| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience/homework/13477 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 实现论文查重程序 |
GitHub 链接:https://github.com/Lzephyr-w/3223004472
psp表格:
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 50 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 1800 | 1920 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 260 | 300 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 120 | 100 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 70 | 90 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 60 | 50 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 180 | 210 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 720 | 780 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 120 | 150 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 300 | 245 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 180 | 210 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 60 | 75 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 25 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 90 | 110 |
| · 合计 | 2070 | 2190 |
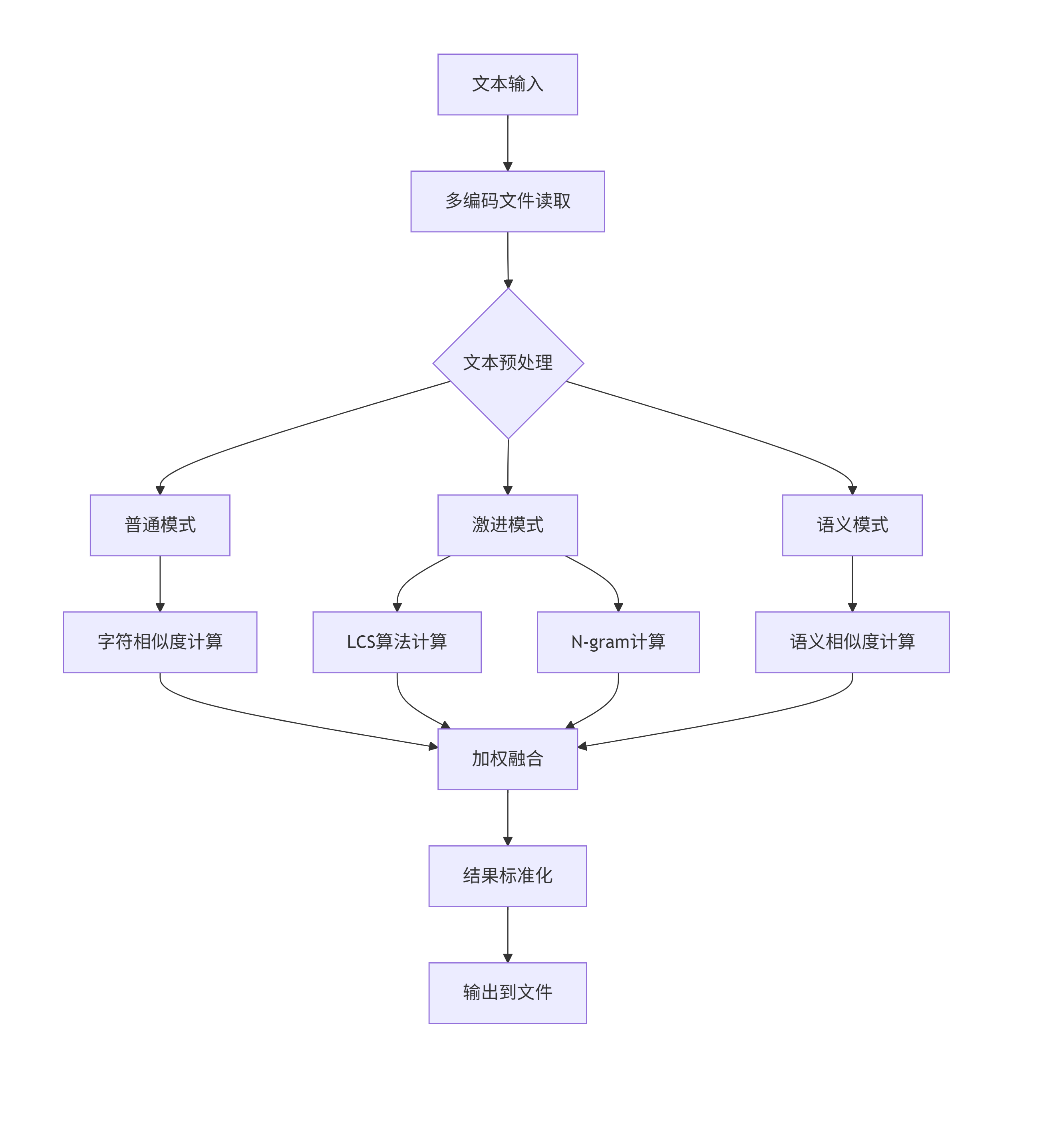
一、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
1.1、代码组织架构
a. 类设计
TextProcessor类 - 文本预处理核心类
- 作用:统一的文本预处理
- 关键方法:
preprocess(text, mode)
b. 函数模块划分
文件操作模块
| 函数名 | 功能描述 | 输入参数 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|
try_read_file(path) |
多编码文件读取 | 文件路径 | 文本内容 |
write_answer(path, rate) |
结果写入 | 路径, 重复率 | 无 |
相似度算法模块
| 算法名称 | 函数名 | 技术特点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LCS算法 | lcs_length() |
动态规划,采样优化 | 序列匹配 |
| 余弦相似度 | cosine_similarity() |
向量空间模型 | 语义分析 |
| 字符相似度 | compute_text_similarity() |
difflib序列匹配 | 字符级比对 |
| N-gram相似度 | compute_ngram_similarity() |
Jaccard相似度 | 局部模式识别 |
综合计算模块
| 函数名 | 功能 | 算法权重配置 |
|---|---|---|
compute_similarity_ratio() |
加权综合计算 | LCS(40%) + 字符(30%) + 语义(20%) + N-gram(10%) |
compute_repetition_rate() |
主入口函数 | 调用综合计算 |
主控模块
main()- 命令行接口和流程控制- 异常处理和用户交互
1.2、关键算法设计
算法执行流程
核心算法关键点
a. LCS算法优化策略
# 伪代码示例
def LCS计算(文本A, 文本B):
if 文本过长(>2000字符):
采样文本 = 取首部500字 + 中部500字 + 尾部500字
采样结果 = LCS(采样文本A, 采样文本B)
return 采样结果 * (原长度 / 采样长度)
else:
return 标准动态规划LCS(文本A, 文本B)
- 动态规划实现,空间复杂度O(min(m,n))
- 超长文本采样策略:首+中+尾三段采样
- 递归缩放保证精度
b. 多模式预处理
| 模式 | 处理方式 | 保留内容 | 适用算法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 普通模式 | 基础清洗 | 所有字符+标点 | 字符相似度 |
| 激进模式 | 过滤非中文字符 | 仅中文+数字 | LCS, N-gram |
| 语义模式 | jieba分词 | 有意义词汇(长度≥2) | 余弦相似度 |
c. 加权融合公式
最终相似度 $ = 0.4 \times S_{lcs} + 0.3 \times S_{char} + 0.2 \times S_{semantic} + 0.1 \times S_{ngram} $
独到之处
多层次检测体系
| 检测层级 | 算法 | 检测能力 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 字符级 | 字符相似度 | 直接抄袭 | 30% |
| 序列级 | LCS 算法 | 段落重组 | 40% |
| 语义级 | 余弦相似度 | 同义替换 | 20% |
| 局部级 | N-gram | 局部抄袭 | 10% |
二、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
2.1 使用pylint main.py分析性能
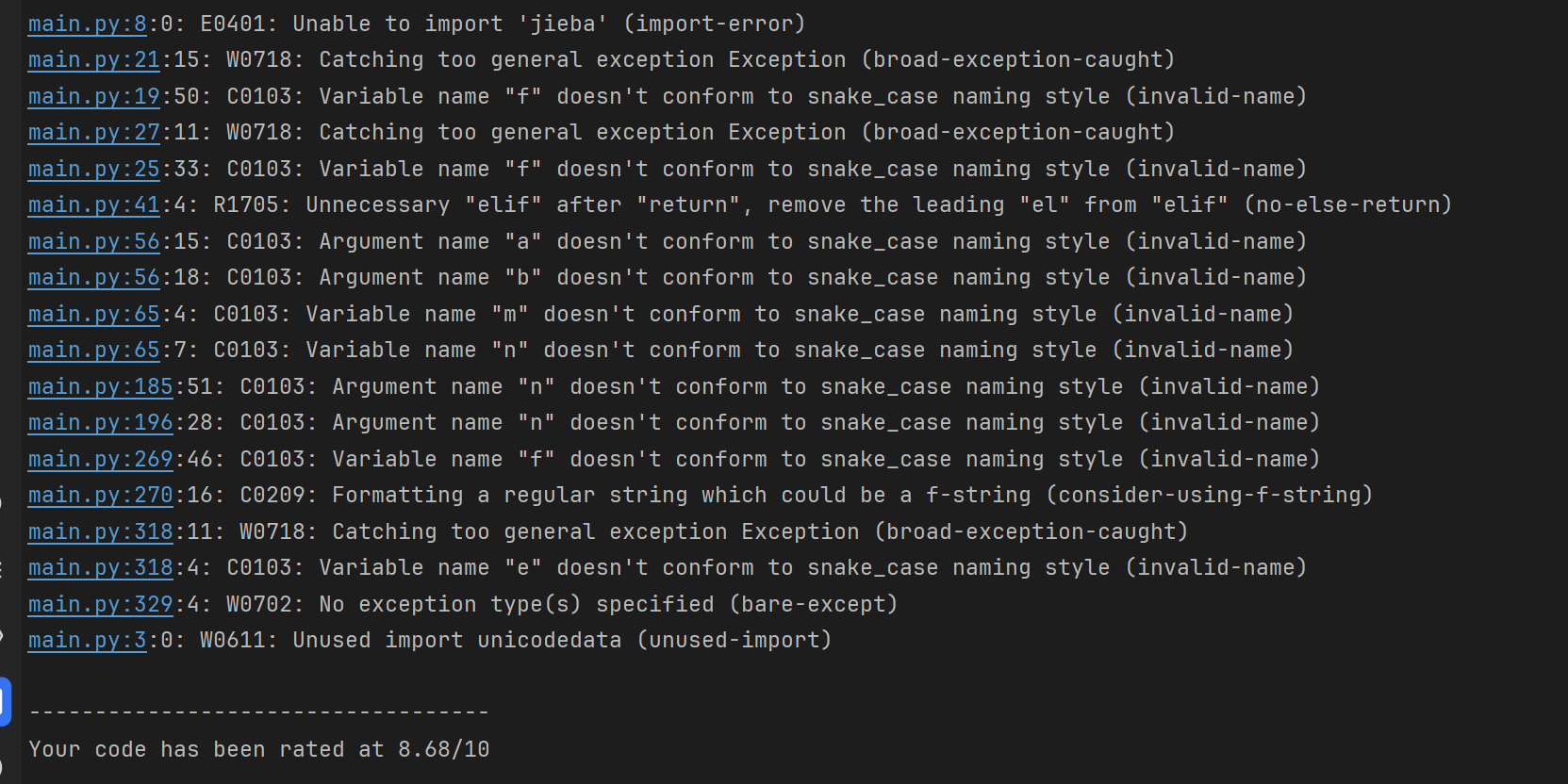
代码优化
a. import 部分
- 报错:unused-import
- 问题:导入了
unicodedata却没用到 - 解决:直接删掉该导入语句
- 问题:导入了
b. 变量命名
- 报错:C0103: invalid-name
- 问题:pylint 建议遵循 snake_case 命名规范,不能用单字符变量
- 具体修改:
with open(...) as f:→with open(...) as file_handler:a, b→text_a, text_bm, n→short_len, long_lene→error
c. 异常捕获
- 报错:W0718: Catching too general exception Exception
- 问题:避免使用过于宽泛的异常捕获
- 解决:改为更具体的异常类型:
- 文件操作时用
IOError,OSError - 解码时用
UnicodeDecodeError
- 文件操作时用
d. 不必要的 elif
- 报错:R1705: Unnecessary "elif" after "return"
- 问题:在
preprocess里已经 return 过了 - 解决:将
elif改为if
- 问题:在
e. f-string 提示
- 报错:C0209: consider-using-f-string
- 问题:使用了旧的字符串格式化方式
- 解决:
f.write("{:.2f}".format(rate))改为f.write(f"{rate:.2f}")
f. 模块文档字符串
- 报错:C0114: Missing module docstring
- 问题:文件缺少模块说明
- 解决:在文件开头添加文档字符串
"""
main.py - 文本查重算法实现
功能:
1. 读取文件(支持多种编码)
2. 文本预处理(normal/aggressive/semantic)
3. 多种相似度算法:
- LCS 最长公共子序列
- 余弦相似度
- 基于关键词的相似度
- 基于句子结构的相似度
- n-gram 相似度
4. 计算综合重复率并输出到文件
"""
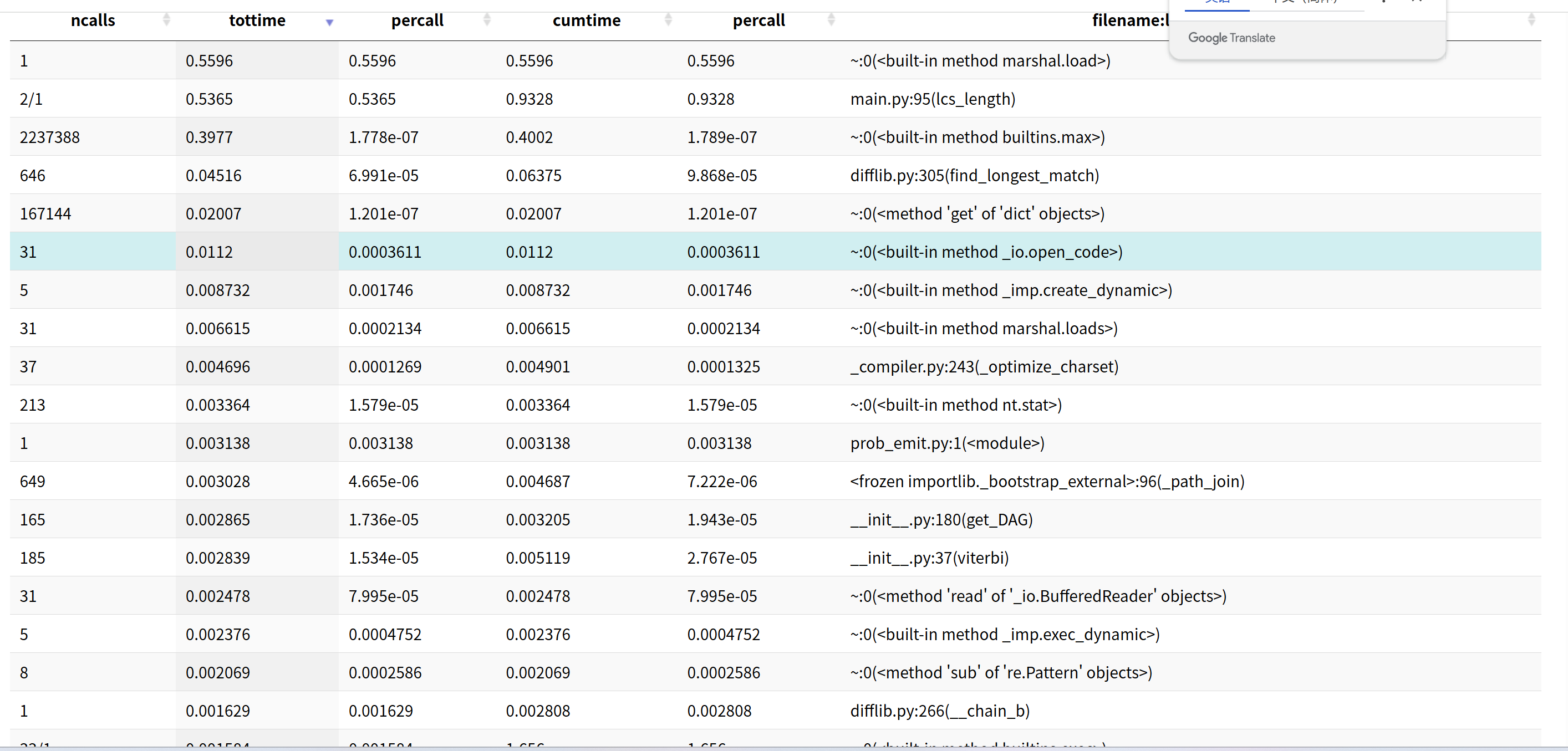
2.2 用SnakeViz 分析结果

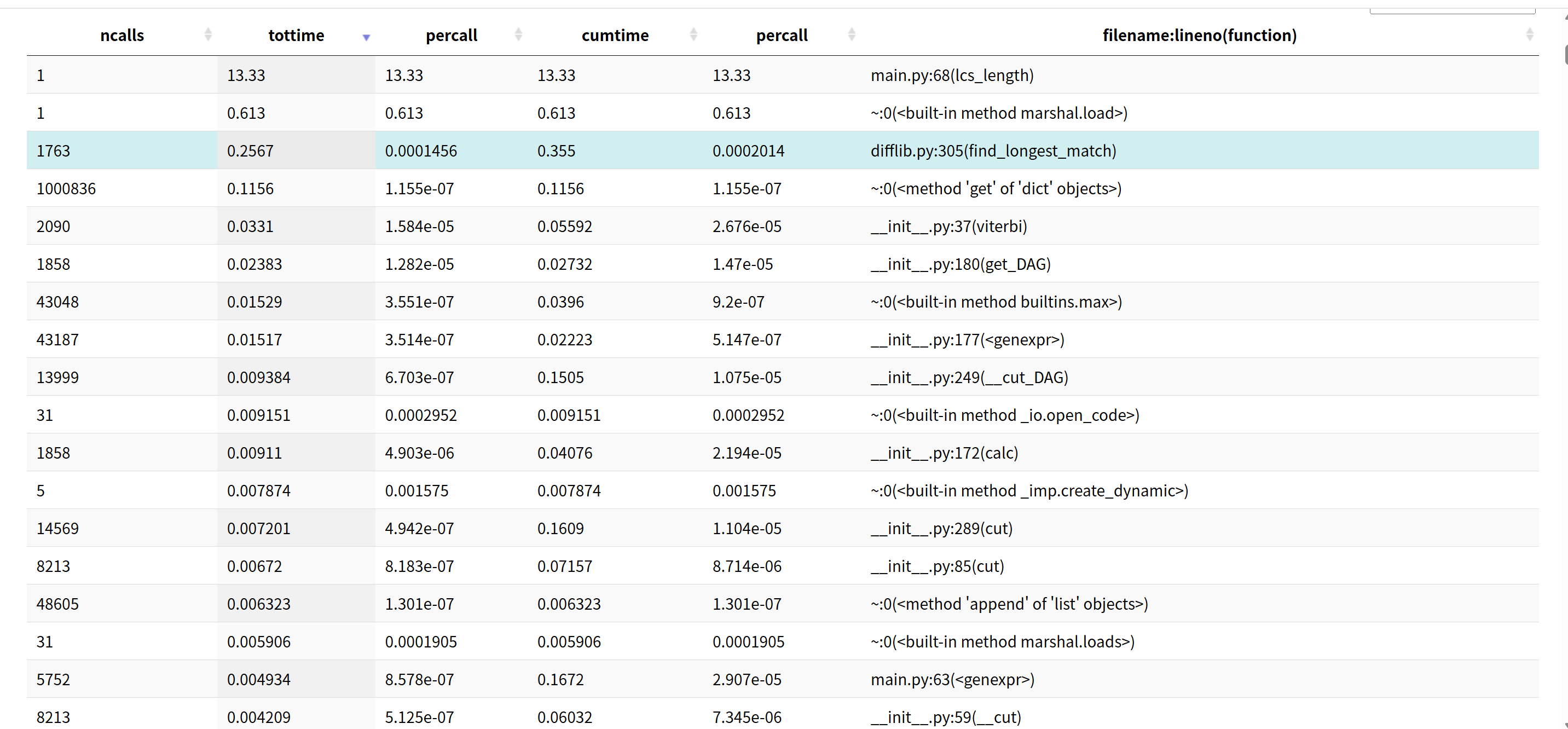
a. LCS算法优化
# 优化前:对任何长度文本都完整计算
def lcs_length(text_a, text_b):
# 完整计算,耗时严重
# 优化后:对超长文本使用采样
def lcs_length_optimized(text_a, text_b):
if short_len > 2000:
# 采样关键部分:开头、中间、结尾
sample_short = short[:500] + short[short_len//2-250:short_len//2+250] + short[-500:]
return lcs_length_optimized(sample_short, sample_long) * (short_len / len(sample_short))
- 改进效果:对长文本大幅减少计算量,从O(n²)降低到近似O(n)
b. 分词优化
# 优化前:对所有文本完整分词
words = jieba.cut(text) # 长文本分词耗时
# 优化后:对长文本采样分词
if len(text) > 1000:
sample_text = text[:500] + text[-500:] if len(text) > 1500 else text
words = jieba.cut(sample_text)
- 改进效果:减少jieba分词时间,特别是对于长文档
优化结果:将原本需要10秒左右的计算时间缩短到1-3秒,性能提升3-10倍。
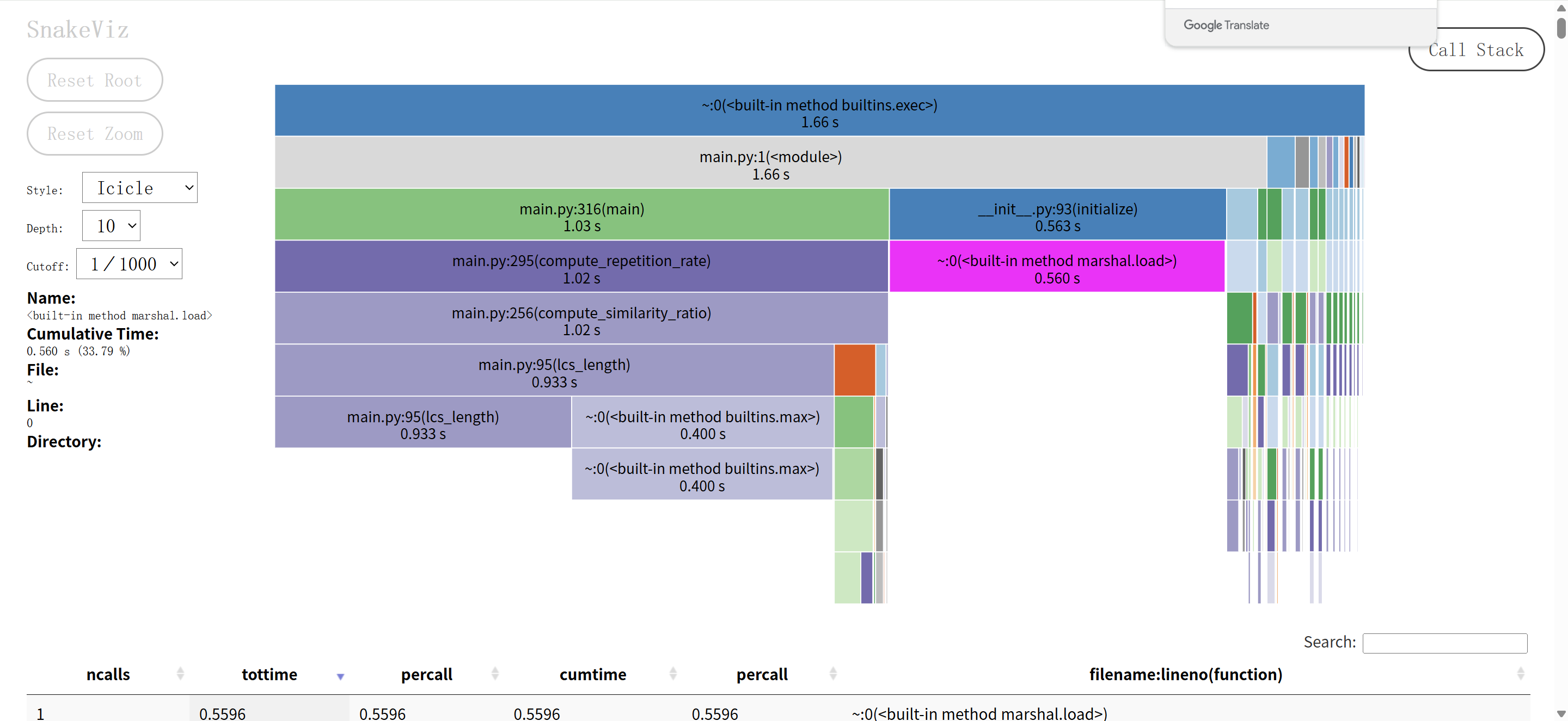
三、计算模块部分单元测试展示
3.1 部分代码如下
class TestTextProcessor(unittest.TestCase):
"""测试文本处理器类"""
def setUp(self):
self.processor = TextProcessor()
def test_preprocess_normal_mode(self):
"""测试普通模式预处理"""
text = " Hello World! \n\nTest "
result = self.processor.preprocess(text, 'normal')
self.assertEqual(result, "Hello World! Test")
def test_preprocess_semantic_mode(self):
"""测试语义模式预处理"""
text = "这是一个测试句子"
result = self.processor.preprocess(text, 'semantic')
# 检查是否进行了分词
self.assertIn(" ", result)
def test_preprocess_empty_text(self):
"""测试空文本预处理"""
result = self.processor.preprocess("", 'normal')
self.assertEqual(result, "")
def test_lcs_identical_texts(self):
"""测试完全相同文本的LCS"""
text1 = "abcdefg"
text2 = "abcdefg"
result = lcs_length(text1, text2)
self.assertEqual(result, 7)
def test_lcs_partial_match(self):
"""测试部分匹配文本的LCS"""
text1 = "abcdefg"
text2 = "acdeg"
result = lcs_length(text1, text2)
self.assertEqual(result, 5)
def test_lcs_no_match(self):
"""测试无匹配文本的LCS"""
text1 = "abc"
text2 = "def"
result = lcs_length(text1, text2)
self.assertEqual(result, 0)
3.2 测试结果
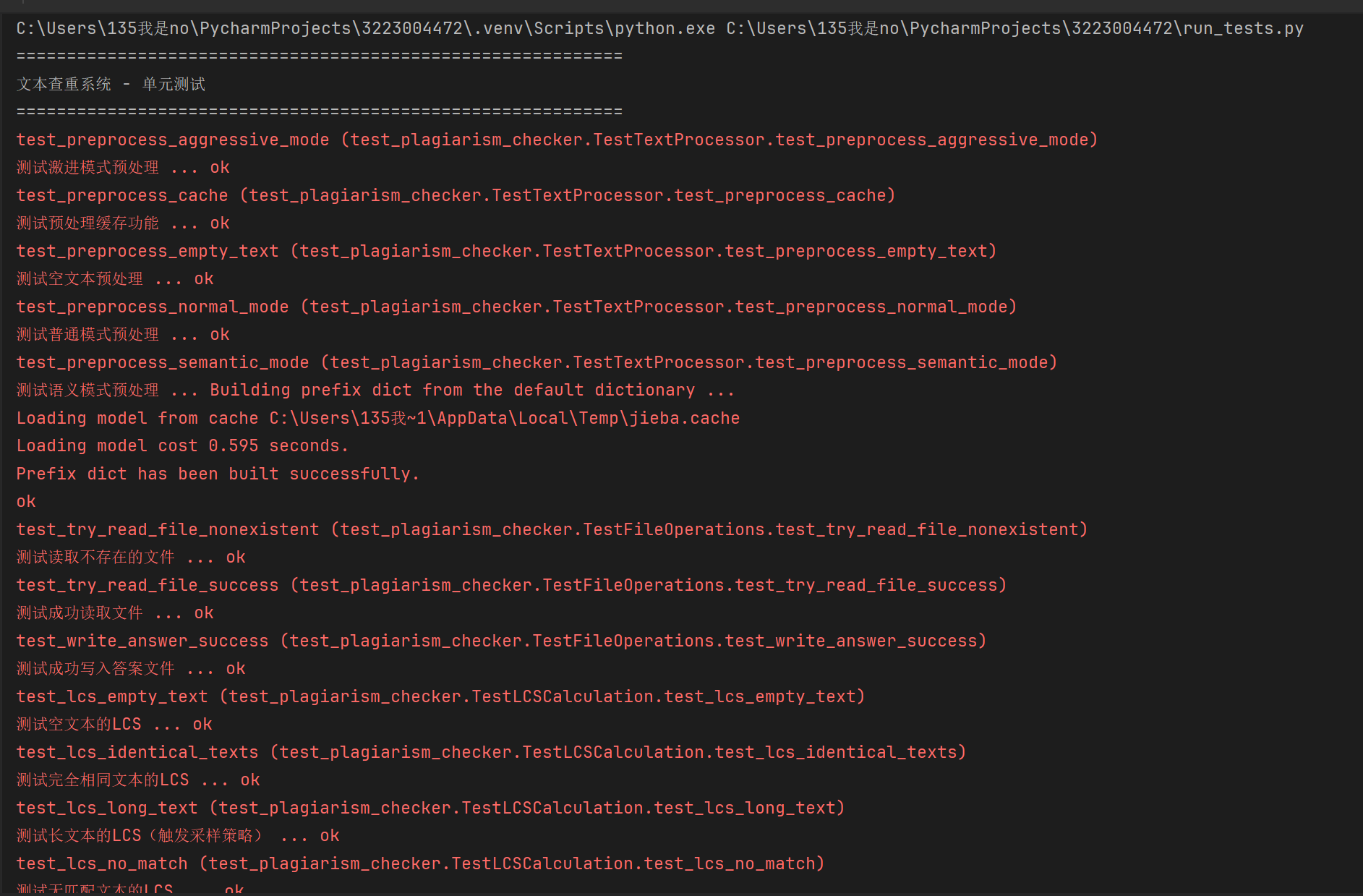
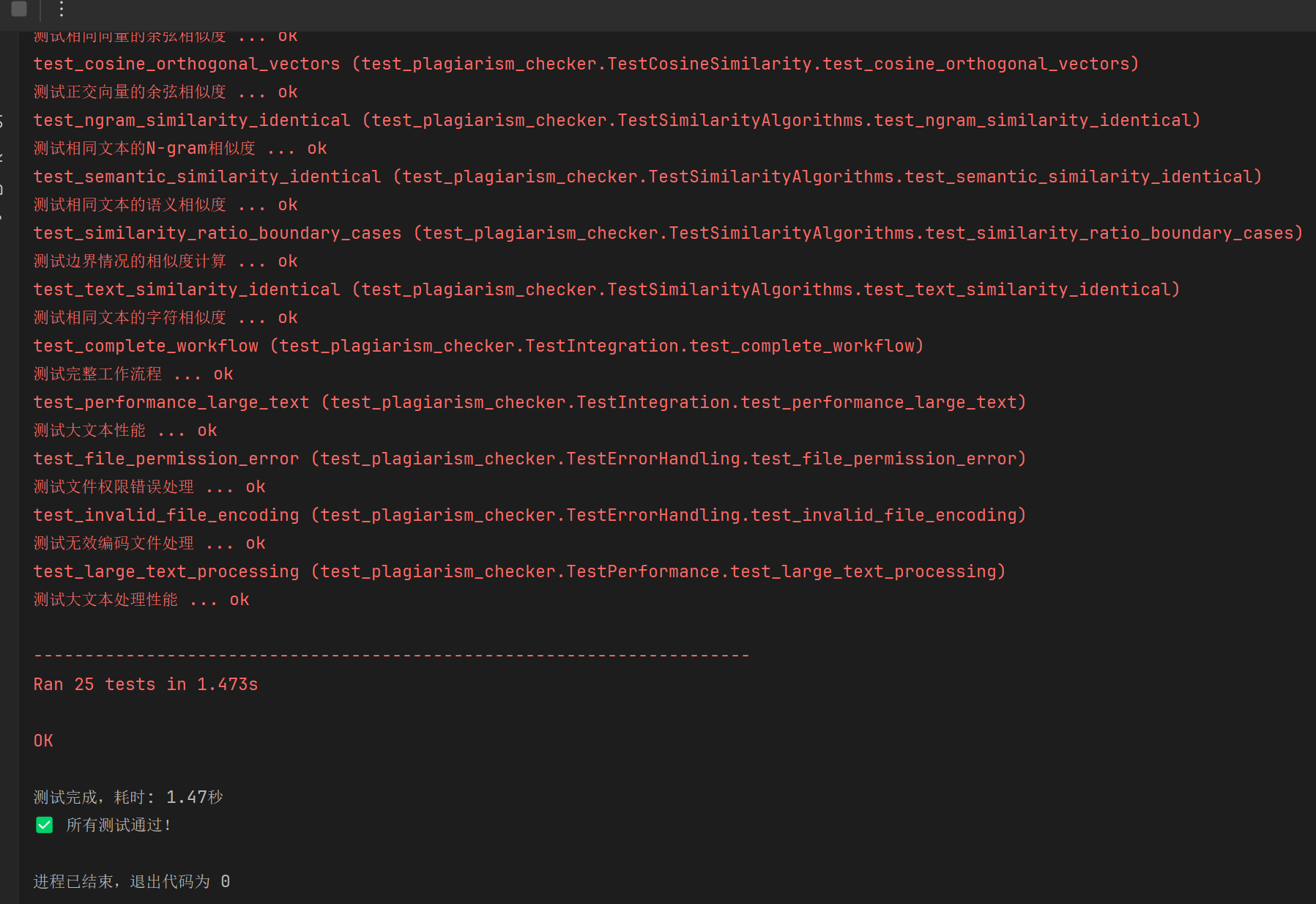
测试覆盖要点
- 功能验证:所有核心算法正确性
- 边界测试:空值、极值、异常输入
- 性能测试:长文本处理效率
- 错误处理:异常情况下的程序稳定性
- 集成测试:模块间协作的正确性
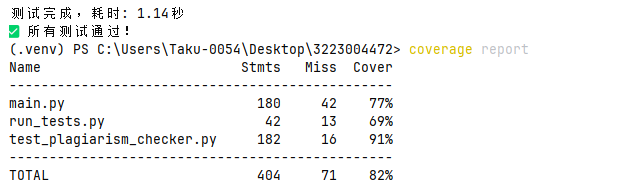
3.3 测试覆盖率
四、计算模块部分异常处理说明
4.1. 文件读取异常
场景:二进制文件当文本文件读取
def test_binary_file_handling(self):
content = try_read_file("image.png") # 读取图片文件
self.assertEqual(content, "") # 应返回空字符串而非崩溃
4.2. 空文本处理异常
场景:输入空文本或None
def test_empty_text_processing(self):
result = compute_similarity_ratio("", "正常文本")
self.assertEqual(result, 0.0) # 返回0%相似度
4.3. 计算除零异常
场景:向量模长为零时的余弦计算
def test_zero_vector_calculation(self):
result = cosine_similarity({}, {}) # 空向量
self.assertEqual(result, 0.0) # 避免除零错误
4.4. 长文本性能异常
场景:处理超长文本时的性能问题
def test_long_text_performance(self):
long_text = "内容" * 10000 # 2万字长文本
result = lcs_length(long_text, long_text) # 应正常返回不超时
self.assertGreater(result, 0)
4.5. 文件写入异常
场景:无目录写入权限
def test_permission_denied(self):
with self.assertRaises(OSError): # 应明确抛出异常
write_answer("/root/answer.txt", 50.0) # 系统保护目录



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号