nginx 配置详解
一.nginx的配置文件
配置文件默认为安装目录下的conf/nginx.conf,如果有使用到其他子配置文件,可以在nginx.conf中使用include 文件路径;的方式加载使用,比如server段,就可以单独写成一个配置文件,在http段下面使用include加载使用。
... #全局块
events { #events块
...
}
http #http块
{
... #http全局块
server #server块
{
... #server全局块
location [PATTERN] #location块
{
...
}
location [PATTERN]
{
...
}
}
server
{
...
}
... #http全局块
}
1、全局块:配置影响nginx全局的指令。一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组,nginx进程pid存放路径,日志存放路径,配置文件引入,允许生成worker process数等。
2、events块:配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。有每个进程的最大连接数,选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求,是否允许同时接受多个网路连接,开启多个网络连接序列化等。
3、http块:可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入,mime-type定义,日志自定义,是否使用sendfile传输文件,连接超时时间,单连接请求数等。
4、server块:配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。
5、location块:配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。#################
#user administrator administrators; #配置用户或者组,默认为nobody nobody。
#worker_processes 2; #允许生成的进程数,默认为1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #指定nginx进程运行文件存放地址
error_log log/error.log debug; #制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块,级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on
multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off
#use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512
}
http {
include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain
#access_log off; #取消服务日志
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #自定义格式
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined为日志格式的默认值
sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块。
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。
keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。
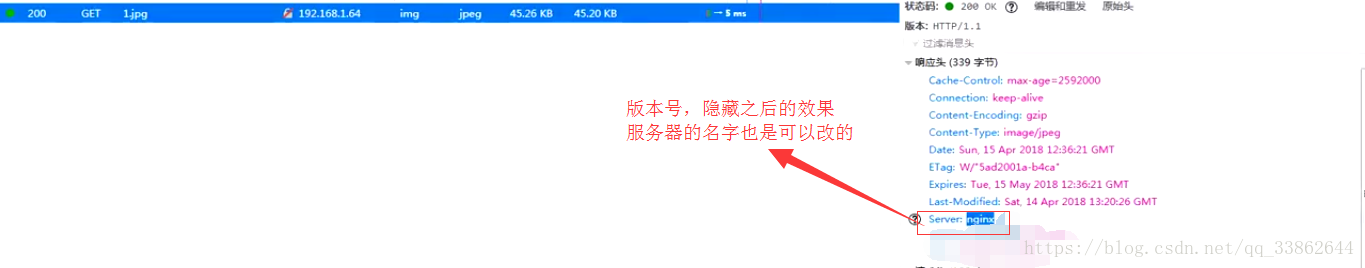
# 隐藏nginx版本号,不再浏览显示
server_tokens off;
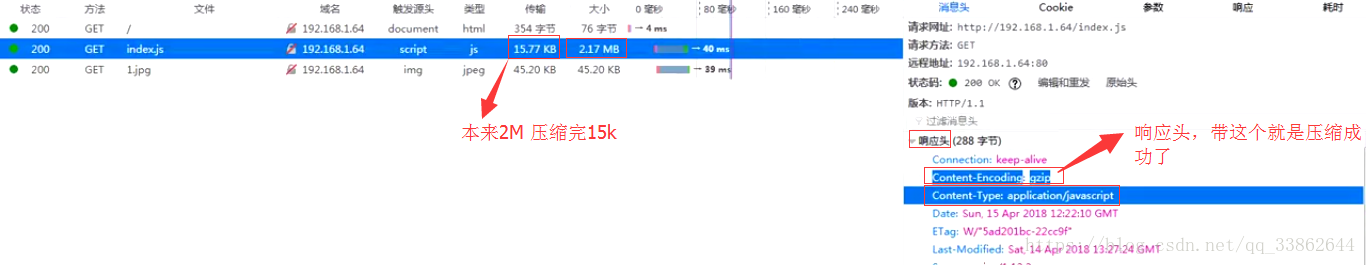
#gzip加速
#gzip on;
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; #错误页
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。
listen 4545; #监听端口
server_name 127.0.0.1; #监听地址
location ~*^.+$ { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。释义为:不区分大小写,以1个以上的 非换行符的字符 开始并结束
#root path; #根目录
#index vv.txt; #设置默认页
proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表
deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip
allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip
}
}
}
1、1.$remote_addr 与$http_x_forwarded_for 用以记录客户端的ip地址; 2.$remote_user :用来记录客户端用户名称; 3.$time_local : 用来记录访问时间与时区;4.$request : 用来记录请求的url与http协议;
5.$status : 用来记录请求状态;成功是200, 6.$body_bytes_s ent :记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小;7.$http_referer :用来记录从那个页面链接访问过来的; 8.$http_user_agent :记录客户端浏览器的相关信息;
2、惊群现象:一个网路连接到来,多个睡眠的进程被同事叫醒,但只有一个进程能获得链接,这样会影响系统性能。
3、每个指令必须有分号结束。
server { listen 80; server_name score.devops.com; # 域名重定向 rewrite / http://shop.devops.com permanent; } server { listen 80; server_name shop.devops.com; root html/tp5shop/public; # gzip on压缩功能,将服务器传输的文件压缩返回给浏览器,可以减少传输的数据量,提供性能,一般浏览器是支持解压的 gzip on; #开启压缩功能 gzip_http_version 1.0; # 指定http的版本 gzip_disable 'MSIE [1-6]'; # 禁止IE的1~6版本使用该功能 gzip_types application/javascript text/css image/jpeg image/png; # 指定压缩哪些类型的文件 # 禁止ip访问,当有匹配时,就不会在向下匹配 # deny all; # 拒绝所有 # allow 192.168.211.1; # 允许192.168.211.1 # 用户访问限制 # auth_basic 'pls login:'; # 指定提示语"pls login:" # auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/conf/userlist; # 指定授权用户所在文件 # 基于域名的日志分割,所有访问shop.devops.com域名的访问日志记录在该文件中 access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/shop.devops.com shoplog; location / { # expires 设置客户端缓存 #expires 1h; index index.php index.html; # 资源重定向,如访问http://shop.devops.com/index.html后会被重写为访问http://shop.devops.com/index.php,permanent表示永久重定向 rewrite /index.html /index.php permanent; # 资源重定向,$request_filename为nginx的内置变量,表示资源文件路径 if (!-e $request_filename) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.php?s=/$1 last; break; } } # 资源重定向 #location /index { # rewrite /index.html /index.php last; #} location ~ \.(js|css|jpg|png) { # 告诉客户端所有js,css,jpg,png文件都可以缓存1小时,不用重新在服务器下载 expires 1h; # 防盗链实现,所有不是从shop.devops.com跳转过去访问js|css|jpg|png文件的都被拦截,返回404 valid_referers shop.devops.com; if ($invalid_referer) { return 404; } } # php解析 location ~ \.php$ { # root html; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } }
location的路由匹配规则
语法规则: location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … }
-
=开头表示精确匹配 -
^~开头表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url路径即可。nginx不对url做编码,因此请求为/static/20%/aa,可以被规则^~ /static/ /aa匹配到(注意是空格)。以xx开头 -
~开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配 以xx结尾 -
~*开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配 以xx结尾 -
!~和!~*分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配 的正则 -
/通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到。
多个location配置的情况下匹配顺序为(参考资料而来,还未实际验证,试试就知道了,不必拘泥,仅供参考):
首先精确匹配 =-》其次以xx开头匹配^~-》然后是按文件中顺序的正则匹配-》最后是交给 / 通用匹配。
当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
例子,有如下匹配规则:
location = / { #规则A } location = /login { #规则B } location ^~ /static/ { #规则C } location ~ \.(gif|jpg|png|js|css)$ { #规则D,注意:是根据括号内的大小写进行匹配。括号内全是小写,只匹配小写 } location ~* \.png$ { #规则E } location !~ \.xhtml$ { #规则F } location !~* \.xhtml$ { #规则G } location / { #规则H }
nginx的其他配置信息介绍
三、ReWrite语法
last – 基本上都用这个Flag。break – 中止Rewirte,不在继续匹配redirect – 返回临时重定向的HTTP状态302permanent – 返回永久重定向的HTTP状态301
1、下面是可以用来判断的表达式:
-f和!-f用来判断是否存在文件-d和!-d用来判断是否存在目录-e和!-e用来判断是否存在文件或目录-x和!-x用来判断文件是否可执行
2、下面是可以用作判断的全局变量
例:http://localhost:88/test1/test2/test.php
$host:localhost $server_port:88 $request_uri:http://localhost:88/test1/test2/test.php $document_uri:/test1/test2/test.php $document_root:D:\nginx/html $request_filename:D:\nginx/html/test1/test2/test.php
附:一些可用的全局变量
$args $content_length $content_type $document_root $document_uri $host $http_user_agent $http_cookie $limit_rate $request_body_file $request_method $remote_addr $remote_port $remote_user $request_filename $request_uri $query
一些常用的配置
1、普通的(静态的)http服务器
这样如果访问http://localhost 就会默认访问到E盘wwwroot目录下面的index.html,如果一个网站只是静态页面的话,那么就可以通过这种方式来实现部署。
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
client_max_body_size 1024M;
location / {
root e:wwwroot; //思路:通过/将所有的请求,转发给root处理
index index.html;
}
}
2、反向代理
localhost的时候,就相当于访问localhost:8080了
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
client_max_body_size 1024M;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port; //思路:通过/,将所有的请求,转发给第3方处理
}
}
既然服务器可以直接HTTP访问,为什么要在中间加上一个反向代理,不是多此一举吗?反向代理有什么作用?
负载均衡、虚拟主机等,都基于反向代理实现,当然反向代理的功能也不仅仅是这些。
3、Redirect(重定向)语法
server { listen 80; server_name start.igrow.cn; index index.html index.php; root html; if ($http_host !~ "^star\.igrow\.cn$" { rewrite ^(.*) http://star.igrow.cn$1 redirect; } }
4、防盗链
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|png|bmp)$ { valid_referers none blocked *.ttlsa.com server_names ~\.google\. ~\.baidu\.; if ($invalid_referer) { return 403; #rewrite ^/ http://www.ttlsa.com/403.jpg; } }
5、根据文件类型设置过期时间
location ~* \.(js|css|jpg|jpeg|gif|png|swf)$ {
if (-f $request_filename) { //只能是文件,因为这用-f判断了
expires 1h;
break;
}
}
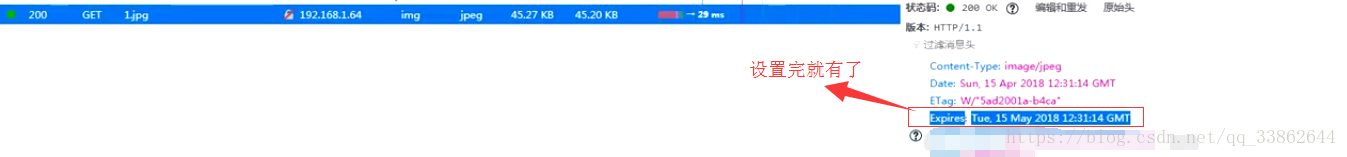
6、设置图片缓存(过期)时间
7、禁止访问某个目录
location ~* \.(txt|doc)${ root /data/www/wwwroot/linuxtone/test; #所有用户都禁止访问这个目录 deny all; }
8、隐藏版本号的作用
通过你所用的版本,找其漏洞,进行攻击你
在http中添加该配置:server_tokens off;
alias和root区别
root和alias都可以定义在location模块中,都是用来指定请求资源的真实路径,比如:
location /i/ { root /data/w3; }
请求 http://foofish.net/i/top.gif 这个地址时,那么在服务器里面对应的真正的资源是 /data/w3/i/top.gif 文件
注意:真实的路径是root指定的值加上location指定的值 。
而 alias 正如其名,alias指定的路径是location的别名,不管location的值怎么写,资源的 真实路径都是 alias 指定的路径 ,比如:
location /i/ {
alias /data/w3/;
}
同样请求 http://foofish.net/i/top.gif 时,在服务器查找的资源路径是: /data/w3/top.gif
其他区别:
1、 alias 只能作用在location中,而root可以存在server、http和location中。
2、alias 后面必须要用 “/” 结束,否则会找不到文件,而 root 则对 ”/” 可有可无。







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号