nginx配置
location区段,通过指定模式来与客户端请求的URI相匹配
//功能:允许根据用户请求的URI来匹配定义的各location,匹配到时,此请求将被相应的location配置块中的配置所处理,例如做访问控制等功能
//语法:location [ 修饰符 ] pattern {......}
常用修饰符说明:
| 修饰符 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| = | 精确匹配 |
| ~ | 正则表达式模式匹配,区分大小写 |
| ~* | 正则表达式模式匹配,不区分大小写 |
| ^~ | 前缀匹配,类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模块开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了,不支持正则表达式 |
| @ | 定义命名location区段,这些区段客户端不能访问,只可以由内部产生的请求来访问,如try_files或error_page等 |
| 没有修饰符表示必须以指定模式开始,如: |
location /test {
echo "test";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/test
test
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/test/
test
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/testabc
test
= : 表示必须与指定模式精确匹配:
location = /testa {
echo "test2";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/testa
test2
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/testa?abc
test2
如下内容则无法匹配:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/testa/
<html>
<head>
<title>test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a>
</body>
</html>
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/testa/testabcd
<html>
<head>
<title>test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a>
</body>
</html>
~:表示指定的正则表达式要区分大小写,如:
abc
location ~ ^/abc$ {
echo "abc";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abc
abc
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abc?abc
abc
如下内容则无法匹配:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abc/
<html>
<head>
<title>test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a>
</body>
</html>
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/ABC/
<html>
<head>
<title>test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a>
</body>
</html>
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abcde
<html>
<head>
<title>test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a>
</body>
</html>
[root@localhost ~]#
~*:表示指定的正则表达式不区分大小写,如:
location ~* ^/abc$ {
echo "abc";
}
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abc
abc
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/ABC
abc
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abc?ABC
abc
如下内容则无法匹配:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abc/
<html>
<head>
<title>test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a>
</body>
</html>
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.170.135/abccdf
<html>
<head>
<title>test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a>
</body>
</html>
[root@localhost ~]#
43 location = / {
44 echo "[ configuration A ]";
45 }
46
47 location / {
48 echo "[ configuration B ]";
49 }
50
51 location /documents/ {
52 echo "[ configuration C ]";
53 }
54
55 location ^~ /images/ {
56 echo "[ configuration D ]";
57 }
58
59 location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
60 echo "[ configuration E ]";
61 }
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://192.168.170.135
[ configuration A ]
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://192.168.170.135/index.html
[ configuration B ]
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://192.168.170.135/documents/document.html
[ configuration C ]
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://192.168.170.135/images/1.gif
[ configuration D ]
[root@localhost ~]# curl http://192.168.170.135/documents/1.jpg
[ configuration E ]
~:类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模式开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,则停止搜索其他模式
查找顺序和优先级:由高到底依次为
- 带有=的精确匹配优先
- 正则表达式按照他们在配置文件中定义的顺序
- 带有^~修饰符的,开头匹配
- 带有或*修饰符的,如果正则表达式与URI匹配
- 没有修饰符的精确匹配
优先级次序如下:
( location = 路径 ) --> ( location ^~ 路径 ) --> ( location ~ 正则 ) --> ( location ~* 正则 ) --> ( location 路径 )
访问控制
allow:设定允许哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
deny:设定禁止哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
配置测试文件
[root@localhost html]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx/html
[root@master html]# echo 'hello' > index.html
[root@master html]# systemctl stop nginx.service
[root@master html]# systemctl start nginx.service
[root@master html]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
[root@master html]# curl 192.168.170.135
hello
[root@localhost conf]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx/conf
[root@master conf]# vim nginx.conf
location / {
allow 192.168.170.1;
deny all;
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
[root@localhost conf]# curl 192.168.170.138
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.20.2</center>
</body>
</html>
基于用户认证
[root@master conf]# yum install httpd-tools -y
[root@master conf]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx/conf
[root@master conf]# vim nginx.conf
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /xixi {
auth_basic "欢迎信息";
auth_basic_user_file "/usr/local/nginx/conf/.pass";
root html;
index index.html;
}
//生成用户和密码
[root@master conf]# htpasswd -cm /usr/local/nginx/conf/.pass kurumi
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user kurumi
[root@master conf]# cat .pass
kurumi:$apr1$j9fgHUtO$hAANaUpzMUsg4YZjr0h8u1

https配置
生成证书
[root@master pki]# cd CA/
[root@master CA]# mkdir private
[root@master CA]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out private/cakey.pem 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
..................................................................+++++
............................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
[root@master CA]# ls private
cakey.pem
CA生成自签署证书
[root@master CA]# openssl req -new -x509 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem -days 365
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN //国家
State or Province Name (full name) []:HB //省
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:WH //市
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:HHHH //公司
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:www.example.com //域名
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.example.com
Email Address []:
[root@master CA]# mkdir certs newcerts crl
[root@master CA]# touch index.txt && echo 01 > serial
客户端(例如httpd服务器)生成密钥
[root@master ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/ && mkdir ssl && cd ssl
[root@master ssl]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out nginx.key 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
......................................................................+++++
.....................................................................................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
[root@master ssl]# ls
nginx.key
客户端生成证书签署请求
[root@master ssl]# openssl req -new -key nginx.key -days 365 -out nginx.csr
Ignoring -days; not generating a certificate
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:HB
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:WH
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:ZCH
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:www.example.com
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.example.com
Email Address []:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
CA签署客户端提交上来的证书
[root@master ssl]# openssl ca -in nginx.csr -out nginx.crt -days 365
Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
Certificate Details:
Serial Number: 1 (0x1)
Validity
Not Before: Sep 5 03:30:15 2022 GMT
Not After : Sep 5 03:30:15 2023 GMT
Subject:
countryName = CN
stateOrProvinceName = HB
organizationName = ZCH
organizationalUnitName = www.example.com
commonName = www.example.com
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:FALSE
Netscape Comment:
OpenSSL Generated Certificate
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
70:2E:06:73:37:36:54:67:77:0F:23:D6:A3:C9:98:63:45:F7:6C:45
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:5E:B9:23:5F:A2:69:99:2E:4B:24:94:FB:17:87:03:5B:52:9A:87:CA
Certificate is to be certified until Sep 5 03:30:15 2023 GMT (365 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
[root@master ssl]# ls
nginx.crt nginx.csr nginx.key
生成私钥,生成证书签署请求并获得证书,然后在nginx.conf中配置如下内容:
//搜素HTTP 取消下面的注释 并修改两行
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.example.com;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/conf/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/conf/ssl/nginx.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
[root@master conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
[root@master conf]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
rewrite
语法:rewrite regex replacement flag;,如:
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 break;
此处的$1用于引用(.*.jpg)匹配到的内容,又如:
rewrite ^/bbs/(.*)$ http://www.idfsoft.com/index.html redirect;
如上例所示,replacement可以是某个路径,也可以是某个URL
常见的flag
| flag | 作用 |
|---|---|
| last | 基本上都用这个flag,表示当前的匹配结束,继续下一个匹配,最多匹配10个到20个一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,就不再被后面其它的rewrite规则进行处理而是由UserAgent重新对重写后的URL再一次发起请求,并从头开始执行类似的过程 |
| break | 中止Rewrite,不再继续匹配一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,由UserAgent对新的URL重新发起请求,且不再会被当前location内的任何rewrite规则所检查 |
| redirect | 以临时重定向的HTTP状态302返回新的URL |
| permanent | 以永久重定向的HTTP状态301返回新的URL |
[root@master ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@master html]# ls
50x.html index.html
[root@master html]# mkdir images
[root@master html]# cd images/
[root@master images]# ls
1.jpg

[root@localhost html]# mv images/ imgs //正常情况下当修改了目录名 就不能访问
[root@master conf]# vim nginx.conf
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /imgs/$1 break; //所有以images开头访问的 用imgs响应
}
[root@master conf]# nginx -s reload
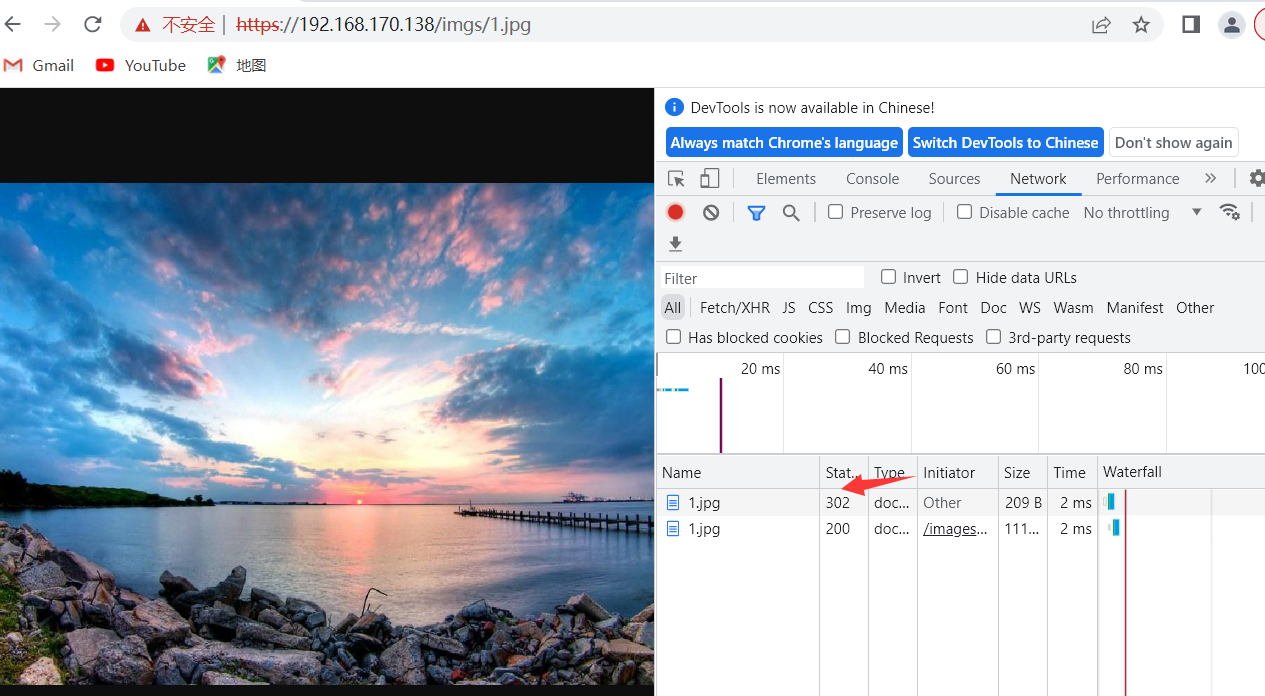
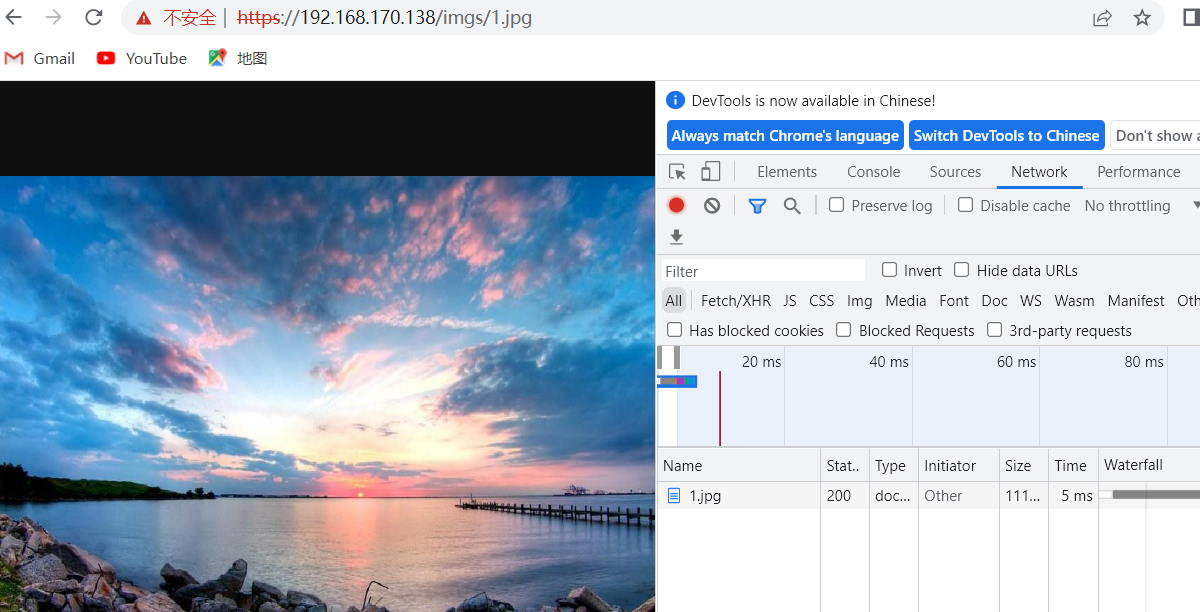
使用imgs/1.jpg也可以访问
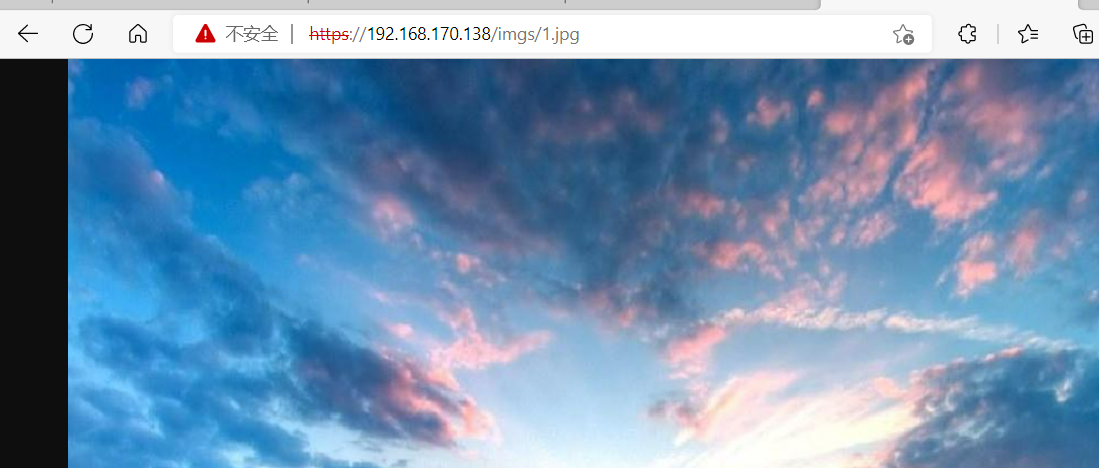
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ http://images.baidu.com break;
}
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
浏览器访问images/1.jpg 跳转到了网页图片

当前匹配结束 继续匹配下一个
location /images{
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 last;
}
location /imgs {
rewrite ^/imgs/(.*\.jpg)$ http://www.baidu.com break;
}
[root@master conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
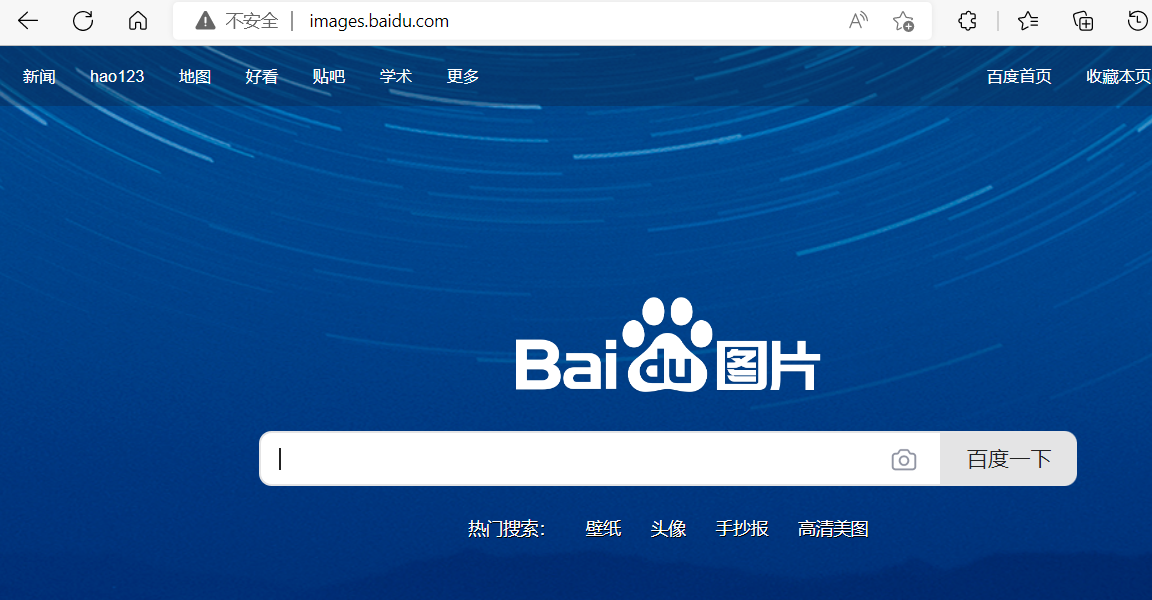
redirect临时重定向
[root@master conf]# vim nginx.conf
location /images{
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 redirect;
}
[root@master conf]# systemctl restart nginx.service
permanent永久重定向
[root@master conf]# vim nginx.conf
location /images{
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 permanent;
}
[root@master conf]# nginx -s reload
if
语法:if (condition) {...}
应用场景:
- server段
- location段
常见的condition
-
变量名(变量值为空串,或者以“0”开始,则为false,其它的均为true)
-
以变量为操作数构成的比较表达式(可使用=,!=类似的比较操作符进行测试)
-
正则表达式的模式匹配操作
-
- ~:区分大小写的模式匹配检查
-
- ~*:不区分大小写的模式匹配检查
-
- !和!*:对上面两种测试取反
-
测试指定路径为文件的可能性(-f,!-f)
-
测试指定路径为目录的可能性(-d,!-d)
-
测试文件的存在性(-e,!-e)
-
检查文件是否有执行权限(-x,!-x)
Examples:
if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break;
}
if ($http_cookie ~* "id=([^;]+)(?:;|$)") {
set $id $1;
}
if ($request_method = POST) {
return 405;
}
if ($slow) {
limit_rate 10k;
}
if ($invalid_referer) {
return 403;
}
基于浏览器实现分离案例
if ($http_user_agent ~ Firefox) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /firefox/$1 break;
}
if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break;
}
if ($http_user_agent ~ Chrome) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /chrome/$1 break;
}
防盗链案例
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|jpeg|png)$ {
valid_referers none blocked www.idfsoft.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite ^/ http://www.idfsoft.com/403.html;
}
}
反向代理与负载均衡
nginx通常被用作后端服务器的反向代理,这样就可以很方便的实现动静分离以及负载均衡,从而大大提高服务器的处理能力。
nginx实现动静分离,其实就是在反向代理的时候,如果是静态资源,就直接从nginx发布的路径去读取,而不需要从后台服务器获取了。
但是要注意,这种情况下需要保证后端跟前端的程序保持一致,可以使用Rsync做服务端自动同步或者使用NFS、MFS分布式共享存储。
Http Proxy模块,功能很多,最常用的是proxy_pass和proxy_cache
如果要使用proxy_cache,需要集成第三方的ngx_cache_purge模块,用来清除指定的URL缓存。这个集成需要在安装nginx的时候去做,如:
./configure --add-module=../ngx_cache_purge-1.0 ......
nginx通过upstream模块来实现简单的负载均衡,upstream需要定义在http段内
在upstream段内,定义一个服务器列表,默认的方式是轮询,如果要确定同一个访问者发出的请求总是由同一个后端服务器来处理,可以设置ip_hash,如:
upstream idfsoft.com {
ip_hash;
server 127.0.0.1:9080 weight=5;
server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=5;
server 127.0.0.1:1111;
}
注意:这个方法本质还是轮询,而且由于客户端的ip可能是不断变化的,比如动态ip,代理,FQ等,因此ip_hash并不能完全保证同一个客户端总是由同一个服务器来处理。
定义好upstream后,需要在server段内添加如下内容:
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://idfsoft.com;
}
}
nginx实现负载均衡
环境说明:
| 系统平台 | 主机IP | 需要安装的服务 |
|---|---|---|
| centos8 | 192.168.170.138(nginx) | nginx |
| centos8 | 192.168.170.135/(node1) | httpd |
| centos8 | 192.168.170.139(node2) | httpd |
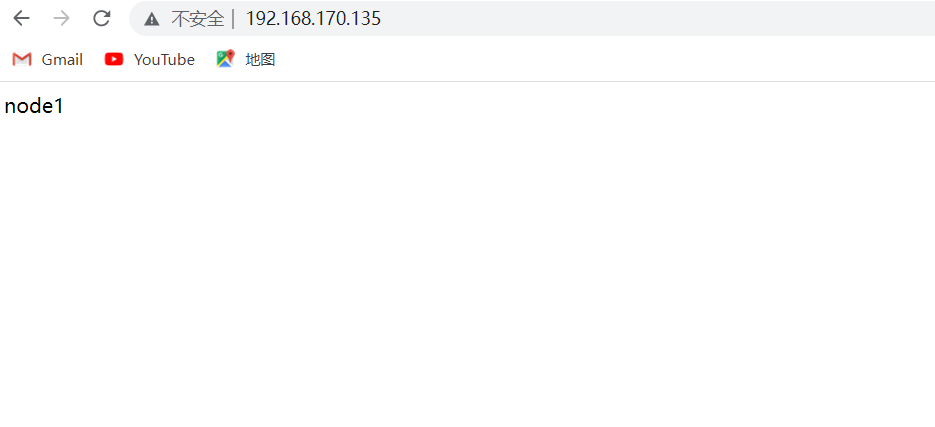
node1主机
[root@node1 ~]# yum -y install httpd
[root@node1 ~]# echo node1 > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@node1 ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
node1
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service 鈫� /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
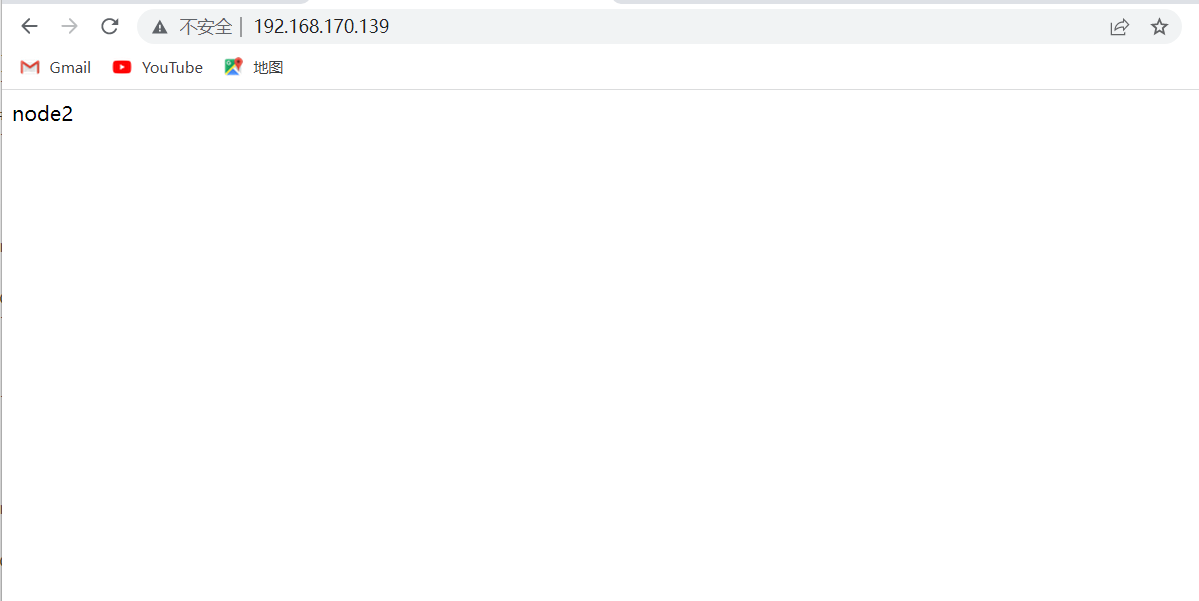
node2主机
[root@node2 ~]# yum -y install httpd
[root@node2 ~]# echo node2 > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@node2 ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
node2
[root@node2 ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
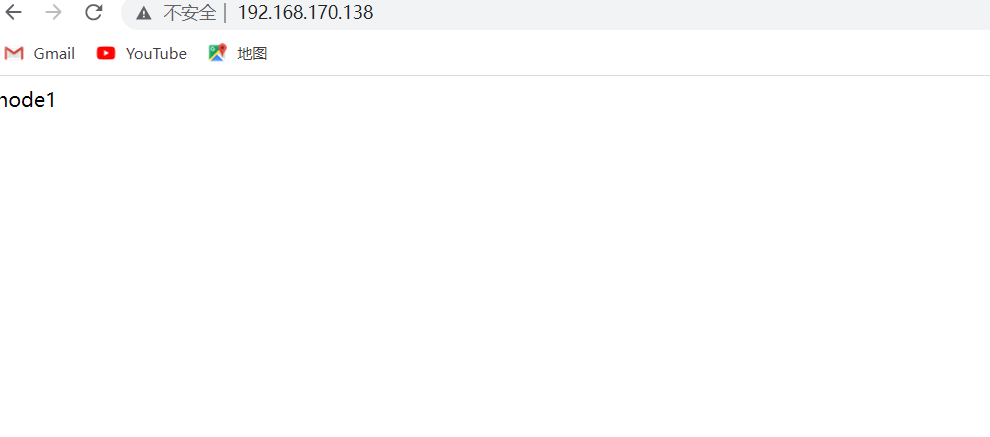
nginx主机
//修改配置文件,添加以下内容
[root@master ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
34 upstream webservers {
35 server 192.168.170.135;
36 server 192.168.170.139;
37 }
46 location / {
47 proxy_pass http://webservers;
48 }
[root@master ~]# systemctl restart nginx.service
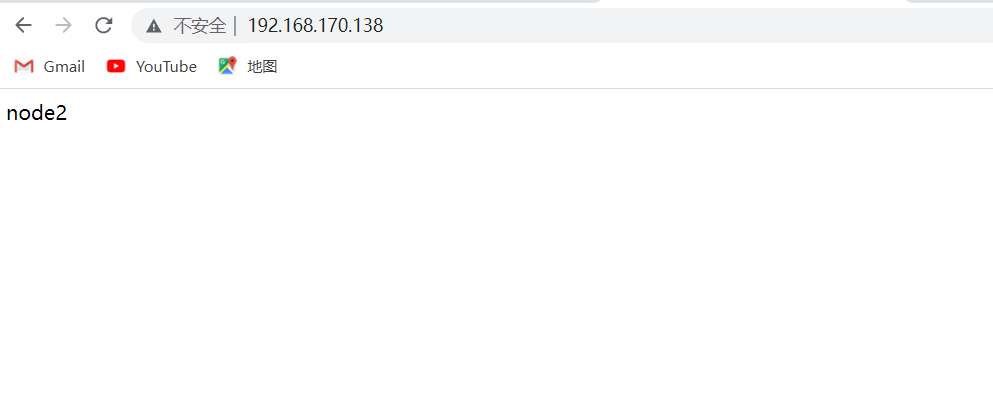
再次访问


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号