第一次作业
Tkinter库:Tkinter是Python的标准GUI库。使用Tkinter库可以可以快速的创建GUI应用程序。
1、创建计算器的窗口
# 创建一个窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.minsize(300, 480)
root.title('计算器')
result1 = tk.StringVar()
result1.set(0)
result2 = tk.StringVar()
result2.set('')
2、设置屏幕显示
#算式显示
screen2 = tk.Label(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#EEE9E9', bd='9', fg='black', textvariable=result1, anchor='se')
screen2.place(width=300, height=170)
#结果显示
screen1 = tk.Label(root, font=('微软雅黑', 30), bg='#0000FF', bd='9', fg='black', textvariable=result2, anchor='se')
screen1.place(width=300, height=110)
3、申明并定义点击函数
# 操作函数
lists = []
ispressfunction = False
ispressnumber = False
ispressequal = False
1、#点击数字定义
def pressnumber(num):
global lists
global ispressfunction
global ispressequal
if ispressequal == False:
pass
else:
ispressequal = False
result1.set('')
if ispressfunction == False:
pass
else:
result1.set(0)
ispressfunction = False
oldnum = result1.get()
if oldnum == '0':
result1.set(num)
else:
newnum = oldnum + num
result1.set(newnum)
2、# 点击功能键定义
def pressfunction(stringlist):
global lists
global ispressfunction
global ispressequal
num = result1.get()
lists.append(num)
shizi = ''
ispressfunction = True
if stringlist in ['-', '+', '/', '*']:
lists.append(stringlist)
for each in lists:
shizi += each
result2.set(shizi)
if stringlist == '1/2':
list1 = []
numnow = result1.get()
list1.append("sqrt(" + numnow + ")")
sqrt1 = m.pow(int(numnow),1/2)
result2.set(list1)
result1.set(sqrt1)
if stringlist == 'C':
lists.pop()
result1.set(0)
ispressfunction = False
ispressnumber = False
ispressequal = False
if stringlist == 'CE':
lists.clear()
result1.set(0)
result2.set('')
if stringlist == '←':
a = num[0:-1]
lists.pop()
result1.set(a)
4、定义按键位置
# 第一行
buttonce = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='1/2', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('1/2'))
buttonce.place(x=140, y=170, width=60, height=50)
buttonc = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='C', bd='0.5', bg='orange', fg='black', command=lambda: pressfunction('C'))
buttonc.place(x=70, y=170, width=60, height=50)
buttondelete = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='←', bd='0.5',bg='orange', fg='black',command=lambda: pressfunction('←'))
buttondelete.place(x=0, y=170, width=60, height=50)
buttondiv = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='÷', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('/'))
buttondiv.place(x=220, y=170, width=70, height=50)
# 第二行
button7 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='7', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('7'))
button7.place(x=0, y=230, width=60, height=50)
button8 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='8', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('8'))
button8.place(x=70, y=230, width=60, height=50)
button9 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='9', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('9'))
button9.place(x=140, y=230, width=60, height=50)
buttonmul = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='×', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('*'))
buttonmul.place(x=220, y=230, width=70, height=50)
# 第三行
button4 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='4', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('4'))
button4.place(x=0, y=290, width=60, height=50)
button5 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='5', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('5'))
button5.place(x=70, y=290, width=60, height=50)
button6 = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='6', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('6'))
button6.place(x=140, y=290, width=60, height=50)
buttonsub = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='-', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('-'))
buttonsub.place(x=220, y=290, width=70, height=50)
# 第四行
button1 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='1', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('1'))
button1.place(x=0, y=350, width=60, height=50)
button2 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='2', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('2'))
button2.place(x=70, y=350, width=60, height=50)
button3 = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='3', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('3'))
button3.place(x=140, y=350, width=60, height=50)
buttonadd = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='+', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('+'))
buttonadd.place(x=220, y=350, width=70, height=50)
# 第五行
buttoninverse = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='CE', bg='orange', bd='0.5', fg='black',command=lambda: pressfunction('CE'))
buttoninverse.place(x=0, y=410, width=60, height=50)
button0 = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='0', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('0'))
button0.place(x=70, y=410, width=60, height=50)
buttonpoint = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='.', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressnumber('.'))
buttonpoint.place(x=140, y=410, width=60, height=50)
buttonvalue = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='=', bd='0.5', bg='orange', fg='black',command=lambda: pressequal())
buttonvalue.place(x=220, y=410, width=70, height=50)
5、#申明并定义结果函数
def pressequal():
global lists
global ispressfunction
global ispressequal
ispressequal = True
curnum = result1.get()
lists.append(curnum)
computrStr = ''.join(lists)
endnum = eval(computrStr)
result1.set(endnum)
result2.set(computrStr)
lists.clear()
root.mainloop()
运算结果计算得知:
程序流程图:
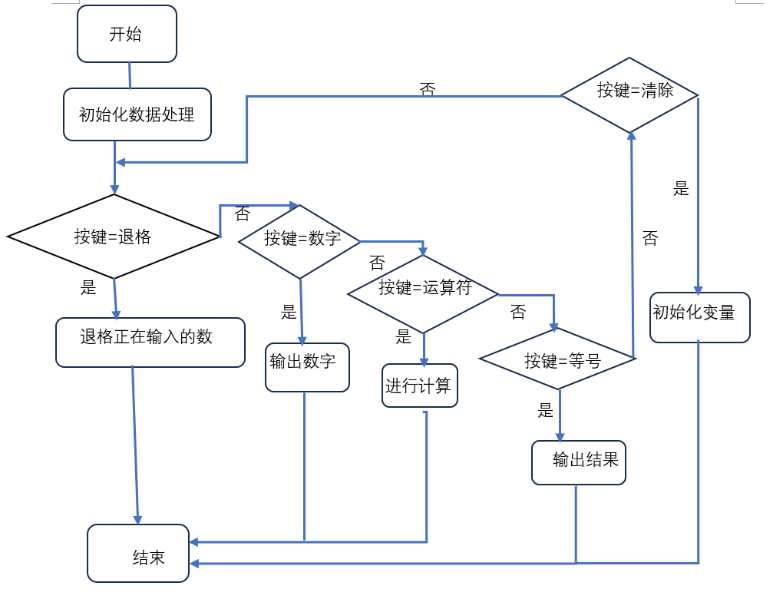
以下是关键代码:
import tkinter as tk # 导入tkinter模块
import math as m
# 创建一个窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.minsize(300, 480)
root.title('计算器')
result1 = tk.StringVar()
result1.set(0)
result2 = tk.StringVar()
result2.set('')
# 显示屏幕
#算式显示
screen2 = tk.Label(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), bg='#EEE9E9', bd='9', fg='black', textvariable=result1, anchor='se')
screen2.place(width=300, height=170)
#结果显示
screen1 = tk.Label(root, font=('微软雅黑', 30), bg='#0000FF', bd='9', fg='black', textvariable=result2, anchor='se')
screen1.place(width=300, height=110)
# 第一行
buttonce = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='1/2', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('1/2'))
buttonce.place(x=140, y=170, width=60, height=50)
buttonc = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='C', bd='0.5', bg='orange', fg='black', command=lambda: pressfunction('C'))
buttonc.place(x=70, y=170, width=60, height=50)
buttondelete = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='←', bd='0.5',bg='orange', fg='black',command=lambda: pressfunction('←'))
buttondelete.place(x=0, y=170, width=60, height=50)
buttondiv = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='÷', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('/'))
buttondiv.place(x=220, y=170, width=70, height=50)
# 第二行
button7 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='7', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('7'))
button7.place(x=0, y=230, width=60, height=50)
button8 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='8', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('8'))
button8.place(x=70, y=230, width=60, height=50)
button9 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='9', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('9'))
button9.place(x=140, y=230, width=60, height=50)
buttonmul = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='×', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('*'))
buttonmul.place(x=220, y=230, width=70, height=50)
# 第三行
button4 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='4', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('4'))
button4.place(x=0, y=290, width=60, height=50)
button5 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='5', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('5'))
button5.place(x=70, y=290, width=60, height=50)
button6 = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='6', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('6'))
button6.place(x=140, y=290, width=60, height=50)
buttonsub = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='-', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('-'))
buttonsub.place(x=220, y=290, width=70, height=50)
# 第四行
button1 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='1', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('1'))
button1.place(x=0, y=350, width=60, height=50)
button2 = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='2', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('2'))
button2.place(x=70, y=350, width=60, height=50)
button3 = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='3', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('3'))
button3.place(x=140, y=350, width=60, height=50)
buttonadd = tk.Button(root, font=('微软雅黑', 20), text='+', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressfunction('+'))
buttonadd.place(x=220, y=350, width=70, height=50)
# 第五行
buttoninverse = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='CE', bg='orange', bd='0.5', fg='black',command=lambda: pressfunction('CE'))
buttoninverse.place(x=0, y=410, width=60, height=50)
button0 = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='0', bd='0.5', bg='white', command=lambda: pressnumber('0'))
button0.place(x=70, y=410, width=60, height=50)
buttonpoint = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='.', bd='0.5', fg='blue', command=lambda: pressnumber('.'))
buttonpoint.place(x=140, y=410, width=60, height=50)
buttonvalue = tk.Button(root, font=("微软雅黑", 20), text='=', bd='0.5', bg='orange', fg='black',command=lambda: pressequal())
buttonvalue.place(x=220, y=410, width=70, height=50)
# 操作函数
lists = []
ispressfunction = False
ispressnumber = False
ispressequal = False
# 数字按键定义
def pressnumber(num):
global lists
global ispressfunction
global ispressequal
if ispressequal == False:
pass
else:
ispressequal = False
result1.set('')
if ispressfunction == False:
pass
else:
result1.set(0)
ispressfunction = False
oldnum = result1.get()
if oldnum == '0':
result1.set(num)
else:
newnum = oldnum + num
result1.set(newnum)
# 功能键定义
def pressfunction(stringlist):
global lists
global ispressfunction
global ispressequal
num = result1.get()
lists.append(num)
shizi = ''
ispressfunction = True
if stringlist in ['-', '+', '/', '*']:
lists.append(stringlist)
for each in lists:
shizi += each
result2.set(shizi)
if stringlist == '1/2':
list1 = []
numnow = result1.get()
list1.append("sqrt(" + numnow + ")")
sqrt1 = m.pow(int(numnow),1/2)
result2.set(list1)
result1.set(sqrt1)
if stringlist == 'C':
lists.pop()
result1.set(0)
ispressfunction = False
ispressnumber = False
ispressequal = False
if stringlist == 'CE':
lists.clear()
result1.set(0)
result2.set('')
if stringlist == '←':
a = num[0:-1]
lists.pop()
result1.set(a)
# 结果
def pressequal():
global lists
global ispressfunction
global ispressequal
ispressequal = True
curnum = result1.get()
lists.append(curnum)
computrStr = ''.join(lists)
endnum = eval(computrStr)
result1.set(endnum)
result2.set(computrStr)
lists.clear()
root.mainloop()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号