java——SpringBoot(3)
通过增删改查案例了解SpringBoot各种功能;
为了增加Mvc功能,我们会经常覆写 extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport、implements WebMvcConfigurer接口,需要注意的是: extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport将会覆盖原本的自动装配,即需要自己补充覆写所需要的功能,如访问静态文件等等,加上目前接口已有默认的方法了,所以建议还是直接implements WebMvcConfigurer接口,这样我们只需要覆写所增加的方法即可;而@EnableWebMvc实际上是引入一个DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration,而DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport,因此SpringBoot2.0版本不可再@EnableWebMvc,以上就是刚接触SpringBoot2.0所踩的坑;
进入主题首先我们可以覆写addViewControllers来简化访问对应的页面:
@Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login"); }
对页面进行国际化管理:
在resources下编写装换配置文件:
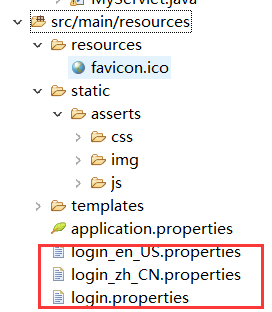
修改html文件,进行绑定:

SpringBoot自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件;
国际化Locale(区域信息对象);LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象);
覆写其方法返回类:
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver { @Override public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Locale locale = Locale.getDefault(); String l = request.getParameter("l"); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(l)) { String[] split = l.split("_"); locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]); } return locale; } @Override public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }
要记得将修改类注入容器中:
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport{ @Bean public LocaleResolver localeResolver() { return new MyLocaleResolver(); }
登录检验:
编写控制器:
@Controller public class LoginController { @PostMapping(value = "/user/login") //@RequestMapping(value="/user/login",method = RequestMethod.POST) public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") String password, Map<String,Object> map,HttpSession session) { if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username) && "123456".equals(password)) { session.setAttribute("loginUser",username); return "redirect:/main.html"; }else { map.put("msg","用户名密码错误"); return "login"; } } }
这里的/main.html会映射到首页里;redirect:作用就是将返回变成一个访问路径/main.html而不是一个字符串;
对其他页面进行登录限制:
编写拦截器:
public class LoginHandlerIntercep implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser"); if(user == null) { request.setAttribute("msg", "未登录请先登录"); request.getRequestDispatcher("/login").forward(request, response); return false; }else { return true; } } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub HandlerInterceptor.super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView); } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub HandlerInterceptor.super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex); } }
增加 拦截器并避免拦截静态资源:
@Override protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //super.addInterceptors(registry); registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerIntercep()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/login","/user/login","/","/css/**","/js/**","/img/**"); }
编写逻辑功能:

目录结构:
查询:
添加:先来到添加页面 ,按提交键进行提交:
,按提交键进行提交:
修改:先来到修改页面: ,按修改键进行修改:
,按修改键进行修改:
删除:删除也是post,相当于提交一次表单,为了避免每次删除都要编写一个<form>标签,我们可以把标签写在外面,通过js进行调用,页面的所有删除都调用这个表单就好:



在编写html页面需要注意的是:如果我们将增加和修改页面共用一页面的话,也就是add.html和change.heml共用,但需要他们的回显不能一样,增加页面回显的是默认的样例,而修改页面回显的是所选修改id对应的属性值:

这样如果emp有值的话说明调用的是修改页面,因为修改页面我们有返回一个emp对象,而增加页面是没有的;
控制类编写:
@Controller public class EmployeeController { @Autowired DepartmentDao departmentDao; @Autowired EmployeeDao employeeDao; @GetMapping("/emps") public String list(Model model) { Collection<Employee> employees = employeeDao.getAll(); model.addAttribute("emps", employees); return "emp/list"; } @GetMapping("/emp") public String toAddPage(Model model) { Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments(); model.addAttribute("depts", departments); return "emp/add"; } @PostMapping("/emp") public String Addemp(Employee employee) { System.out.println(employee); employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/emps"; } @GetMapping("/emp/{id}") public String changePage(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Model model) { Employee employee = employeeDao.get(id); model.addAttribute("emp", employee); Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments(); model.addAttribute("depts", departments); return "emp/change"; } @PutMapping("/emp") public String update(Employee employee) { employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/emps"; } @DeleteMapping("/emp/{id}") public String delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { employeeDao.delete(id); return "redirect:/emps"; } }
错误处理机制:
可以参照ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;
这个配置类加入了以下组件:
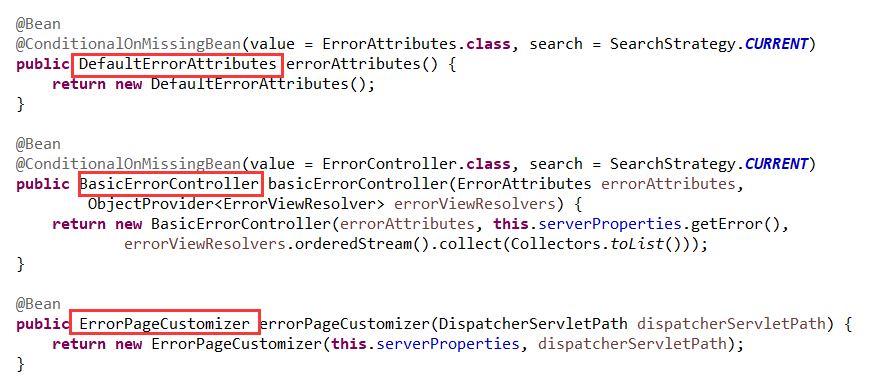

DefaultErrorAttributes:定制错误页面的共享信息;、BasicErrorController:处理默认/error请求(这里会根据请求的来源进行区分,如果是网页的会产生html类型数据返回,如果是客户端会返回json数据);
ErrorPageCustomizer:会产生/error(默认)请求然后交给BasicErrorController;DefaultErrorViewResolver:具体去到哪个页面,如error/4xx.html或者error/5xx.html
错误处理的自动配置;一但系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误;ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则);就会来到/error请求;就会被BasicErrorController处理;去哪个页面是由DefaultErrorViewResolver解析得到的;
因此我们如果只想改其网页显示只需在resources下建个errou目录然后创建4xx.html或者5xx.html即可;
自制错误页面:
首先设置好访问抛出异常路径:
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(@RequestParam("user") String user) { if(user.equals("aaa")) { throw new UserNotException(); }else { return "hahahaha"; } }
再来自定义UserNotException()类:
public class UserNotException extends RuntimeException { public UserNotException() { super("用户不存在"); } }
创建ExceptionHangder类处理controller类抛出的异常:
@ControllerAdvice public class MyExceptionHandler { /***@ResponseBody @ExceptionHandler(UserNotException.class) public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e) { Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap(); map.put("code","user.notexist"); map.put("message",e.getMessage()); return map; }***/ @ExceptionHandler(UserNotException.class) public String handleException(Exception e,HttpServletRequest request) { Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap(); request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code", 401); map.put("code","user.notexist"); map.put("message",e.getMessage()); return "forward:/error"; } }
此时我们访问/hello?user=aaa时就会抛出自定义好的异常,转到error/401.html页面上;
这里如果使用html静态页面:在resources/public/error/ 下定义;
如果使用模板引擎页面:在templates/error/下定义;
templates/error/ 这个的优先级比较 resources/public/error/高;
将我们的定制数据携带出去:
来编写一个ErrorController的实现类【或者是编写AbstractErrorController的子类】,放在容器中;
页面上能用的数据,或者是json返回能用的数据都是通过errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes得到;
容器中DefaultErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes();默认进行数据处理的;
@Component public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes { @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes, boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(requestAttributes, includeStackTrace); map.put("company","atguigu"); return map; } }
配置嵌入式Servlet容器:
由于SpringBoot默认是以jar包的方式启动嵌入式的Servlet容器来启动SpringBoot的web应用,没有web.xml文
件。
注册三大组件用以下方式:
过滤器:
public class MyFilter implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Filter.super.init(filterConfig); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("MyFilter"); chain.doFilter(request, response); } @Override public void destroy() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Filter.super.destroy(); } }
监听器:
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener{ @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("Listener开启"); } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("Listener关闭"); } }
Servlet:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet{ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub resp.getWriter().write("Hello MyServlet!"); } }
将这3大组件分别注入:
@Configuration public class MyServletConfig { @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean myServlets() { ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(),"/myServlet"); return servletRegistrationBean; } @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean=new FilterRegistrationBean(); filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter()); filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/hello","/myServlet")); return filterRegistrationBean; } @Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener() { ServletListenerRegistrationBean servletListenerRegistrationBean=new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(new MyListener()); return servletListenerRegistrationBean; } }
SpringBoot帮我们自动SpringMVC的时候,自动的注册SpringMVC的前端控制器;DIspatcherServlet;
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration中:
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME) @ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME) public ServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration( DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) { ServletRegistrationBean registration = new ServletRegistrationBean( dispatcherServlet, this.serverProperties.getServletMapping()); //默认拦截: / 所有请求;包静态资源,但是不拦截jsp请求; /*会拦截jsp //可以通过server.servletPath来修改SpringMVC前端控制器默认拦截的请求路径 registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME); registration.setLoadOnStartup( this.webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup()); if (this.multipartConfig != null) { registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig); } return registration; }
替代为其他的Servlet容器:
tomcat为默认使用,在pom.xml文件中引入web模块默认就是使用嵌入式的Tomcat作为Servlet容器;
引入Jetty:
<!‐‐ 引入web模块 ‐‐> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐web</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐tomcat</artifactId> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <!‐‐引入其他的Servlet容器‐‐> <dependency> <artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐jetty</artifactId> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> </dependency>
引入Undertow是同样的道理;
对于想改容器默认配置的有两种方法:一种是在配置文件通过属性server.xxx或server.tomcatxxx来修改;
另一种是实现实现WebServerFactoryCustomizer接口,重写它的customize()方法,对容器进行定制配置:
/***@Bean public WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory> webServerFactoryCustomizer(){ return new WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory>() { @Override public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory factory) { factory.setPort(8081); } }; }***/
至于原理可看下面网站,该内容还是比较重要的,不可忽略;
嵌入式Servlet容器的自动装配原理:
可参考网站:https://www.jianshu.com/p/017a7f40efff
外置的Servlet容器:外面安装Tomcat---应用war包的方式打包;
步骤
1)、必须创建一个war项目;(利用idea创建好目录结构)
2)、将嵌入式的Tomcat指定为provided;
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐tomcat</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
3)、必须编写一个SpringBootServletInitializer的子类,并调用configure方法
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer { @Override protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) { //传入SpringBoot应用的主程序 return application.sources(SpringBoot04WebJspApplication.class); } }
4)、启动服务器就可以使用;





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号