtest [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/top.sls base: '*': - packages - test #- services 'mcw[0-9]*': - role.base [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /srv/pillar/test.sls a: b [root@mcw01 ~]# [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /tmp/ pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-elasticsearch.service-etizSP systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-vgauthd.service-GPQ382 pymp-a2qgw4s2 systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-chronyd.service-nn8Nt6 systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-vmtoolsd.service-r4n4T4 pymp-jicisk0n systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-elasticsearch.service-2czSvC [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw01 state.sls test mcw01: ---------- ID: /tmp/test Function: file.managed Result: True Comment: File /tmp/test updated Started: 08:29:06.257497 Duration: 82.981 ms Changes: ---------- diff: New file mode: 0644 Summary for mcw01 ------------ Succeeded: 1 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 1 Total run time: 82.981 ms [root@mcw01 ~]# ls /tmp/ pymp-951xj82h systemd-private-1694b2a8c81e44569a83c4159855bbe0-elasticsearch.service-etizSP systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-vgauthd.service-GPQ382 pymp-a2qgw4s2 systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-chronyd.service-nn8Nt6 systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-vmtoolsd.service-r4n4T4 pymp-jicisk0n systemd-private-8b22f8d8932548d3a88138c2c7dbaae7-elasticsearch.service-2czSvC test [root@mcw01 ~]# cat /tmp/test mcwtest [root@mcw01 ~]#
mine组件
第一种方式
一开始没有,send之后保存下来了,然后就能get到
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 mine.get mcw03 network.ip_addrs mcw03: ---------- [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 mine.send network.ip_addrs interface=ens33 mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 mine.get mcw03 network.ip_addrs mcw03: ---------- mcw03: - 10.0.0.13 [root@mcw01 ~]#
这里只保存了一个,
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 mine.send network.ip_addrs interface=ens34 mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 mine.get mcw03 network.ip_addrs mcw03: ---------- mcw03: [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 mine.send network.ip_addrs interface=ens33 mcw03: True [root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw03 mine.get mcw03 network.ip_addrs mcw03: ---------- mcw03: - 10.0.0.13 [root@mcw01 ~]#
第二种方式
没有获取到地址
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw04 mine.get mcw04 network.ip_addrs mcw04: ---------- mcw04: [root@mcw01 ~]#
minion配置文件里面配置
[root@mcw04 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion [root@mcw04 ~]# tail -3 /etc/salt/minion mine_functions: network.ip_addrs: interface: ens33 [root@mcw04 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@mcw04 ~]#
然后再次获取
[root@mcw01 ~]# salt mcw04 mine.get mcw04 network.ip_addrs mcw04: ---------- mcw04: - 10.0.0.14 [root@mcw01 ~]#
peer组件,在minion上让master执行salt任务
配置master
[root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master [root@mcw01 ~]# tail -6 /etc/salt/master peer: mcw04: - test.ping peer_run: mcw04: - manage.up [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master [root@mcw01 ~]#
客户端执行命令,后面那个,目标不是只能自己主机,可以是所有主机
[root@mcw04 ~]# salt-call publish.publish mcw04 test.ping local: ---------- mcw04: True [root@mcw04 ~]# salt-call publish.publish mcw01 test.ping local: ---------- mcw01: True [root@mcw04 ~]#
下面运行其它模块,
这个模块不可以,因为master上没有配置 minion上可以用这个命令
[root@mcw04 ~]# salt-call publish.publish mcw04 test.echo machangwei local: ---------- [root@mcw04 ~]#
修改master上,改为test.*,这样就能用test.echo了
[root@mcw01 ~]# tail -6 /etc/salt/master peer: mcw04: - test.ping peer_run: mcw04: - manage.up [root@mcw01 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master [root@mcw01 ~]# tail -6 /etc/salt/master peer: mcw04: - test.* peer_run: mcw04: - manage.up [root@mcw01 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master [root@mcw01 ~]#
再次执行,可以打印出来信息了
[root@mcw04 ~]# salt-call publish.publish mcw04 test.echo machangwei local: ---------- mcw04: machangwei [root@mcw04 ~]#
运行runner,没有任何返回,也就是没有成功,
[root@mcw04 ~]# salt-call publish.runner mcw04 manage.up local: ---------- [root@mcw04 ~]# salt-call publish.runner mcw04 manage.down local: ---------- [root@mcw04 ~]#
salt file.recurse 实际使用案例
salt file.recurse 是 SaltStack 中的一个模块,用于递归地管理文件。SaltStack 是一个开源的配置管理和远程执行系统,用于自动化管理网络中的多个系统和服务器。
使用 salt file.recurse 模块,你可以对指定目录下的所有文件进行递归操作。这些操作包括但不限于复制、移动、删除、修改等。
例如,如果你想在所有的 Minion 上递归地删除 /tmp/old_files 目录及其所有内容,你可以使用以下命令:
salt '*' salt.states.file.recurse: - name: /tmp/old_files - state: absent
这条命令会确保在所有的 Minion 上 /tmp/old_files 目录及其所有内容都被删除。
这只是 salt file.recurse 的一个基本用法。你可以根据自己的需求进行更复杂的操作和定制。
ls .//salt/nginx/files/ssl/xxxxcn/ xx.com.crt xx.com.key less salt/nginx/zz_nginx/ssl.sls nginx_ssl: file.recurse: - name: /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/ssl - source: salt://nginx/files/ssl/xxxxcn - backup: minion - makedirs: True - clean: True - user: root - group: root - file_mode: 644 - dir_mode: 755 - include_empty: True - recurse: - user - group - mode grep "zz_nginx.ssl" -r * salt/nginx/zz_nginx/init.sls: - nginx.zz_nginx.ssl cat salt/nginx/zz_nginx/init.sls include: - nginx.zz_nginx.conf - nginx.zz_nginx.vhost - nginx.zz_nginx.ssl - nginx.service_openresty - nginx.luascripts
salt 推送文件到远程服务器
将脚本传送到远程机器执行
salt机器上推送本地文件/home/ares/xiao1.log,到远程机器/home/ares/
# salt-cp 'vm-rancher001.xxx.com' /home/ares/xiao1.log /home/ares/ vm-rancher001.xx.com: ---------- /home/ares/xiao1.log: True #
远程机器上查看,正常接收到文件xiao1.log
# ls bao2.txt jiandan.py mcw.log xiao1.log bao.txt libiconv-1.14 mm xiaomaopenresty ares cosfs-1.0.21-centos7.0.x86_64.rpm libiconv-1.14.tar.gz mysql-5.7.30-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz asciidoc-8.6.9 git-2.2.1 machangwei.sh openresty.repo asciidoc-8.6.9.zip git-2.39.3.tar.gz mcw v2.2.1.tar.gz # tail xiao1.log Feb 18 09:59:49 salt002 pdns[27465]: Remote 10.xx.xx.12 wants 'app-assets-mysql-rw-zz.x.com|A', do = 1, bufsize = 1232 (1680): packetcache MISS Feb 18 09:59:51 salt002 pdns[27465]: Remote 10.xx.xx.12 wants 'ai-open-redis-x.x.com|A', do = 1, bufsize = 1232 (1680): packetcache MISS
问题处理
修改主机名后,salt-key加的主机名一直是旧的主机名
这是因为旧主机名已经在slat客户端的配置上了。
# grep otter006 -r /etc/salt/*
/etc/salt/minion_id:otter006.xxx.axxs.com
手动修改为当前主机名,然后重启salt客户端
# vim /etc/salt/minion_id
# systemctl restart salt-minion.service
# cat /etc/salt/minion_id
otter007.axx.axx.com
然后可以在salt服务端看到正常的主机名key
然后删掉旧的,添加新的
# salt-key -d otter006.axx.axx.com
# salt-key -a otter007.axxx.axx.com
https://blog.51cto.com/aaronsa/1742456
https://www.cnblogs.com/LYCong/p/7873871.html





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号